TEAS Biology Flashcard Study Material
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
List the Components of the Biological Hierarchy of life
Atoms > Molecules > Organelles> Cells > Tissues > Organs > Organ Systems > Organism
Prokaryotes

Eukaryotes

Cell membrane (plasma membrane)
This defines the cell by acting as a barrier. It keeps cytoplasm in, and substances located outside the cell out. It also determines what is allowed to enter and exit the cell, " Gatekeeper"
Golgi apparatus
Helps process and package proteins and lipids, specifically proteins to be exported out of the cell.
Cytoplasm
Supports and suspends structures inside the cell membrane; transfer materials required for cellular processes
Lysosome
Aids in digestion of macromolecules, the recycling of old cell materials; may help destroy invading viruses and bacteria.
Mitochondrion
"Powerhouse of the cell": Generates chemical energy in the form of ATP molecules
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Contains ribosomes; synthesizes and processes proteins in the cell
Nucleus
"Control center of the Cell": a small structure that contains the chromosomes and regulates the DNA of a cell
Nucleous
Area inside the nucleus which assembles RNA+ proteins into Ribsosomes
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
> Does not contain ribosomes; synthesizes and processes lipids in the cell
> Inactivates toxins and harmful metabolic products
Vacuoles
Sacs used for storage, digestion, and waste removal.
-Plant: Has one large vacuole
-Animal: Has small, sometimes numerous vacuoles.
Ribsosomes
"Site of protein synthesis" (many are found on the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum although some can be free floating in the cytoplasm.
Chromatin
This consists of DNA and proteins that make up chromosomes
Nuclear Envelope
This encloses the structure of the nucleus. It consists of inner and outer membranes of lipids.
Nuclear Pores
They are involved in the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Vesicle
This is a small organelle within a cell. It has a membrane and preforms varying functions including moving materials within a cell.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Cytosol
This is the liquid material in the cell. It is mostly water, but also contains some floating molecules.
Microtubules
These are part of the cytoskeleton and help support the cell. They are made of protein.
Mitosis
Cell Division that results in 2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells, with each having the same # and kind of chromosomes (46): 23 from mom + 23 from dad
Mitosis- Interphase
DNA replicates
Mitosis-Prophase
Chromosomes become visible as they condense and thicken
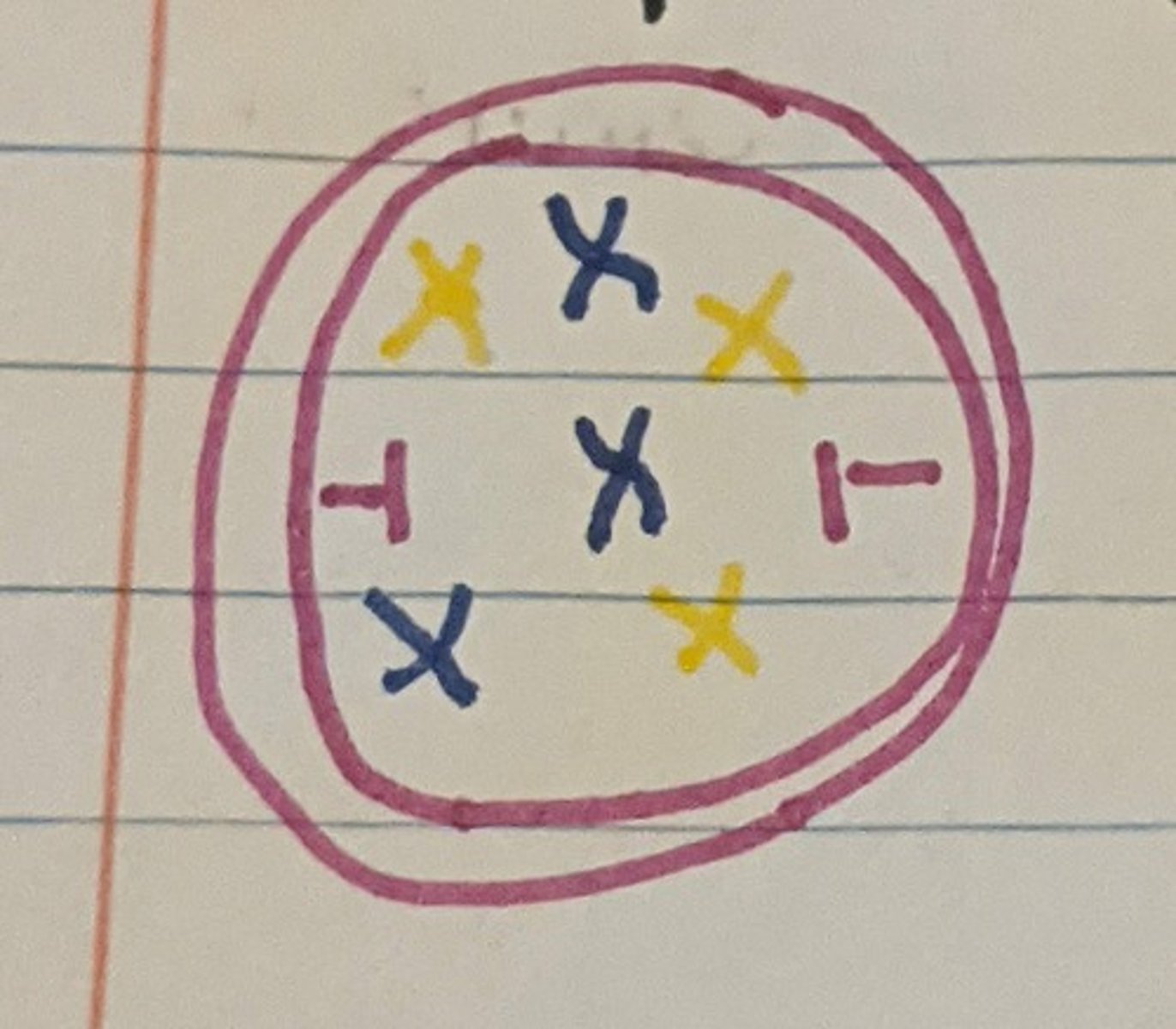
Mitosis: Metaphase
Chromosomes align in the middle of the cell's center, forming a single row.
