Midterm 2 : Non-Coding RNAs
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are non-coding RNAs?
mRNAs that do not code for proteins but instead perform functions as RNA molecules.
What are four types of non-coding RNAs?
Short RNAs derived from processing and cutting longer precursor mRNAs:
MicroRNAs
siRNAs
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA)
Circular RNAs — resistant against endonucleases that require 3’ or 5’ ends to digest.
Piwi-associated RNAs (piRNAs)
What three RNAs are implicated in gene regulation?
microRNA-mediated transcriptional gene regulation;
RNA interference (RNAi) and chromatin;
The PIWI proteins (transposons regulation)
What are the steps to microRNA biogenesis?
Primary microRNAs are recognized by Drosha — endonuclease that creates a 3’ overhang.
Exportin 5 takes pre-miRNA to the cytoplasm.
Dicer + TRBP + PACT (RNA 3-type endonuclease) recognizes the pre-miRNA and creates a microRNA duplex (clips off the loop) and creates a 3’ overhang, 5’ phosphorylation.
The RISC complex, with argonaut, uses ATP for loading.
The guide strand with more thermodynamic stability at the 3’ end is retained in the argonaut complex.
Passenger strand is lost in the unwinding of miRNA.
During target recognition, the mature miRNA seed site attaches to an mRNA. Argonaut recruits GW182 family proteins downstream of Ago and inhibitis translation.
Pre-initiation and post-initiation.
Target binding results in one of three fates:
Target cleave (<10-11 nt match);
Accelerated deadenylation;
Translational inhibition.
What promotes the unwinding of pre-miRNA?
Mismatches in 2-8 nt and 12-15 nt promote unwinding.
What controls Ago’s nuclease activity?
The extent of activity is dependent on the degree of complementarity between the miRNA and mRNA.
What kind of RNAs enter the Dicer-associated complexes?
In-vitro synthesized dsRNA
miRNA precursors
Transgene dsRNA
Viral dsRNA
Transposon dsRNA
Heterochromatic dsRNA
What are the kinds of fates of RNAs exit the argonaute-associated complexes?
mRNA degradation
Translational inhibition
mRNA cleavage
Heterochromatic domain formation
What enzymes process miRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs?
miRNA : Drosha and Dicer
siRNA : Dicer
piRNA : Zucchini and unknown trimming enzymes
What are the mechanisms of action of miRNAs, siRNAs, and piRNAs?
miRNA : Translational repression, mRNA degradation.
siRNA : RNA cleavage.
piRNA : Transcriptional / post-transcriptional repression of transposons.
Multigenerational epigenetic phenomena in worms.
What is the function of miRNAs, siRNAs, and piRNAs?
miRNAs : Regulation of protein-coding genes.
siRNAs : Regulation of protein-coding genes and transposons.
Antiviral defence.
piRNAs : Transposon silencing.
How were miRNAs? discovered?
They were discovered by the investigation of genes controlling cell growth — non-coding genes were observed effecting the development of C. elegans (worms).
What two miRNAs were controlling development of C. elegans?
lin-4
lin-14
The genes are linked through the same pathway for miRNA formation.
What does a lin-4 knockout lack?
Unable to lay eggs due to failure to develop vulva.
What does a lin-14 knock out do?
Develop adult features precociously at early larval stages, resulting in smaller, poorly formed adults.
What did researchers notice about the lin-4 / lin-14 complementarity?
Researchers noticed that lin-4 had high sequence complementarity with the 3’UTR of lin-14 and that it may be associated with translation inhibition. When lin-4 is expressed, it silences lin-14. When lin-4 is knocked out, lin-14 is expressed.
How are microRNAs typically transcribed?
miRNAs are transcribed by RNA pol 2, with long (>1 kb) highly structured primary microRNAs (pri-miRNA transcripts). These pri-miRNAs can also be coding.
miRNA loci are often polycistronic possessing introns of coding or non-coding transcripts, or exonic regions too. Some viral miRNAs are transcribed by RNA pol 3.
What is Drosha?
An RNAse type 3 endonuclease that processes pri-miRNAs into 65 nt stem-loop precusor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs).
These have 5’ phosphate and 2 nt, 3’ overhang.
