612 - Malignant tumors of the jaw 5/8
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
How do malignant tumors of the jaw show up clinically?
as expansive masses
Difference between sarcoma and carcinoma?
Sarcoma: start from connective tissue (i.e. squamous cell carcinoma comes from covering tissue)
• grow faster
Carcinoma: start from epithelium
• most of the malignancies we will see in our careers
Malignant tumors of the jaw (5)
- Osteosarcoma
- Chondrosarcoma
- Burkitt's Lymphoma
- Multiple myeloma
- Metatstatic malignancy in the jaws
Radiographic signs of osteosarcoma
- Bone above CEJ
- Fuzziness - instead of normal trabecular pattern
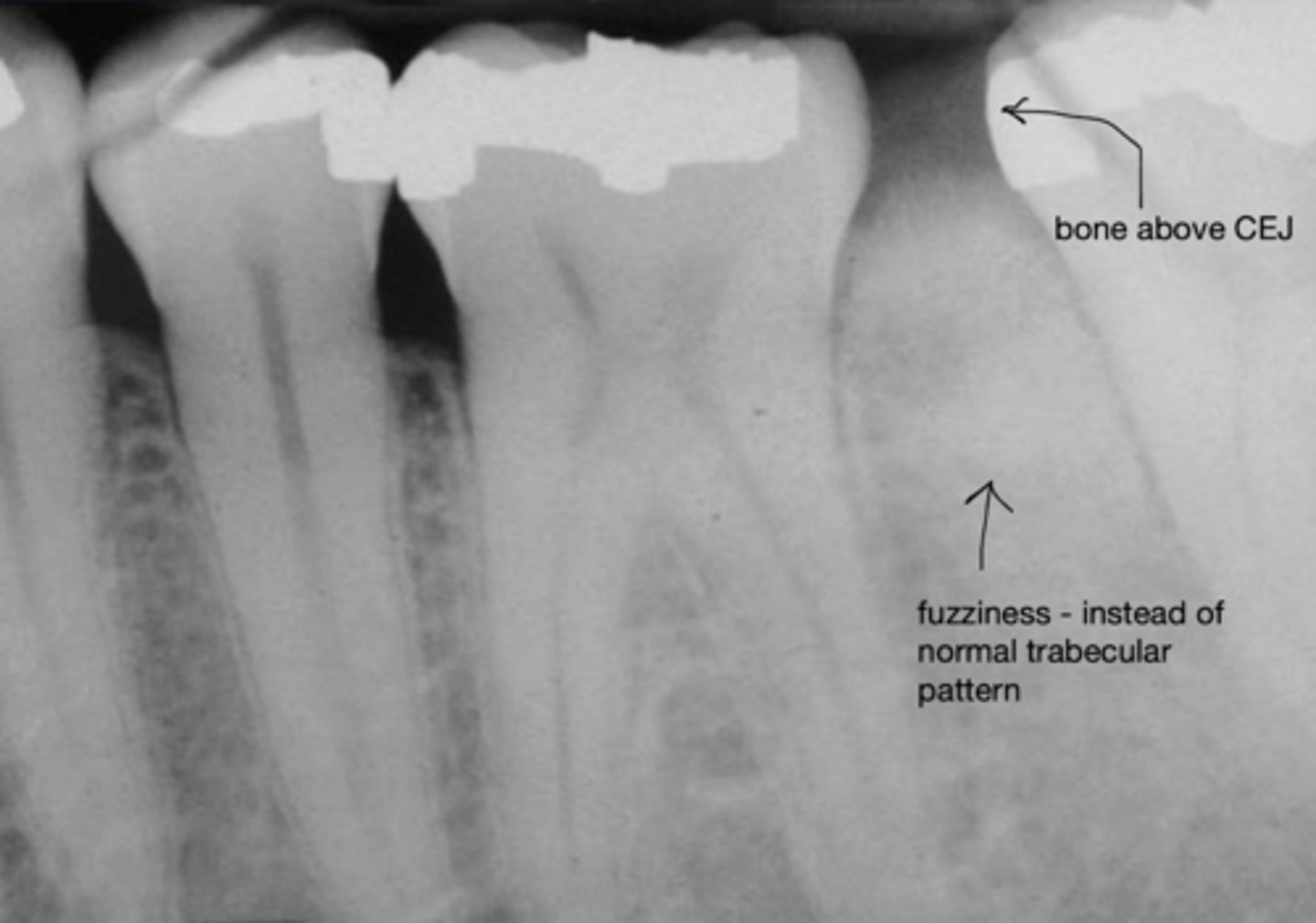
Osteosarcoma - radiographic ex
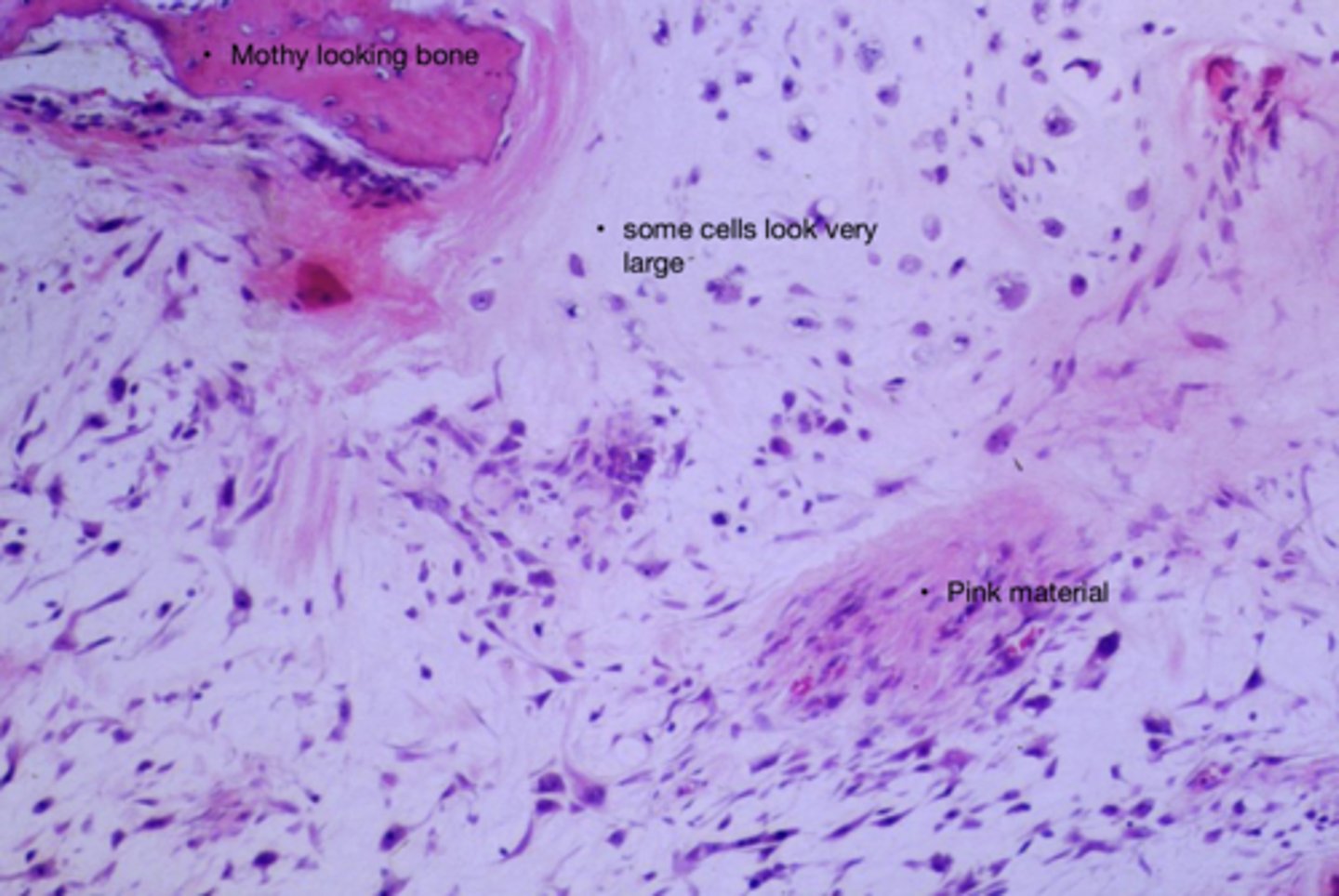
Osteosarcoma - histology
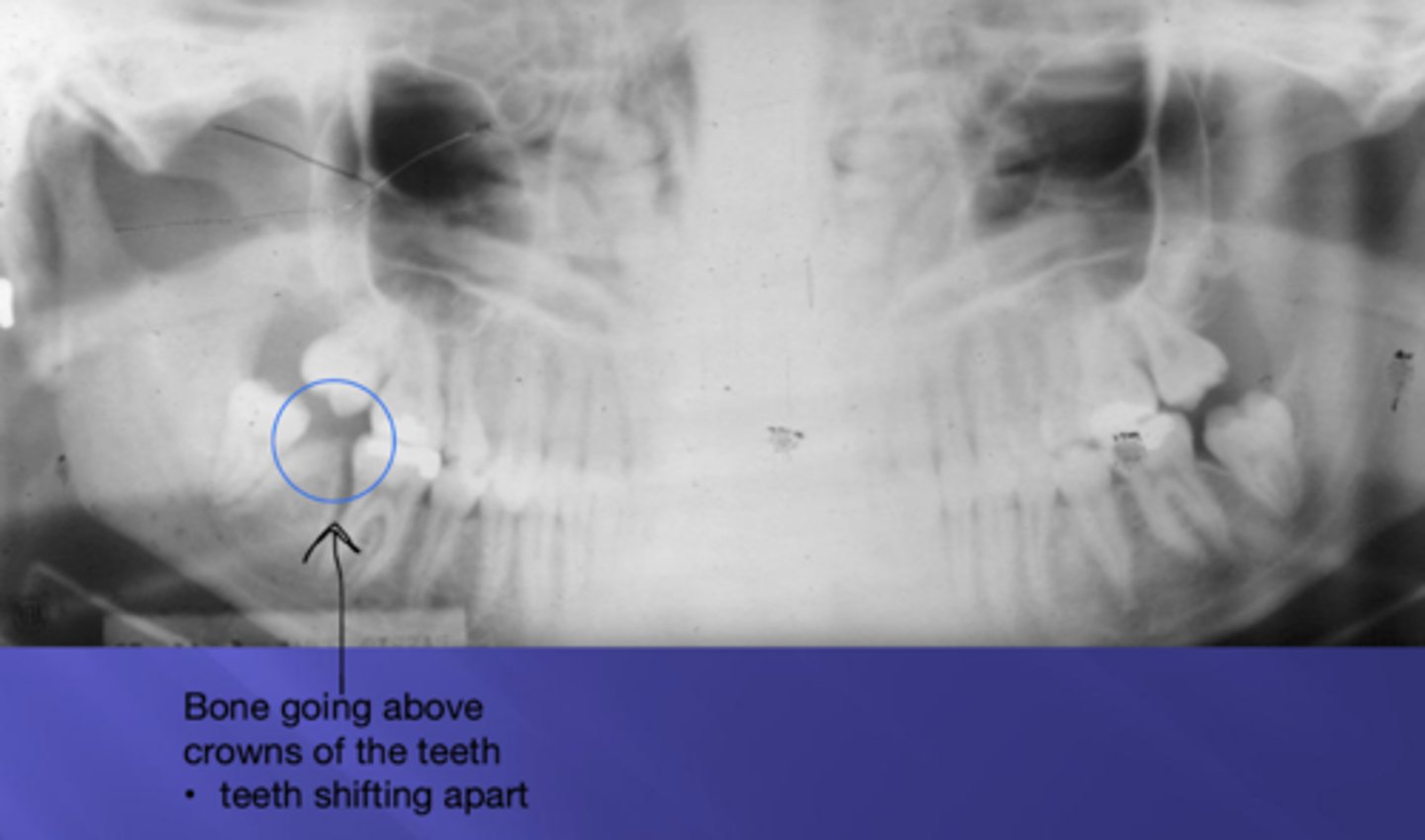
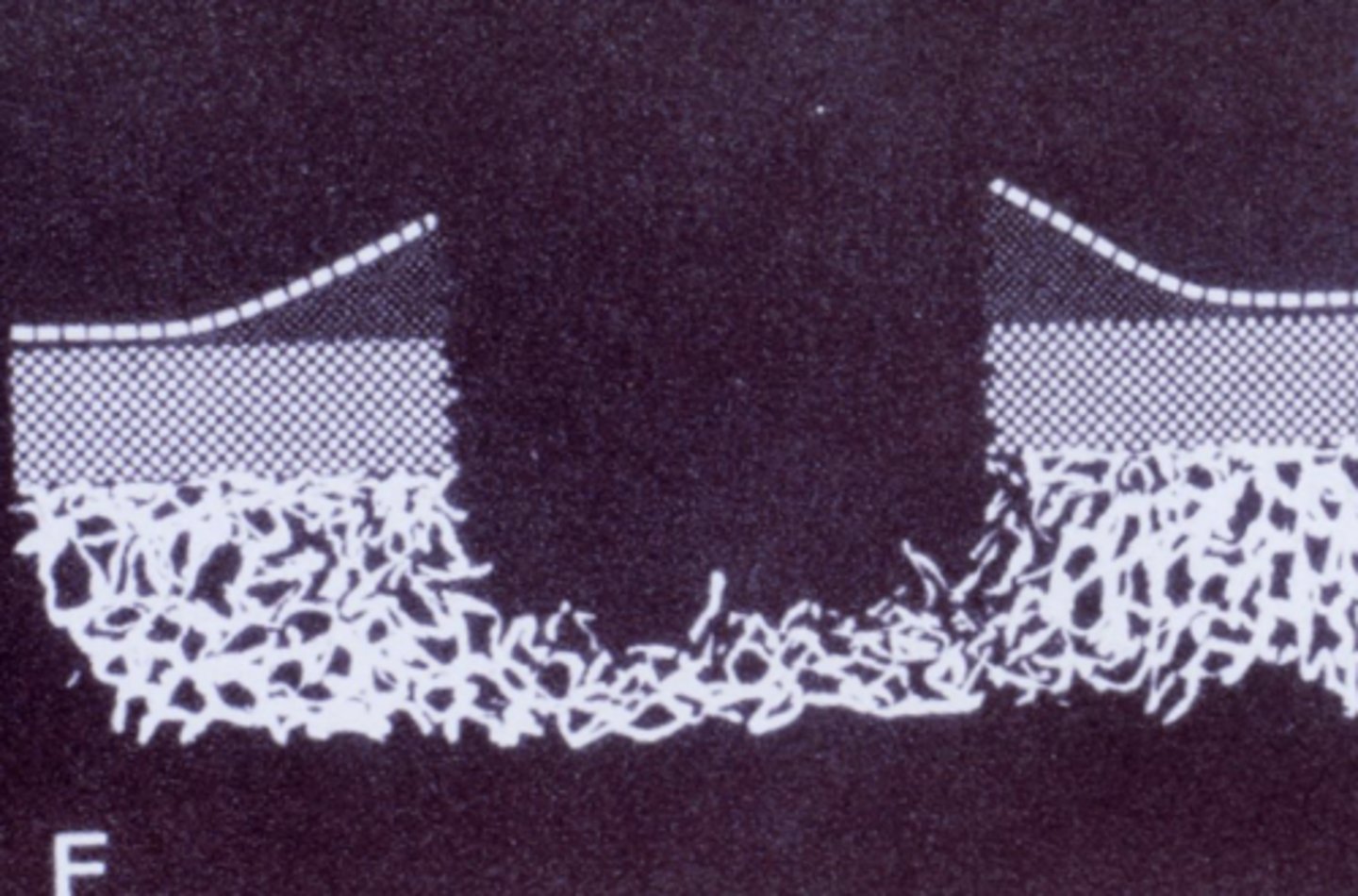
What is Codman's Triangle?
