1st page mod sir yuan splinting and casting
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
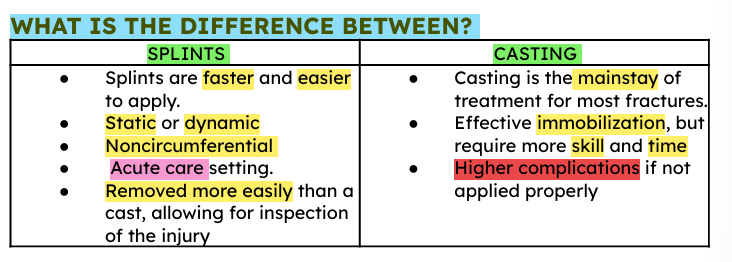
difference between splinting and casting
SO WHY DON’T WE USE SPLINTING INSTEAD OF CASTING? WHAT IS THE INDICATION OF IT?
Fracture reduction and immobilization, it is helpful in the correction of pediatric deformities, dysplastic hip disease, scoliosis, and foot deformities such as clubfoot
● Maintain or obtain a correction of deformity
● Promote alignment following surgery
● Give support to damaged soft tissues in the healing process of fractures, dislocations, and sprains.
FROM MC TO LEAST COMMON: CONDITIONS THAT BENEFIT FROM IMMOBILIZATION
1. Fractures
2. Sprains
3. Severe soft-tissue injuries
4. Reduced joint dislocations Inflammatory conditions: arthritis, tendinopathy, tenosynovitis
5. Deep laceration repairs across joints
enumerate the casts of the upper limb
below elbow cast
scaphoid cast
bennett’s type cast
above elbow or full arm casts
smith’s cast
humeral brace
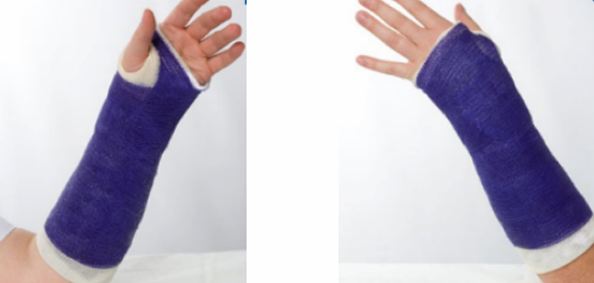
below elbow cast
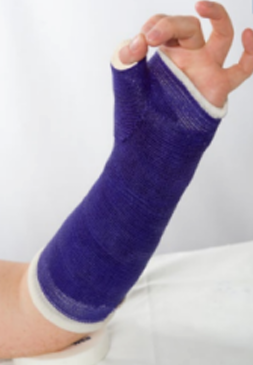
scaphoid cast