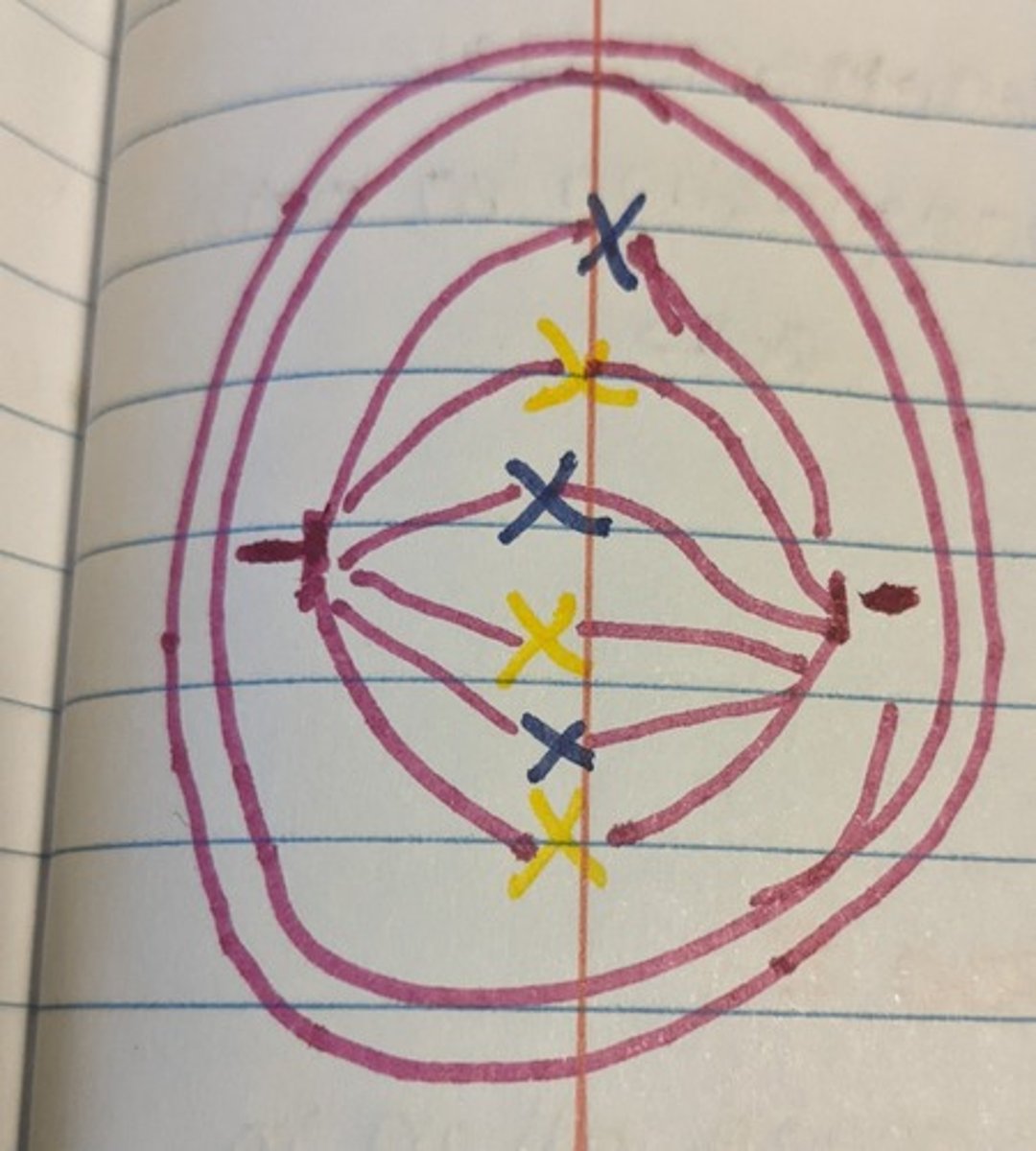
Mitosis: Anaphase
Sister chromatids are split at the centromere and pulled apart. (A= Anaphase)
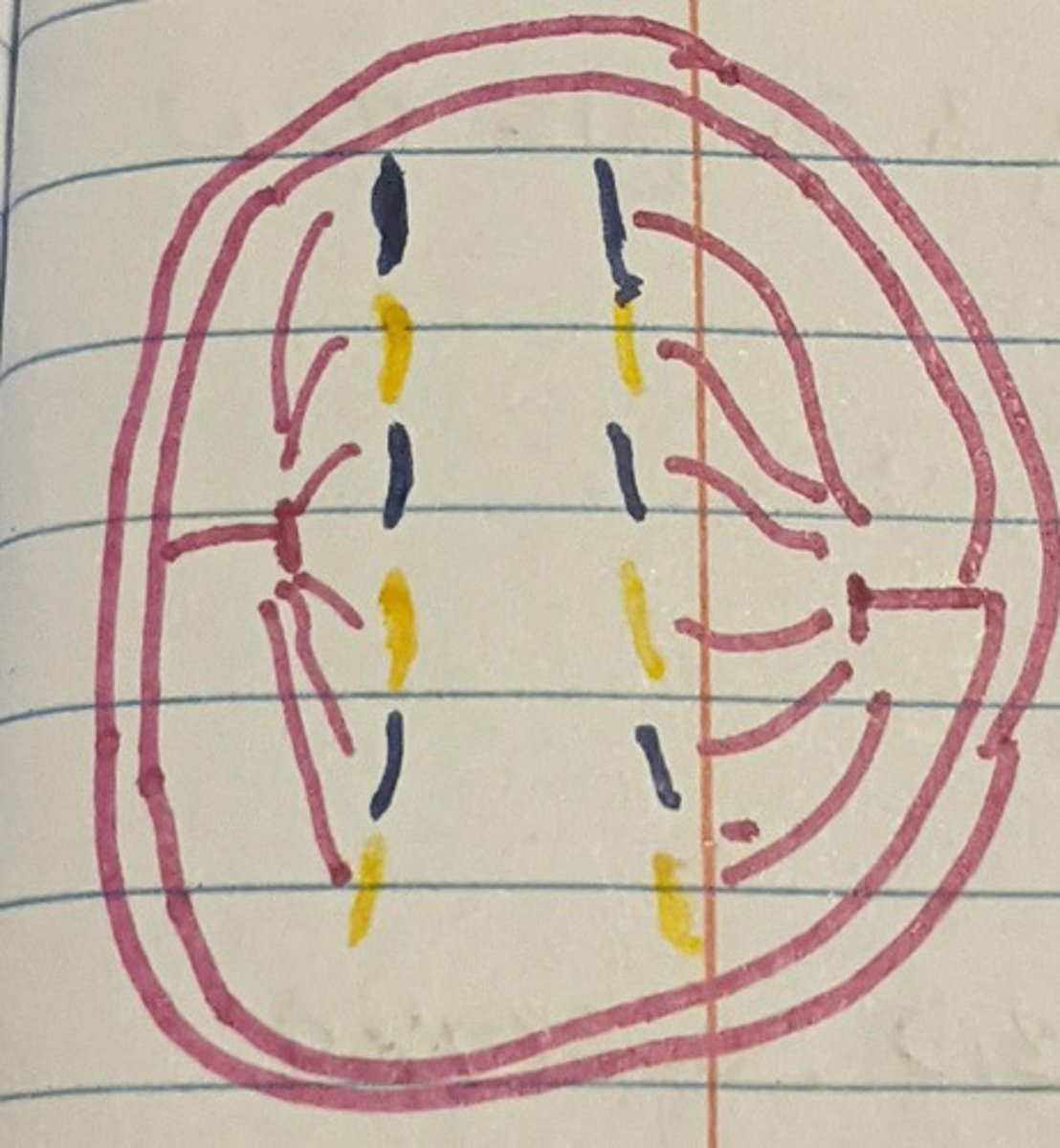
Mitosis-Telophase
> Chromosomes uncoil
> A nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
>A nucleolus forms in each new nucleus
> The mitotic spindle breaks down
> Cytokinesis begins
