CLCIV 101 Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
1
New cards
Cimon
510-450 BC, Athenian leader, son of Militiades. The leader of the Delian League. He lead aggressive attacks on Persia, and made friendly relations with Sparta. Thasos then rebelled the League, and then the people wanted to break away with Sparta. Cimon was exiled, and then Athens made an alliance with Sparta's enemy, causing them to break ties.

2
New cards
Ephialtes
fifth century BC, an Athenian democratic political reformer. Traitor that showed the Persians the goat path that led to the Greeks' defeat at Thermopylae
3
New cards
Pericles
495-429 BC, Athenian statesman noted for advancing democracy in Athens and for ordering the construction of the Parthenon.

4
New cards
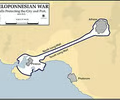
Long Walls
defensive walls built between Athens and Piraeus
5
New cards
Old Oligarch
unknown author of oligarchic pamphlet from the 5th century BC
6
New cards
metics
non citizen foreigners living in Athens
7
New cards
liturgies
a public service established by the city-state whereby its richest members financed state events with their personal wealth
8
New cards
Corcyra
Corinthian colony that wanted independence; it reached out to Athens for help which led to the Battle of Sybota.
9
New cards
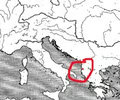
Epidamnus
Location of civil war between Corcyra and Corinth, leading to second Peloponnesian war
10
New cards
demagogue
a leader who exploits popular prejudices and false claims and promises in order to gain power
11
New cards
daedalic style
The Greek Orientalizing sculptural style of the seventh century BCE named after the legendary artist Daedalus

12
New cards
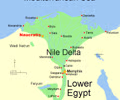
Naucratis
Greek trading colony in Egyptian delta
13
New cards
Kore/Kouros
a Greek statue of a clothed maiden/ a Greek statue of a male youth who may have been a god or an athlete

14
New cards
Doric Order
the simplest of the classical Greek architectural styles, featuring unadorned columns with no base

15
New cards
Ionian Order

16
New cards
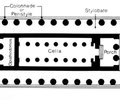
Cella
the inner area of an ancient temple, especially one housing the hidden cult image in a Greek or Roman temple.
17
New cards
pediment
the triangular upper part of the front of a building in classical style, typically surmounting a portico of columns.

18
New cards
orientalizing phase
19
New cards
protoattic

20
New cards
black figured style

21
New cards
red figured style

22
New cards
severe style
Early phase of Classical sculpture characterized by reserved, remote expressions, c. 480-450 BCE

23
New cards
lost wax technique
24
New cards
high classical
c. 450-400 BCE

25
New cards
Parthenon
A large temple dedicated to the goddess Athena on the Acropolis in Athens, Greece. It was built in the 5th century BCE, during the Athenian golden age.

26
New cards
Elgin Marbles
27
New cards
Propylaea
28
New cards
Erechtheum
29
New cards
Athena Nike
Athena as goddess of victory (Nike)

30
New cards
caryatids
31
New cards
white ground style
Style of pottery. Surface covered in chalky white, figures drawn in black, then colored.

32
New cards
Praxitiles
33
New cards
Corinthian capitals
A more ornate form than Doric or Ionic; it consists of a double row of acanthus leaves from which tendrils and flowers grow, wrapped around a bell-shaped echinus.

34
New cards
tholos
A temple with a circular plan. Also, the burial chamber of a tholos tomb.

35
New cards
Mausoleum at Halicarnassus
in Turkey and was a white tomb built for the Persian King Mausolus wife Artemisia, it was a 135 foot tomb and was destroyed by an earthquake, the British museum has a lot of sculptures from this place

36
New cards
Priene
grid-planned town on sloped hillside in Ionia, western Asia Minor

37
New cards
Posiden
God of the sea, earthquakes, and horses

38
New cards
Aphrodite
goddess of love and beauty and daughter of Zeus in ancient mythology

39
New cards
psyche
Goddess of The Soul. So beautiful that Venus had her son Cupid make her fall in love with someone unsuitable. Cupid falls in love with her. Then Venus puts a curse on her that she cant fall in love or marry again.

40
New cards
miasma
41
New cards
Eleusinian Mysteries
The cult of the mother goddess Demeter and a very popular Athenian festival celebrated each year for the mother and the maiden, Persephone. This cult promised all its members a blissful afterlife.
42
New cards
Persephone
Queen of the underworld; daughter of demeter and was kidnapped by Hades and made his queen; must stay in the underworld for 6 months of the year because she ate 6 pomegranate seeds

43
New cards
Demeter
goddess of the harvest; mother of Persephone

44
New cards
Orphics
This mystery cult had an unfavorable view of life, that the way to avoid reincarnation was to follow a strict moral code, abstain from the flesh of living creatures and avoid wearing wool

45
New cards
Dionysus
god of wine and fertility and drama

46
New cards
Bacchus
Dionysus

47
New cards
Bacchae
(Euripides, c. 405 BC) At the start of this tragedy, the god Dionysus arrives in Thebes to seek vengeance against his aunt Agave, who has denied his immortality, and her son Pentheus, who as King of Thebes bans worship of Dionysus. The god first drives the women of the city mad, causing them to act as wild Maenads. He then convinces Pentheus to disguise himself in animal skins, and spy on the maddened women. However, the demented Agave mistakes Pentheus for a mountain lion, and dismembers her own son. The climax of the play occurs when Agave presents the head of Pentheus to her horrified father, Cadmus. As Agave realizes what she has done, Dionysus chastises her for her lack of respect, and foretells how Cadmus will spend his final days.

