Consumer behaviour - Chapter 10: Group influence and social media
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
How are the decisions we make "collaborative”
Other people join in on the problem solving process
Requester
The person who asks
e.g. What movie should we see?
Responder
The person who responds
e.g. Let’s see Terrifier 3
What sort of decision do groups make?
Riskier and different decisions than those made alone
Caveats of group decision making
The multitude of things that need to be considered can ultimately reduce attention and consumption of an activity
Decision polarization
When people become more extreme in their decision-making during or after group discussions
Deindividuation
When one’s identity becomes submerged in a group as the restraints on normal behaviour are lessened
Bandwagon effect
When group members “cave in” to conform to group pressures
Social loafing
When people don’t dedicate much effort to a task when they’re contributing to a group effort
The roles in group decisions
Initiator
Gatekeeper
Influencer
Buyer
User
Initiator
The person who brings up/identifies a need
Gatekeeper
The one who goes about the information search and controls what info gets to the group
Influencer
The one who sways the decision’s outcome, varies on motivation
Buyer
The one who actually purchases the product, though they may not actually use it
User
The person(s) who actually consumes the product
Norms
Informal rules which govern behaviour in order for a society to function
Social norms
Indicators of acceptable standards of behaviour shared by members of a group
Normative influence
The process where a reference group aids in setting and enforcing fundamental standards of conduct
Descriptive norms
Info that conveys what’s common and/or what people usually do
e.g. An ad which shows that 85% of people recycle
Injunctive norms
Info that conveys what’s commonly approved/disapproved by others
e.g. An ad which shows people approve of recycling
Dynamic norms
Sheds light on how people’s behaviour(s) change over time
e.g. Expanding efforts to reduce electricity consumption by 60% of Canadians over 5 years
What can communicating that others are engaging in a particular activity/behaviour do?
Increase compliance with said activity/behaviour
Conformity
Changes in beliefs or actions as a result of real or imagined group pressures
Unspoken norms govern many aspects of consumption that we conform to daily
Personal hygiene, giving gifts on birthdays, showing up on time to work
Reactance
When one tries to overcome the negative emotional state of perceived loss of freedom
How may one solve the conflict of wanting to be unique with the pressure to conform?
They’ll pick a popular brand (e.g. Nike) and choose a unique trait, such as colour
Red sneakers effect
People who exhibit non-conforming behaviour, which leads to positive impressions which may disappear when others are unsure of why that person’s doing what they’re doing
What influences conformity?
Cultural pressures
Fear of deviance
Commitment
Group unanimity, size, and expertise
Environmental cues
Word-of-mouth communication (WoM)
Consumption info that gets shared amongst individuals on an informal basis
Word-of-mouth communication (WoM) [con’t]
Can be more powerful than ads put out by firms as it influences 2/3 of sales of all consumer goods
How do we use Word-of-mouth?
We use it for the later stages of product adoption
Negative Word-of-Mouth
It can spread quicker/easier and is weighed more than positive WoM
Social media
Forms of electronic communication through which users create online communities to share information, ideas, personal messages, and other content; as about online community
Nodes
Members of a network who are connected to each other via relationships (i.e. common interests, friendships, etc.)
Nodes (con’t)
They go through interactions within a network
e.g. Talking to each other, going to events with each other, forging new connections, etc
Flows
The exchanges of resources, information, or influence that occur between nodes
Flows (con’t)
They may be sent to entire communities, networks, several people independently
Media multiplexity
The many directions and platforms in which flows of communication may travel
How are flows important for marketers?
They’re actionable components of any social network system in terms of the sharing of information, delivery of promotional materials, and sources of influences (similar to Word-of-Mouth)
Social object theory
An object of common theory
Object sociality
The extent of objects which can be shared
Lukers
People apart of a community who absorb content as opposed to posting their own content more often than not
What makes for an effective and working online community?
Standards of behaviour
Member contributions
Degree of connectedeness
Network effects
Megaphone effect
How the web provides a mass audience to the ordinary consumer
Why may people post on social media?
Communicate something about our identity
Manage the impression we make on others
Regulate emotions
Share and acquire information
Entertain others
Inspire or persuade others
Why may people post on social media? (con’t)
Arousal from physical activities (e.g. Working out) or emotions (e.g. Memes)
Dispreffered markers
Couching negative product views in softer terms to avoid looking snobbish
What happens when we share an identity-relevant product on social media?