she said this is not on her test
as tumor grows, it pops up the periosteum - may show as dark triangle on radiograph
= lifting up of periosteum in response to a malignant tumor
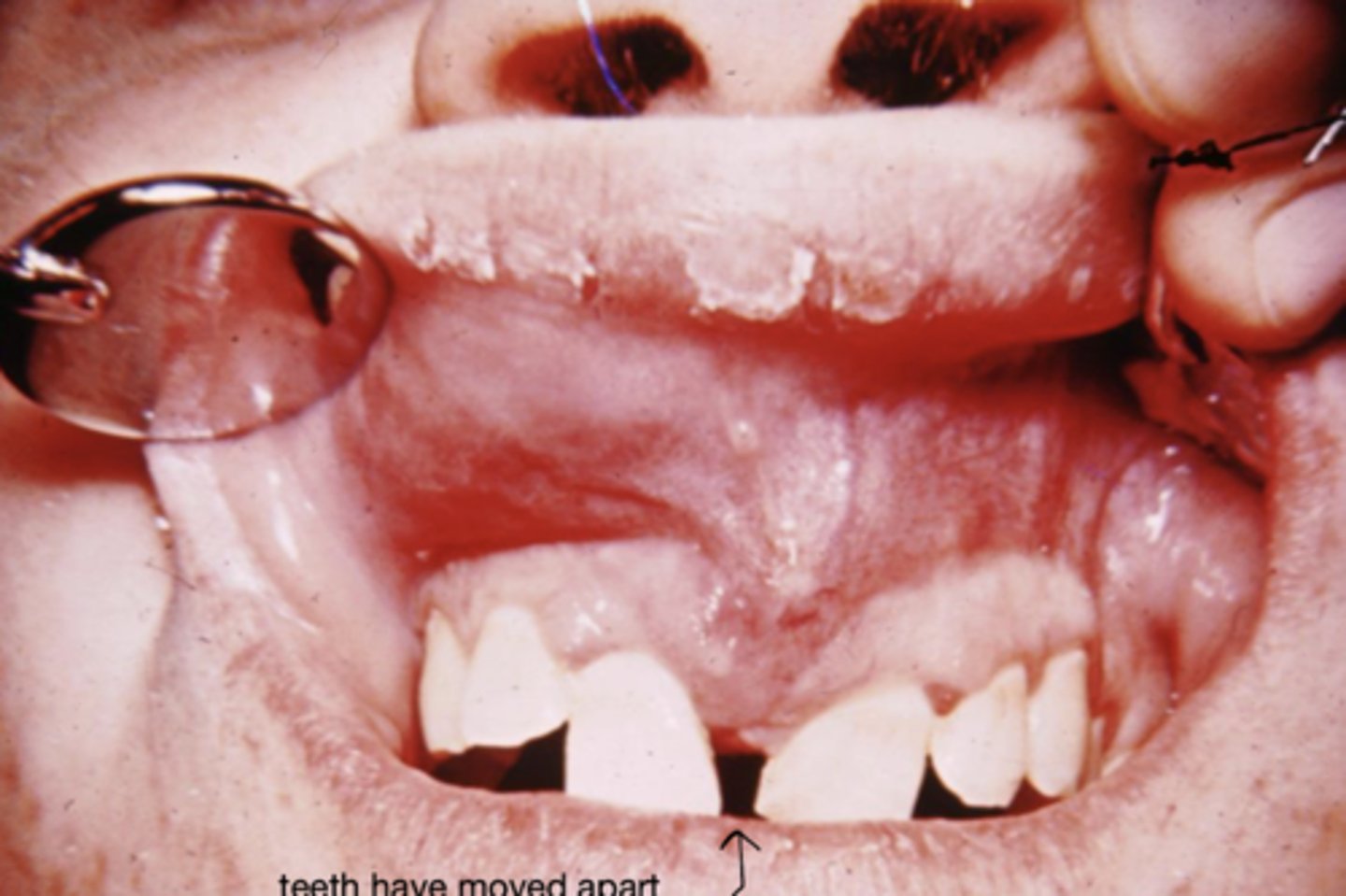
What is a Chondrosarcoma?
- where can you get one?
