Human Bio T2 W7
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Small intestine structure
Smaller in diameter, 6-7m long
Where does the small intestine receive materials from
materials are pushed through pyloric sphincter from the stomach
Regions of small intestine
Duodenum, Jejunum and Ileum
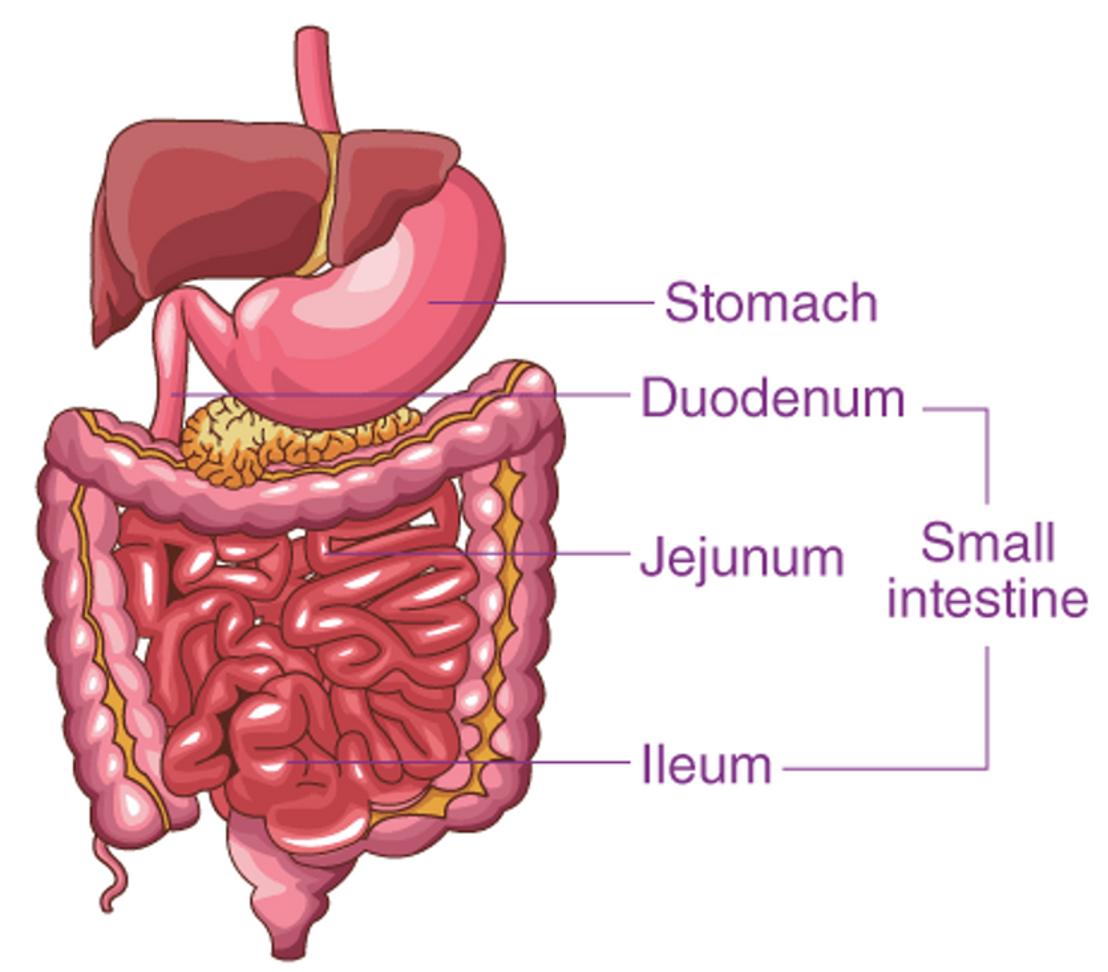
Duodenum region
First part, only 25cm, most chemical digestion occurs here
Jejunum region
Middle section, most carbohydrates and proteins absorbed here
Ileum region
Final section, remaining products of digestion absorbed here
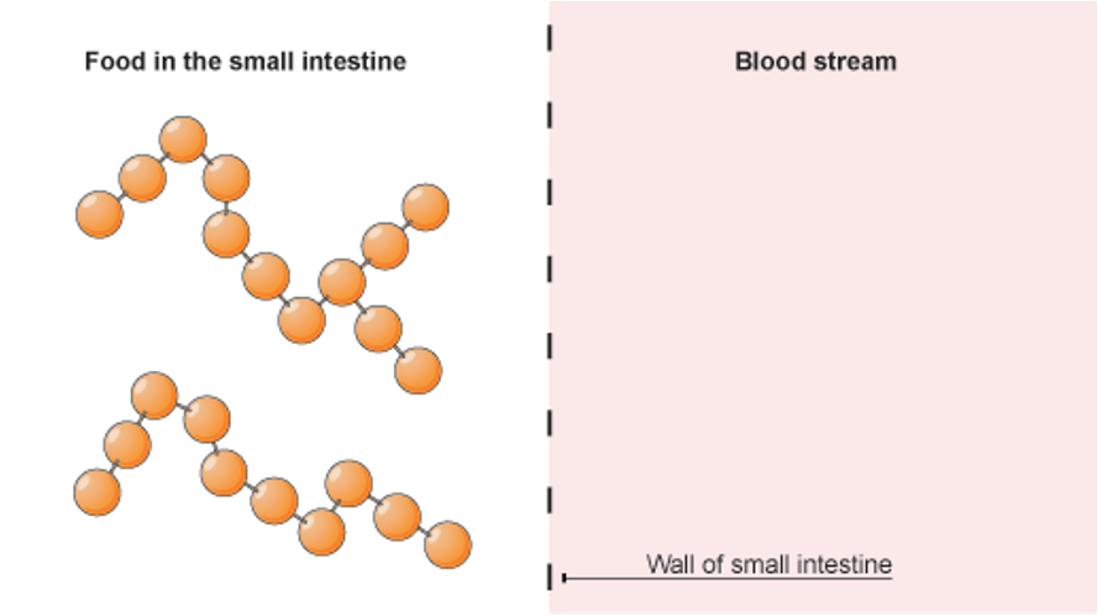