48
New cards
oligarchy
a small group of people having control of a country, organization, or institution.

49
New cards
agathoi
"The Good People" aristocrats
50
New cards
kakoi
"The bad people". The poor
51
New cards
demos
the people, the citizens
52
New cards
talents
units of money in ancient Greece

53
New cards
hoplite
Heavily armored Greek infantryman of the Archaic and Classical periods who fought in the close-packed phalanx formation. Hoplite armies-militias composed of middle- and upper-class citizens supplying their own equipment. Famously defeated superior numbers of opponents by fighting as a unit.

54
New cards
phalanx
Formation of soldiers carrying shields close together for defense; any very close group of people

55
New cards
Nicias
(470 - 413 BCE): Athenian general who brokered a temporary peace between Athens and Sparta and subsequently helped lead the Sicilian expedition, a disastrous attempt by Athens to invade Sicily.

56
New cards
Archimadian War
57
New cards
Demosthenes
Athenian orator who tried to warn the Greeks of the threat Philip and his army posed

58
New cards
Sphacteria
Island where the Spartans were marooned and surrendered to the Athenian army under Cleon. Series of accidents that left the Athenians in a good position. Cleon greatly benefited from this. Greece was very surprised that the Spartans surrendered.
59
New cards
Brasidas
Spartan general that led their resurgence in the second half of the Archidamian phase. He captured Amphipolis, but later died defending it.

60
New cards
Cleon
Ruthless ruler in Athens after the death of Pericles; he opposed the Peace of Nicias

61
New cards
Peace of Nicias
50 year peace treaty that concluded the first phase of the Great Peloponnesian war. It lasted 7 years.
62
New cards
Alcibiades

63
New cards
Melos
64
New cards
Gylippus
65
New cards
Decelea
66
New cards
Dionysius
67
New cards
The Four Hundred
In Athens, in 411, the assembly voted itself out of power, placed the safety of the state in in the hands of a new provisional council, which would soon turn into one of 500. Created an oligarchy.
68
New cards
Xenophon
Greek historian; student of Socrates; anecdotal use of history; used history to fulfill his own philosophical agenda

69
New cards
Lysander
70
New cards
Ionia
Area along the central west coast of Asia Minor colonized by settlers from mainland Greece from about 1000 BC. Ionian Greeks, including Homer, played a central role in the early development of Greek history and literature following the Dark Ages.
71
New cards
Miletus
Greek/Ionian settlement on outskirts of Persian empire; beginning site of revolts (499) and Athenian aid (498); Persian reconquer and begin Persian war in 494

72
New cards
Ionian Enlightenment
a set of advances in scientific thought, explanations on nature, and discovering the natural and rational causes behind observable phenomena, that took place in archaic Greece beginning in the 6th century BC.
73
New cards
Anaximander
early Greek naturalist who advocated spontaneous generation as the origin of life
74
New cards
Anaximenes
75
New cards
Pythagoras
A Greek philosopher and mathematician, this man was credited with the discovery that numbers are useful for more than counting physical things.

76
New cards
Herodotus
Greek Historian, considered the father of History. He came from a Greek community in Anatolia and traveled extensively, collecting information in western Asia and the Mediterranean lands.

77
New cards
historie
78
New cards
Heraclitus
a presocratic Greek philosopher who said that fire is the origin of all things and that permanence is an illusion as all things are in perpetual flux (circa 500 BC)
79
New cards
Anaxoragoras
80
New cards
Parmenides
a pre-socratic Greek philosopher born in Italy. Denied the existence of time, plurality, and motion. NO Change. Founder of Metaphysics.

81
New cards
Zeno
Greek philosopher who founded the school of philosophy called Stoicism

82
New cards
paradoxes of Zeno
83
New cards
pluralists
84
New cards
Empedocles
440 B.C. - Greek who stated that all matter was composed of 4 elements: earth, air, fire, & water

85
New cards
Democritus
(460-370 BCE) A Greek philosopher who theorized that all matter could be reduced to particles that could not be divided, which he described as "atomos."

86
New cards
atomic theory
87
New cards
sophists
Athenian men who opened schools for boys to study government, mathematics, ethics, and rhetoric
88
New cards
arete
89
New cards
Moral Relativism
90
New cards
Protagoras

91
New cards
Socrates
(470-399 BCE) An Athenian philosopher who thought that human beings could lead honest lives and that honor was far more important than wealth, fame, or other superficial attributes.

92
New cards
inductive method
93
New cards
Aristophanes
an ancient Greek dramatist remembered for his comedies (448-380 BC)

94
New cards
old comedy
Classical Greek comedy that pokes fun at social, political, or cultural conditions and at particular figures.

95
New cards
Plato
(430-347 BCE) Was a disciple of Socrates whose cornerstone of thought was his theory of Forms, in which there was another world of perfection.

96
New cards
The Republic
created a utopian, ideal state composed of three social classes.
97
New cards
Theory of Forms
Plato's contention that ultimate reality consists of abstract ideas or forms that correspond to all objects in the empirical world. Knowledge of these abstractions is innate and can be attained only through introspection.
98
New cards
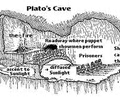
Parable of the Cave
Plato's idea. Illustrated pure ideas. Prisoners in a cave only experience shadows on a wall casted by a fire. They are living a life of illusion.
99
New cards
Academy
school of philosophy founded by Plato
100
New cards
Aristotle
A Greek Philosopher, taught Alexander the Great, started a famous school, studied with Plato
