SLP 261 - Ch. 6 Study Questions
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1. The region posterior to the oral cavity is the:
a. larynx
b. oropharynx
c. glottis
d. epiglottis
b
3. The orifice of the eustachian (auditory) tube is located in the:
a. nasopharynx
b. oropharynx
c. laryngopharynx
d. esophagus
a
5. This cavity contains the torus tubarius.
a. oropharynx
b. nasopharynx
c. laryngopharynx
d. none of the above
b
7. In the Source-Filter theory of speech production:
a. the oral cavity is the source and the nasal cavity provides the filter.
b. the vibrating vocal folds are the source and the oral/nasal cavities provide the filter.
c. the respiratory system is the source and the articulatory/resonatory system provides the filter.
d. none of the above
b
9. This articulator is used to differentiate the /m/ from /b/ phonemes.
a. tongue
b. teeth
c. cheeks
d. velum
d
11. This bone provides the posterior component of the zygomatic arch.
a. frontal
b. zygomatic
c. temporal
d. lacrimal
c
13. This bone makes up what we term the "cheekbone."
a. temporal
b. maxilla
c. mandible
d. zygomatic
d
15. This muscle makes up the bulk of the velum.
a. tensor veli palatine
b. levator veli palatine
c. uvular muscle
d. palatopharyngeus
b
17. This muscle makes up the bulk of the tongue.
a. palatoglossus
b. styloglossus
c. genioglossus
d. hyoglossus
c
19. This muscle is a major depressor of the velum.
a. palatoglossus
b. styloglossus
c. hyoglossus
d. glossopalatine
e. both a and d
e
21. All facial muscles insert into this muscle.
a. buccinator
b. orbicularis occuli
c. temporalis
d. orbicularis oris
d
23. These muscles are both innervated by the V trigeminal nerve.
a. masseter and temporalis
b. tensor veli palatine and digastricus anterior
c. levator veli palatine and superior pharyngeal constrictor
d. a & b
e. b & c
d
25. This muscle is the most massive mandibular elevator.
a. levator veli palatine
b. masseter
c. temporalis
d. internal (medial) pterygoid
b
27. The _________________________consists of the oral, pharyngeal, and nasalcavities
vocal tract
29. The condyloid process of the mandible articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone, becoming the _________________________ joint.
temporomandibular
31. _________________________are the sacs or cavities within the mandible in which teeth reside.
alveoli
33. The _________________________suture separates the palatine processes of themaxillae
intermaxillary
35. The _________________________plate of the palatine bone makes up the posterior 1/4 of the hard palate.
horizontal
37. The inferior _________________________are small, scroll-like bones placed on the lateral surface of the nasal cavity.
nasal conchae; turbinates
39. The nasal septum is made up of three components. The component that is anunpaired bone is called the _________________________bone.
vomer
41. The _________________________cartilage makes up a component of the nasalseptum.
septal
43. The _________________________ of the ethmoid bone protrudes into the nasal space, providing partial separation of the paired nasal cavities.
perpendicular plate
45. The pituitary gland (hypophysis) resides within the ______________________bone.
sphenoid
47. The foramen magnum of the _________________________bone provides the conduit for the spinal cord to enter the cranial cavity.
occipital
49. The _________________________is the visible 1/3 of the tooth
crown
51. Bicuspids are also known as _________________________.
premolars
53. _________________________teeth are those in the permanent arch that replace deciduous teeth.
successional
55. _________________________teeth are those in addition to those found in the permanent arch.
supernumerary
57. In a Class _________________________malocclusion between the upper and lower dental arches, the first molar of the mandibular arch is retracted at least one tooth from the first maxillary molars.
