Unit 14. Infectious Diseases Affecting the Skin and Eyes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
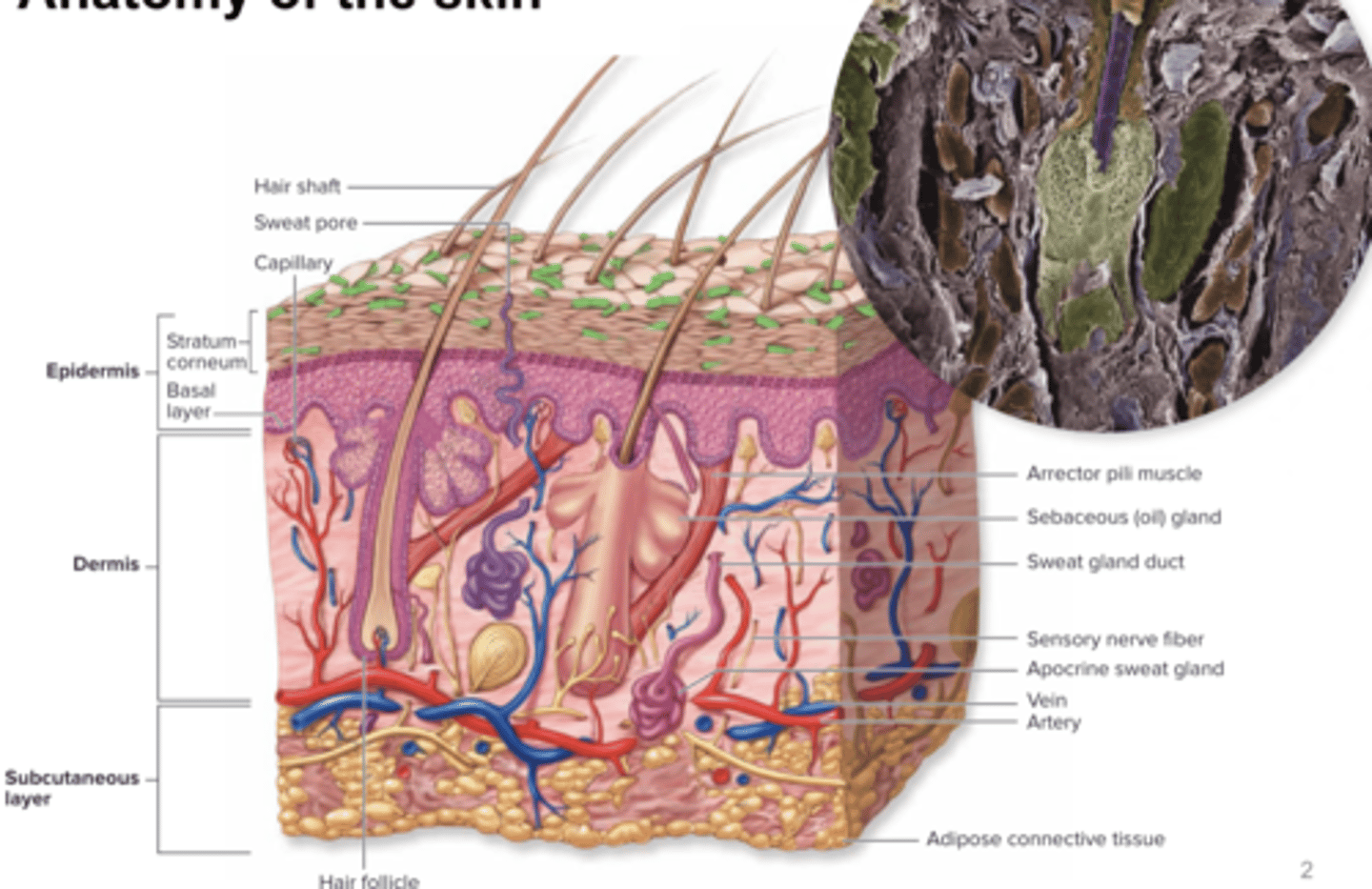
Anatomy of the skin image
-Stratum Corneum consists of keratinized cells and is constantly shedding to get rid of fungi
Defenses of the skin
Defenses on graph
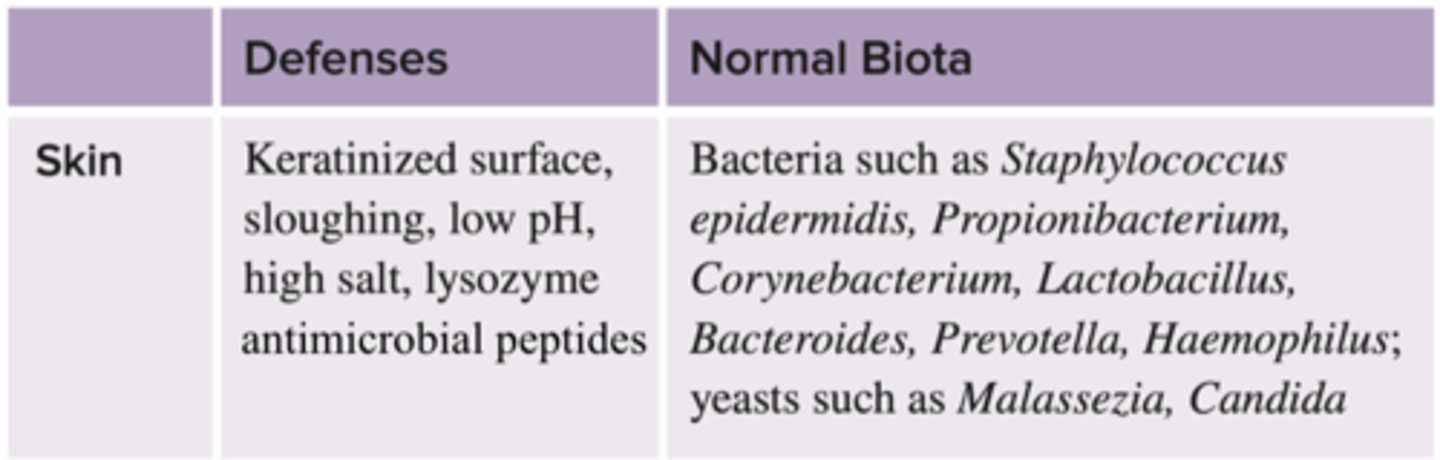
Defenses of the Normal Biota of the skin
Bacteria such as: Staphylococcus, epidermis, propionibacterium, corynebacterium, lactobacillus, bacteroides, prevotella, haemophilus: yeasts like Malassezia, Candida
Types of skin lesions: Macule
flat demarcated lesion determined by color change, ex: freckle, tinea versicolor
Types of skin lesions: Papule
small elevated solid bump, ex: warts, cutaneous leishmaniasis
Types of skin lesions: Maculopapular rash
flat-slightly raised colored bump, ex: measels, rubella, fifth disease, roseola
Types of skin lesions: Plaque
elevated flat topped lesion, >1cm, ex: psoriasis
