2.1 Introduction to Energy + 2.2 Activation Energy & Enzymes
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is thermodynamics?
The study of the flow of energy in systems
First Law of Thermodynamics:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be converted from one form to another
Second Law of Thermodynamics:
Energy transfers are never 100% efficient
Always accompanied by a loss of energy in the form of heat
What is energy?
The ability to:
Do work
Bring about a change
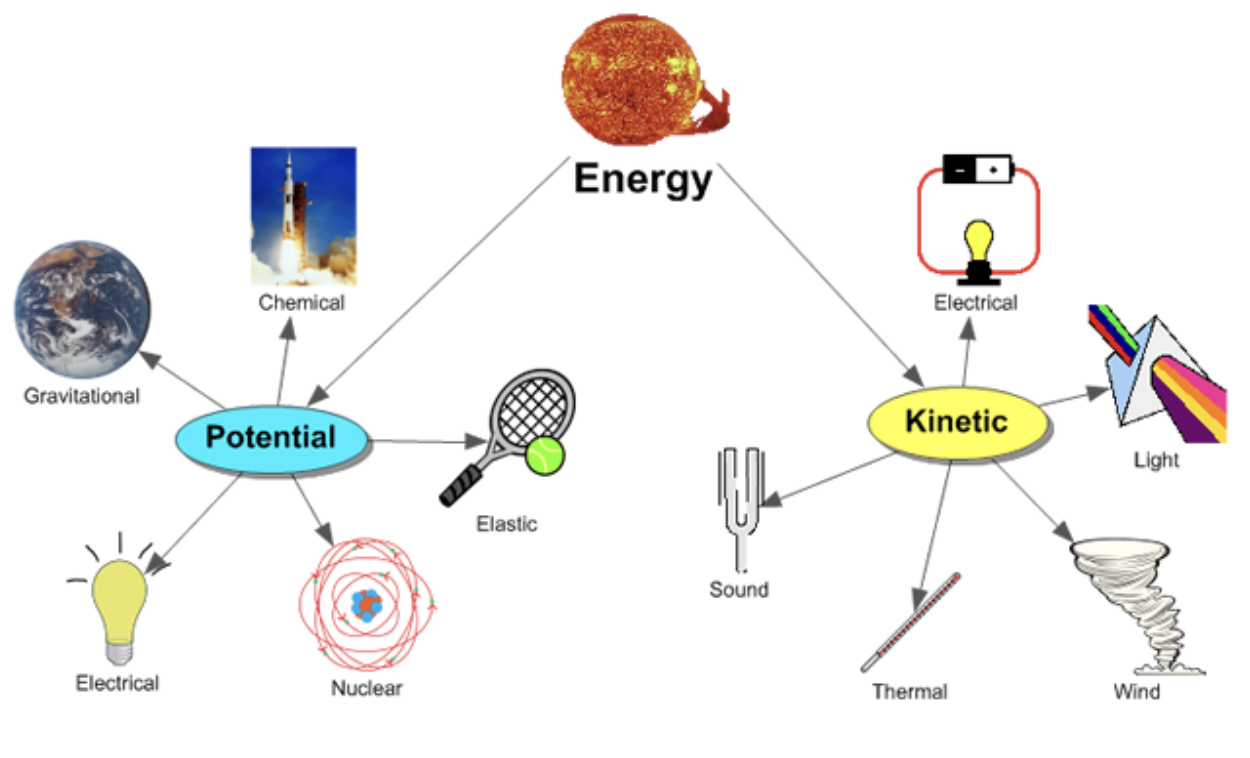
What are the two states of energy?
Kinetic
Energy of motion
Potential
Stored energy
What are the different forms of energy?
Thermal
Heat
Electrical
Flow of charged particles
Nuclear
Radioactive decay
Light
Waves of photons
Sound
Mechanical waves moving through air
Chemical
Potential energy stored in chemical bonds
Only type of energy organisms can use
Glucose contains chemical potential energy stored in its covalent bonds
Organisms need energy every second. What for?
Active transport
Nerve transmission
Homeostasis
Muscle contraction
Anabolic reactions
Synthesis reactions
Endothermic
Energy provided by hydrolysis of ATP
Catabolic reactions
Release of stored chemical potential energy in bonds
Exothermic
Digestion/cellular respiration
Organisms depend on the ability to transfer energy in & out of their cells
Energy is transferred mostly through redox reactions
What is entropy?
A measurement of the degree of disorder and randomness in a system
The higher the more random
In a closed system it always increases
Entropy and energy are inversely related
Higher entropy = lower amount of available energy to do work
If a reaction increases the randomness of the universe, the reaction will occur spontaneously
What is activation energy (EA)?
Energy required to initiate a reaction
For chemical reaction
It helps destabilize existing bonds
Increases entropy
Is usually in the form of heat
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts
Proteins
Have specific 3° structure
Initiates and speeds up reactions
How do enzymes work?
Substrate binds to enzyme’s active site
After binding they form the enzyme-substrate complex which decreases EA
When the enzyme and substrate react, the chemical bonds in the substrate weaken which causes them to link together
The chemical reaction at the active site leads to the formation of a different molecule (product)
The product is then released and the enzyme returns to its original state
What do the rates of reaction depend on?
Temperature
Concentration
Pressure