II
59. _________________________is the projection of the maxillary incisors beyond the mandibular incisors.
overjet
61. _________________________refers to a tooth rotated or twisted on its long axis
torsiversion
63. _________________________refers to a tooth tilted toward the tongue.
linguaverted
65. The ________________________ surface of a tooth is that which could come in contact with the cheek wall.
a. buccal
b. occlusal
c. lingual
d. medial
e. distal
a
67. The _________________________ surface is the contact region between teeth of the upper and lower arches.
a. buccal
b. occlusal
c. lingual
d. medial
e. distal
b
69. _____ are the sacs or cavities within the mandible in which teeth reside.
a. condyloid
b. temporomandibular
c. symphysis mente
d. alveoli
e. palatine
f. intermaxillary
g. horizontal
i. premaxillary
d
71. The _____ process of the mandible articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone, becoming the temporomandibular joint.
a. condyloid
b. temporomandibular
c. symphysis mente
d. alveoli
e. palatine
f. intermaxillary
g. horizontal
i. premaxillary
a
73. The _____ suture separates the palatine processes of the maxillae.
a. condyloid
b. temporomandibular
c. symphysis mente
d. alveoli
e. palatine
f. intermaxillary
g. horizontal
i. premaxillary
f
75. The _____ plate of the palatine bone makes up the posterior 1/4 of the hard palate.
a. condyloid
b. temporomandibular
c. symphysis mente
d. alveoli
e. palatine
f. intermaxillary
g. horizontal
i. premaxillary
g
77. The _____ (prominence) of the ethmoid bone protrudes into the cranial space.
a. nasal conchae
b. vomer
c. perpendicular
d. septal
e. crista galli
f. cribriform
e
79. The inferior _____ are small, scroll-like bones placed on the lateral surface of the nasal cavity.
a. nasal conchae
b. vomer
c. perpendicular
d. septal
e. crista galli
f. cribriform
a
81. The pterygoid hamulus projects from the _____ plates.
a. medial pterygoid
b. sphenoid
c. root
d. crown
e. occipital
f. enamel
a
83. The _____ is the portion of the tooth hidden beneath the gum line.
a. medial pterygoid
b. sphenoid
c. root
d. crown
e. occipital
f. enamel
c
85. The visible surfaces of the tooth are covered with _____.
a. medial pterygoid
b. sphenoid
c. root
d. crown
e. occipital
f. enamel
f
87. _____ teeth are those in the permanent arch that replace deciduous teeth.