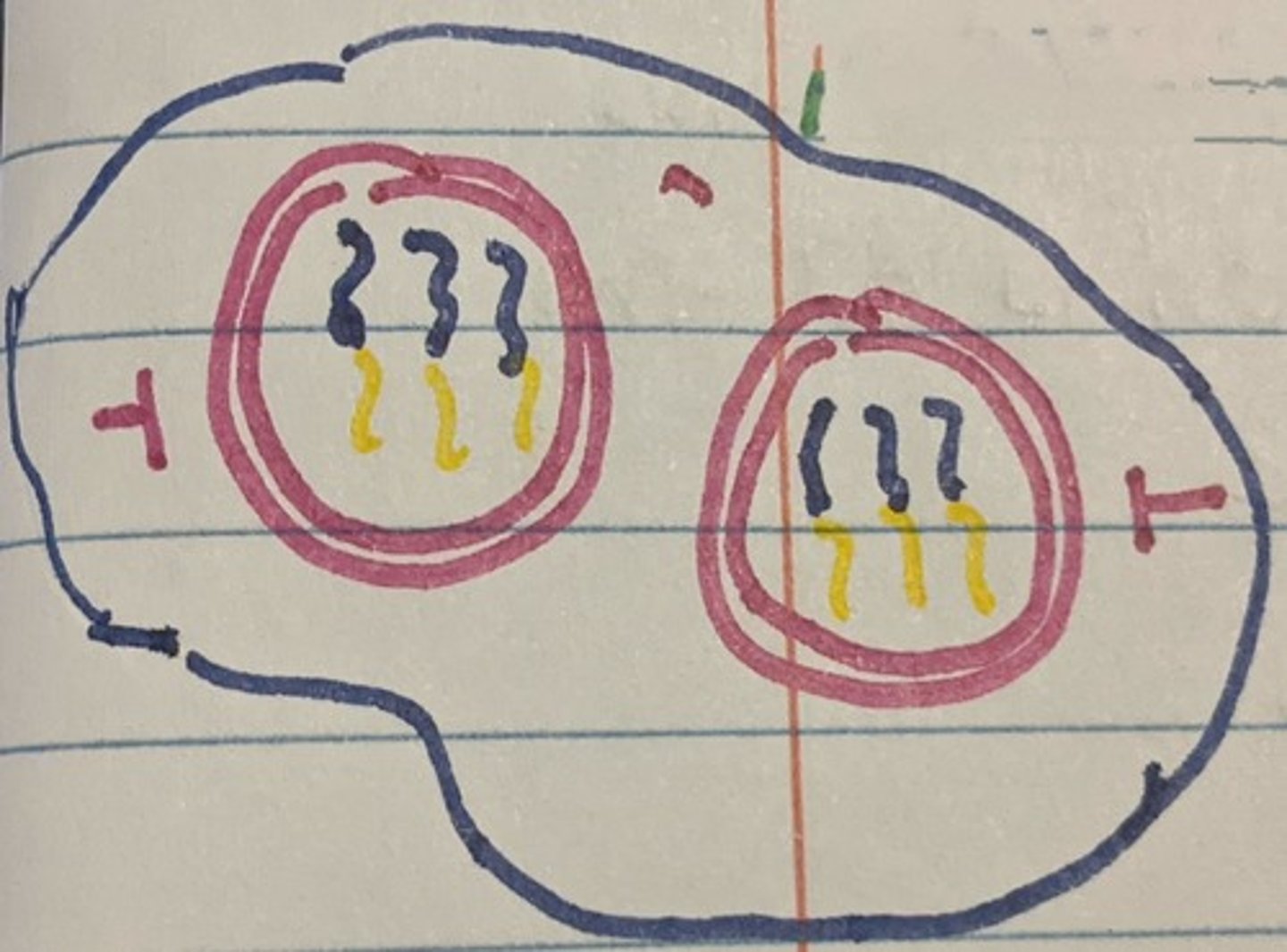
Mitosis- Cytokinesis
Splits the cytoplasm of the cell
(* Two genetically Identical Daughter Cells)
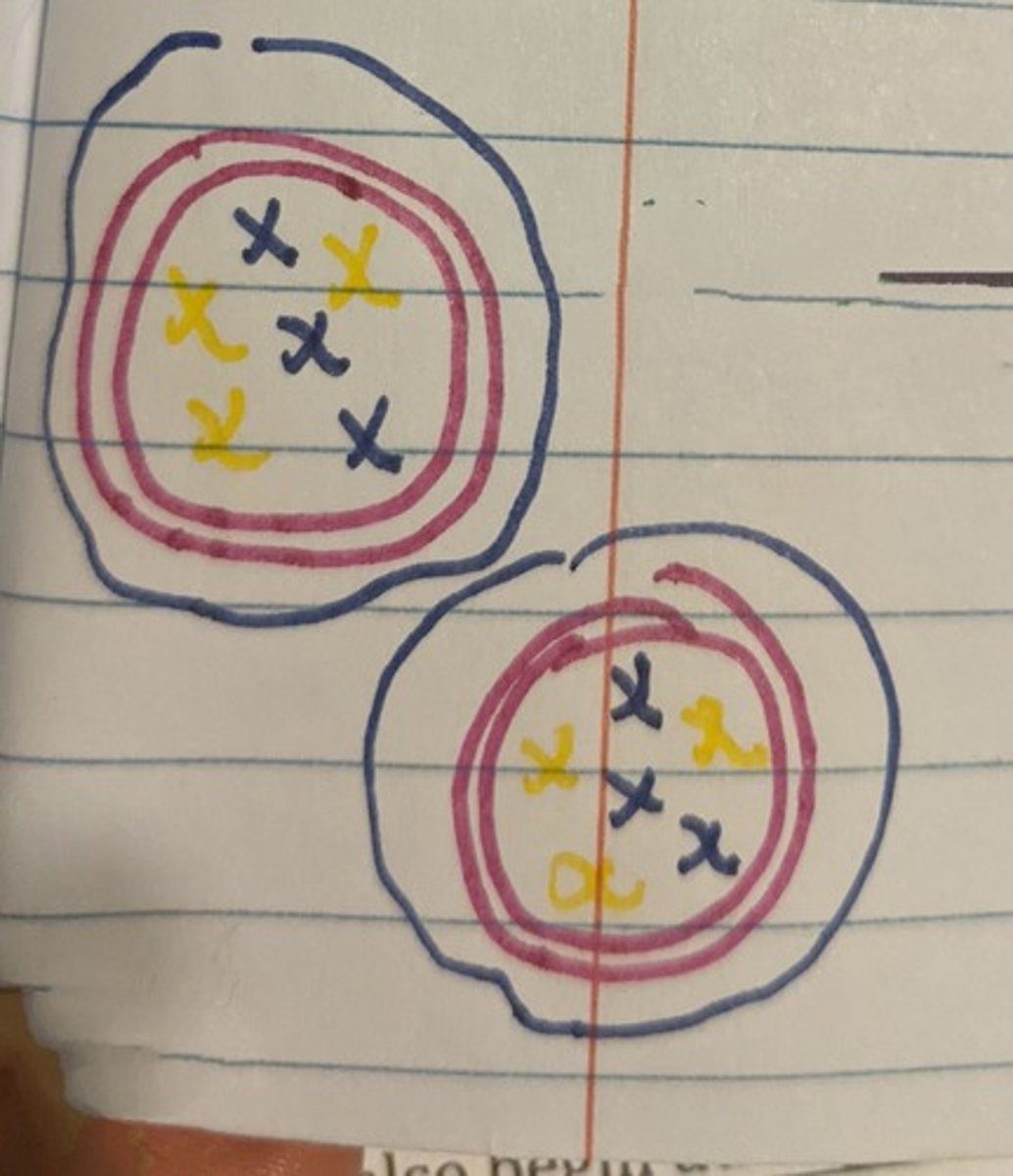
Meiosis
Cell Division that results in 4 Haploid Gametes/ Cells, with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell (23)
> undergoes two stages of meiosis
Meiosis-Interphase
