Biofilms and Bioluminescence Lecture Notes
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about biofilms, quorum sensing and bioluminescence.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
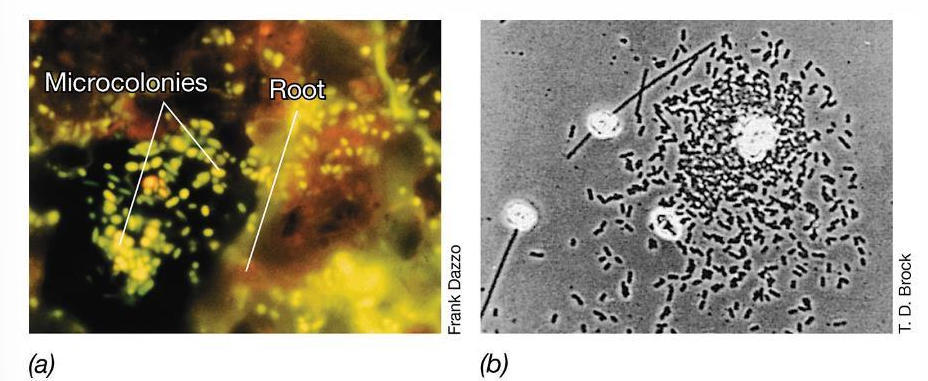
Why are surfaces important microbial habitats?
Nutrients adsorb to surfaces, allowing microbial cells to attach.
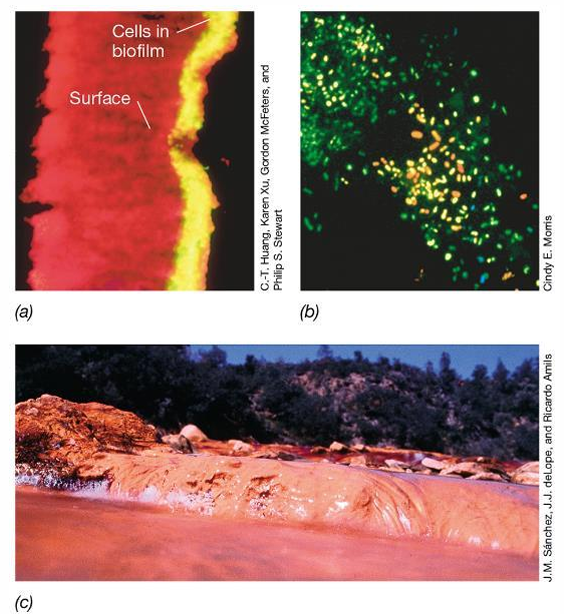
What are biofilms?
Assemblages of bacterial cells adhered to a surface and enclosed in an adhesive matrix excreted by the cells. .
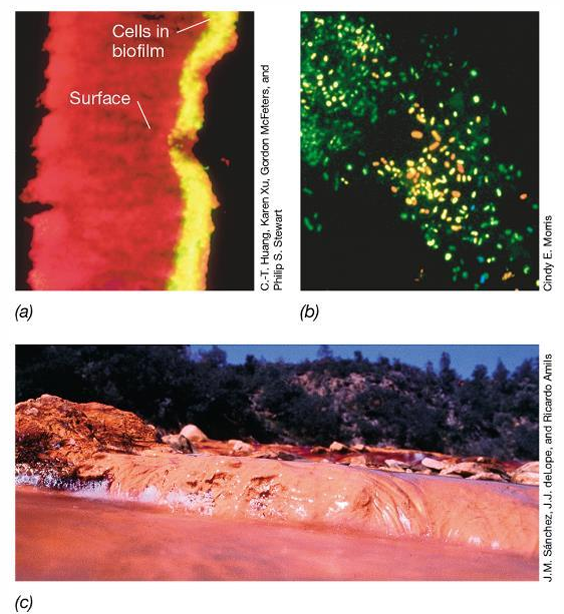
What do biofilms do?
Biofilms trap nutrients for microbial growth and help prevent detachment of cells in flowing systems.