Types of skin lesions: vesicle
Elevated lesion with clear fluid, ex: chickenpox
Types of skin lesions:Bulla
Large (wide) vesicle, ex: blister, gas blister in gengrene
Types of skin lesions: Pustule
Small, elevated lesion filled with purulent fluid (pus), ex: Acne, smallpox, mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, cutaneous anthrax
cyst
raised encapsulated lesion, usually solid or semisolid when palpated (severe acne)
Purpura
reddish purple discoloration due to blood in small areas of tissue, does not blanch when pressed (meningococcal bloodstream infection)
petechiae
small purpura (meningococcal bloodstream infection)
scale
flaky portions of skin separated from deeper portions (ringworm, athlete's foot)
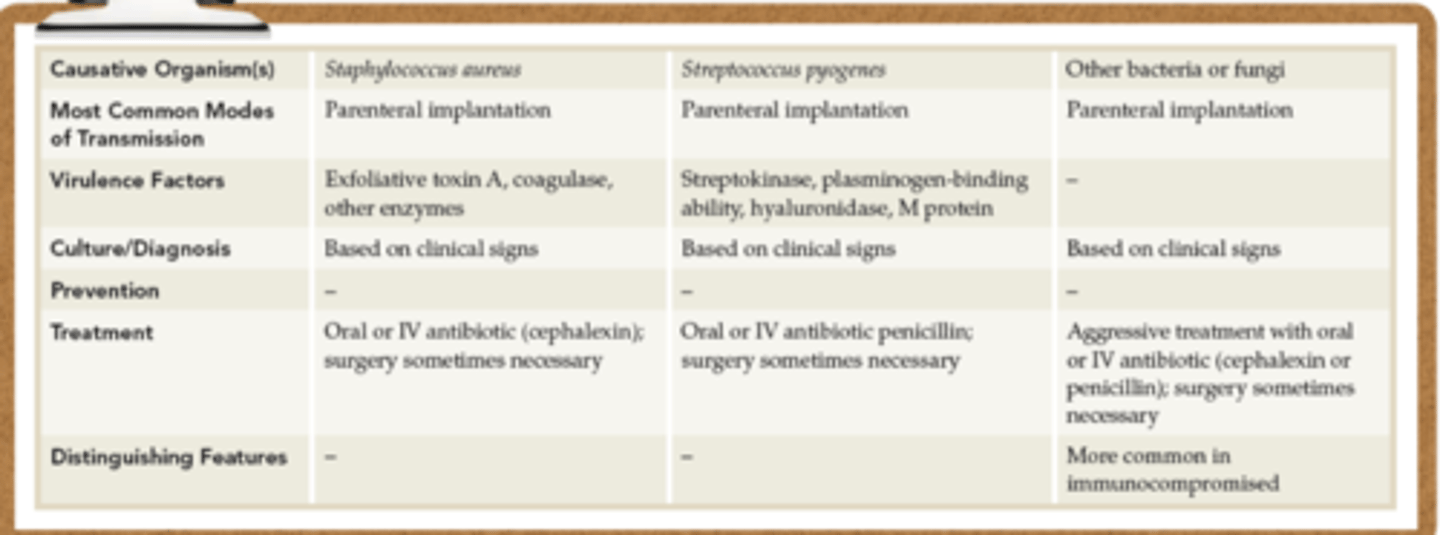
MRSA skin and soft tissue infections treatment & causative organisms
T: vancomycin
C: methicillin resistant straphylococcus aureus
MRSA Skin & soft tissue infections: what is it
-Raised, red, tender, localized lesions, often featuring pus and feeling hot to the touch
what is Impetigo & what causes it
• Superficial bacterial infection that causes the skin to flake or peel off, Superficial, itchy lesions
• Caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, or both
Impetigo treatment
topical mupirocin, retapamulin, oral cephalex, dicloxacilin
Cellulitis identification & causation
• Fast spreading infection in the dermis and subcutaneous tissues, red lesions, often surrounded by red lines, signs of inflammation
• Caused by bacteria or fungi. Most common, S.aureus or S. pyogenes/other fungi
cellulitis treatment
antibiotics cephalex & topical mupirocin
Scalded skin syndrome identification & causation
• Dermolytic condition, affecting mostly newborns/babies
• Bullous lesions, forming large blisters that evolve to widespread desquamation
-Caused by toxigenic S. aureus bearing a lysogenic phage.