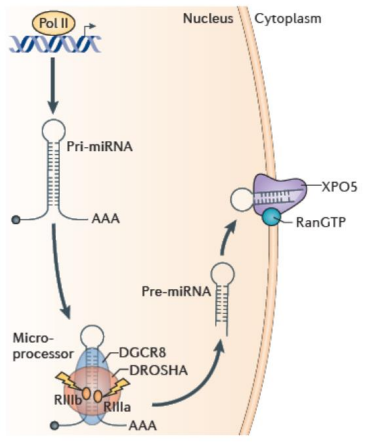
What is DGCR8?
An essential cofactor for pri-miRNA processing in Drosha.
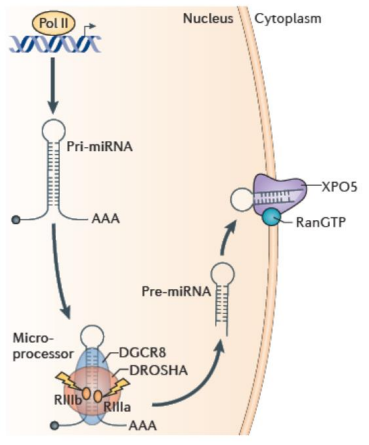
How do pre-miRNAs export out of the nucleus?
Exportin 5 (XPO-5) exports pre-miRNAs out of the nuclease into the cytoplasm.
Exportin-5 is a GTP-dependent exporter that recognizes miRNA.
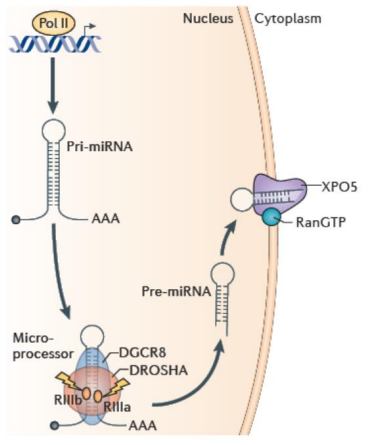
What is Dicer?
An RNAse type-3 endonuclease with a preference for Drosha products (with 2 nt, 3’ overhang). Processes pre-miRNAs into small RNA duplexes (~21-25 nt). 5’ phosphate and 2 nt, 3’ overhang.
What are the two cofactors for Dicer? What do they do?
TRBP for processing efficiency and tunes length.
PACT, role unclear.
What two proteins are important for the structure of Argonaute?
PAZ and PIWI control the binding of mRNA and microRNA into the pocket of Argonaute. If there is no complementarity to a certain degree, then the endonuclease activity may not be fully accomplished, and other translation inhibition approaches must be initiated.
What is characteristic of the Drosha microprocessor/ cofactor interactions?
The interactions are largely conserved between DROSHA and DGCR8. The cofactors keep the structure in the right conformation for cutting.
Where is the seed sequence typically located?
The seed sequence is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 2-7 from the miRNA 5’-end.
What are the two phases of RISC assembly?
Loading (+ATP) of the miRNA duplex into an Ago protein.
Unwinding (-ATP, ‘rubber band’ model).
Mature ‘guide’ miRNA vs passenger strand.
Dependent on the thermodynamic stability at the 4’ end (preference for a 5’ Uridine).
Mismatches in the miRNA duplex at 2-8 and 12-15 promote unfinding (seed site is important for unwinding/mRNA interaction).
What does MID do in the Argonaut structure?
It catalyzes the hydrolysis of the phosphodiester bond (5’ end, U/A) with a Magnesium cofactor.
Summarize how a mature mRNA is bound by a single-stranded siRNA or miRNA in the argonaut structure?
Argonaut binds:
5’ phosphate is bound by MID
5’ is bound by MID and PIWI
3’ end of is bound by PAZ
PIWI folds into an RNAse H domain and carries out “slicer” activity.
Argonaut scans RNAs in the cell for complementarity. The extensive base-pairing with the target, base-pairing at nt 10-11 trigger a conformational change and slicing.
What does complementarity of miRNA determine?
It determines whether Argonaut will cleaves self or non-self proteins. SiRNAs have better base-pairing and leads to perfect viral genome pairing — triggering cleavage.
What are other parameters important for miRNA targetting?
3’ UTR structure — miRNA starts scanning from 3’UTR until it finds complementarity (binds the 3’UTR for stability).
Distance from the ORF and/or poly(A) tail.
RBP sites in the the 3’ UTR.
miRNA cooperation (8-30 nts) — there can be multiple bind/seed sites in an mRNA for multiple microRNAs to promote variance in inhibition.
What are GW182 proteins?