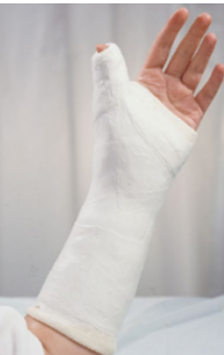
bennett’s type cast
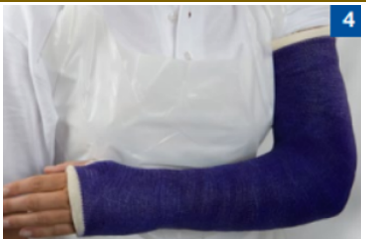
above elbow / full arm casts

smith’s cast

humeral brace
enumerate the casts if the lower limb
slippers
below knee cast
tibial bracing sarmiento
cylinder cast
above knee or long leg cast
broomstick casts
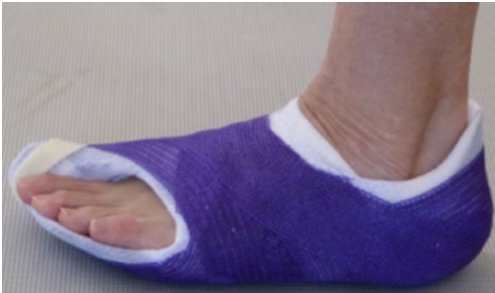
slippers
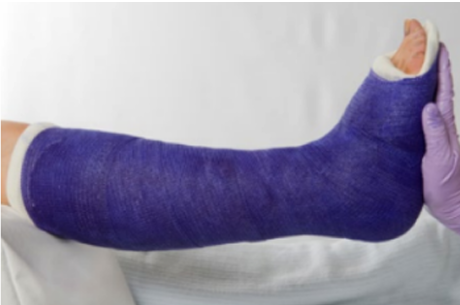
below knee cast
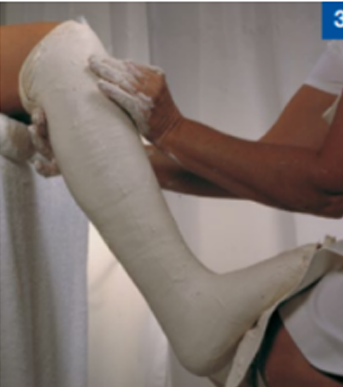
tibial bracing sarmiento

cylinder cast
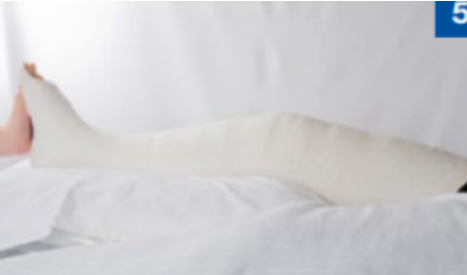
above knee / long leg cast
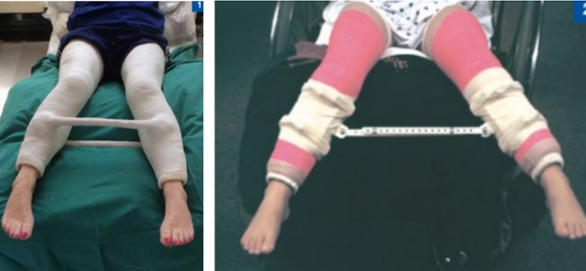
broomstick casts
enumerate the casting of the trunk
spica
single hip spica
one and a half spica
double hip spica
plaster jacket
anterior view (gamgee pad, felt pads)
posterior view (plaster slabs)
anterior view
plaster corset
minerva jacket
shoulder spica
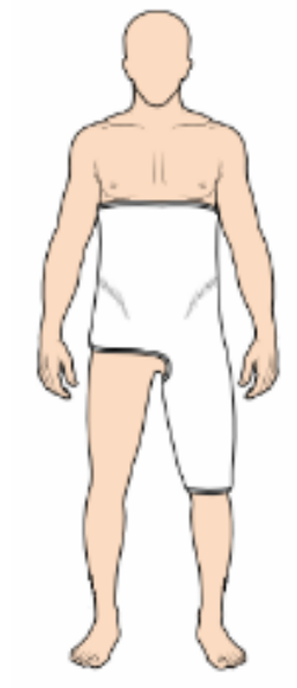
single hip spica
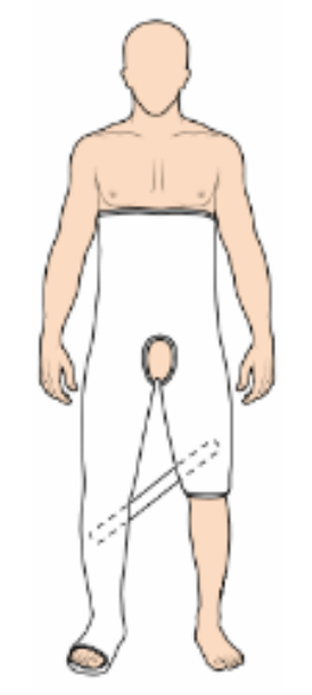
one and a half hip spica
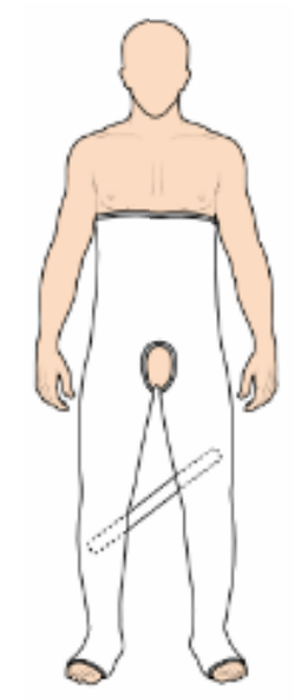
double hip spica
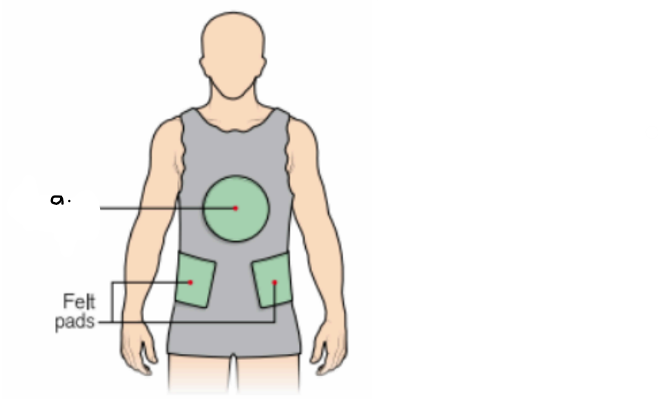
what type of cast is this? (indicate the view)
label the letter a.
