Decision Making to Improve Operational Performance (3.4)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Operational Objectives
Costs
Quality
Speed of response
Flexibility
Environmental objectives
Added value
Capacity Utilisation
The % of capacity being used at a time. (Want to be high but not too high as it leads to the business being inflexible)
Efficiency
Reducing waste.
Labour Productivity
The output per worker.
Lean Production
Minimizing waste while still achieving good quality.
Just In Time Production (JIT)
Materials used for production are delivered just before they are needed as this will minimize storage costs.
Just In Case Production (JIC)
Stock is held just in case there is a change in demand or an issue with materials being delivered. This leads to some flexibility.
Mass Customisation
Still mass production but with the option to change a simple thing. Example colour of Iphone.
Labour Intensive
Production relies heavily on people doing the work.
Capital Intensive
Production relies on machinery doing the majority of the work.
Quality Assurance
Aims for zero defects by preventing mistakes from ever happening. (Example TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Quality checks at each stage of the production to ensure there is no issues and if there are issues they can be solved quickly and easily.
Quality Benchmarking
Comparing the businesses operational performance against competitors. To try and find places to improve on, to insure the business is operating the best in the industry.
Quality Control
Inspecting products at the end of production to ensure the products meet the required quality.
Kaizen
Continuous improvement that involves the entire businesses work force, gives everyone a say and could bring new ideas not thought of beforehand.
Quality Circles
Small groups of workers at different levels of workforce who come together to discuss issues in production.
Cell Production
Each cell (group of people) is responsible for completing a specific task.
Outsourcing
Using other businesses to produce your products could be done in other countries which could reduce cost as labour may be cheaper.
Producing to Order
The business will only manufacture the product once it has been ordered this will reduce storage space needed.
Inventory Control Chart
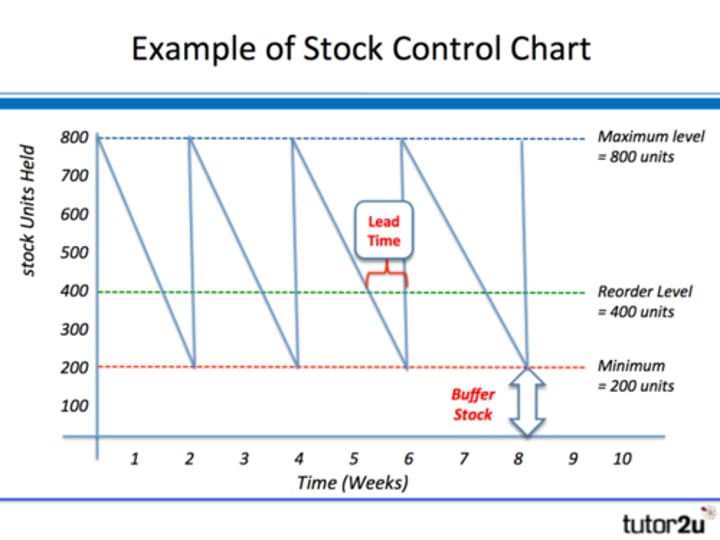
Lead Time
Time it takes for materials to be delivered from the moment they are ordered.
Re-Order Level
Level of current stock when new orders should be placed.
Buffer Level of Inventory
Minimum amount of inventory the business wants to hold, allows the business to be a tiny bit more flexible.
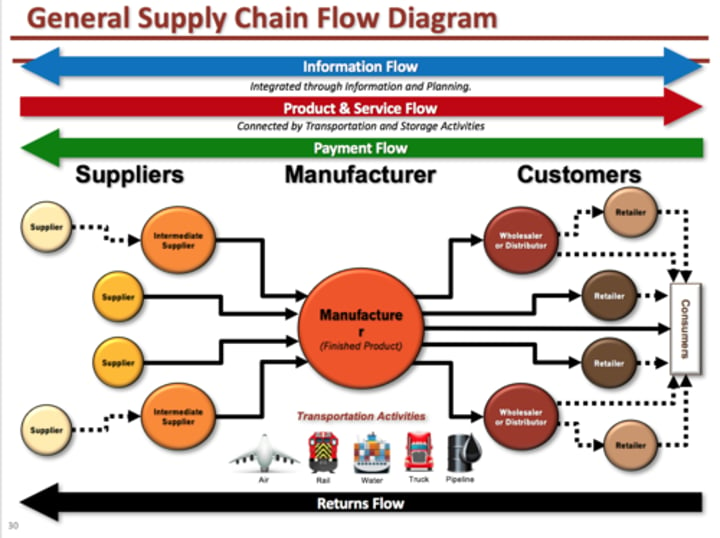
Logistics
Transporting and storing raw materials, finished goods, inventory, and other resources.
Supply Chain Diagram
Economies of Scale
Buying - Bulk buying
Technical - Use equipment to boost production
Marketing - Spreading fixed marketing spend over large range of products, markets, and customers
Network - Mobile phones
Financial - Benefit from access to more and cheaper finance
Diseconomies of Scale
Poor communication
Complex/Large business
Capacity utilisation is too high
Loss of management focus