Derangements in Tonicity (II)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
hyponatremia
-serum sodium is an excellent surrogate for serum osmolality, but not perfect
-normal serum osmolality = 290 ± 5 mOsm/kg

iso-osmolar
-lipids/proteins
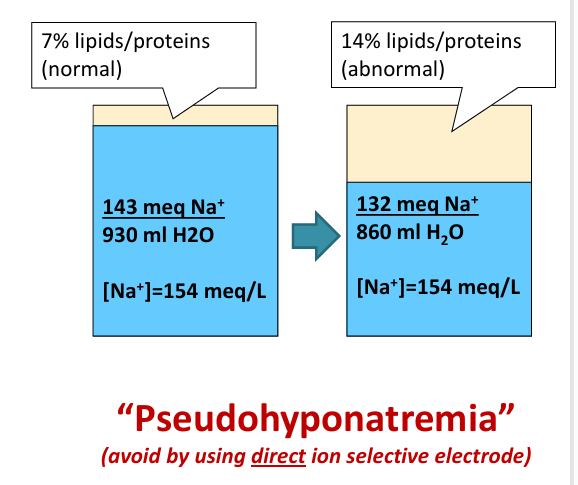
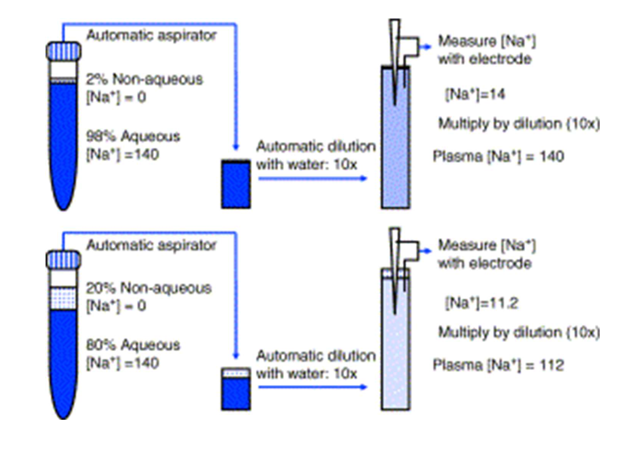
pseudohyponatremia- indirect ion specific electrode
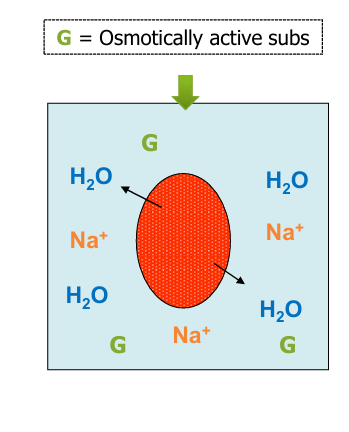
hyponatremia- hyper-osmolar
-unmeasured solutes
-”translocational” hypoNa
hyperglycemia and translocational hyponatremia
-in hyperglycemia can “adjust” [Na+] for the glucose level using a correction factor to better represent osmolality
-[Na+] decreases 1.6-2.4 meq/L for every 100 mg/dl increase in glucose above 100 mg/dl
hyponatremia- hypoosmolar
-increased free water intake