The future purchase intentions are reduced as we’ve already fulfilled the need to share the identity aspect
Opinion leaders
People who are knowledgeable about certain types of products and can influence other people’s behaviours as a result
What traits define an opinion leader?
Technically competent
Possess knowledge power
Socially active, highly interconnected
Possess referent power
Are often the first to buy
The two-step flow model of influence
A small group of influencers that change the opinions of many people and are thus responsible for the distribution of information
Influence network
Interactions and communications between influencers and those who are easily influenced
Generalized opinion leader
Someone whose recommendations are sought out for all sorts of products
Monomorphic
Experts in limited fields
Polymorphic
Experts in multiple fields, though concentrate on one broad domain
e.g. Electronics, cars, etc
What phenomenon is the influencer marketing strategy akin to?
The “cool kid” that everyone follows/imitates
What phenomenon is the influencer marketing strategy akin to? (con’t)
Said “cool kid” is now online and reachable by millions of people all over the world
What are consumers’ perception of influencers?
They perceive influencers as the third most trustworthy source of information after friends and family
Power leaders
What opinion leaders are referred to in online groups as they have a strong communications network that gives them the ability to directly and indirectly affect consumption decisions for a number of other consumers
Power leaders (con’t)
They’re active participants in their communities and are trusted as a result, being as seen as credible information sources. They also have a natural sense of intellectual curiosity which may lead them to new information sources.
Mass connectors
High influential members of social networks
Content marketing
A strategic marketing approach focused on creating & distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent material to attract and retain a clearly defined audience in order to yield a consumer response
Market maven
A person who serves as an information source regarding market activity; they aren’t exactly interested in products nor be early buyers of products
Market maven (con’t)
They know of how and where to get products and what’s generally going on in the marketplace
The surrogate consumer
One who provides input into consumer decisions and is usually paid for their work; consumers usually give up all control to them
Can be in the form of a interior decorators, stockbrokers, professional shoppers, or university consultants, etc
The surrogate consumer (con’t)
They can be very influential regardless if they’re acting on the consumer’s behalf or not
Product curators
A person(s), or sometimes celebrity, who assembles the product on a manufacturer’s behalf who include recommendations one how to use the items, and may share their stories about how they use them in their own lives
Crowd power
A major change in how new media companies think of marketing as a strategy of committee
How may influencers operate at a local level?
They may influence 5 to 10 people at a time rather than an entire market segment
The Self-designated method for identifying influencers
The act of simply asking people if they consider themselves to be opinion leaders, and is very easy to apply to a large group of potential opinion leaders
The sociometry method of identifying influencers
Tracing communication models in and among groups and systematically map out interactions that take place among group members
Tie strength
The strength of bonds of any given relationship between people
Tie strength (con’t)
It can range from strong primary (e.g. A romantic partner), to weak primary (e.g. An acquaintance seen once in a while in passing)
Reference group
A group (actual or imaginary), that has a profound effect on one’s evaluations, decisions, behaviour, etc
Reference group (con’t)
Is often used to describe any external influence that provides social cues
Reference group (III)
They can be large and formal with recognized structures, or small and informal (e.g. A friend group)
Large formal groups are easier to find, but smaller informal groups have greater influences on the individual consumer
How may reference groups impact consumers?