DNA replicates
Meiosis- Prophase I
homologous chromosomes pair and cross over
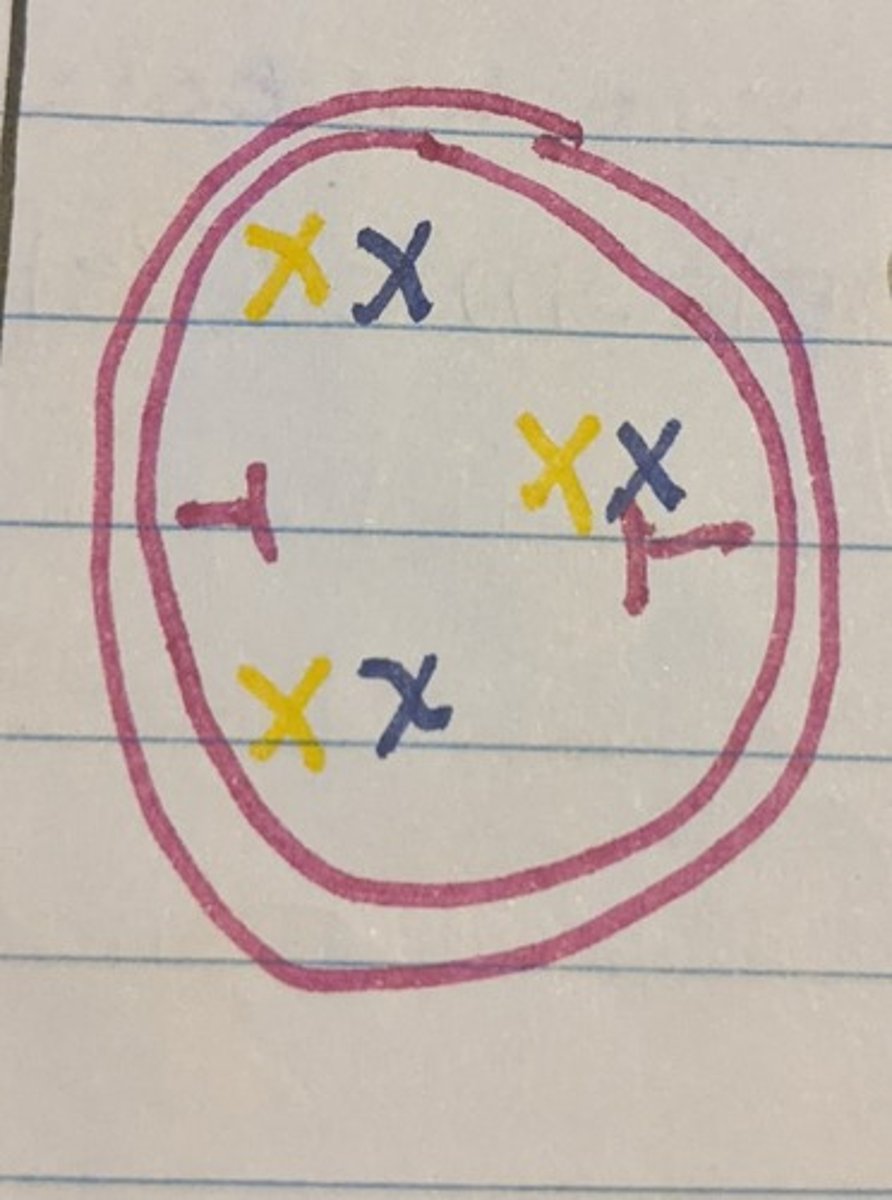
Meiosis- Metaphase I
Chromosomes align in the middle of the cell's center maintaining their homologous pairing
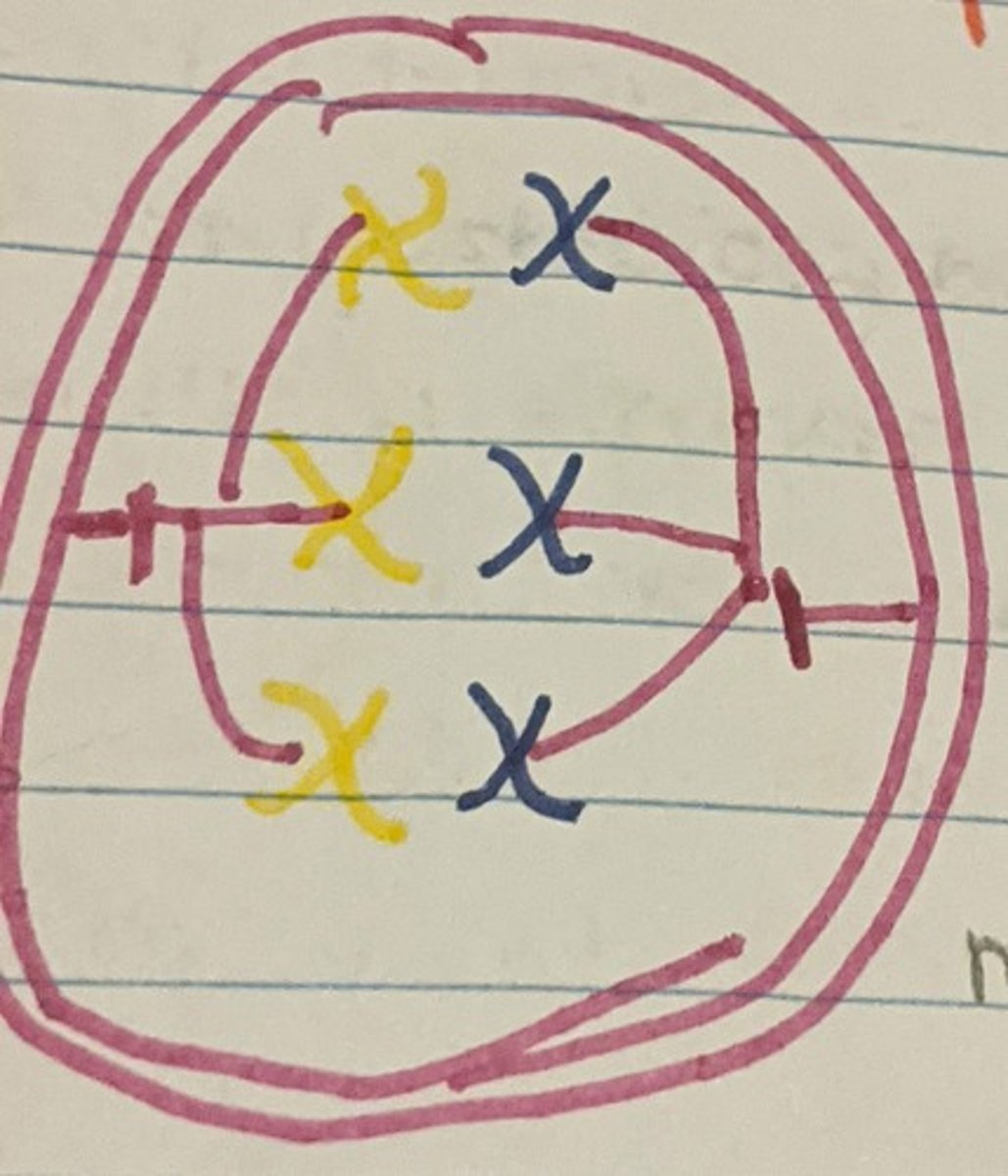
Meiosis- Anaphase I
Chromosomes are pulled apart towards separate ends of a pole.
