Soil fertility previous midterms, MC
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
As nutrient concentration in plant tissue increases, we categories these concentrations in the following sequence of ranges
(a ) start with deficiency, then adequate, then luxury, then deficiency
(b ) start with toxicity, then luxury, then adequate, then deficiency
( c) from luxury to adequate, then deficiency and then finally toxicity
(d ) stays in adequate all the time
( e) start with deficiency, then adequate, then luxury, then toxicity
c
A key aspect of essentially of plant nutrients (how essential nutrients are defined to be essential for plants)
( a) Other element are able to completely substitute for a plant nutrient
(b ) Plants are able to complete their life cycle in the absence of the nutrient.
( c) The nutrient does not have specific action or function in the plant
( d) The mere presence of an element in a plant does not establish essentiality.
(e ) The nutrient is not a constituent of a metabolic pathway or activation of an essential enzyme.
d
Two examples of chemical compounds in plants in which nitrogen is constituent
(a ) phytic acid and DNA
( b) sugars and ATP
(c ) methionine aminoacid and chlorophyll
(d ) phytic acid and sugars
(e ) starch and DNA
c
Two essential nutrients that can show toxicity due to excess accumulation under low pH in soils
( ) potassium and chloride
( ) boron and sulfur
( ) manganese and iron
( ) phosphorus and copper
( ) nickel and nitrogen
( ) manganese and iron
A micronutrient involved in synthesis of growth regulator (hormone)
( ) Zinc
( ) Magnesium
( ) Nickel
( ) Boron
( ) Selenium
zinc
A micronutrient involved in pollination
( ) Zinc
( ) Sulfur
( ) Iron
( ) Boron
( ) Vanadium
boron
Two clear advantages of liming in many agricultural soils
( ) plasmolysis and precipitation aluminum
( ) chelation and acidification
( ) osmosis and apoplastic pathway
( ) increasing phosphorus availability and precipitation of aluminum
( ) chelation and increasing phosphorus availability
increasing phosphorus availability and precipitation of aluminum
A process specifically driven by plants transpiring water through the leaves
( ) Root interception
( ) Diffusion
( ) Mass flow
( ) H pump at the cell membranes
( ) Active transport
mass flow
A process specifically driven by nutrient concentration gradient in the soil solution
( ) Root interception
( ) Diffusion
( ) Mass flow
( ) Aquaporin
( ) Liming
diffusion
Active transport of nutrients across membranes uses
( ) Root interception
( ) ATP
( ) Chelation
( ) Protein carriers
( ) Mass flow
atp
Two micronutrients that are absorbed by plants as cations
( ) boron and copper
( ) nickel and chloride
( ) copper and zinc
( ) molybdenum and boron
( ) manganese and potassium
copper and zinc
Diffusion of ions (such as NO3-, H2PO4-, and K+) is:
( ) faster in soil solution than pure water
( ) the same in soil solution and pure water
( ) slower in soil solution than pure water
( ) higher or lower in soil solution or pure water depending on the ions
slower in soil solution than pure water
Which of these changing factors increase buffering capacity in soils?
( ) having more 1:1 clays than 2:1 clays in the soil
( ) decreasing cation exchange capacity
( ) having soil textures that are sandier
( ) having lesser 2:1 clays in the soil
( ) increasing soil organic matter
increasing SOM
As intensity (soil solution concentration) increases, buffer capacity:
( ) stays the same
( ) increases
( ) increases or decreases variably
( ) decreases
( ) does not relate at all
increases
A soil with electric conductivity of 4.1 dS m-1 and absorption sodium ratio of 17% can be categorized as:
( ) chelated soil
( ) normal soil
( ) sodic soil
( ) saline-sodic soil
( ) acid soil
( ) saline soil
saline-sodic
Collapse of root tissue due to excess of salts in the soil solution
( ) osmosis
( ) chelation
( ) liming
( ) plasmolysis
( ) passive transport
plasmolysis
In the beginning of the semester we listed different nutrient management strategies according to different perspectives. List two of them:
response, maintenance, build-up
Write two reasons for why one can say that the Law of the Minimum can be considered too simplistic
-multiplicative effects - synergistic or antagonistic
non-additive effects - different ways to reach the same output
Example of a plant species or group of plant species that are susceptible to aluminum toxicity
legume (e.g alfalfa)
The three mechanisms of nutrient-root contact are:
root interception, mass flow, diffusion
The growth stage at which the peak of root growth in annual plants occurs is
Two essential nutrients that are mobile in the soil but immobile inside the plants
Ca, B
Write two options to manage the problem of salt-affected soils
over irrigate, salt-tolerant plants, addition of gypsum, elemental sulfur
What are sink-source relationships within the context of plant nutrients?
Which macronutrient interferes with zinc availability and explain how this interaction works
Phosphorus
antagonistic interaction with Zn- Zn precipitates with phosphate. High P causes Zn deficiency
What is nutrient bioavailability for plants?
the soil plant system’s capacity to supply essential plant nutrients to a target plant species.
