Sport Psychology Exam 4
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Purposes of Communication (5)
Persuasion
Evaluation
Informing
Motivating
Problem Solving
Communication Process (5)
Decision to send a message
Encoding the message
Message is transmitted through a channel or medium
Decoding the message
Internal response to the message
40% of communication is _____ in a typical day, yet there is very little structured training in this skill.
Listening
The % of understanding gained from spoken word is _____ than the meaning that people gain from listening to tone of voice or nonverbal communication
less
Participants in a study could pick out the winning tennis player ___% of the time by only body language
75
Examples of Breakdown in Communication (6)
Giving Unsolicited Advice
Preaching or Moralizing
Giving Orders
Put Downs
Criticisms
Ridicule
Confrontation is _____
a face-to-face discussion among people in conflict
When should you confront? (3)
In control
Thinking clearly
Striving to understand
How should you confront? (3)
Be empathetic
Be cautious
Proceed Gradually
Being Assertive (DESC formula)
Describe the situation
Express your feelings
Specify changes
Consequences that will occur
_____ often makes the difference between success and failure
Effective Communication
3 Components to Receiving Messages Effectively
Active Listening
Supportive Listening
Aware Listening
_____ training is the foundation of performance
Mental
Psychological Skills Training (PST) is the _____, _____ practice of mental or psychological skills
systematic, consistent
PST Methods/Techniques (8)
Behavior Modification
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Rational Emotive Therapy
Goal Setting
Attentional Control
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Systematic Desensitization
Imagery
Mentals Toughness involves (5):
Focusing
Rebounding from failure
Persisting in the face of adversity
Coping with pressure
Mental resilience
Four “C”’s of Mental Toughness
Control
Commitment
Challenge
Confidence
Why Psychological Skills are Neglected (3):
Lack of knowledge (myths)
PSs are viewed as unchangeable
Lack of time
PST Myths
Only for problem or elite athletes
PST is only a quick-fix
PST is not useful
___% of studies found positive performance effects from PST
85
PST Training Phases (3):
Educational Phase
Acquisition Phase
Practice Phase
The primary goal of a PST program is _____; the long-term goal is _____
self-regulation; generalization
Kirschenbaum’s Five-stage Model of Self-Regulation
The person/athlete must recognize the problem and want to change.
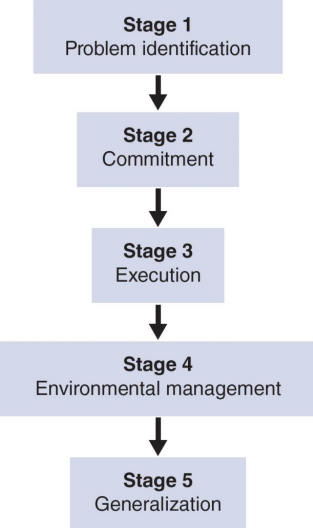
The best time to implement a PST program is _____; the worst time is _____.
during offseason; during competitive season
New mental skills often need to be practiced in ___ minute intervals ___ times per week
15-30; 3-5
Designing a Mental Training Program (5):
Assess the situation
Evaluate individual skills
Determine psychological skills tot each
Establish a training schedule
Evaluate the program
Methods of Assessment (4):
Questionnaire
Interview
Profiling
Observation
The _____ model is one of the best for profiling
Circular
Profiling Methods (3):
Circular Model
Hierarchical Order
Profile Graph
Collecting data is the only way to _____ judge whether a program achieves its goals
objectively
How individuals _____ with anxiety is more important than _____ anxiety they experience
cope; how much
Anxiety Reduction Strategies (3)
Somatic
breath control
progressive muscle relaxation
biofeedback
Cognitive
systematic desensitization
relaxation response
autogenic training
Multimodal
affective stress management
stress-inoculation training
hypnosis (low efficacy)
Most effective pace for Resonance Breathing Frequency
6 Breaths per Minute
_____ involves managing external and/or internal demands appraised as too taxing or exceeding one’s resources; list (2) types
coping; problem-focused, emotion-focused, and social support
Problem-focused coping is best for situations that are _____; emotion-focused coping is best for situations that are _____
amenable to change; not changeable