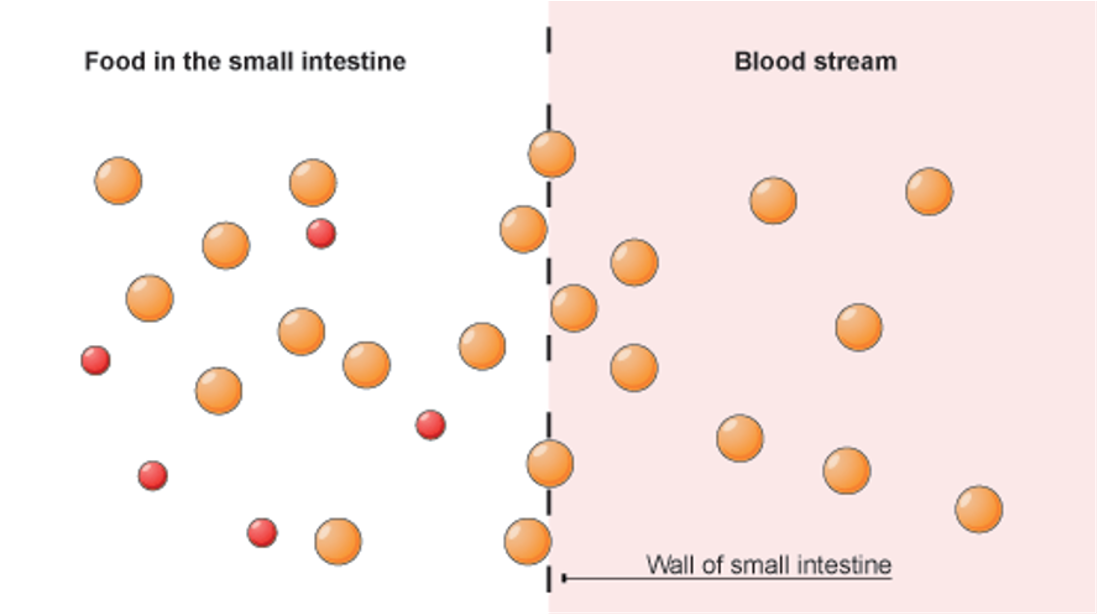
Small intestine function
2 major functions:
1. Complete digestion of nutrient macromolecules.
2. Absorption of these nutrient molecules across the wall of the intestines into the blood and lymph.
Digestion key structures
Pancreatic juices, Bile and intestinal juices
Where are pancreatic juices secreted
secreted by pancreas via pancreatic duct
Bile
produced by liver but stored in gall bladder. Secreted into small intestine via bile duct. Contains bile salts to emulsify lipids.
Intestinal juices
secreted by glands in the lining of small intestine.