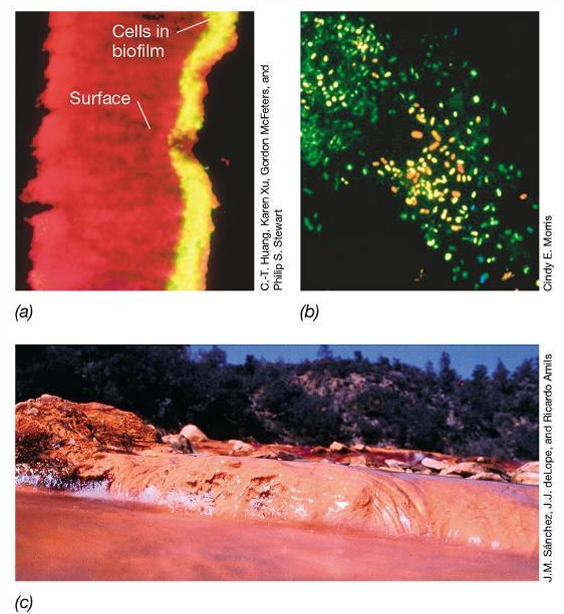
What is the matrix and what does it consists of?
The matrix is a complex mixture of polysaccharides and creates a sticky surface
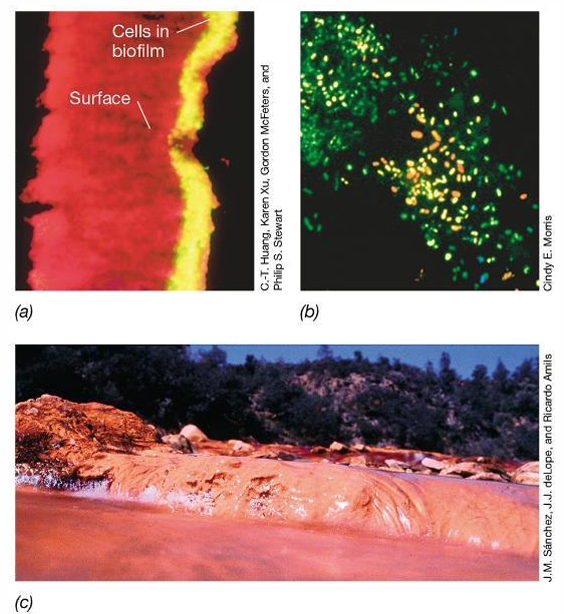
What are the features that distinguish biofilm populations from their planktonic counterparts?
The association with a surface, high population densities (on the order of 10^{10} cells per ml of hydrated biofilm), an extracellular polymer (EPS) slime matrix, and a wide range of physical, metabolic and chemical heterogeneities.
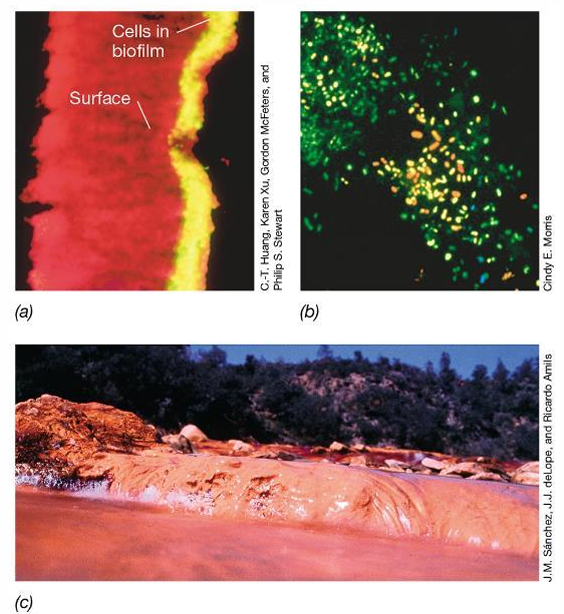
Biofilms, along with flocs and microbial mats, drive most microbial conversions in natural environments.
