Genetics with Dr. Sotoro chapter 04-Extensions pt1
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Alleles
Different variants of a gene that map to the same locus on homologous chromosomes.
Null allele
A mutant allele that causes the absence of gene product or gene product function due to a loss-of-function mutation.
Wild type
The most common phenotype of a species as it occurs in nature.
Incomplete dominance
A type of inheritance where heterozygous individuals have a phenotype that is an intermediate of the two contrasting traits.
Penetrance
The frequency with which individuals of a given genotype manifest at least some degree of the trait.
Expressivity
The degree or range in which a phenotype for a given trait is expressed.
Pleiotropy
A condition in which a single mutation causes multiple phenotypic effects.
Marfan syndrome
autosomal dominant mutation in fibrillin, a gene that codes for a connective tissue protein present in many tissues in the body.
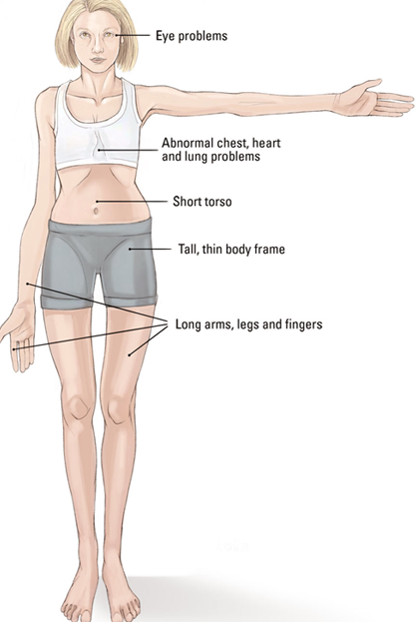
Essential gene
A gene that is necessary for growth and survival; its absence results in lethality.
Lethal allele
An allele that results in the death of an organism when present in a homozygous state.
Multiple alleles
The existence of more than two allele variants for a given gene.
Codominance
A mode of inheritance in which both alleles contribute to the phenotype of an organism.
A and B antigens are carbohydrate groups that are bound to..
lipids on the surface of erythrocytes
Epistasis
A phenomenon where the effect of one gene masks or modifies the effect of another gene.
Recessive epistasis
A form of epistasis where the recessive allele of one gene masks the effects of alleles of another gene.
Dominant epistasis
A form of epistasis where the dominant allele of one gene masks the phenotypic expression of another gene.
Complementation
The occurrence when two parents exhibiting a recessive phenotype can yield offspring with a dominant phenotype due to different recessive alleles.