Mechanical digestion in small intestine
Larger pieces of food broken down into smaller pieces of food.
Mix food with digestive juices: pancreatic juice and intestinal juice.
2 processes:
1. Bile salts emulsifying fat droplets
2. Segmentation
emulsification
Bile breaks down large fat droplets into smaller droplets.
Why deos emulsification occur
Fats (lipids) will clump together into larger clumps when in contact with each other and will slow down chemical digestion of lipids by lipases. Therefore bile is needed to break down the clumps into fat droplets.
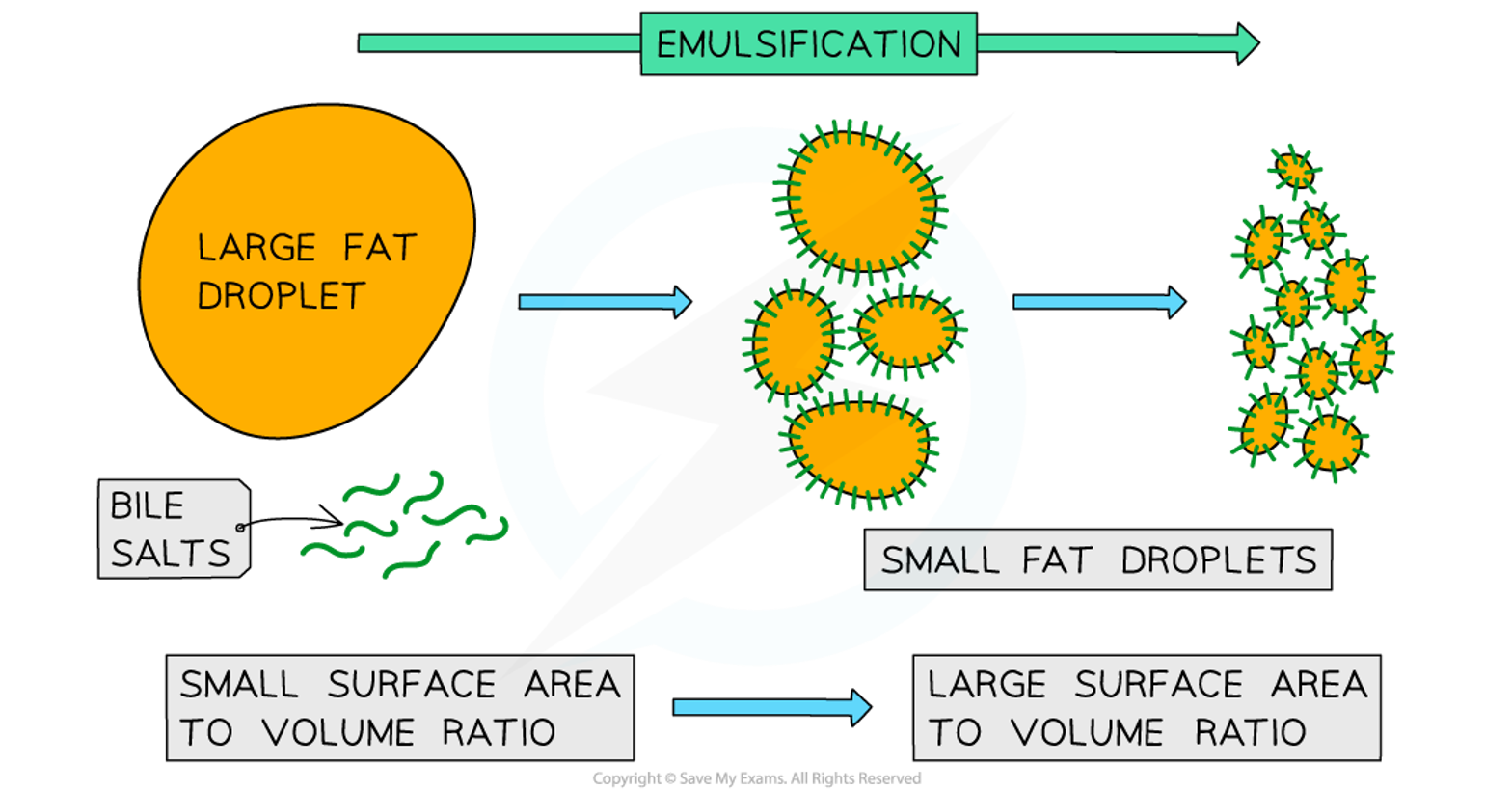
Why do fat droplets have a large surface area
So the lipases can more efficiently chemically digest lipid molecules. Bile doesn’t contain enzymes therefore it isn’t a chemical digestion process.