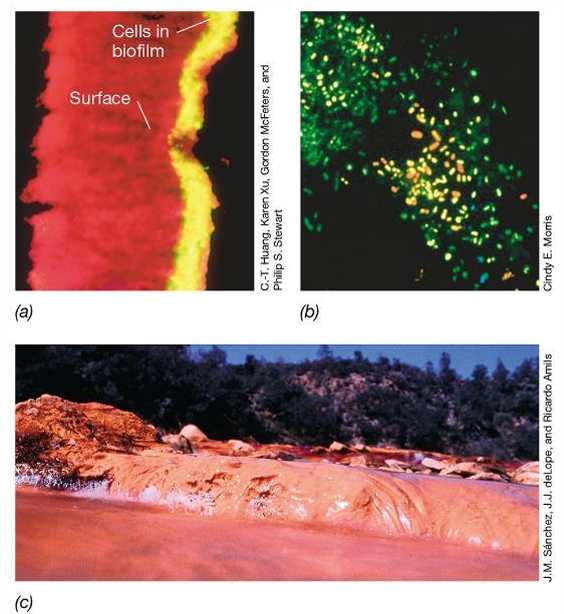
Biofilms are ubiquitous, covering rocks, plants, sediment grains, and sediment surfaces in seawater and freshwater.
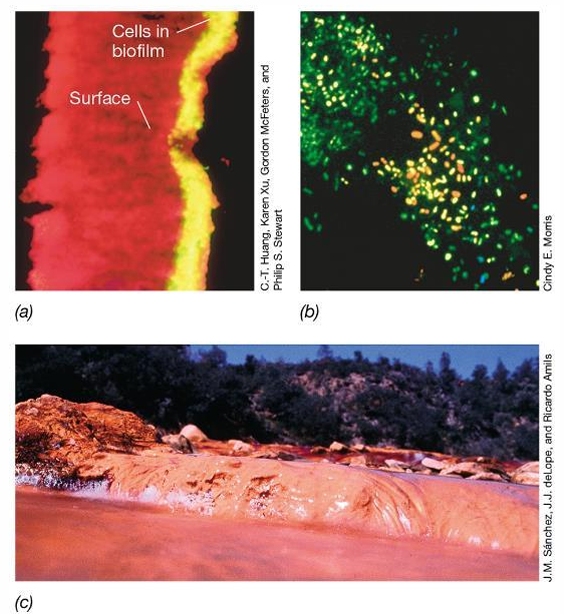
It starts with a cell attaching to a surface, followed by the expression of biofilm
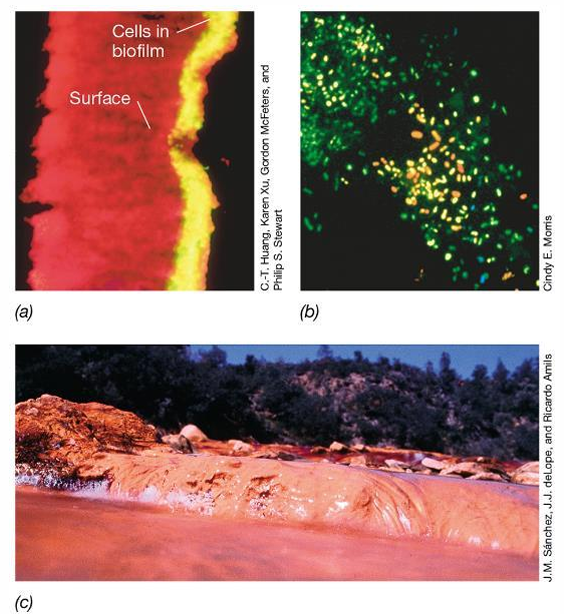
What do biofilm-specific genes encode?
encode proteins that synthesize intercellular signaling molecules and initiate matrix formation.