a. second bicuspid
b. premolars
c. superadded
d. third molar
e. successional
f. supernumerary
g. first bicuspid
e
89. _____ teeth are those in addition to those found in the permanent arch.
a. second bicuspid
b. premolars
c. superadded
d. third molar
e. successional
f. supernumerary
g. first bicuspid
f
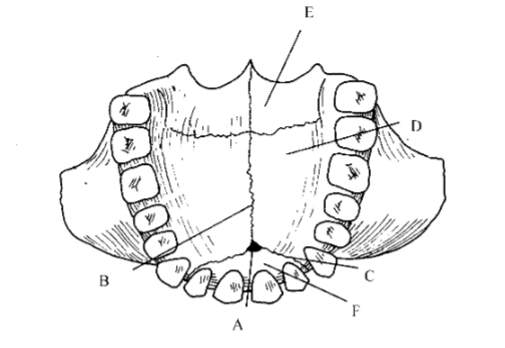
91. _____ premaxillary suture
c
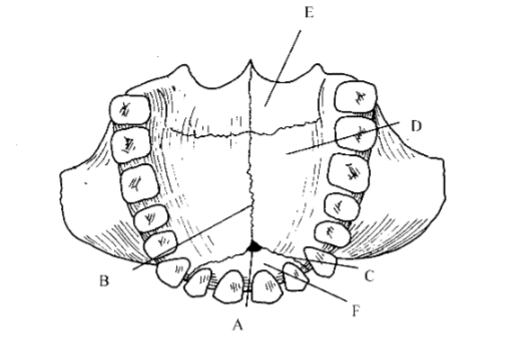
93. _____ incisive foramen
a
95. _____ vomer
c
97. _____ cribriform plate
b
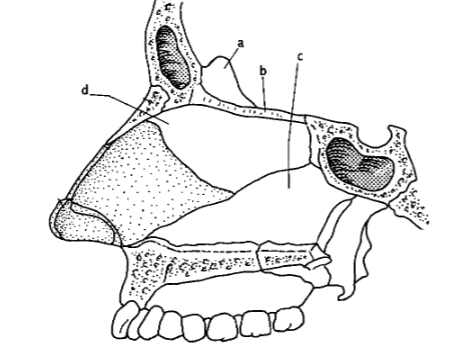
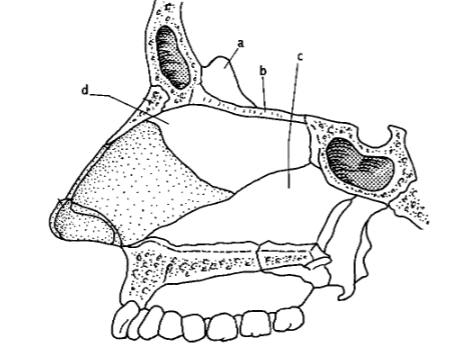
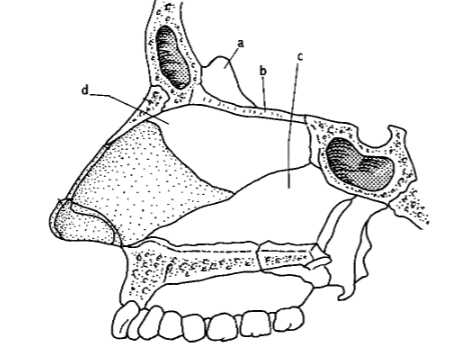
99. _____ process of lower portion ethmoid bone
d
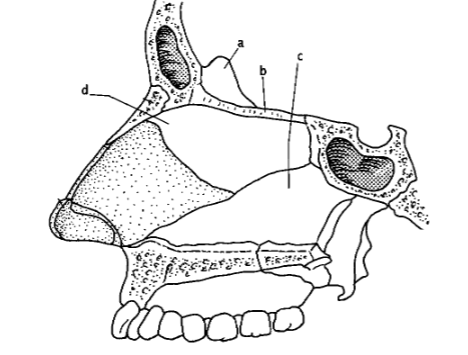
101. _____ process of upper portion of ethmoid bone.
a
103. _____ inferior nasal concha
L
105. _____ anterior nasal spine
k
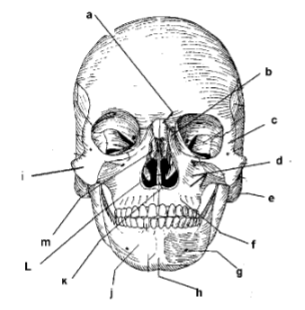
107. _____ mandible
j
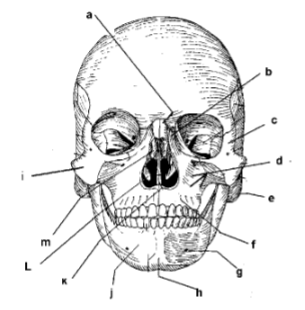
109. _____ symphysis mente
h
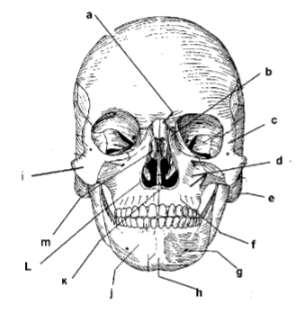
111. _____ mental foramen
g
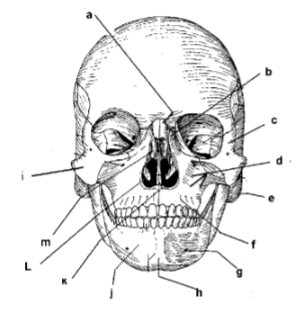
113: _____ middle nasal concha