scalded skin treatment
systemic antibioitics; cephalexin
Gas gangrene image
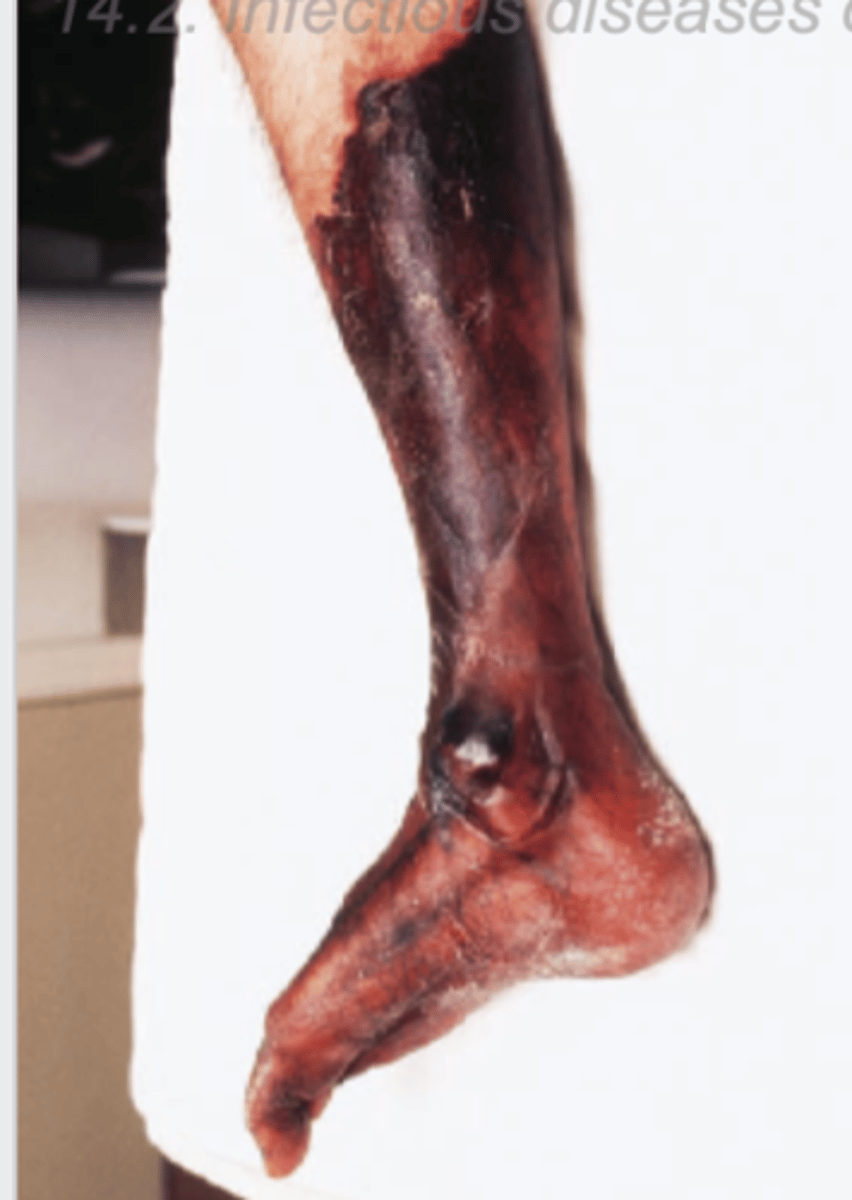
gas gangrene identification & causation
• Clostridial myonecrosis, an aggresive infection of muscles
• Local necrosis of muscles and nearby tissues with gas bubbles.
• Caused by Clostridium perfringens, a spore-forming, toxigenic, strictly anaerobic Gram-positive bacterium
gas gangrene treatment
oxygen therapy, surgical removal, penicillin, clindamycin

Vesicular/pustular rash diseases
chickenpox, smallpox, HFMD, monkeypox
Chickenpox identification & causation, & treatment
-Maculopapular lesions evolving to fluid-filled vesicles. Centripetal distribution.
-caused by Herpesvirus 3 (varicella),
-no treatment in uncomplicated cases,acyclovir for high risk
Smallpox identification, causation, & treatment
-Fever and malaise followed by rash spreading from the pharynx. Maculopapular lesions evolving to vesicles and pustules
-caused by Variola virus.