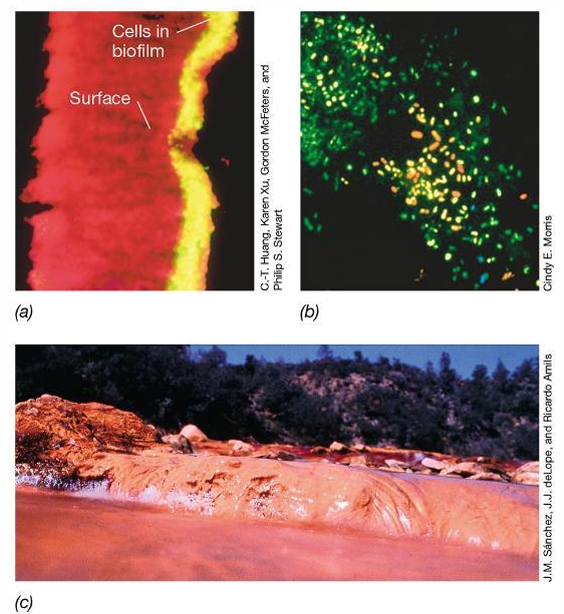
What are flocs?
Aggregates of cells and extracellular matrix that are like floating surfaces
What are microbial mats?
are like layers of metabolisms based on reduced compounds on bottom and oxidized on top
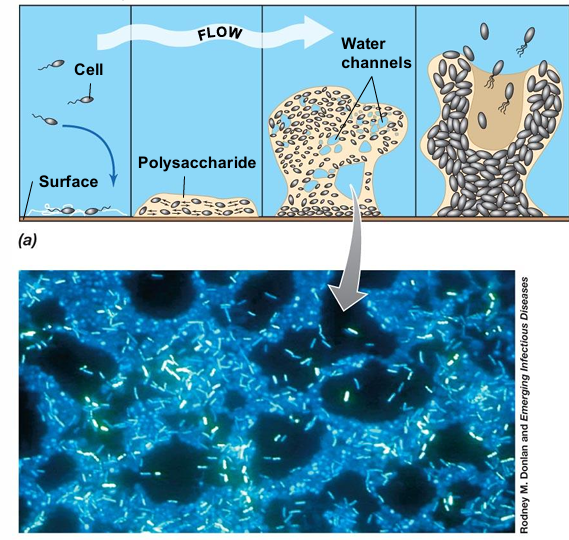
Attachment: Individual bacterial cells adhere to a surface using pili, flagella, or adhesive proteins.
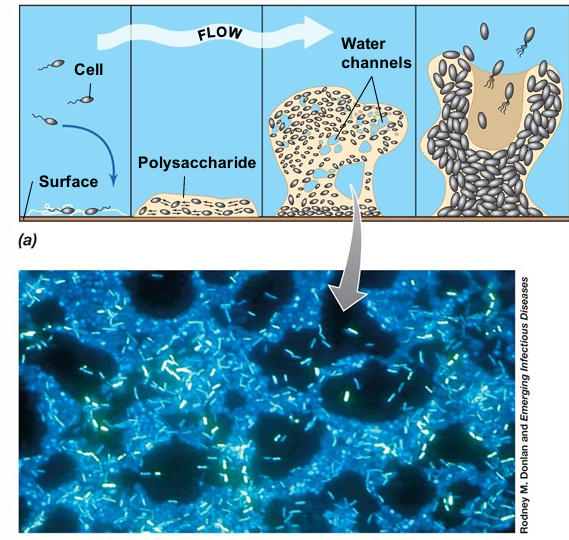
Microcolony Formation: Attached cells begin dividing and forming small clusters which causes intracellular communication growth and polysaccharide forming.
