esophagus ca all
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
def. A highly muscular collapsible tube of the GI tract
term. esophagus
How long is the esophagus?
25 cm long
The esophagus
begins at:
ends at:
C6: cricoid cartilage
T10-T11: gastroesophageal junction
How do the muscles of the esophagus propel food through it and downward into the stomach?
Peristalisis
What are the 4 ways the esophagus is categorized?
Cervical | Thoracic
Cervical | Lower/ Distal
AJCC: Cervical | Upper Thoracic | Middle Thoracic | Lower Thoracic
The most common one:
Upper 1/3: Cervical Esophagus
Middle 1/3
Lower 1/3: Thoracic Esophagus
The upper 1/3 of the esophagus extends from:
C6-T2: Cricoid Cartilage - Manubrium
The middle 1/3 of the esophagus extends from:
T2-T8: Manubrium - Hilum
The lower 1/3 of the esophagus extends from:
T8-T11: Hilum- GE (gastrointestinal) Junction
Esophageal Cancer Epidemiology (6)
Higher incidence in:
mostly male
African American
ChIA: China, Iran, South Africa
Age
55-65
Location where most occur in
lower 1/3
Uniformly fatal disease

Typical age for esophageal cancer
55-65
In what location of the esophagus does esophageal cancer most commonly occur?
lower third
Esophageal Cancer Etiology (7 underlying conditions)
Alcohol/ Tobacco
Achalasia
Plummer-Vinson Syndrome
Tylosis
Diet: ↓ Fruits & Veggies | ↑ Nitrates
Caustic Injury to Esophagus
Barrett’s Esophagus
AA B C D PT
What is the most common cause of esophageal cancer?
alcohol/ tobacco
__% of esophageal cancer is caused by alcohol/ tobacco
80
How does alcohol + tobacco cause esophageal cancer?
The combination of alcohol + tobacco has a synergistic effect on mucosal surfaces
FYI: Failure of the sphincter to relax with swallowing, the esophagus has lost much of its perstaltic activity
def. Achalasia
fyi: Iron-deficiency anemia characterized by esophageal webs, atrophic glottis and spoon-shaped brittle fingernails
def. Plummer- Vinson Syndrome
Plummer-Vinson Syndrome is most common in what population:
Women
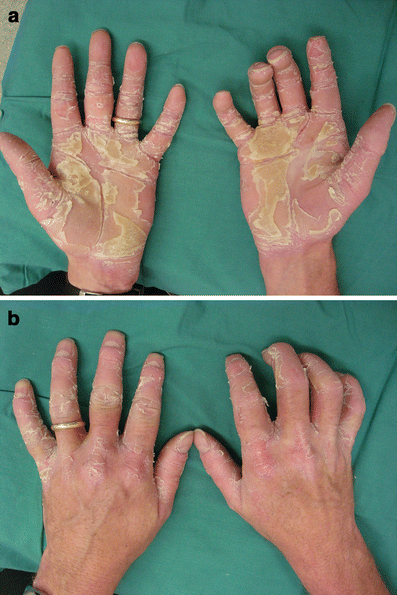
def. An inherited condition characterized by epidermal thickening in the palms and soles of the feet
term. Tylosis
Tylosis predisposes you to what?
Esophageal carcinoma
Individuals with tylosis have a __% change of esophageal carcinoma
37
Patients with caustic injury to the esophagus, the incidence has been reported to be ___X greater than that of a normal individual
1000
What is Barrett’s esophagus
A condition where distal esophagus is lined with columnar epithelium instead of stratified squamous
What causes Barrett’s Syndrome
chronic acid reflux
Clinical presentation for esophageal cancer
List then in order from most common to least common
dysphagia - most common
weight loss - 2nd most common
Odynophagia - not as common
Gastroesophageal reflux- not as common
term. dysphagia
def. difficulty swallowing
term. Odynophagia
def. Pain on swallowing
Diagnostic tests for esophageal cancer (5)
Barium swallow
Chest X-Ray/ CT
Esophagoscopy / Bronchoscopy
Routes of Spread
local mets
lymphatics- skip mets
Hematologic
T/F: Esophageal tumors are detected early cuz they cause obstruction
False: Tumors are often locally advanced
Why can the esophageal cancer tumor grow large before it causes obstruction?