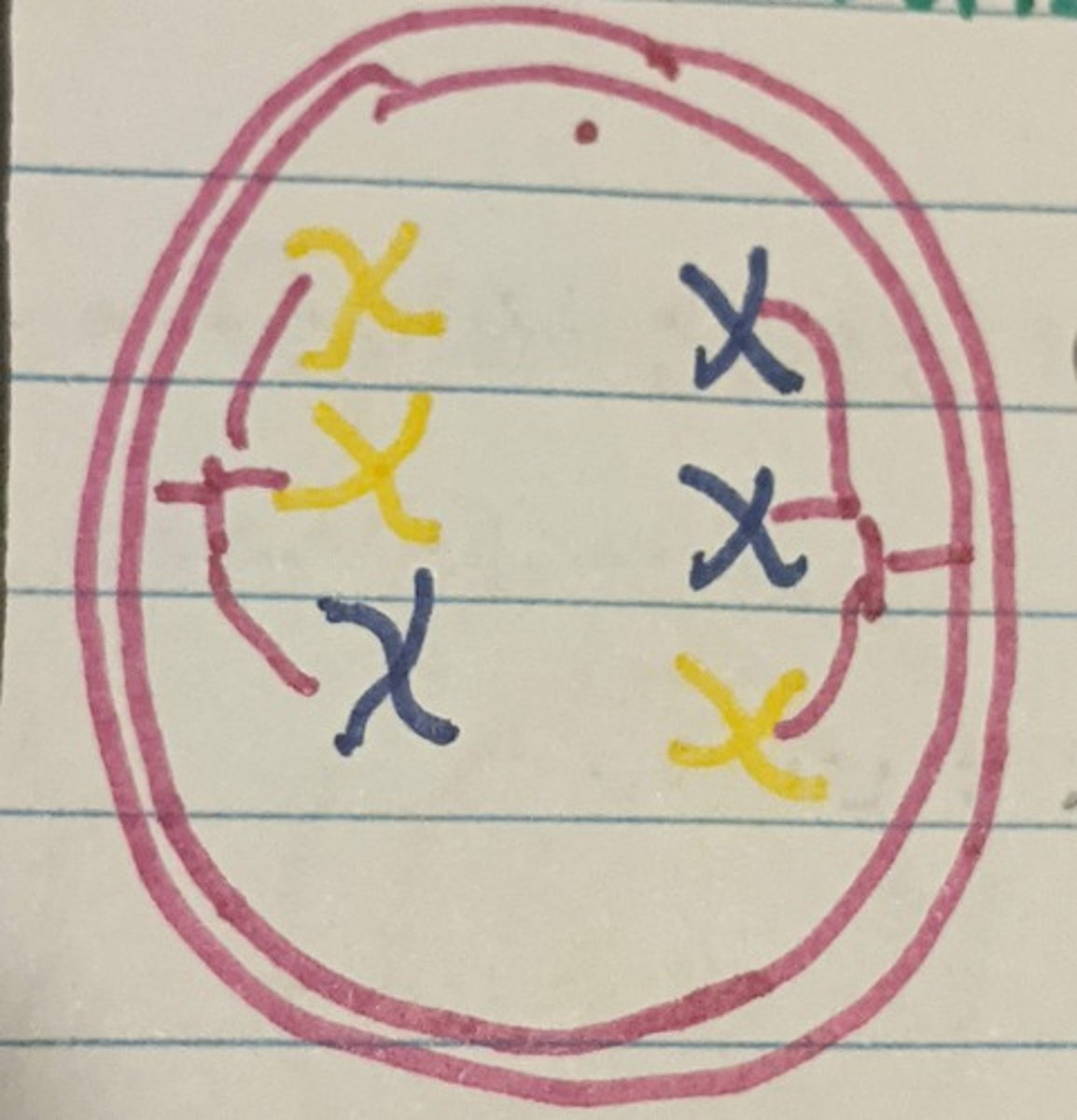
Meiosis-Telophase I
Nuclear membrane forms and cell separates into two, Cytokinesis I begins.