-decreased free water excretion
hypoosmolar hyponatremia- increased free water intake
-primary polydipsia, water intoxication
-ADH- absent
-Uosm: low (<100 mosm/L)
-note: increased water intake exacerbates every kind of hyponatremia
hypoosmolar hyponatremia- decreased free water excretion
-renal failure (severe)
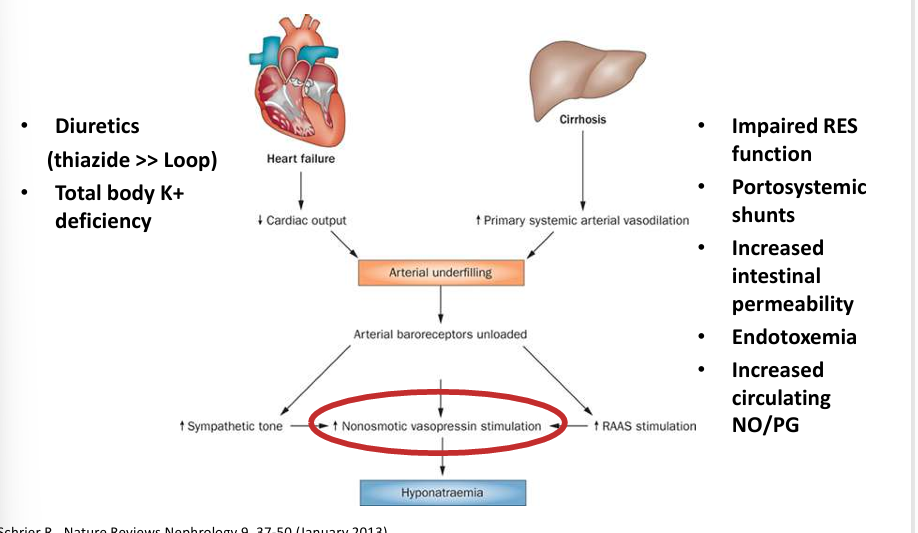
-ADH: appropriate ADH- true volume depletion, sensed volume depletion (CHF, cirrhosis), renal/cerebral salt-wasting (rare); inappropriate ADH- SIADH or SIAD
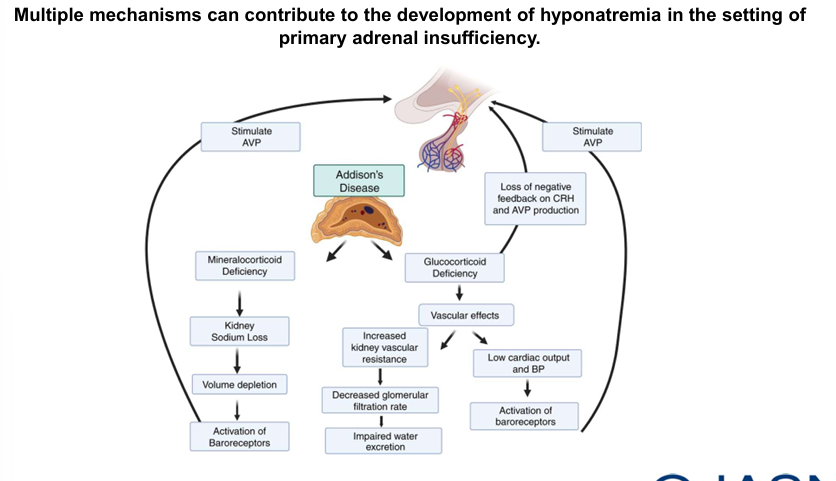
-special cases (antidiuresis independent of ADH): low solute intake, thiazides, adrenal insufficiency (salt wasting + hypotension + increased CRH → ADH)
hyponatremia in edematous states
low solute intake
-urine must contain Osms
-Na+, K+, NH4+, conjugate anions, and urea