Informational
Utilitarian
Value-expressive
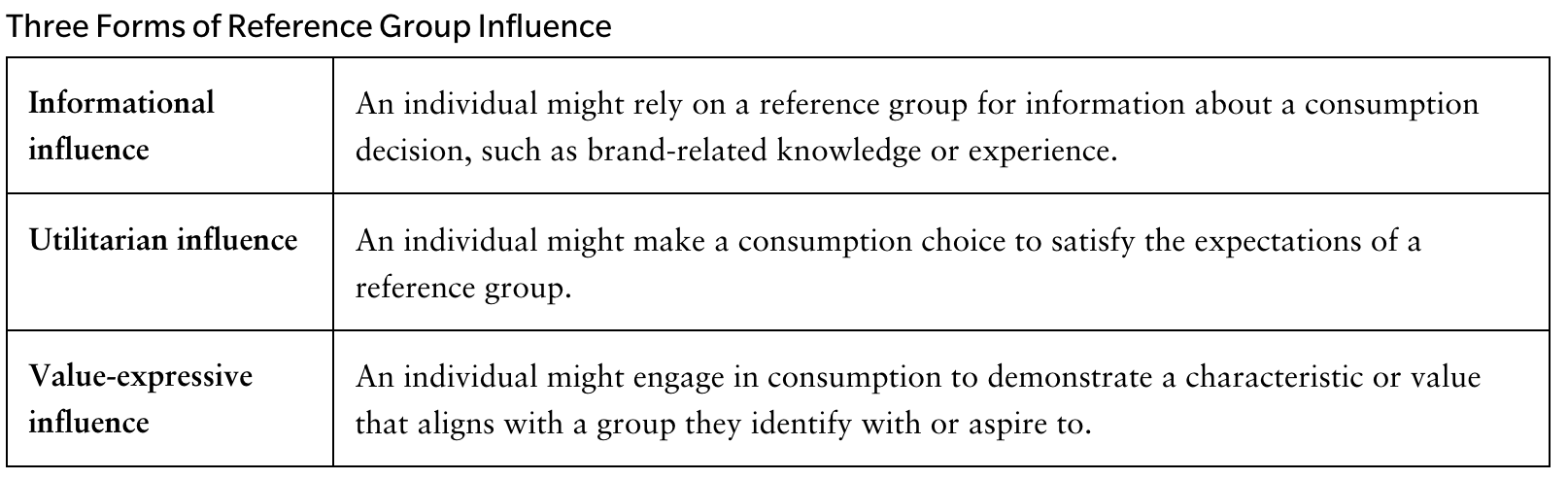
Informational reference
A reliance on a reference group for info about consumption decisions
e.g. Brand related knowledge
Utilitarian
When makes a choice in order to satisfy a reference group’s expectations
Value-expressive
When one makes a choice in order to align with a value or trait of a group they’re a part of or aspire to be a part of
Social identity theory
The idea that each of us has several “selves” that relate to groups
Aspirational reference groups
Comprises of idealized figures, such as successful businesspeople, athletes, or performers
e.g. Business students who aspired to the “executive” role found a strong relationship between products the students associated with their ideal selves
Membership reference groups
Involves other consumers who belong to the same groups as us (e.g. circle of friends, family, classmates, teammates, etc)
We want to conform to those groups ‘cause of what they’re doing
Strategies for aspirational reference groups
Concentrate on highly visible, widely admired figures (athletes or performers)
Strategies for member reference groups
Concentrate on ordinary people whose consumption provides informational social influence, such as:
Propinquity
Mere exposure
Group cohesiveness
Dissociative reference groups
Groups a consumer wants to avoid; marketers may take advantage of this by showing undesirable people using competitor’s product
e.g. A Canucks Fan not wanting to be seen wearing a Calgary Flames jersey
The 2 dimensions that influence the degree to which reference groups are important
If the item’s to be used privately or publically
If the item’s a luxury or necessity
In what situations are reference groups more robust in?
The purchase of luxuries
Socially conspicuous items which could be visible to others (e.g. purses or clothes)
Public necessities
Has weak influences on products but a strong influence on brands
e.g. Suits, cars
Public luxuries
Has weak influences on both products and brands
e.g. Sailboats, golf clubs
Private necessities
Weak influence for both products and brands
e.g. Beds, floor tiles
Private luxuries
Has weak influences on brands but a strong influence on products
Social power
The ability to change the actions of others
Referent power
When one tries to imitate desirable qualities by copying the behaviours of a person(s) they admire
Information power
One possesses it simply because they know something others would like to know and influence consumer opinion with their (assumed) access to knowledge that provides some kind of advantage
Information power (con’t)
Fashion influencers with high expertise may possess power because of their ability to compile and spread information that can make or break individual designers or brands
Legitimate power
Granting power by means of social agreements; this is usually conveyed via uniforms
i.e. Respecting cops, city officials, teachers, etc
Expert power
Is gained from having knowledge or a certain skill revolving around a certain content area, thus people are usually influenced by experts who are assumed to be able to evaluate products or experiences in an objective, informed way
Coercive power
Is given off when someone’s influenced because of social or physical intimidation
It’s effective in the short term but goes away when the exerting party goes back to usual behaviour when the threat is gone