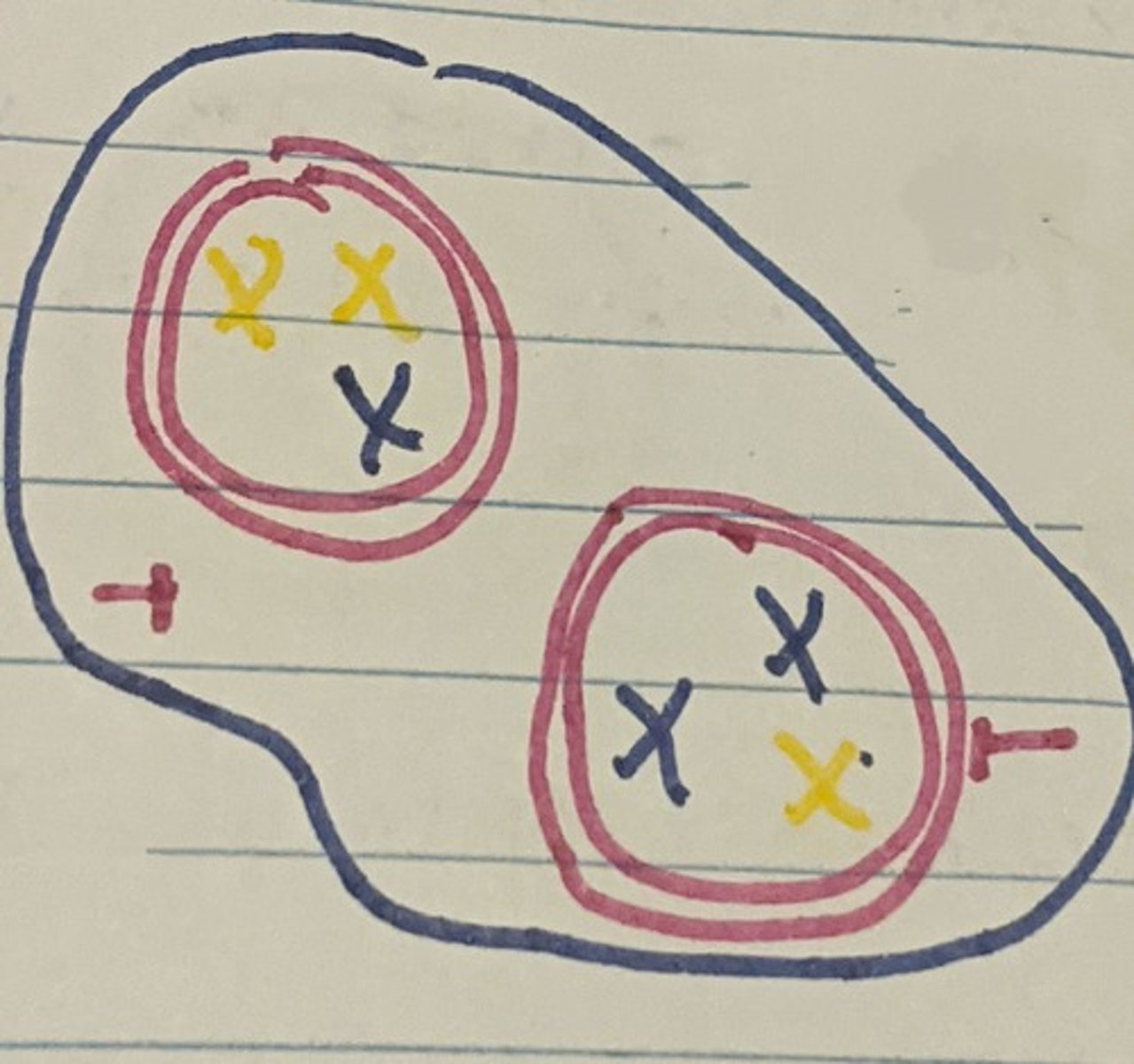
Meiosis: Cytokinesis I
Splits the cytoplasm of the cell
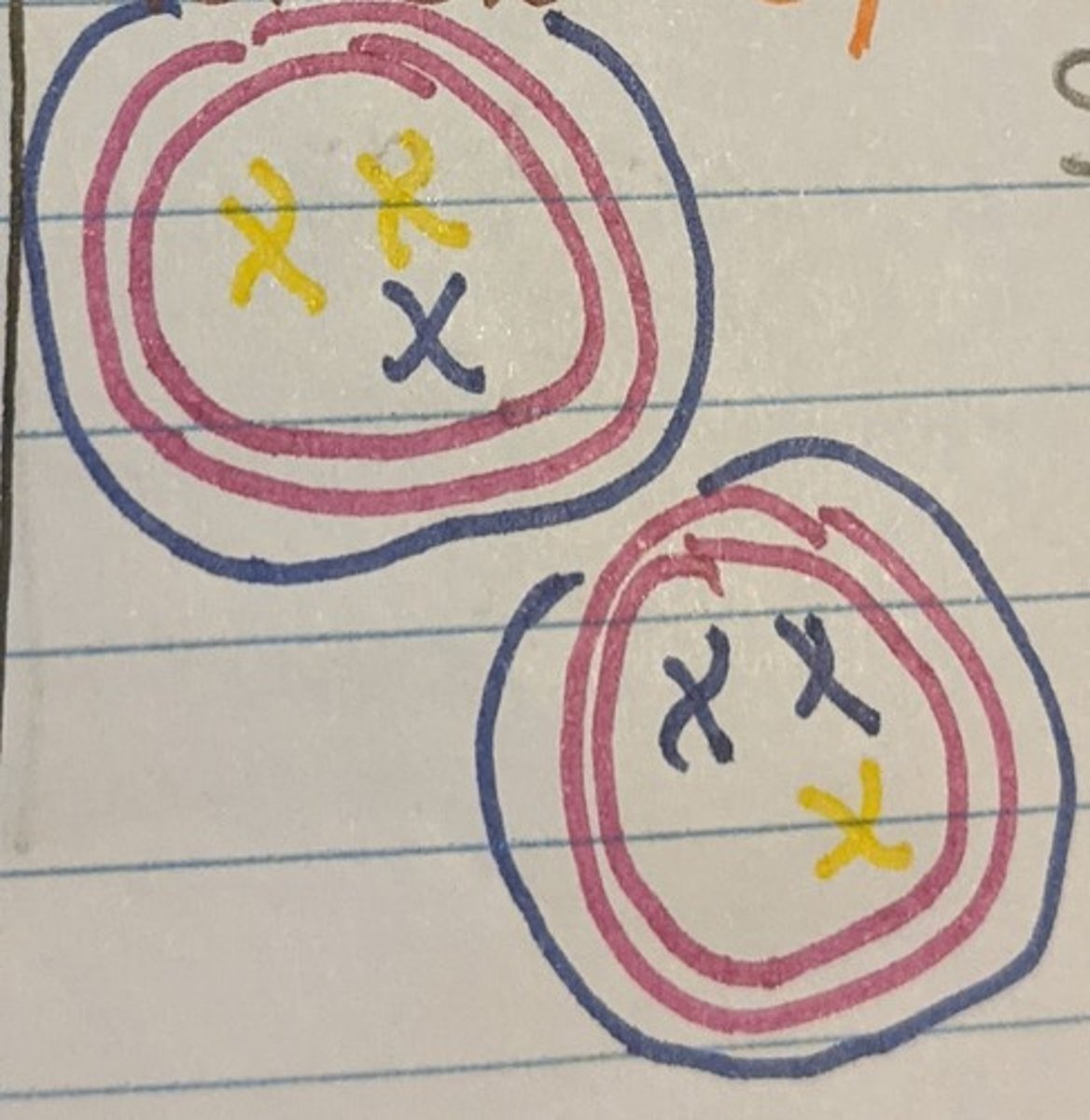
Meiosis: Prophase II
Chromosome condensation in both cells
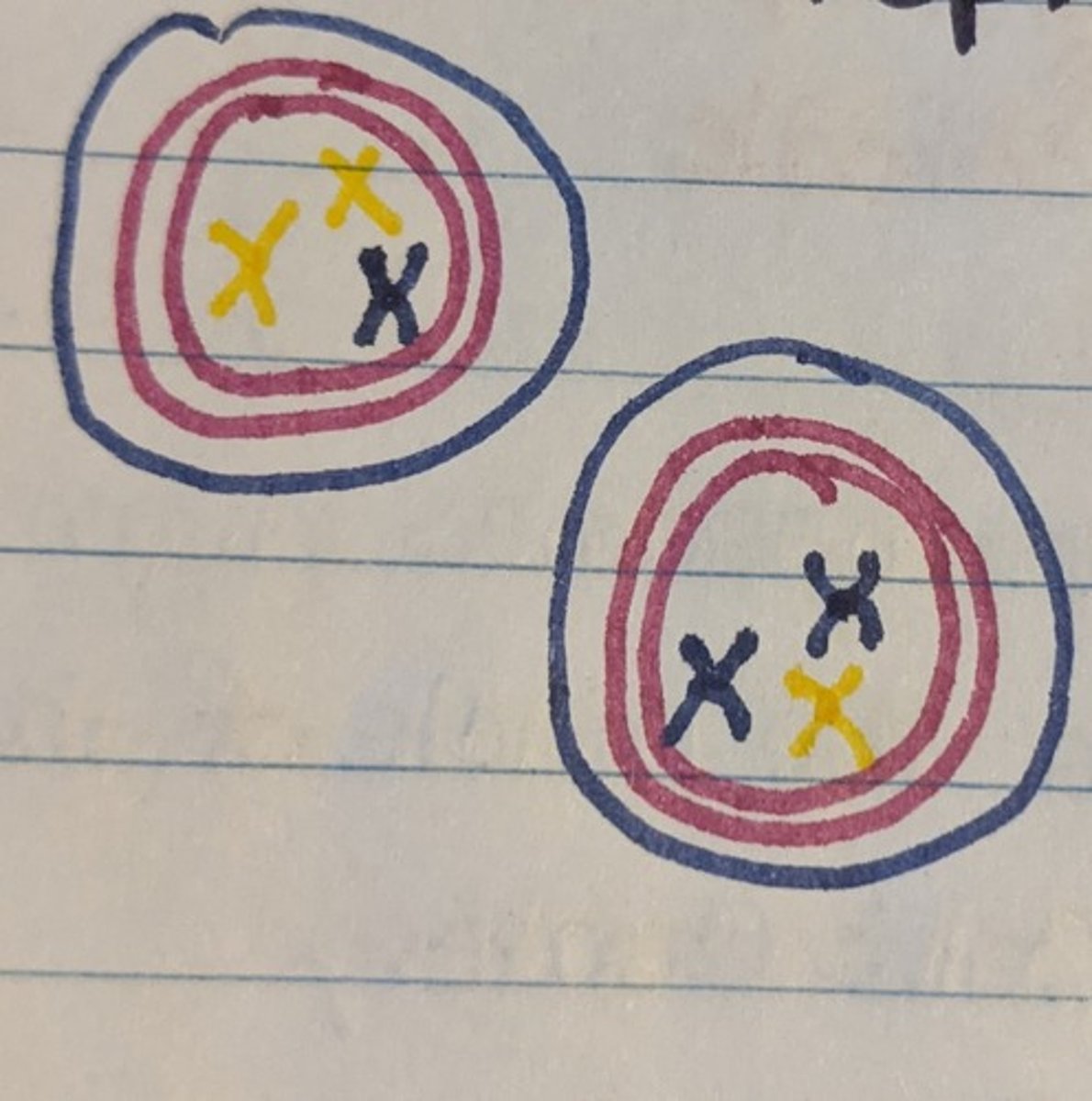
Meiosis: Metaphase II
Chromosomes align in the middle of the cell's center forming a single layer
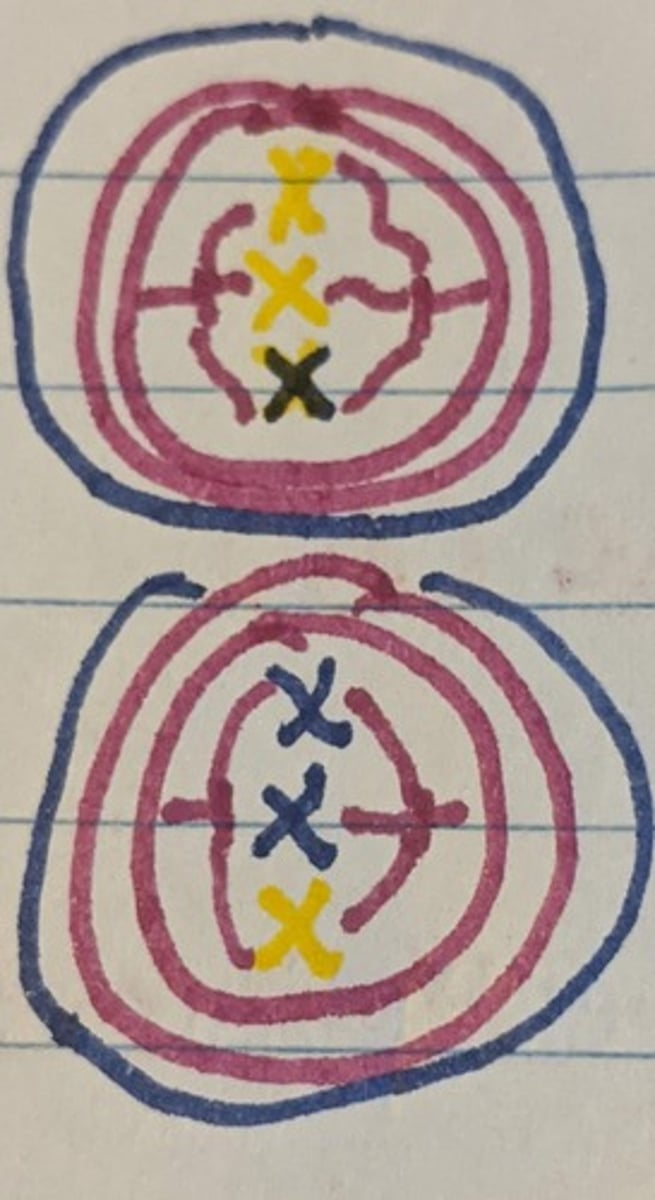

Meiosis: Anaphase II
Sister Chromatids are separated and drawn to opposite ends of the spindle fibers
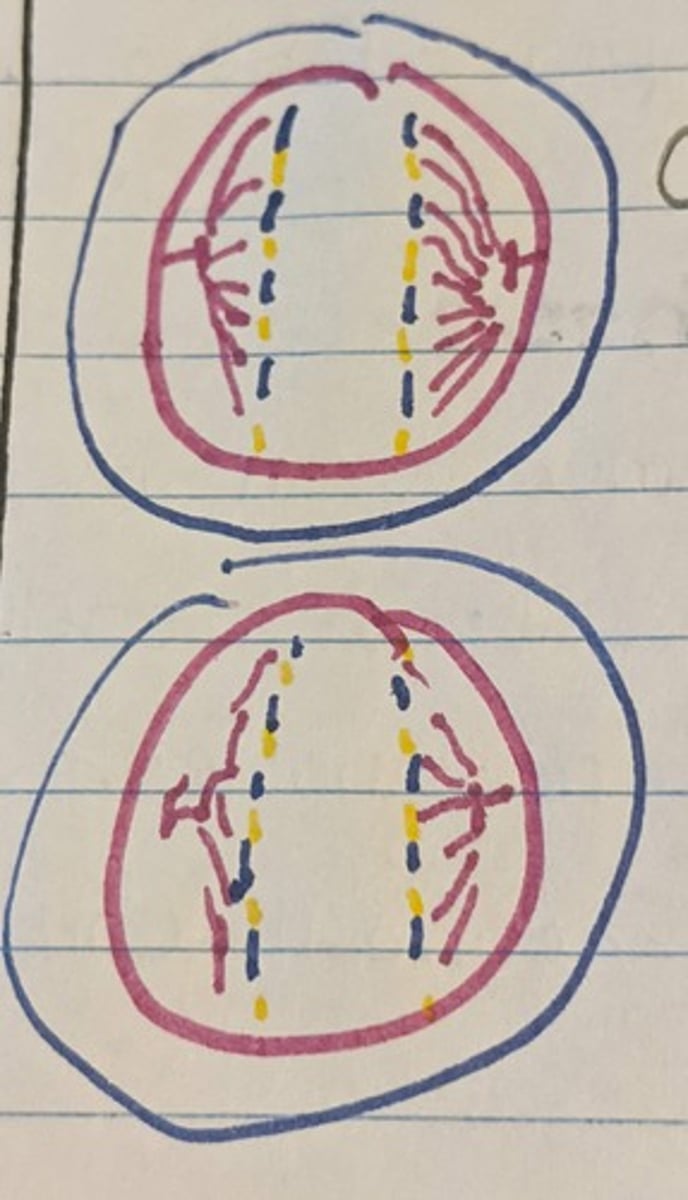
Meiosis: Telophase
> Nuclear membrane forms as two cells separate via Cytokinesis II resulting in
= 4 Genetically Distinct Haploid cells (23 chromosomes)
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
is a macromolecule that contains genes that are coded instructions for a cell to produce proteins
Structures of DNA
" Twisted Ladder or Double Helix"
> The sides: a phosphate and a deoxyribose sugar
> The rungs of the ladder are composed of four nucleotide bases
The four nucleotides of DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
Pairing of DNA Bases
Apple in Tree: Adenine= Thymine
Car in Garage: Cytosine = Guanine
Nucleotide are composed of
5 carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
Genes
segments of DNA that control a trait
Chromosomes
consist of coiled DNA wrapped around histone proteins
Structural Genes
Trait expression
Regulatory Genes
"non-coding regions"
> genes can be activated and deactivated through various mechanisms (gene regulation)
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins
> Present inside and outside the nucleus
Structure of RNA
single chain of ribose sugar (pentose-1 extra oxygen) + phosphate group
4 nucleotides of RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
Pairings of RNA bases
Apple Under the tree: Adenine = Uracil
Car in the Garage: Cytosine = Guanine
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
carries a copy of a strand of DNA and transports it from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Significant structural component for ribosomes themselves
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to growing polypeptide chain
>anticodon (compliment to codon)
Transcription
"to copy" or "to rewrite"
> The process in which RNA polymerase copies DNA into RNA
Translation
is the process where ribosomes use tRNA to put together the needed protein
Codon
are groups of three nucleotides on the messenger mRNA, " three rungs on a ladder''