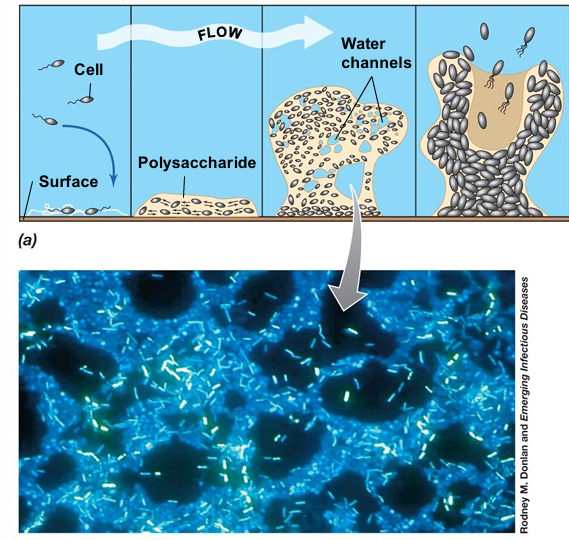
The matrix binds cells together, providing structural support and protection.
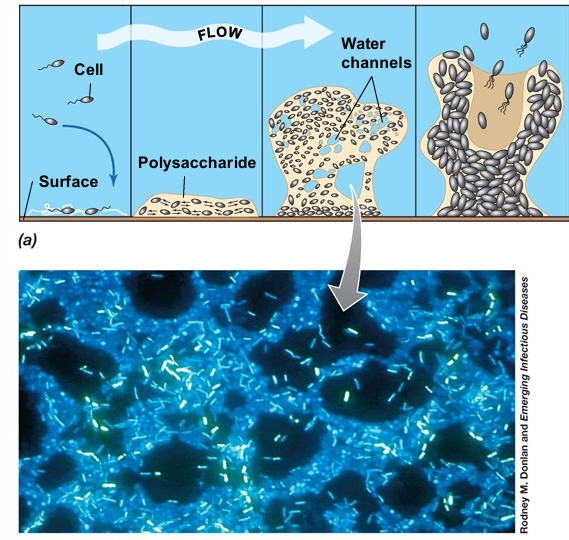
The biofilm develops into a structured, three-dimensional community with nutrient channels and cell differentiation.
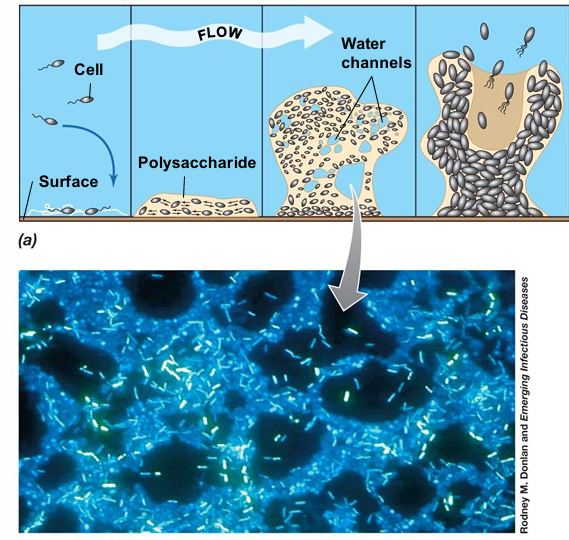
Detachment & Dispersal: Portions of the biofilm break away, spreading bacteria to colonize new surfaces.
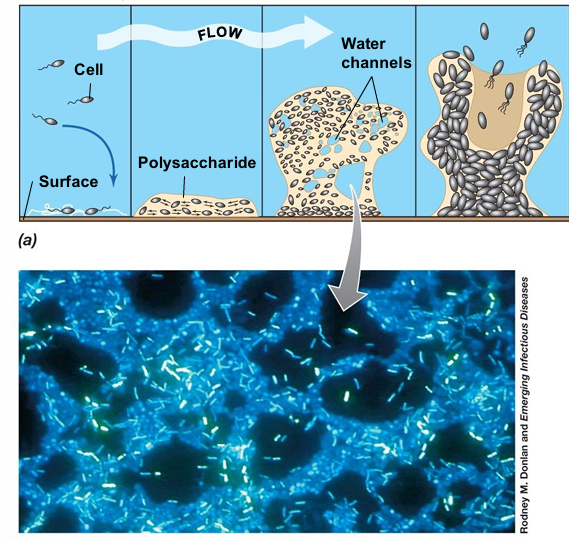
It helps microbes survive in diverse environments, including medical, industrial, and natural ecosystems.