cuz esophagus is distensible
How does esophageal cancer spread by direct invasion?
it is contiguous along the length of the esophagus
T/F: The esophageal area is rich with lymphatics
True
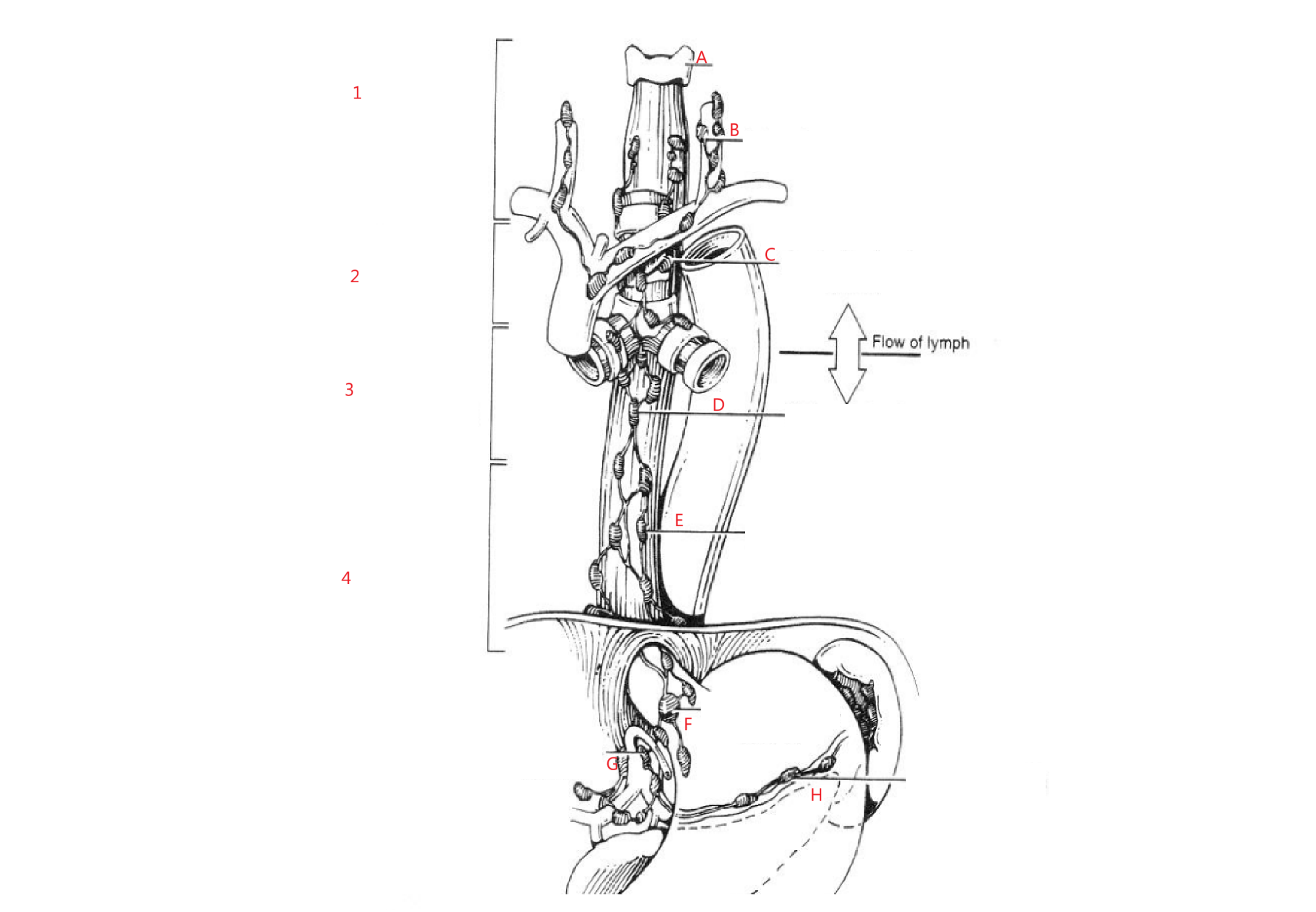
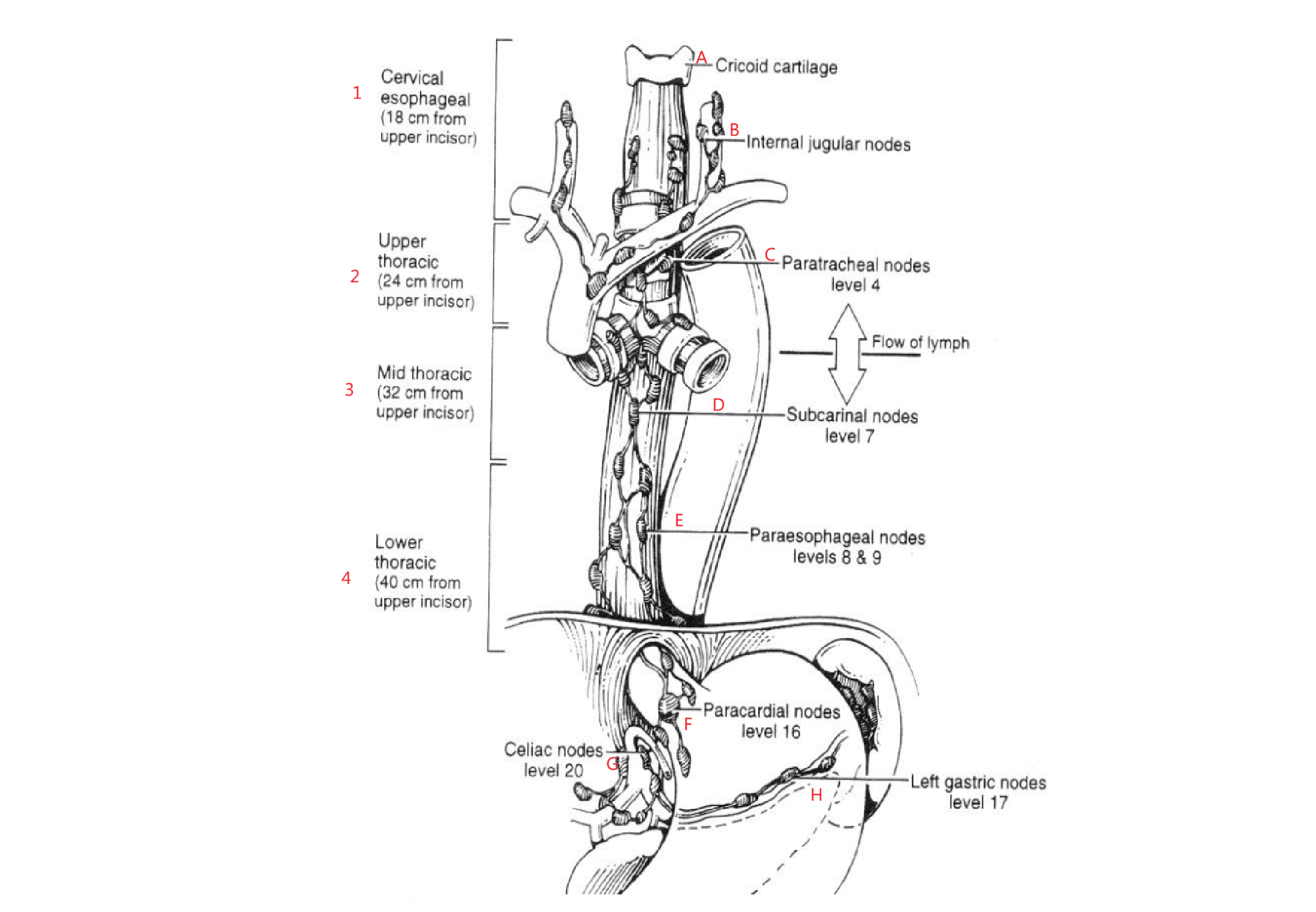
How does lymphatics flow in esophagus? Why is this bad?