= Malignant tumor of cartilage
- Midline of maxilla (embryologic leftover cartilage)
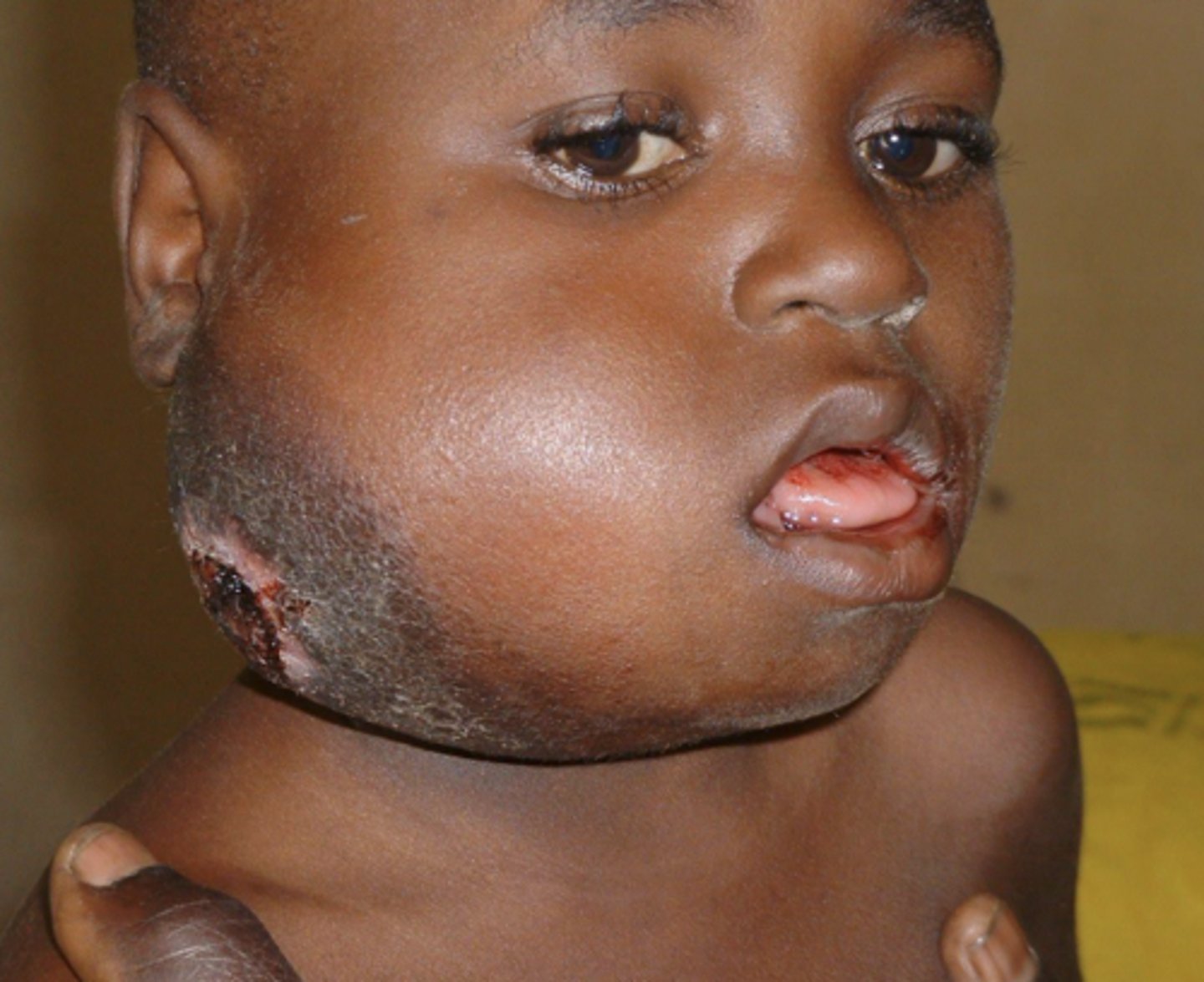
What is Burkitt's Lymphoma?
- how is it treated?
= fastest growing tumor in existence