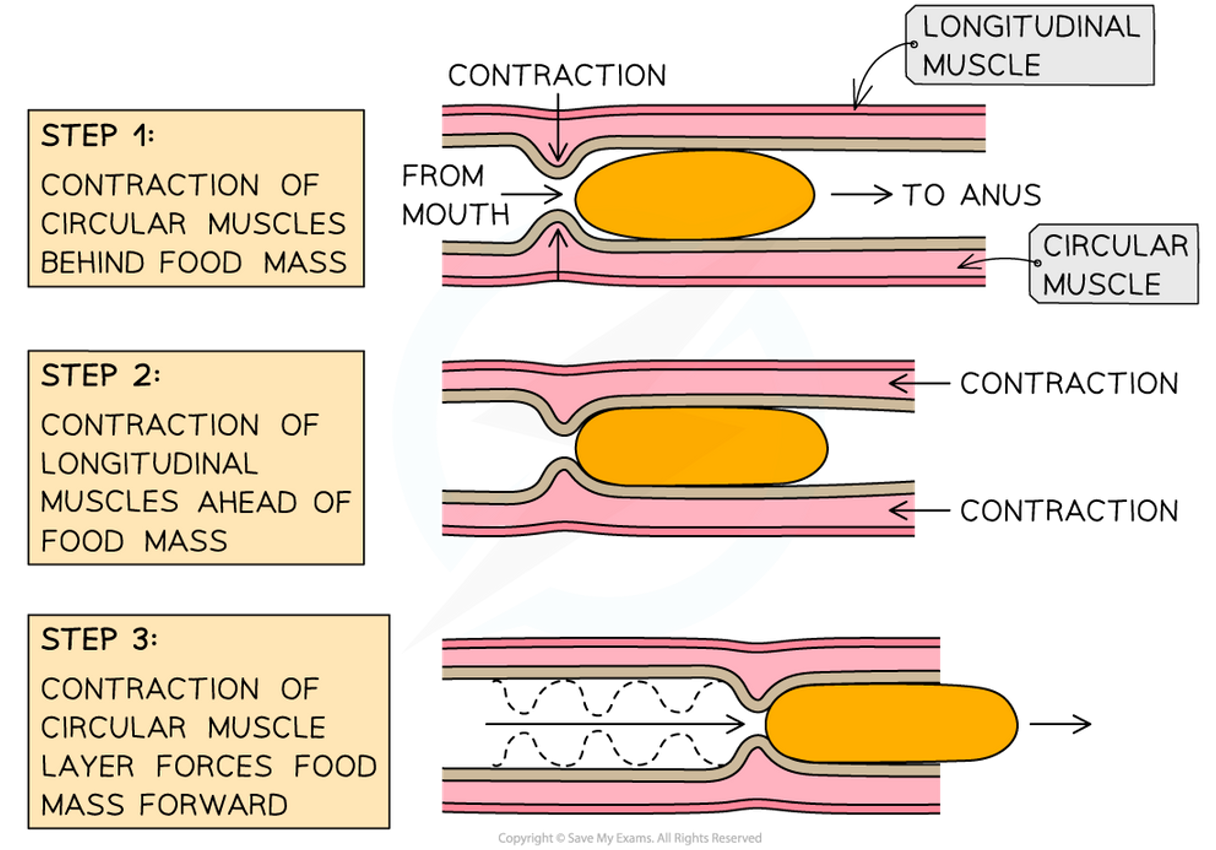
Peristalsis
•During peristalsis, contraction of circular and longitudinal muscles move food along the oesophagus toward the stomach.
