Lecture 1: Introduction
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is a binary system
2 stars orbiting around a common center of gravity under their mutual gravitational attraction
What is an orbit?
The trajectory a star describes over time, typically an ellipse with the center of mass at one of the focus points
What is a barycentric orbit?
Two individual trajectories that describes the motion of each star around the common center of mass
What is a relative orbit?
A single equivalent orbit where a particle of reduced mass (µ) orbits around a central mass (M), located at a focus of the elliptical trajectory. (It replaces the two barycentric orbits)
Why do we use the relative orbit?
It simplifies the two-body problem into a one-body problem.
What is periastron?
The point of closest approach between the two stars.
What is apastron?
The point of maximum separation between the two stars.
What are physical parameters of a binary?
Stellar masses and stellar sizes (radii).
What are dynamical parameters of a binary?
Orbital period (p) , eccentricity (e), semi-major axis (a), and time of periastron passage (T₀)
What are the orientation parameters of a binary?
inclination (i), argument of periastron (ω), longtitude of ascending node (Ω)
What is the inclination (i) of a binary orbit?
The angle between the orbital plane and the plane of the sky.
What does i= 90° correspond to observationally?
An edge-on system (eclipses possible).
What is the argument of periastron ω?
The angle from the ascending node to periastron, measured in the orbital plane.
What is the longitude of the ascending node?
The angle defining the orientation of the orbit on the sky.
What is the true anomaly θ?
The angle between periastron and the star’s current position, measured at the focus.
What leads to interaction in binary stars
Expansion
When stars evolve, the radii increase. But because binaries have fixed orbital separations (initially), the expansion leads to interaction.
What is a optical double
A pair of stars that share a similar line of sight. They appear as binaries, but are not gravitationally bound
What is a visual binary
Both binary components can be seen as separate points on the night sky. The angular separation is greater than the telescope resolution.
(Limitation here is that the resolving power is limited by wavelength/diameter)
What are interferometric binaries?
It are binaries that are found using multiple telescopes as interferometers (to increase the angular resolution )
What is an astrometric binary?
This is when we use astrometry to find the binary. This is used if only 1 component is visible, the position on the sky will vary around the center of mass. Presice measurements of the position of that star can identify binaries.
What is an eclipsing binary?
This is only if the inclination is around 90°. This uses that 1 star can be in front or behind the other star and creates a dip in brightness (eclipse)
The shape of the eclipse depends on stellar & binary properties
What are spectroscopic binaries
This is only when the inclination i>0°. It uses the doppler shift for the stars moving toward or away from us
(It is best for short period binaries with a high i)
How is the period distribution for binary stars
Solar-type stars favour wide periods on the order of several years
Massive binaries have short periods on the order of days
Why do we have a particular period distribution in binaries
There must be different formation processes
Filament fragmentation
Core fragmentation
Disk fragmentation
Capture
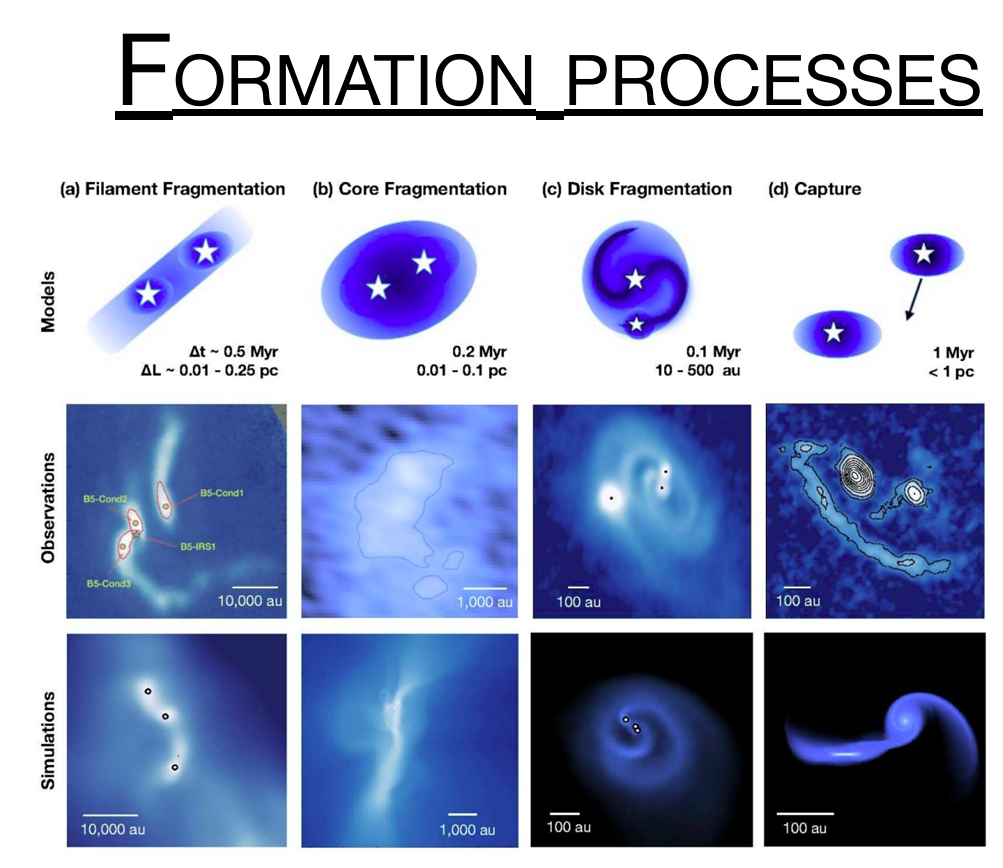
What parameters can be obtained from binary systems
Using spectroscopy:
Temperature, Luminosity, abundances, g (∼M/R²), (Radius)
Using RV & ligth curve fitting:
Mass, radius, period, time of periastron passage (T₀), inclination (i) and other orbital parameters
(Using both can give independent measurements of key physical parameters)