- in Eastern Africa
- affects mandible or maxilla
- May affect vision, very fast growing
- Treated with chemotherapy
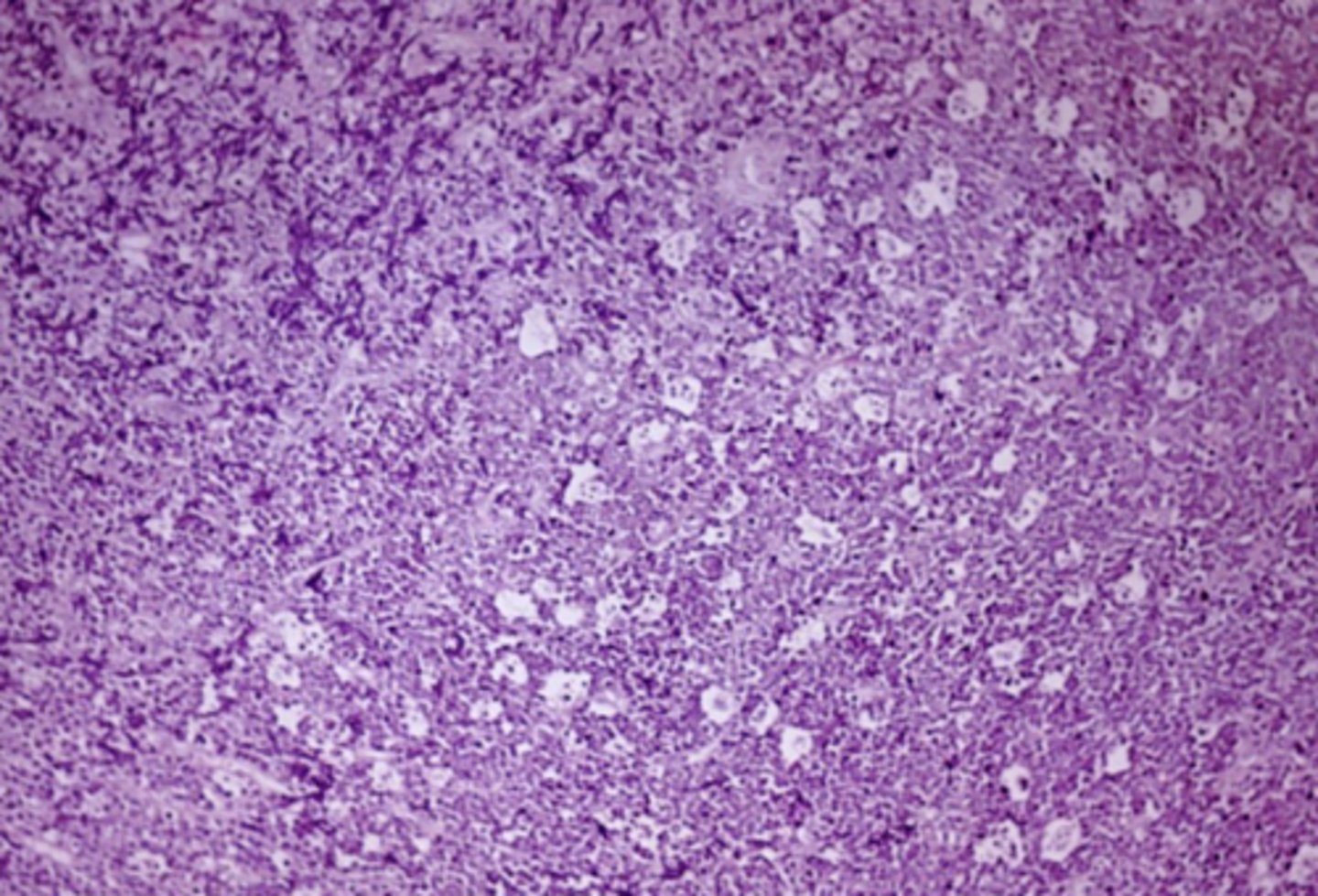
Burkitt's Lymphoma - histology