-”tea and toast”, beer potomania
-low protein intake = inability to generate large volume of dilute urine
-Uosm usually low (<200) compared to SIADH
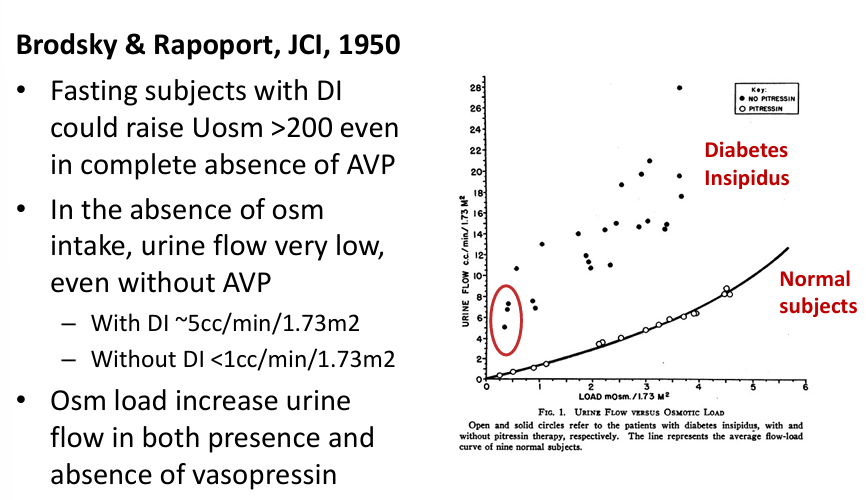
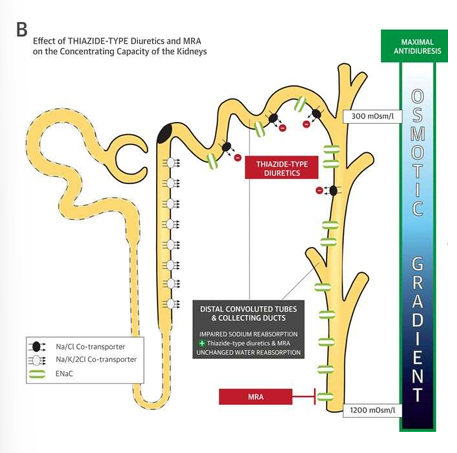
thiazides
-impair urinary dilution
-do not affect medullary concentration gradient
-cause urinary loss of solutes
-enhance water permeability of CD (reabsorption), independent of ADH
-thiazide-induced hyponatremia associated with variant in SLCO2Aq, which encodes a prostaglandin transporter in the distal nephron (increased urinary prostaglandin E2)
adrenal insufficiency
diagnostic approach for hyponatremia
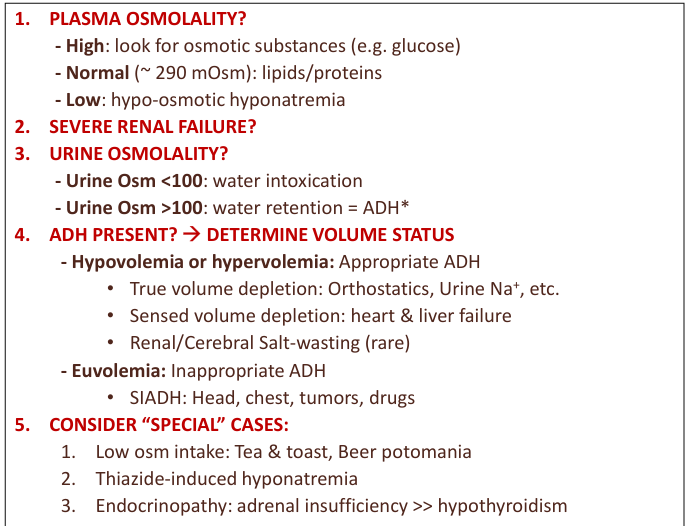
causes of SIADH
-tumors: bronchogenic carcinoma, mediastinal, lymphoma, pancreatic cancer, mesothelioma