Silencing effectors that interact directly with and act downstream of AGOs. Direct tethering of GW182 to mRNA leads to translational suppression and mRNA destabilization.
How does binding of the RISC complex stop RNA translation?
Initiation block — Binding of RISC prevents the 60S ribosomal subunit from binding or reading the ORF.
Postinitiation block — Binding of RISC results in ribosomal drop off or blocks elongation of the peptide, or breaks down the nascent polypeptide through proteolysis.
What is a ribosome assembly assay?
An assay describing when the ribosome falls off.
The 5’ cap is paired with a radiolabeled target mRNA, miRISC, and ribosomal subunits. Ribosomal binding is measured as a function of fraction number and the 80S subunit is detected to describe whether initiation is happening.
What evidence do we have for miRNA effects on mRNA stability?
We can measure the amount of mRNA using qPCR and if it was revealed that the amount of mRNA is the same, we can measure the amount of proteins.
If protein levels are low over time, then we can conclude that translation is being inhibited by non-mRNA degrading mechanism, like miRNA.
E.g. lin-41 is targetted by let-7. When let-7 is introduced to cells, lin-41 protein expression decreases.
What are the two means by which miRNA destabilizes RNA?
Decapping and decay — exonucleases like DCP1/DCP2 cut the cap and break down the strand.
Deadenylation — Proteins like CAF1, CCR4, and NOT1 are summoned by GW182, exonucleases break down the polyA tail.
What are P-bodies?
pBodies are regions with a gel-like consistency with high mRNA turnover. These regions of the cytoplasm contain GW182 proteins, CCR4/NOT, DCP1-2, and XRN1.
These regions have high activity for deadenylation, decapping, and degradation of mRNAs.
What are centered miRNA sites?
Base pairing that occcurs in the center of the mRNA that expands the miRNA targeting code. These sites do not trigger cleavage.
Summarize miRNA:mRNA behaviours and miRISC interactions with mRNA.
Limited miRNA:mRNA base-pairing prevents cleavage due to interaction with the PAZ domain.
miRISC triggers rapid deadenylation of target mRNAs.
Trhough interactions with GW182 and the CCR4/NOT deadenylation complex.
mRNA can be de-capped by DCP1/2 enzymes, activated by cofactors.
mRNA is turned over by scavenging nucleases (exosome, and XRN1/2).
What are the 4 approaches by which miRNAs regulate effects?
Basic approach — single miRNA-mRNA interactions.
Broad effects — one miRNA to many RNAs.
Functional approach — one miRNA affects several mRNAs that have one synergistic effect.
Pathway-based approach to regulation — multiple miRNAs affect multiple mRNAs to produce one effect.
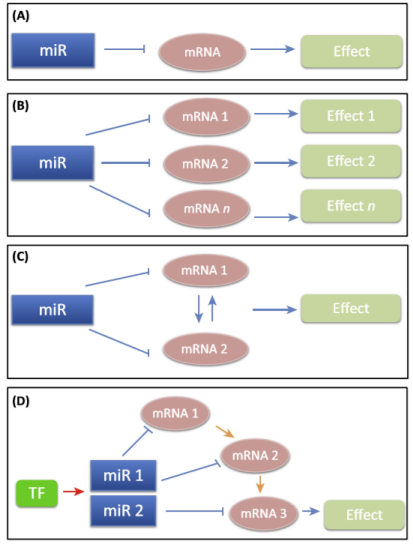
What are three scenarios for miRNA-mediated effects on signaling?
Context-dependent transcriptional activation.
Transcriptional default repression.
Contribution to default repression.
miRNA-125b
YAP/TAZ miRNA interaction
What is context dependent transcriptional activation?
Different cell types respond differently to a signal according to their miRNA program. Some signaling mediator A activates the transcription of gene1 in concert with cofactor (C1).
However, part of the downstream gene expression program cannot be expression in the cell (gene 2), as a cell-specific miRNA represses its corresponding cofactor (C2).
What is transcriptional default repression?
In the absence of the signal, the repressor (R) inhibits the activity of the pathway activator. Signaling relieves this inhibition, activating to transcription.
What is miRNA contribution to default repression?
In the presence of a weak signal, the repressor may still repress gene A resulting in leaky transcription. The addition of an miRNA targeting A will silence the signal entirely.
How does miRNA-125b modulate apoptosis?
The role of miR-125b in the damage response is an example of an miRNA operating as a primary mediator of default repression. In a normal cell, miR-125b targets residual p53 activity, avoiding apoptosis. Following genotoxic inputs, p53 is activated and miR-125b is repressed, inducing apoptosis.