Starry sky appearance
- mitotically active
- small lymphocytes are dark and many mitoses
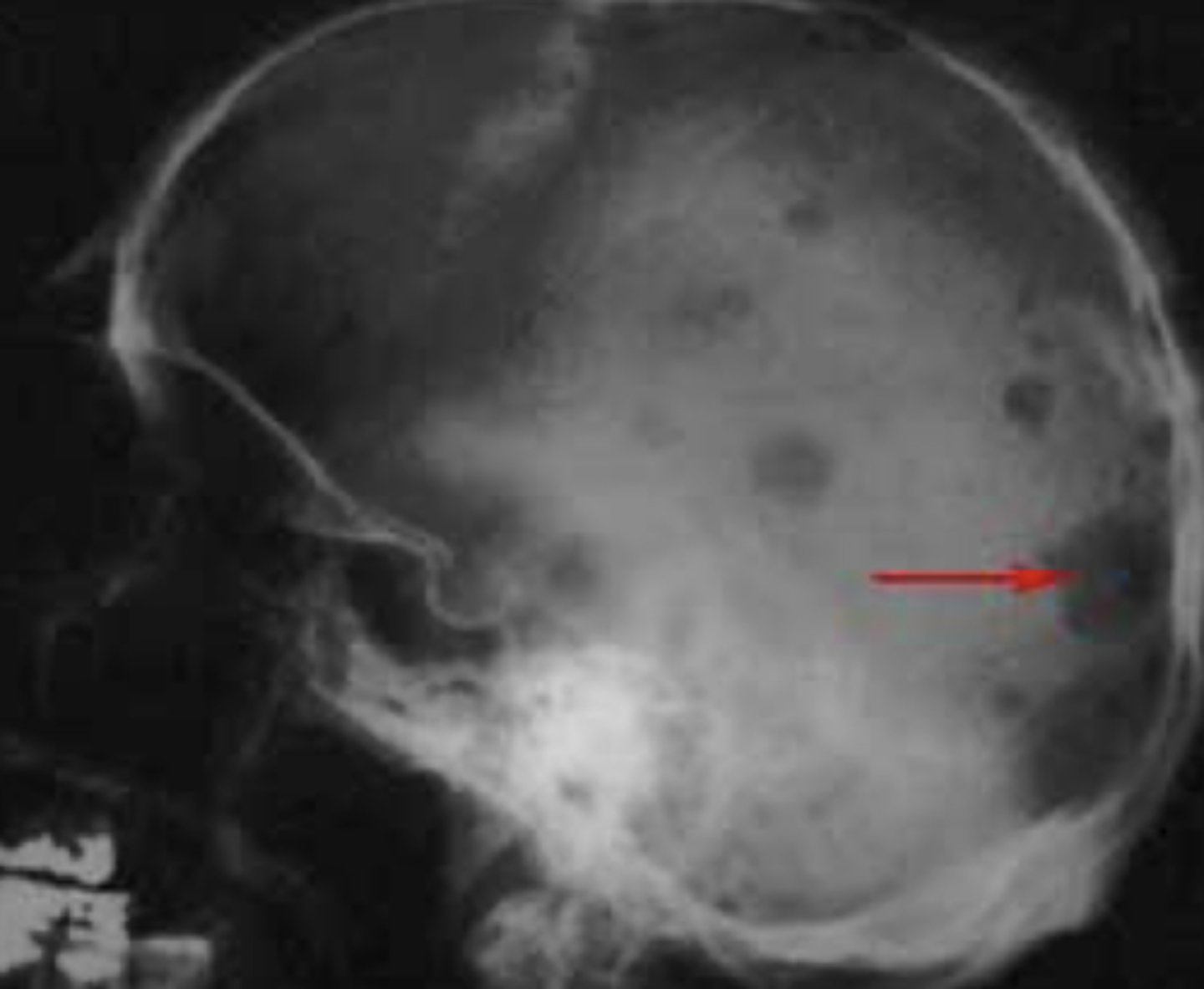
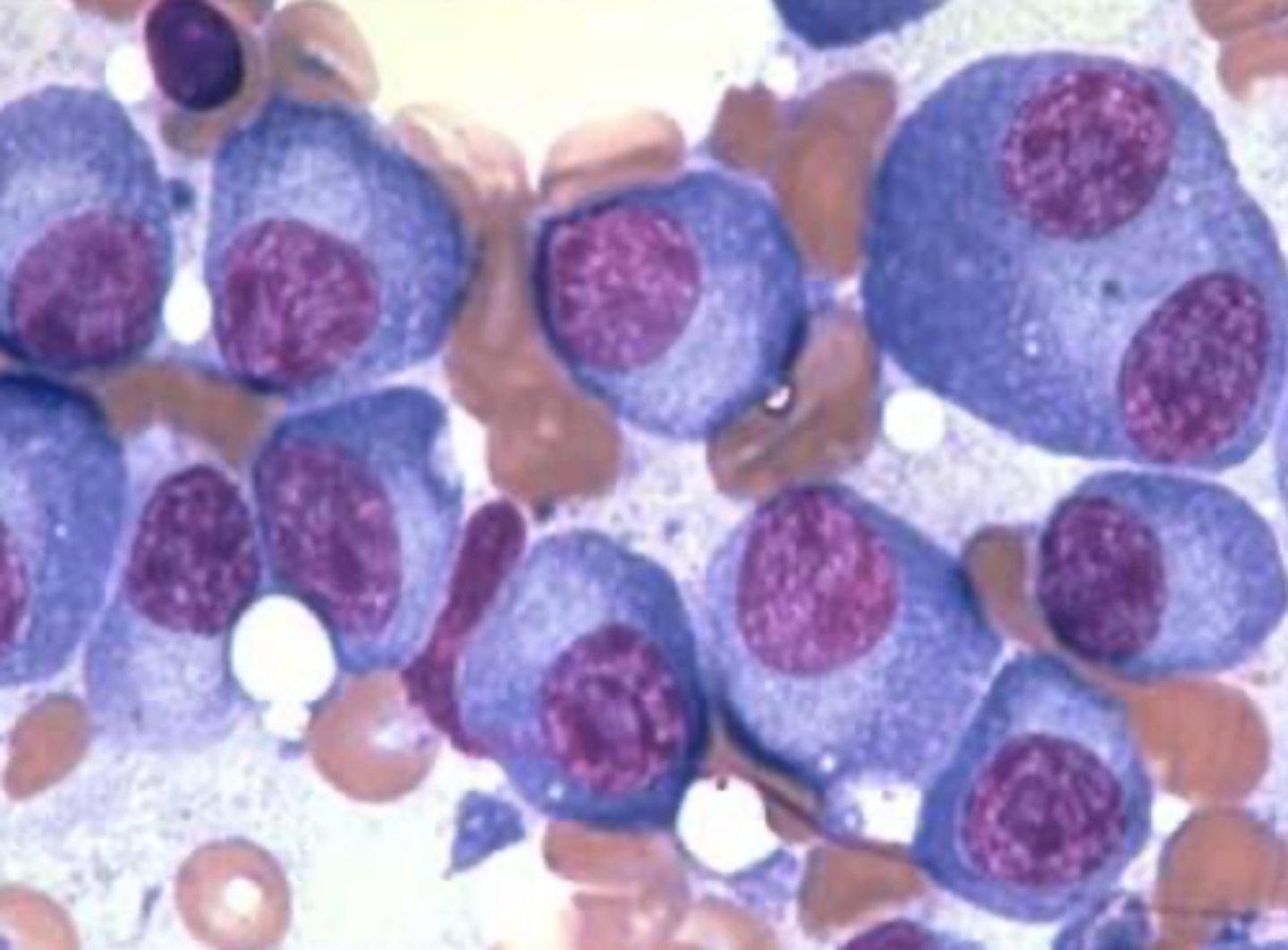
What is multiple myeloma?