plaster jacket (anterior view)
a. gamgee pad
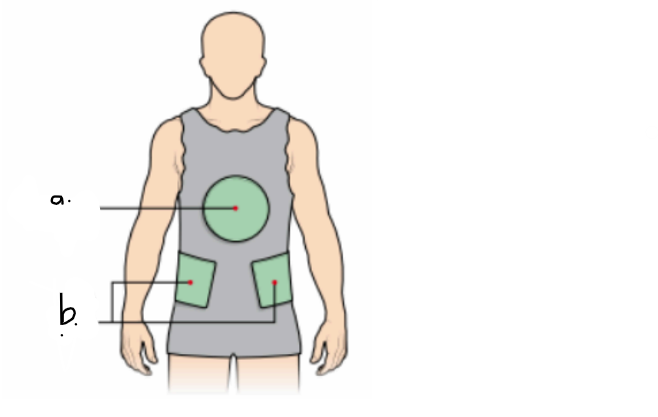
what type of cast is this? (indicate the view)
label the letters a. and b.
plaster jacket (anterior view)
a. gamgee pad
b. felt pads
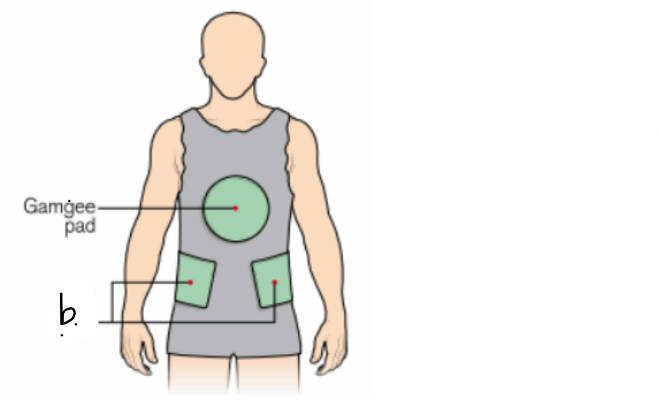
what type of cast is this? (indicate the view)
label the letter b.
plaster jacket (anterior view)
b. felt pads
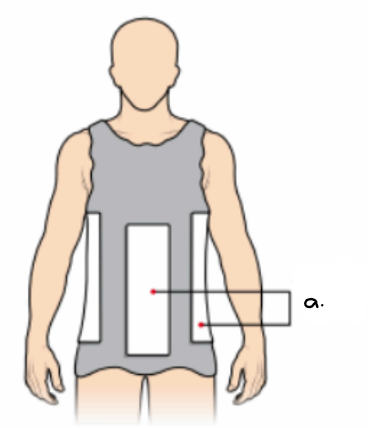
what type of cast is this? (indicate the view)
label the letter a.
plaster jacket (posterior view)
plaster slabs
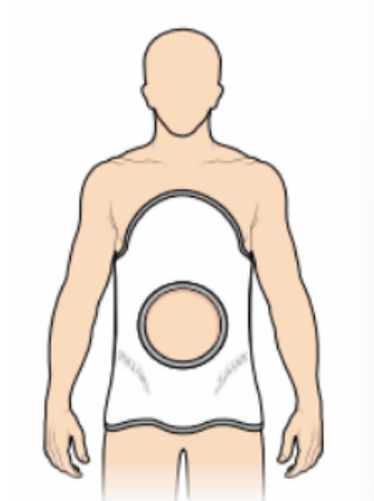
what type of cast is this and indicate the view
plaster jacket (anterior view)

plastic corset
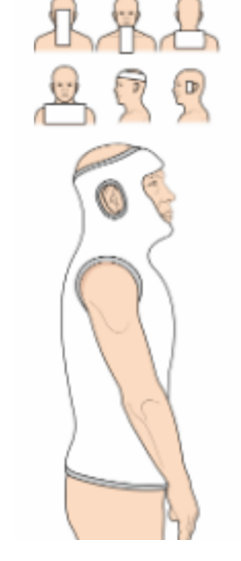
minerva jacket
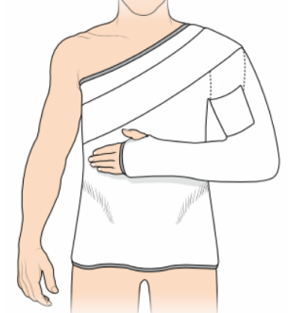
shoulder spica
SO BEFORE WE DO CASTING WHAT ARE THE GENERAL PRECAUTIONS/CONSIDERATIONS?
1. Stage and severity of the injury, the potential for instability, the risk of complications, and the patient's functional requirements.
2. Assessment of the skin, neurovascular status, soft tissues, and bony structures to accurately assess and diagnose the injury.
COMPLICATIONS IN CASTING
[CIPHI NI DJ]
1. Compartment syndrome
2. Ischemia
3. Pressure sores and skin breakdown
4. Heat injury
5. Infection
6. Neurologic injury
7. Dermatitis
8. Joint stiffness
HIGH-RISK THAT MAY DEVELOP INCREASED COMPLICATIONS
1. Pt with an inability to effectively communicate
2. Pt. under general or limb block anesthesia
3. Pt. who are very young or has GDD
4. Pt. with impaired sensations (SCI, DM)
5. Pt. with spasticity