-Treatment: cidofovir vaccine
Hand, foot, & mouth disease (HFMD)
-caused by Enteroviruses (Coxsakie) on Babies and children. Fever, sore throat, and malaise. First lesions in mouth,
-no known treatment
which of these is caused by herpes virus
Roseola
Rubella
-Caused by Rubella virus/rubivirus
-mild red rash, last roughly 3 days
-no treatment
Measels(Rubeola)
-rash that starts on head & spreads over whole body, last over a week, sore throat/dry cough, headache
-caused by measels virus/morbillivirus
-treatment: vitamin A & antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections
Fifth disease(Erythema infectiosum)
-”slapped face” rash, sreads to limbs & trunk, confluent rather than bumps
-caused by Parvovirus B19
-no treatment
Roseola
-High fever which preceded rash stage, rash not always present
-caused by human herpesvirus 6
-no treatment
Molluscum contagiosum
•wartlike eruption
-Smooth, waxy nodules on the face, trunk, and limbs
•Caused by molluscum contagiosum viruses
-no treatment, can be removed at home
Warts (papillomas)
•wartlike eruption
-Benign, squamous epithelial growths, Painless, elevated, rough lesions
•Caused by human papillomaviruses
-treatment:home treatments & cryosurgery
Leishmaniasis
•Large pustular skin lesions,Zoonosis transmitted by bytes of sand flies
•Caused by Leishmania spp.
-treatment: sodium stibogluconate
Cutaneous anthrax
•Large pustular skin lesions, Papular lesions that become necrotic and rupture to form a painless, black eschar
•Caused Bacillus anthracis, a spore- forming Gram-positive bacterium
•Treatment: ciprofloxacin, doxcycline, levofloxacin
Cutaneous mycoses
-fungal infections affecting only the stratum corneum