Along entire length of esophagus draining into any adjacent draining nodal bed
Risk of skip mets
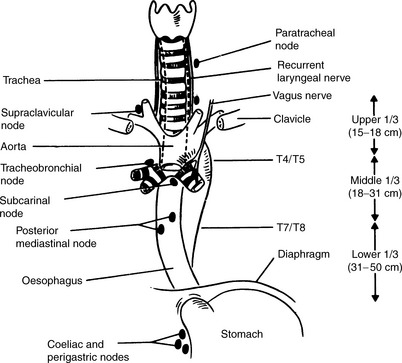
What are the 5 nodes esophageal cancer spreads to?
cervical
supraclavicular
paraoesophageal
celiac axis
paragastric nodes
SCP CP
What organs does esophageal cancer spread to?
Liver- MOST COMMONLY
Lungs- secondly

Why do most esophageal cancer patients die?
Due to mets to liver
What is the pathology/pathologies of esophageal cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma: upper 1/3
Adenocarcinoma: distal esophagus & patients with Barrett’s esophagus
Why is there an issue with differential diagnosis for esophageal tumors?
Cuz many stomach cancers are adenocarcinomas as well that can travel to esophagus
Location of esophageal cancer by %
Upper:
Middle:
Lower:
Upper: 10% of CAs
Middle: 40%
Lower: 50%
What is the single most important factor in selection of the type of therapy (cancer tx) for esophageal cancer
Site of origin of neoplasm
T/F: Treating esophageal cancer is easy.
False: It’s
highly complex
technically challening
In general how is esophageal cancer treated?
Patients do better with…
Upper esophagus: RTT
Lower esophagus: Surgery
Chemo: as a radiosensitizer
Name/ type of surgical procedure to treat esophageal cancer
esophagectomy with anastomosis
List the locations in which surgery with anastomosis for esophageal cancer can be performed
Upper
Middle
Lower
Middle and Lower
Upper is not surgically accessible
How much of the esophagus is removed?
the entire esophagus or as much as possible
Cons of using esophagectomy to treat esophageal cancer
high operative mortality rate
even after resection, most patients die from distant mets (liver)
What chemos are combined with RTT to act as radiosensitizers?
5 FU
Cisplatin
What type of esophageal cancer pathology is fairly radiosensitive?
adenocarcinoma
squamous cell carcinoma
both
2, SCC
Treating esophageal SCC, specially with chemo, achieves:
local tumor control
regional tumor control
mets control
local tumor control
Radiation therapy is useful to treat cancers in the upper 1/3 of the esophagus, but above what anatomical structure specifically?
aortic arch
Types of RTT tx fields used to treat esophageal cancer
for…
Upper 1/3 lesions: APPA + shrinking field (boost)
Middle and Lower lesions: APPA OR Rotational field (boost)
Boost after __ Gy for esophageal cancer. Why?
45
due to lung/ cord tolerance
Boost field options for lesions in the thoracic region
3 field: AP + 2 Posterior Obliques w/ wedges
prone, or
supine on wing board, vac-lok, arms up
OR
POP lats
OR
HDR w/ iridium 192
What are the tumor margins for esophageal cancer?
5 cm above + 5 cm below
(cuz of skip mets)
If you are taking an esophageal cancer sim, what should it be?
Orthogonal films
Total dose for esophageal:
If combined with surgery:
If combined with chemo:
If alone:
If combined with surgery: 45-50 Gy
If combined with chemo: 50 Gy
alone: 60-70 Gy
Why do we treat esophageal patients prone sometimes?
To pull esophagus away from cord
RTT complications of esophageal cancer (4)
esophagitis, substernal pain
Dysphagia
stricture & perforation- late effects
If RTT w chemo: synergistic effect mucosal rxns
EDS are F
At what dose does dysphagia happen
20 Gy
5-year survival for esophageal cancer
6-8%
T/F: esophageal cancer is nearly a uniformly fatal disease
True
What are prognostic factors for esophageal cancer
Tumor size (FYI: tumors less than 5 cm have better survival rate)
Weight loss
Age: >65
Poor Karnofsky