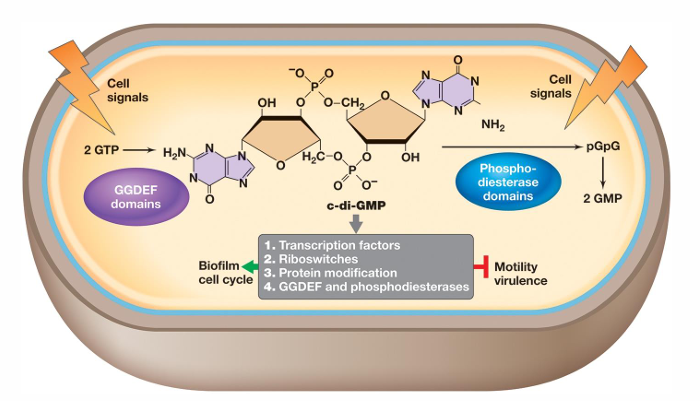
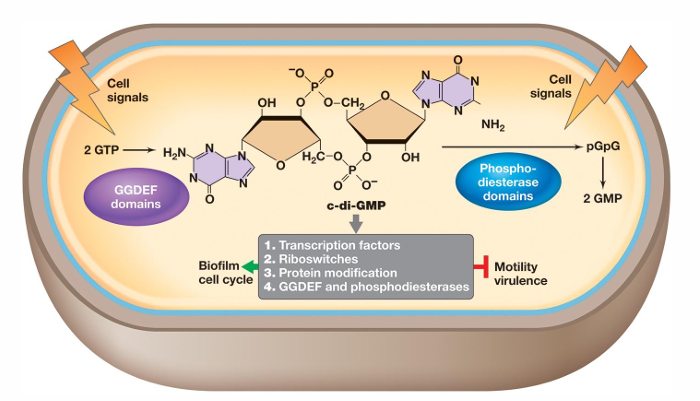
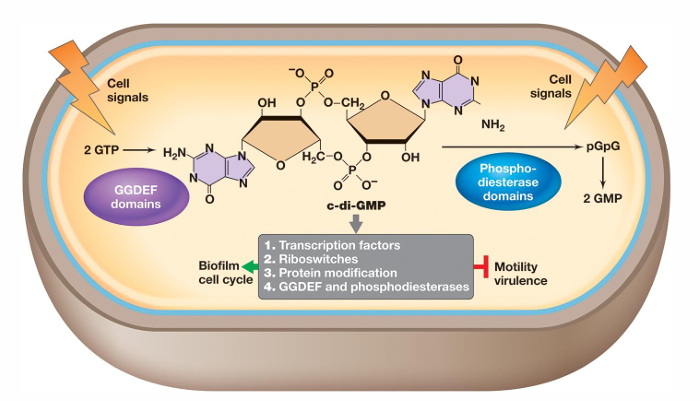
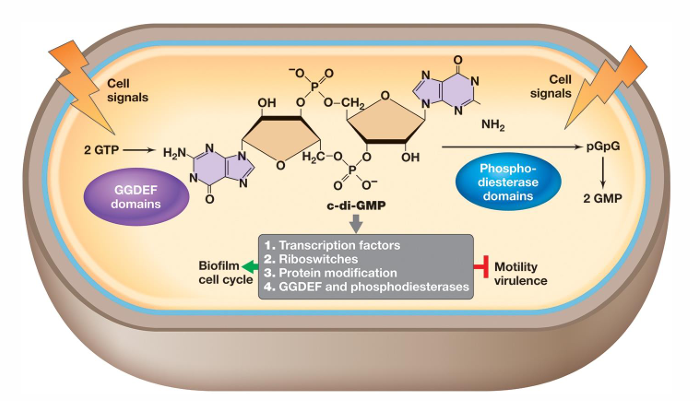
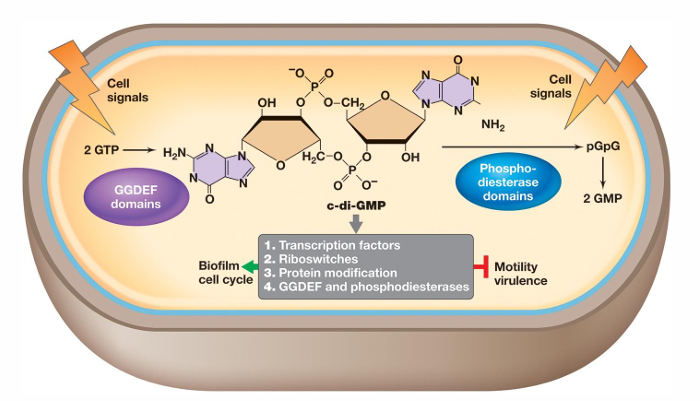
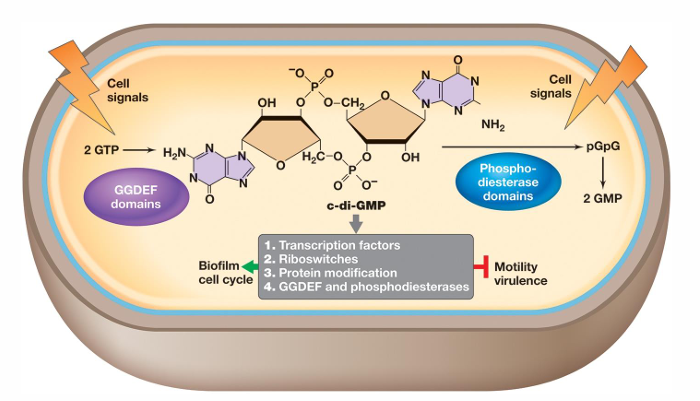