⚬Circular - contracts from behind food to propel food forward
⚬Longitudinal - contracts ahead of food to shorten pathway for food to travel
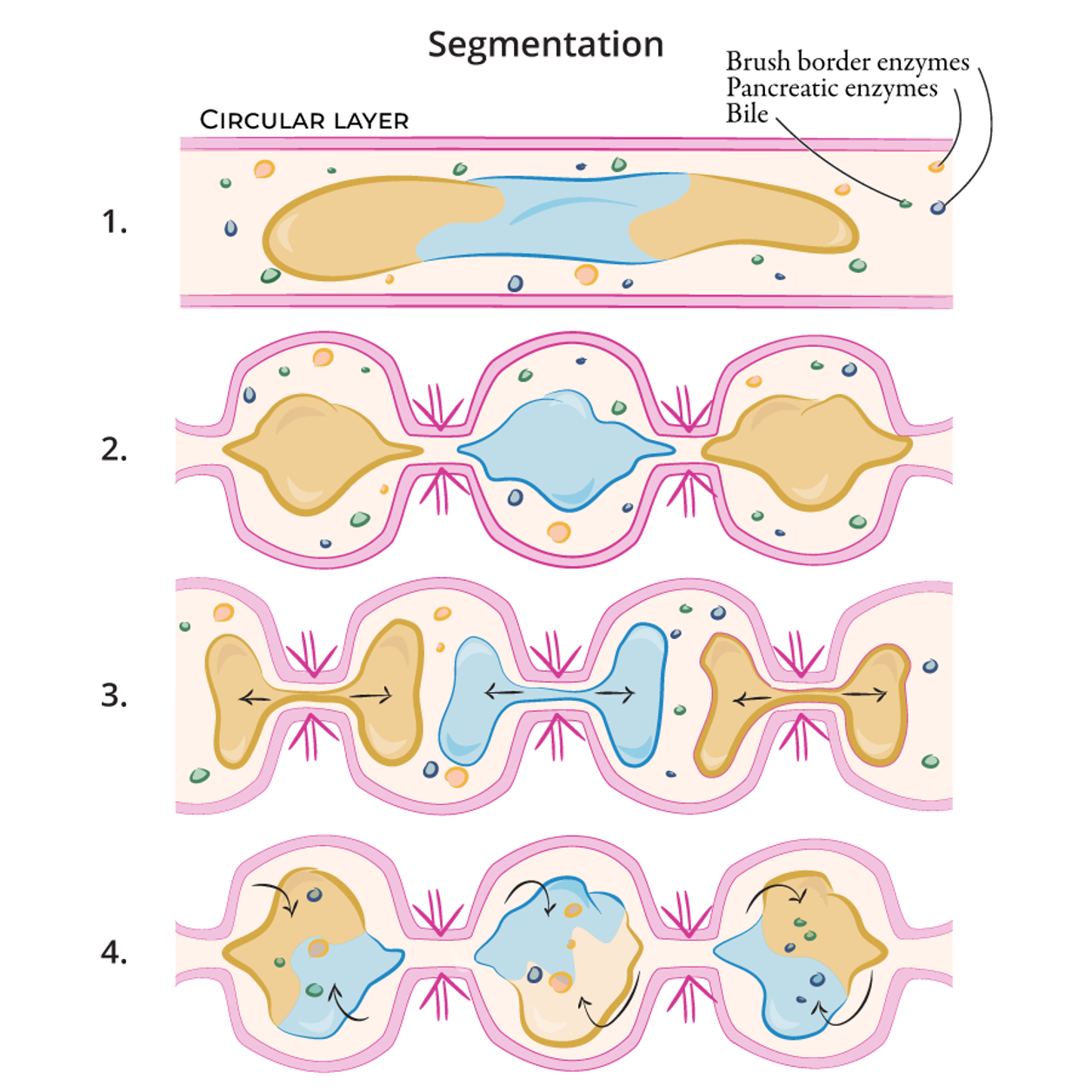
Segmentation
•Mechanical digestion
•Contractions of the circular muscles narrow the intestine which helps to break up the bolus and mix it with the intestinal and pancreatic juices, and the bile.
•This also aids the process of absorption.
small intestine - chemical digestion
•Larger nutrient molecules --> small nutrient molecules.
•Involves the use of digestive enzymes:
⚬Amylases - break down carbohydrates
⚬Proteases - break down proteins
⚬Lipases - break down lipids (fats)
Where pancreatic juice is secreated
•Pancreatic juice is produced by the pancreas.
•It has a pH of 8 and is secreted into the duodenum via the common pancreatic duct.
Pancreatic juice digestion enzymes
⚬Pancreatic amylase breaks down any remaining polysaccharides into disaccharides.
⚬Pancreatic protease (or trypsin) breaks down any remaining polypeptide chains into shorter peptide chains.
⚬Pancreatic lipase breaks down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol.
Where intestinal juice is secreted
Intestinal juice is secreted by the intestinal glands and has a pH of 8.
Intestinal juice digestive enzymes
•It contains the digestive enzymes:
⚬Intestinal amylase (or maltase, sucrase, lactase) breaks down disaccharides into monosaccharides.
⚬Intestinal protease (or peptidase) breaks down peptides into amino acids.