Digital Signal Encoding Format
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Nonreturn to Zero-Level (NRZ-L)
Two different voltages for 0 and 1 bits
Voltage constant during bit interval
0 = high level
1 = low level
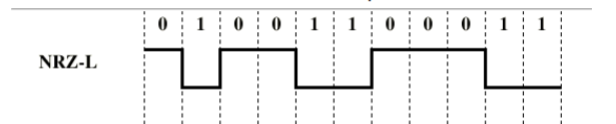
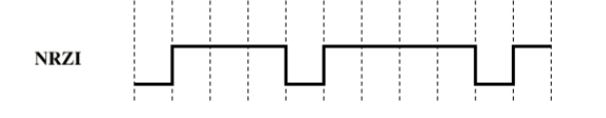
Nonreturn to Zero Inverted (NRZI)
Binary ‘1’ → Transition
The single changes state (from high to low or low to high)
This inversion indicates a binary 1
Binary ‘0’ → No Transition
The signal remains the same as the previous bit
No change in voltage level means a binary 0
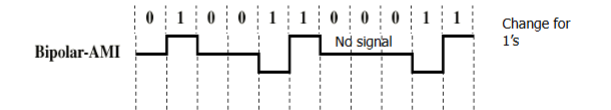
Bipolar - AMI
0: no line signal
1: positive or negative pulse
pulses for 1’s alternate in polarity
No loss of sync if a long string of ones (zeros still a problem)
No net dc component
Lower bandwidth
Easy error detection
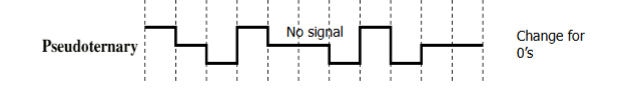
Pseudo-ternary
1: absence of line signal
0: alternating positive and negative
No advantage or disadvantage over bipolar-AMI
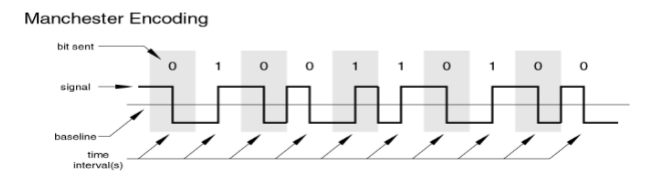
Manchester Encoding
has transition in middle of each bit period
transition serves as clock and data
low to high represents 1
high to low represents 0
used by IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet)
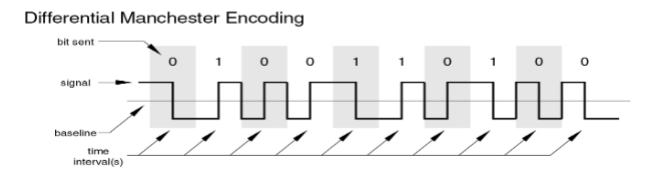
Differential Manchester
Midbit transition is clocking only
0: transition at start of a bit period
1: no transition at start of a bit period
Used by IEEE 802.5 (Token Ring)