-pulmonary: infections (pneumonia, lung abscess, TB), pneumothorax, broncoscopy
-CNS: head injury, neurosurgery, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, meningitis
-drugs: carbamazepine, chlorpropamide, clofibrate, cyclophosphamide, desmopressin, “ecstasy”, NSAIDs, oxytocin, opiates, phenothiazines, SSRI, MAOIs, tricyclic antidepressants, vincristine
-miscellaneous: severe nausea, pain, postoperative, prolonged exercise
treatment of hyponatremia- symptomatic v asymptomatic
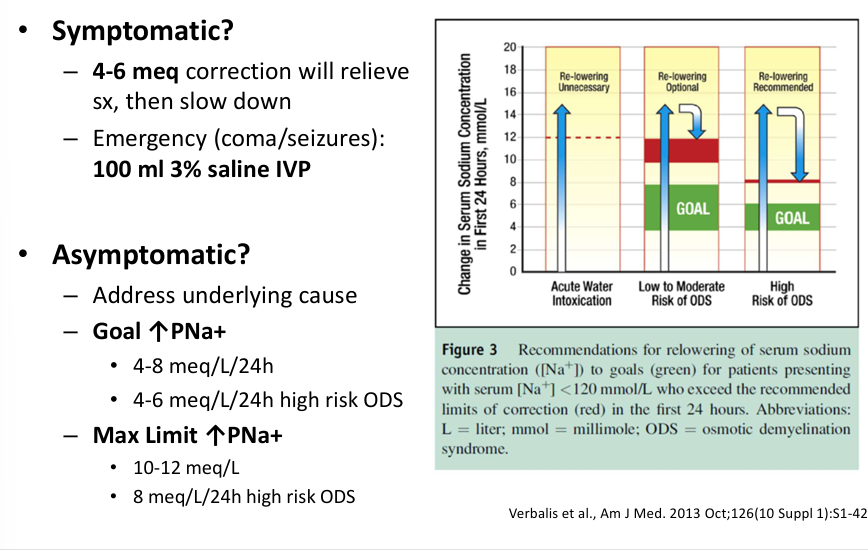
treatment of hyponatremia- renal failure, volume depletion, CHF, cirrhosis, SIADH

urea therapy

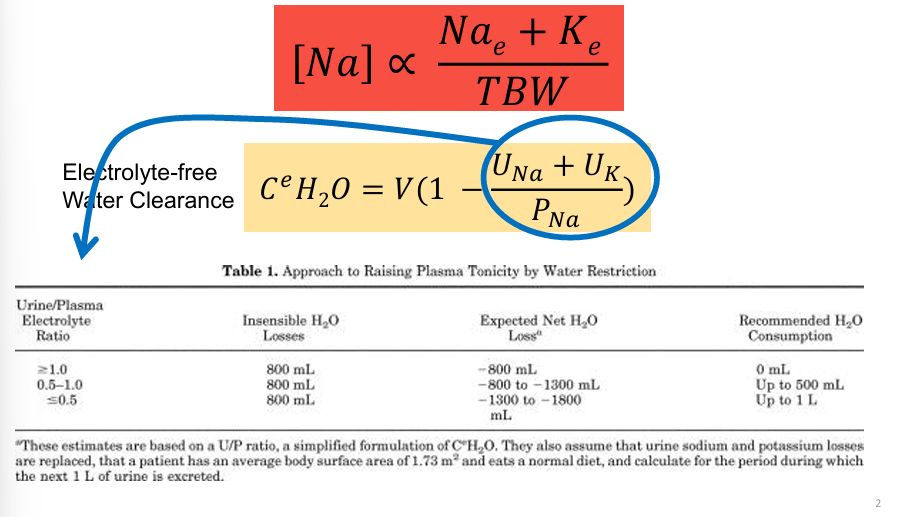
effectiveness of fluid restriction depends on
-urine/plasma electrolyte ratio
treating hyponatremia with fluids (hypertonic saline)
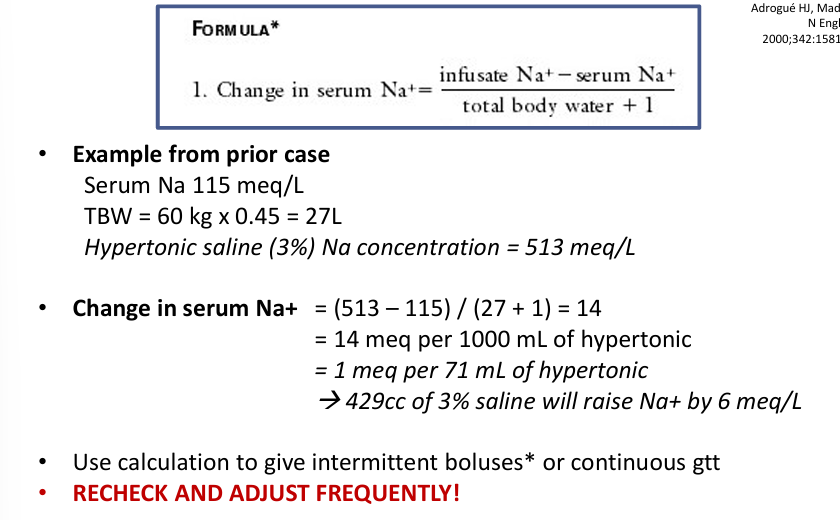
summary