Chapter 9, Lesson 2: Synovial Joints (to slide 44)
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 9, Lesson 2 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
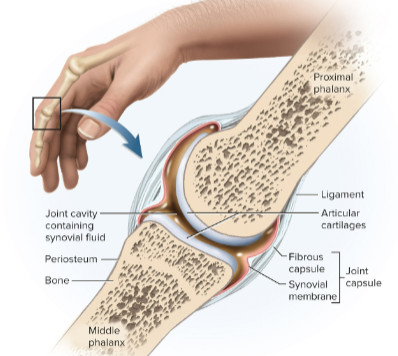
Synovial joints (diarthroses)
Joints in which two bones are separated by a joint cavity; they are the most familiar and mobile type of joint important for quality of life
Articular cartilage
Layer of hyaline cartilage covering the facing surfaces of two bones in a synovial joint
Joint cavity (articular cavity)
Separates the articular surfaces in the synovial joint
Synovial fluid
Slippery lubricant in the joint cavity; it is rich in albumin making it slippery like egg whites while removing waste and reducing friction
Joint capsule (articular capsule)
The connective tissue enclosing the synovial cavity and retaining the fluid; made of an outer layer of the periosteum of the bones and inner layer of fibroblasts and macrophages to remove debris
Articular disc
A growth of fibrocartilage inward from the joint capsule between the articulating bones to form a pad
Meniscus
The moon-shaped cartilage in the knee, extending inward from the left and right to absorb shock and pressure while stabilizing joints
Tendon
The strip of collagenous tissue tying the muscle to bone
Ligament
The strip of collagenous tissue linking one bone to another
Bursa
A fiborus sack filled with synovial fluid between muscle, bone-tendon passes, or bone-skin passes as a cushion or lubricant
Tendon sheath
An elongated cylindrical bursa wrapped around a tendon
Exercise
Warms the synovial fluid and helps cartilage swell to provide a more effective cushion; compression can squeeze metabolic waste out and take in more oxygen and nutrients
Range of motion (ROM)
The degrees through which a joint can move; assesses joint flexibility and performance and is determined by structure, strength of ligaments and joint capsules, and the action of muscles and tendons
Multiaxial joint
Having three degrees of freedom like in the shoulder (abduction, flexion, and internal rotation); others have monoaxial or biaxial movement
Classes of synovial joints
Six classes: ball-and-socket, condylar, saddle, plane, hinge, and pivot
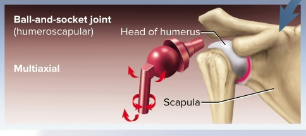
Ball-and-socket joints
Joint where a smooth, hemispherial head fits within a cup-like socket for multiaxial movement, includes the shoulder and hip
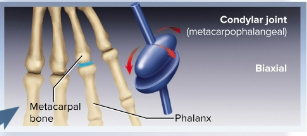
Condylar joints (ellipsoid joints)
Joing where an oval convex surface fits into a complementary-shaped depression on the other; are biaxial for two planes and includes the radiocarpal (radius and wrist) joint and metacarpophalangeal (palm-finger) joints
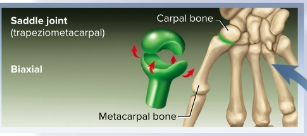
Saddle joints
Joint where bones have a concave and convex surface; are biaxial and are located in the thumb
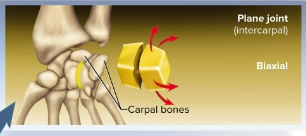
Plane joints (gliding joints)
Joints with flat articular surfaces with sliding bones; usually biaxial and are in the vertebral discs and between carpal bones