- radiographic appearance? (test q)
= Malignancy of plasma cells
- Plasma cells made in the bone marrow
- Called multiple bc there is more than one lesion
- Radiographic: Punched out radiolucencies
- Vertebrae collapse and crush discs, crush nerves --> causes pain (take into account for dental work)
Multiple myeloma - Histology
Plasma cells have purplish nuclei with blue cytoplasm
--> multiply and choke out regular WBCs
- red cells = erythrocytes
Metastatic cancers in jaw
1. Lung cancer
2. Breast cancer (women), Prostate cancer (men)
3. Colon cancer
Metastatic breast cancer in jaw
Tumor settles out by tooth and takes blood supply for its own cells
- Tooth root and bone do not get any nourishment, causes it to resorb
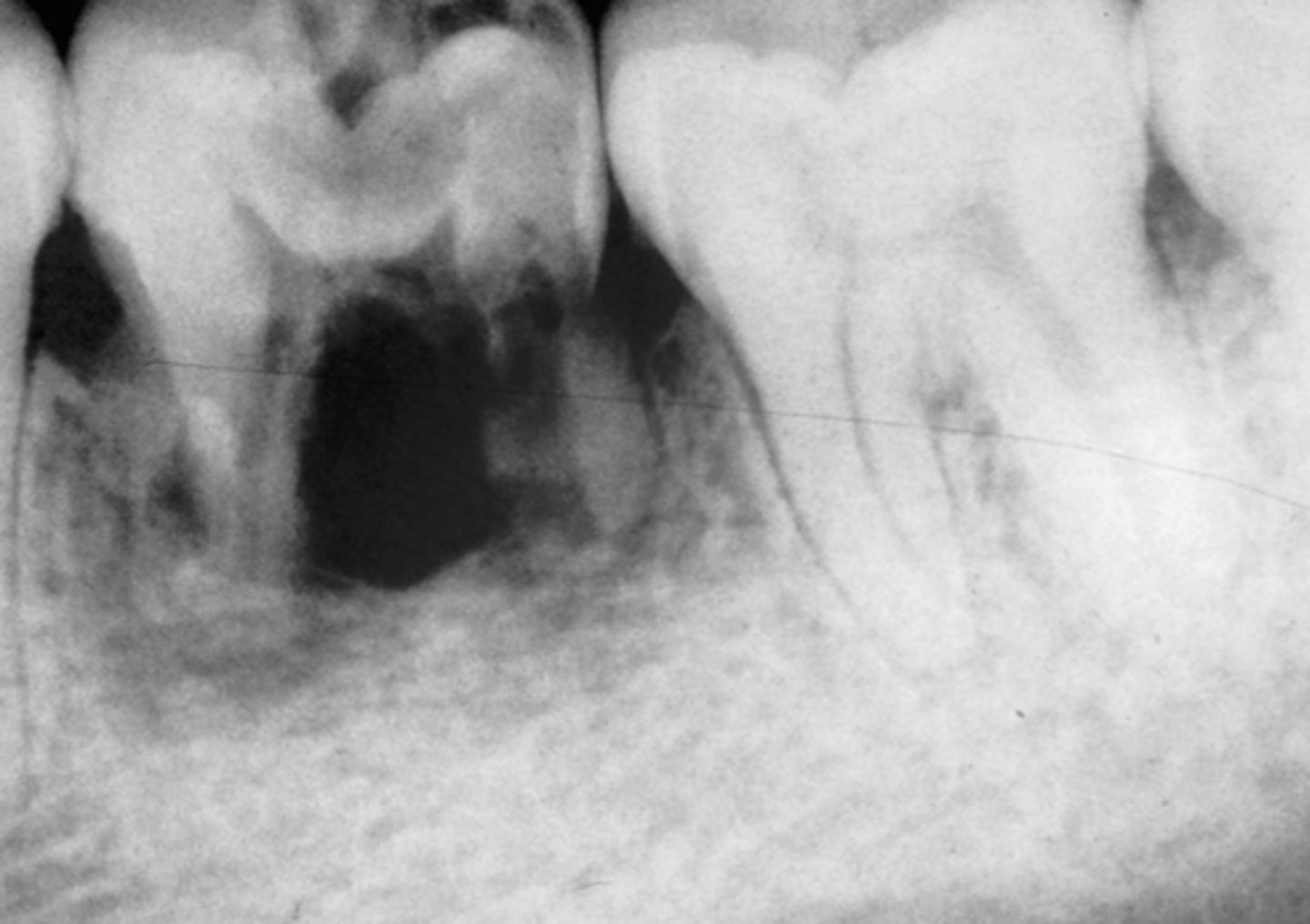
T/F: Pts with a metastatic tumor to the jaw have a fair prognosis
False - poor prognosis
Importance of metastatic malignancy in the jaws
The metastatic malignancy in the jaw may represent the first time that anyone has knowledge about the neoplasm
- Referral to an oncologist for a workup to determine the location of the primary and the extent of involvement of other sites is imperative
What are the features that establish an osteosarcoma as a malignant bone tumor?
Malignant osteoblasts making osteoid
How would osteosarcoma appear radiographically?
RL or RP with more mineral prodcued so it is white
What are the classical radiographic findings associated with osteosarcoma?
Making extra bone - rays come off of alveolus = Sunburst
- Codman's triangle too
The pathologist making the diagnosis of an osteosarcoma must be able to say that what findings are present?
Malignant osteoblasts making osteoid
What are the features of chondrosarcoma that suggest a maligant cartilaginous tumor?
2 cells within 1 lacuna, expanding the bone
How does a chondrosarcoma appear radiographically?
Similar to osteosarcoma, expansion of the jaw
What is the most common location for chondrosarcoma?
Anterior maxilla in the midline
How common are chondrosarcomas in the oral cavity?
Uncommon
What features indicate a metastatic carcinoma is a malignant neoplasm?
Producing more mineral or destroying bone
What features suggest metastatic carcinoma is metastatic?
No radiographic distinguishing features, but pathologist can see cells do not look like normal cells to inhabit oral cavity
What are the 2 most likely sites of primary tumors in metastatic carcinoma?
1. Lung
2. Breast/prostate
3. Colon
What is the prognosis for pts w metastatic carcinoma?
Poor
How does multiple myeloma appear radiographically?
Punched out lesions
What is the prominent cell type in multiple myeloma?
Plasma cells