In which of these compartments, one can typically find the overall lowest concentrations of macronutrients
( ) Plant dry matter and dry soil
( ) Plant dry matter
( ) Dry soil
( ) Soil solution
( ) Parent material
parent material
Essential micronutrient part of the enzyme urease
( ) Nickel
( ) Manganese
( ) Zinc
( ) Nitrogen
( ) Sulfur
nickel
A micronutrient involved in the synthesis of growth regulator (hormone)
( ) Zinc
( ) Magnesium
( ) Nickel
( ) Boron
( ) Selenium
zinc
Two essential nutrients for which chelation support their bioavailable and uptake by plants:
( ) Molybdenum and Zinc
( ) Zinc and Iron
( ) Iron and Boron
( ) Boron and Magnesium
( ) Magnesium and Molybdenum
zinc an iron
Two materials use for liming in agricultural soils
( ) gypsum and dolomite
( ) dolomite and calcite
( ) EDTA and gypsum
( ) calcite and elemental sulfur
( ) elemental sulfur and nitrogen synthetic fertilizers
dolomite and calcite
A process specifically driven by nutrient concentration gradient in the soil solution
( ) Root interception
( ) Diffusion
( ) Mass flow
( ) Aquaporin
( ) Liming
diffusion
A factor that influences notably both mass flow and effective diffusion
( ) plant vigor
( ) amount of water taken up by plants
( ) tortuosity
( ) buffer capacity
( ) root interception
amount of water taken up by plants
A type of carrier protein when one ion goes in and another ion goes out a cell (through a cell membrane):
( ) Symport
( ) Uniport
( ) Chelation
( ) Antiport
( ) Aquaporin
is this the same direction or different directions? symport or antiport
Active transport of nutrients across membranes uses
( ) Root interception
( ) ATP
( ) Aquaporin
( ) Protein carriers
( ) Mass flow
ATP
Two micronutrients that are absorbed by plants as cations
( ) nickel and chloride
( ) copper and boron
( ) iron and magnesium
( ) molybdenum and boron
( ) manganese and nickel
manganese and nickel
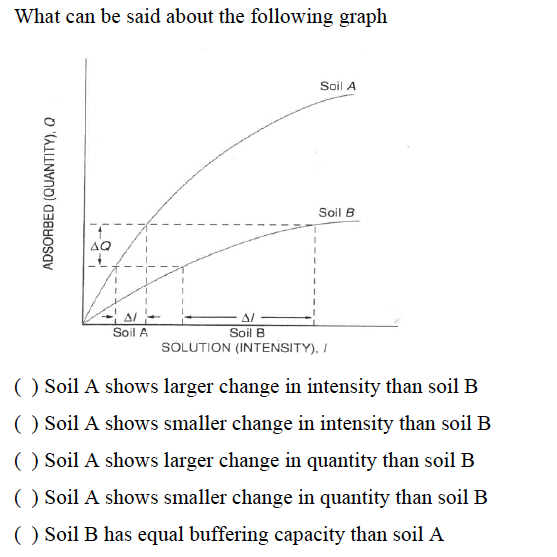
soil A shows larger change in intensity than soil B
Change in intensity (ΔI) refers to the change in solution concentration.
Change in quantity (ΔQ) refers to the amount adsorbed by the soil.
Buffering capacity is indicated by the slope; a steeper slope suggests a higher buffering capacity.
Nutrients for which the primary mechanism for root-nutrient contact is diffusion
( ) potassium and magnesium
( ) potassium and phosphorus
( ) calcium and magnesium
( ) micronutrients in general
( ) phosphorus and calcium
phosphorous and calcium
A soil with electric conductivity of 1.4 dS m-1 and absorption sodium ratio of 17% can be categorized as:
( ) normal soil
( ) sodic soil
( ) saline-sodic soil
( ) acid soil
( ) saline soil
A soil with a high sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) but lower electrical conductivity (EC) is classified as sodic soil, indicating high sodium content.
Two ways that soils can become high in salts
( ) Manure applications and organic matter decomposition
( ) Acidity in rainwater and aluminum
( ) Synthetic fertilizer and root exudation
( ) Manure applications and geological parent material
( ) Geological parent material and organic matter decomposition
manure applications and gelogical PM
Two driving factors of how leaf elongation and canopy expansion happens in plants.
cell division and cell expansion
water and nutrient availability

magnesium
Two ways or approaches to manage aluminum toxicity in cropped soils
Explain why the amount of nutrients used by crops have increased over the last decades.