Transcription and translation process
1.DNA in the nucleus serves as a template for mRNA
>( RNA polymerase)
2. mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus
3. mRNA moves into the cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes
4. tRNAs with anti-codons carry amino acids to mRNA
5. anticodon-codon complementary base pairing occurs
6. polypeptide synthesis takes place one amino acid at a time in ribosome by rRNA
Start Codon
AUG (methionine)
Stop Codons
UAA, UGA, UAG also known as ocher, opal, and amber
Peptide Bond
the link between amino acids in a protein
Genome
all of an organism's genetic material
Inheritance
transmission of characteristics to offspring
Law of Segregation
States that an organism receives half of its total number of alleles from each parent
Law of Dominance
States that when two different alleles are present in a pair, the dominant one is expressed
Law of Independent Assortment
States that traits are passed on randomly and are not influenced by other traits, the exception being linked traits
Allele
A variant of a gene (aka a trait), often recognized by letters
(F= fur, f= no fur)
Genotype
refers to the combination of two alleles present in the genetic makeup of an individual
Homozygous genotype
"Homo" means same
> FF= Homozygous Dominant
> ff= Homozygous Recessive
Heterozygous genotype
"Hetero" means different
> Ff= heterozygous dominant
Phenotype
Physical appearance of a trait formed by genetics and the environment
Genetic crosses
are the possible combinations of alleles and can be represented using Punnett squares.
Punnett Square
A square diagram used to determine the various genotype combinations that may be passed from parent to offspring and their likelihood of occurring
Monohybrid Cross
refers to a cross involving only one trait
> 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive
Dihybrid Cross
refers to a cross involving more than one trait (two traits)
> ratio of 9:3:3:1 when traits are not linked
Co-Dominance
refers to the expression of both alleles so that both traits are fully expressed and showing distinct traits together
(Cows and blood types)
Incomplete Dominance
Heterozygous phenotype that is a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes
(Snapdragons: RR=red pigment, rr= no pigment. (Rr) Pink pigment occurs because 1 gene is for red+ one is for no pigment
> 1:2:1
polygenetic inheritance
refers to traits that are influence by more than one gene