-caused by trichophyton, microsporum, epidermophyton.
-treatment: topical tolnaftate, itraconazole, terbinafine, miconazole, thiabendazole, oral terbinafine
Superficial mycoses
-benign infections that do not cause inflammation
-caused by Malassezia species
- treatment: topical antifungus
defenses of the eye chart
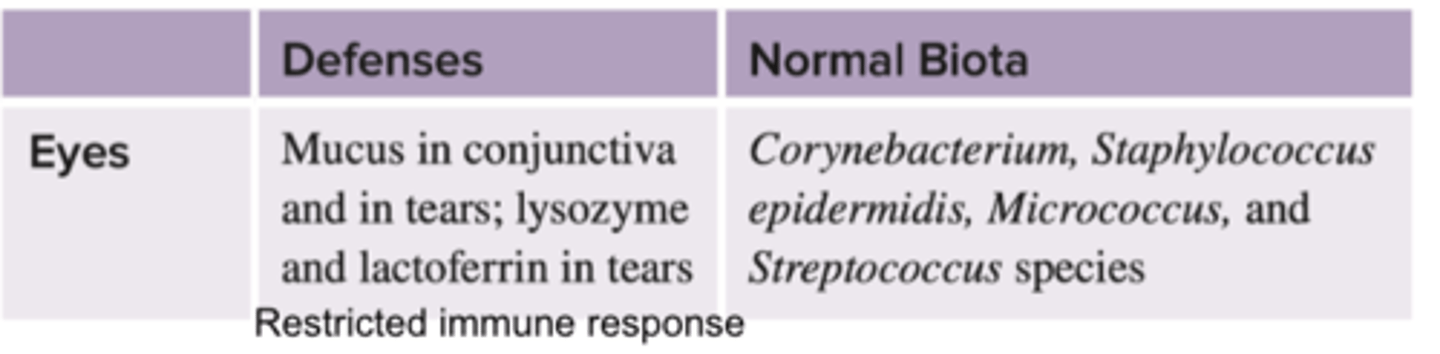
Normal Biota of the eye
corynebacterium, staphylococcus epidermis, micrococcus, & streptococcus species
Conjunctivitis
• Infection of the conjunctiva, inflammation, discharge, pain, redness, photophobia
neonatal conjunctivitis
-caused by chlamydia trachomatis or neisseria gonorrhoeae
-babies <28 days old
-treatment: oral antibiotics
Bacterial conjuntivitis
-caused by streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae
-mucopurulent discharge
-treatment: gatifloxacin or levofloxacin ophthalmic solution
viral conjunctivitis
-caused by adenoviruses & others
-serous/clear discharge
-treatment: none
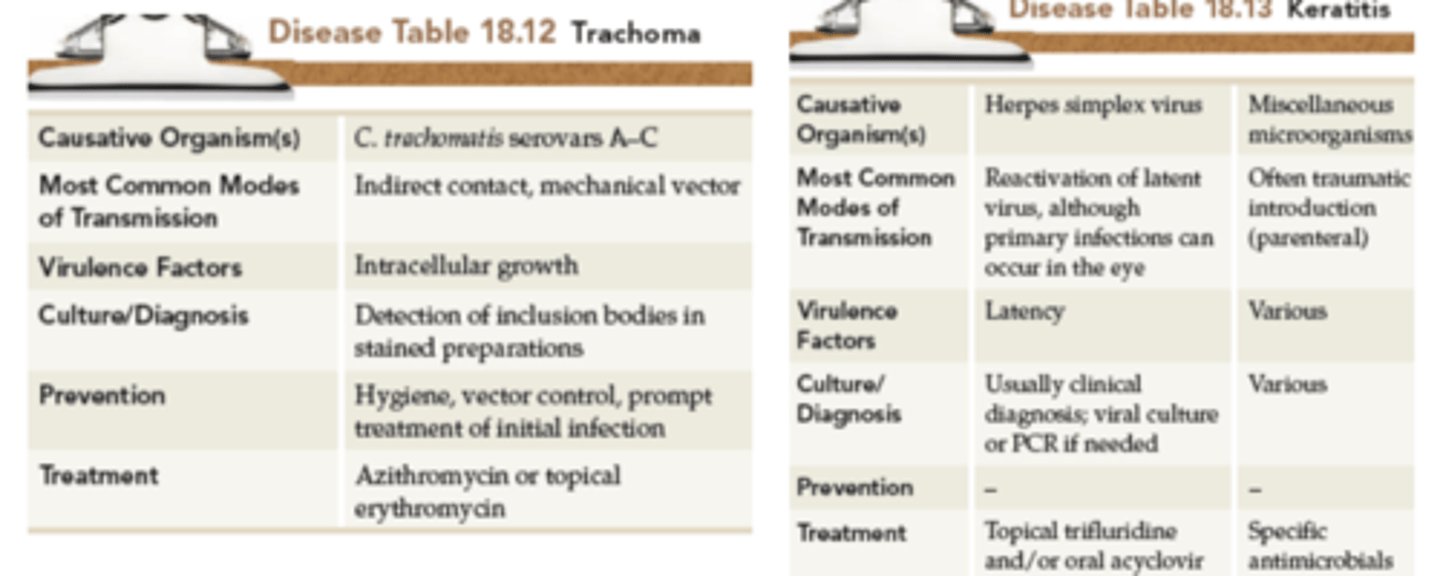
Trachoma
-caused by Chlamydia trachomatis
-infection of the eye's epithelium, inflammation & discharge in conjunctiva, followed by infiltration of WBCs.may lead to impaired vision
-treatment: Azithromycin or topical erythromycin
Keratitis
•caused by reactivated herpes simplex virus
-Infection of deep eye tissues that may lead to corneal destruction
-treatment: topical trifluridine and or oral acyclovir
Trachoma and Keratitis chart
River blindness
• Caused by the worm Onchocerca volvulus, infected with Wolbachia
• Helminth(worm) infection transmitted by bytes of black flies, worm can often be seen in eye
-treatment: ivermectin