What is mass flow of nutrients? And explain how it happens.
the movement of dissolved nutrients in the soil solution towards plant roots, driven by water uptake through transpiration
plants lose water through transpiration
water moves towards the roots to replace the lost soil
How does buffer capacity stabilizes soluble nutrient concentrations in soils?
soil’s ability to resist changes in nutrient concentrations in the soil solution
adsorption and desportion - nutrients are adsorbed onto soil particles and released when concentrations in the soil solution drop
Two essential nutrients that are directly involve in photosynthesis
( ) Calcium and phosphorus
( ) Sulfur and potassium
( ) Magnesium and nickel
( ) Manganese and chloride
( ) Molybdenum and sodium
manganese and chloride
An essential micronutrient that is mobile inside plants
( ) Manganese
( ) Boron
( ) Potassium
( ) Zinc
( ) Silicon
zinc
One example of a chelate
( ) uniport
( ) calcite
( ) osmosis
( ) EDTA
( ) H+ pump
edta
Under which conditions aluminum toxicity for plants can manifest
( ) base saturation > 50% and pH > 5.5
( ) base saturation < 50% and pH < 5.5
( ) base saturation < 50% and pH > 5.5
( ) base saturation > 50% and pH < 5.5
( ) acid saturation = 0% and pH > 5.5
base saturation < 50% and pH < 5.5
Active uptake of nutrients increases with
( ) lower temperature and higher substrate concentration
( ) quelation and lower temperature
( ) higher temperature and higher substrate concentration
( ) root interception and lower substrate concentration
( ) higher temperature and lower substrate concentration
higher temp and higher substrate concentration
A process specifically driven by plants transpiring water through the leaves
( ) Root interception
( ) Diffusion
( ) Mass flow
( ) H pump at the cell membranes
( ) Active transport
mass flow
Two examples of channel proteins:
( ) H+ pump and chelation
( ) Plasmolysis and potassium channel
( ) Aquaporin and potassium channel
( ) Chelation and aquaporin
( ) Aquaporin and osmosis
aquaporins and potassium channel
Active transport of nutrients across membranes uses
( ) Root interception
( ) ATP
( ) Chelation
( ) Protein carriers
( ) Mass flow
ATP & protein carriers?
Two micronutrients that are absorbed by plants as anions
( ) nickel and chloride
( ) copper and boron
( ) iron and zinc
( ) molybdenum and boron
( ) manganese and nickel
molybdenum & boron
As intensity (soil solution concentration) increases, buffer capacity:
( ) stays the same
( ) increases
( ) decreases
( ) increases or decreases variably
( ) does not relate at all
increases or decreases variably
The mobility of these pairs of essential nutrients in soils follows this order
( ) Phosphorus > nitrate
( ) Potassium > nitrate
( ) Nitrate > phosphorus
( ) Phosphorus > potassium
( ) Phosphorus = nitrate
nitrate > phosphorus
A soil with electric conductivity of 5.4 dS m-1 and extractable sodium ratio of 12% can be categorized as:
( ) neutral soil
( ) saline-sodic soil
( ) acid soil
( ) saline soil
( ) normal soil
( ) sodic soil
saline soils
Saline soils have EC > 4 dS m⁻¹ but low sodium levels (SAR < 13 or ESP < 15%).
A soil with electric conductivity of 1.4 dS m-1 and absorption sodium ratio of 17% can be categorized as:
( ) chelated soil
( ) normal soil
( ) sodic soil
( ) saline-sodic soil
( ) acid soil
( ) saline soil
sodic soil
Sodic soils have SAR > 13 and EC < 4 dS m⁻¹.
Two crops that are intolerant to salinity
( ) A native bush and barley
( ) Wheat and barley
( ) Carrot and alfalfa
( ) Rice and beans
( ) Beans and maize
carrot and alfalfa
Two ways or approaches to manage aluminum toxicity in cropped soils
liming -precipitates solube Al, changes pH
Law of the minimum. Draw “a barrel containing a fluid” representing the law of the minimum. This barrel has at least five staves (lateral pieces of the barrel) that symbolize five nutrients: iron, potassium, copper, phosphorus, and boron. And phosphorus is the most limiting nutrient
What is nutrient bioavailability for plants
the soil-plant system’s capacity to supply essential plant nutrients to a target plant species
–
1) What is meant by fertility x cultivar interactions?
–
2) How fertilizers support food security?
–
3) Which is the best focus in nutrient management: response, maintenance, build up? Why?
–
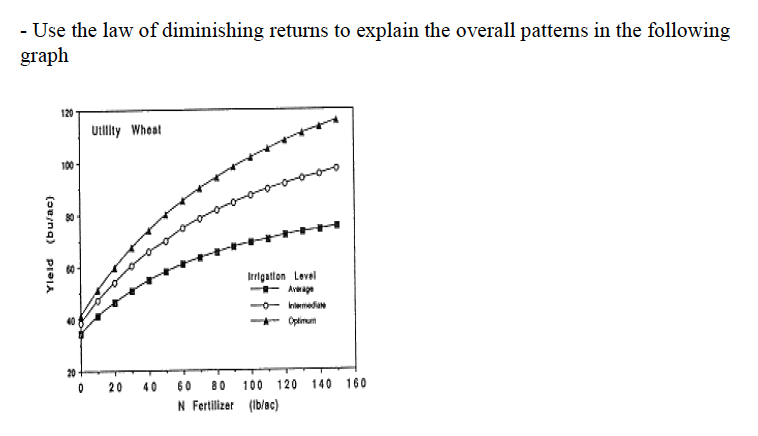
4) What are the differences and similarities between law of the minimum and the law of diminishing
returns?
–
5) What are source sink relationships when thinking about nutrients?
–
6) What is the importance of water availability in converting plant canopy into a sink of nutrients?