EX: skin
multiple alleles
refers to a gene with more than two possible alleles
EX: blood
Blood typing: 3 alleles: A, B, O: only have two
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
inheritance of traits that do not follow Mendelian patterns of inheritance (factors other than Dom -recessive relationships at play)
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Polymers
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Macromolecule
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
Carbohydrates
Primary source of energy and are responsible for providing energy as they can easily be converted to glucose
> take on the form CH20
Simple sugars
are grouped into monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, and galactose)
Lipids
Composed of 3 fatty acids + one glycerol
> hydrophobic
> do not have a true monomer because they do not have repeating units
> cell membrane: phospholipids
>Numerous C-H bonds
Proteins
Polymer unit made of amino acids
> composed of a central carbon, an anime group, carboxylic acid and a side group
> Enzymes: are biological catalysts: speed up chemical reactions: Endergonic: release energy, Exergonic: require energy
Nucleic Acids:
are polymers that are made up of monomers called nucleotides that contain CHNOP
4 macromolecules produced by Anabolic reactions
Carbohydrates, Lipids, proteins, Nucleic acids (DNA or RNA)
Anabolic Reaction
the synthesis of larger and more complex molecules (macromolecules) from smaller ones; require energy
4 Building Blocks involved in Catabolic Reactions
monosaccharides (glucose)
amino acids
fatty acids (glycerol)
nucleotides.
5 components of the cycle of infection
reservoir host, portal of exit, method of transmission, route of entrance, susceptible host
microbes/ microorganism
organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye and may be classified as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa
Parasites
Microbes that are not free-living and must find a host from which to gain nutrients
Host
An organism on which a parasite lives.
Pathogen
an infectious agent capable of causing disease
Virulence
the severity or harmful potential of a pathogen
1. Reservoir (host)
an animal, insect, or human whose body is susceptible to growth of a pathogen
2. Portal of Exit
a way for the infectious agent to escape from the reservoir in which it has been growing+ infect another
(Ex: via mouth nose, blood, urine, vaginal fluid, feces, eyes)