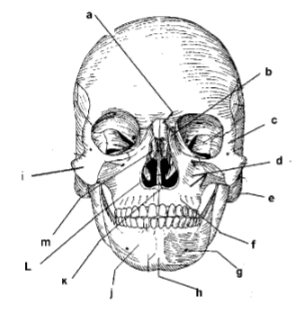
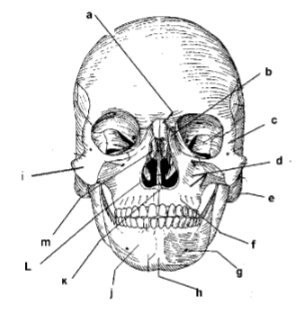
m
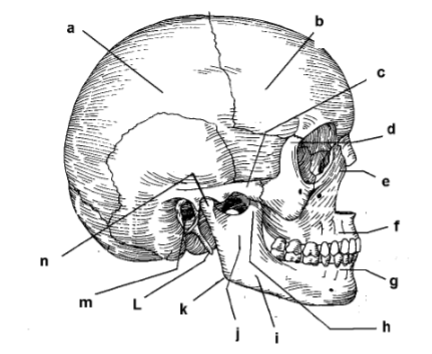
115. _____ parietal bone
a
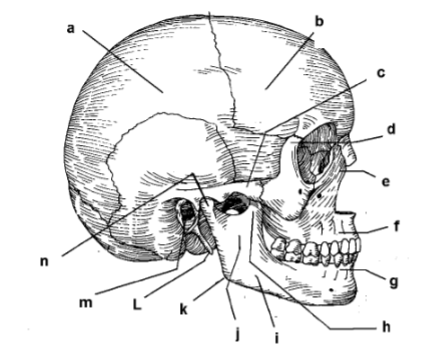
117. _____ zygomatic arch
c
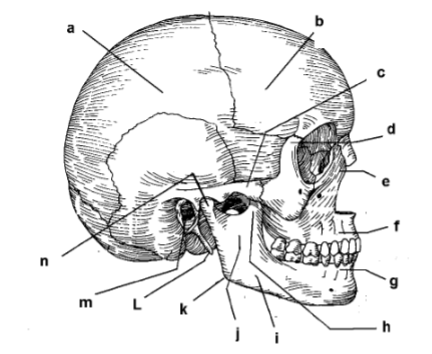
119. _____ frontal process of maxilla
e
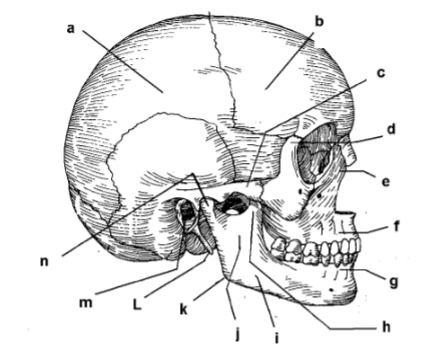
121. _____ alveolar portion of mandible
g
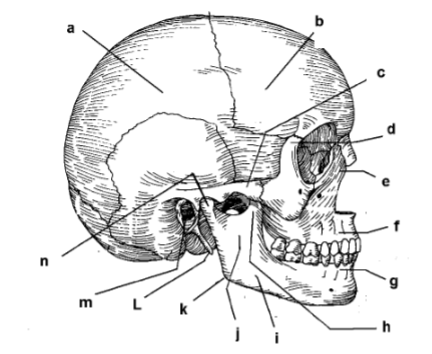
123. _____ corpus of mandible
i
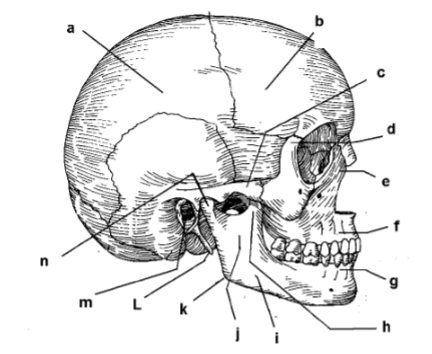
125. _____ angle
k
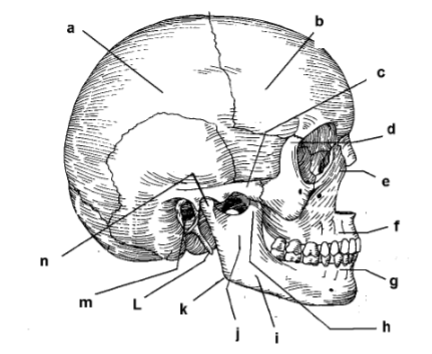
127. _____ external auditory meatus
m
129. _____ intermaxillary suture
d
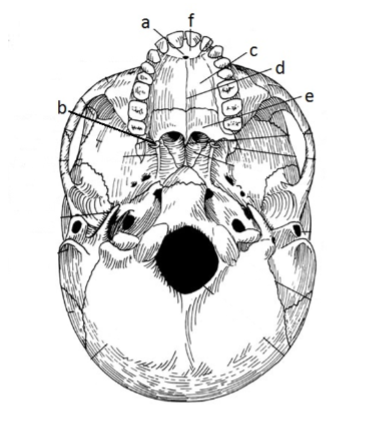
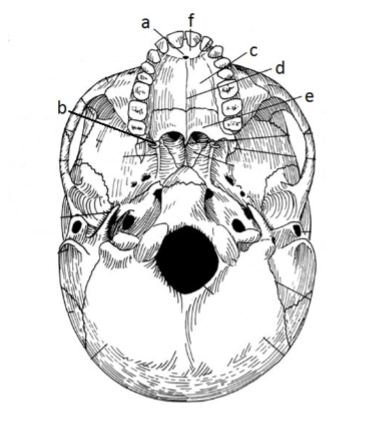
131. _____ palatine process
c
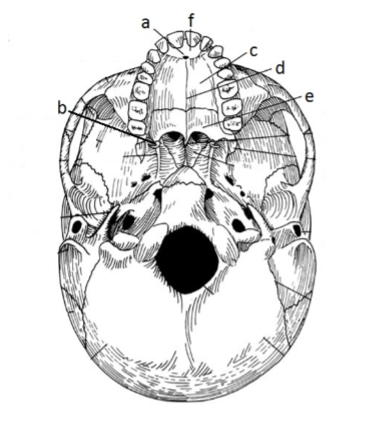
133. _____ incisive foramen
a
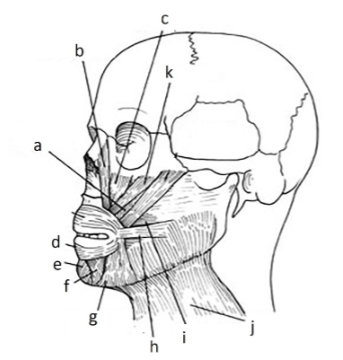
135. _____ platysma
j
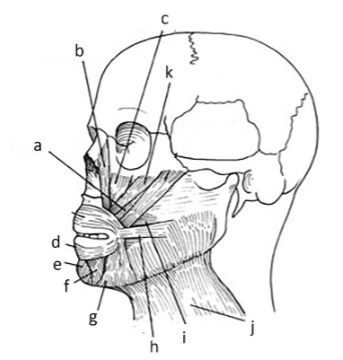
137. _____ buccinator
i
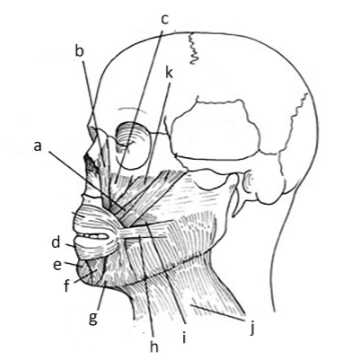
139. _____ risorius
h
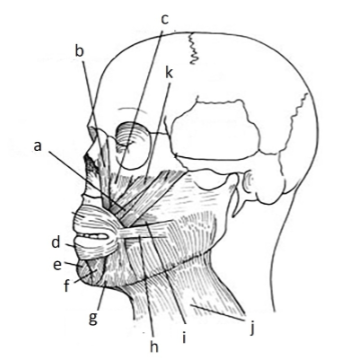
141. _____ depressor anguli oris inferioris
g
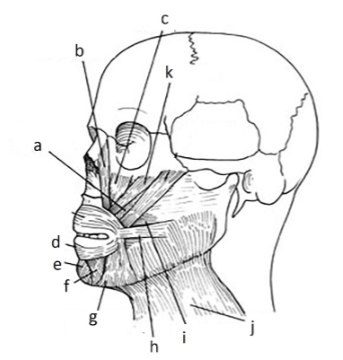
143. _____depressor labii inferioris
f