How do miR-372 and miR-373 affect YAP/TAZ signaling?
The role of miR-372 and miR-373 in the default activation of the genes that are activated by the transcription factors YAP and TAZ. In cells in which the Hippo signal is off, transcription of YAP and TAZ target genes is active. Following Hippo signaling, large tumour suppressor (LATS) phosphorylates and inhibits YAP and TAZ; this is prevented by high levels of miR-372 and miR-373, which targets LATS.
How can miRNAs modify tissue responsiveness over time?
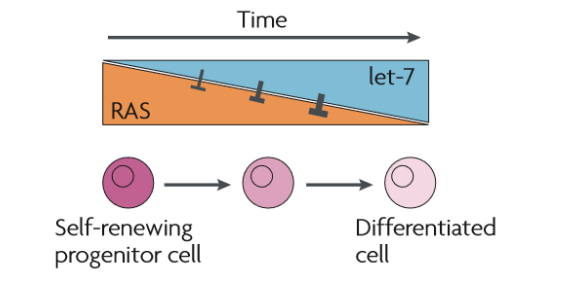
miRNAs modify tissue responsiveness like in the case of let-7. Let-7 expression increases during differentiation, resulting in progressive inhibition of RAS signaling. This enables self-renewal of progenitor cells, but restrains it while cells differentiate.
How does downstream miRNA signaling work?
There are two downstream signaling branches through receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs):
Phosphoinositide 3- kinase (PI3K)-AKT
RAF-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades.
Some miRNAs, such as miR-21 and miR-126, target inihibitors of both branches, leading to a general upregulation of RTK signaling.
How do miRNAs effect bistable fate choices?
In a cell, a transcription factor (TF) inhibits the expression of an miRNA. In turn, the miRNA inhibits expression of the TF.
The cell can adopt two alternative fates:
State A is the default fate, in which miRNA expression dominates and the expression of the TF is turned off.
State B, an extrinsic signal stabilize the TF, promoting cell differentiation and leading to repression of the miRNA and gives a different cellular outcome.
How does reciprocal inhibition affect epithelial and mesenchymal states?
Recipirocal inhibition occurs between the transcription factors zinc finger e-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1), ZEB2, and miR-200 family. These regulate the switch between epithelial and mesenchymal states.
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGFb) signalling induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) by stabilizing the expression of ZEB1 and ZEB2 at the expense of miR-200 and MET, mesenchymal to epithelial transition.
What are the two ways miRNAs can act in terms of cancer?
Tumour suppressors;
Oncogenes.
How do miRNAs act as tumor suppressors?
Tiumour suppressor miRNAs exert their functions by targeting oncogenic protein-coding genes.
E.g. miR-15a-miR-16 cluster targets the genes coding for the anti-apoptotic proteins B cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) and induced myeloid leukaemia cell differentiation protein (MCL1). Let-7 negatively regulates the oncogenes KRAS and MYC. miR-34 mediates p53 signalling by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 4, MYC, and MET.
How can miRNAs act as oncogenes?
It has been shown that miR-21 overexpression induces pre-B cell lymphoma in mice, promotes KRAS-dependent lung carcinogenesis by activating the RAS-MEK (MAPK/ERK kinase)-ERK pathway.
Enhances metastasis of colorectal cancers by targetting programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4).
miR-17-miR-92 cluster is upregulated in many cancers as they are direct downstream targets of oncogene MYC and attenuate MYC-induced apoptosis.
At what points in mRNA biosynthesis can therapeutic interventions be generated?
Blocking production of miRNAs by Dicer.
Enhancing production (enoxacin) of miRNAs by dicer.
miRNA mimics.
Anti-miR drugs (e.g. MiR sponges).
How can miRNA levels be increased with synthetic oligonucleotides?
MRX34 can be intravenously injected as a liposome-formulated miR-34 mimic.
Tail vein injections of MRX34 reduced tumor growth and survival in orthotopic mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Antagomirs target anti-sense oligonucleotides.
What is an example of an antagomir for viruses?
miR-122 interacts with the 4’ and 3’ end of the hepatitis C virus, HCV. Antagonist of miRNA-122 is the first miRNA based drug in clinical trials.
miR-122 stabilizes the heptatis C virus genome allowing for it to remain inside the body chronically. The antagonist inhibits the miRNA-122.