What is cyclic di-GMP?

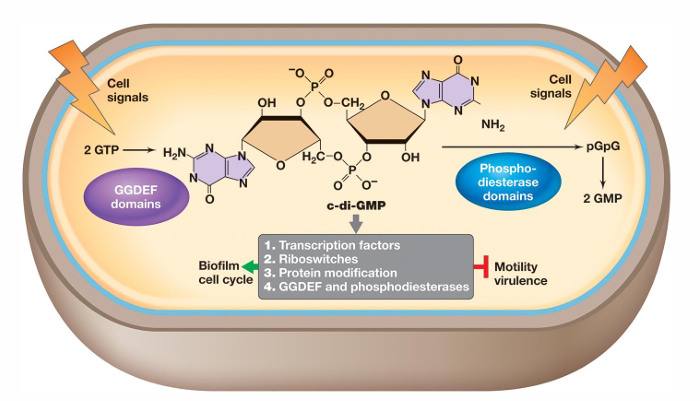
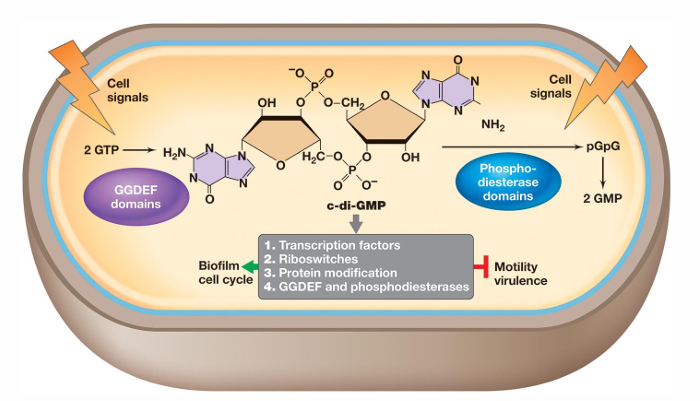
It can either promote or inhibit physiological events such as differentiation, development, and biofilm-relevant functions
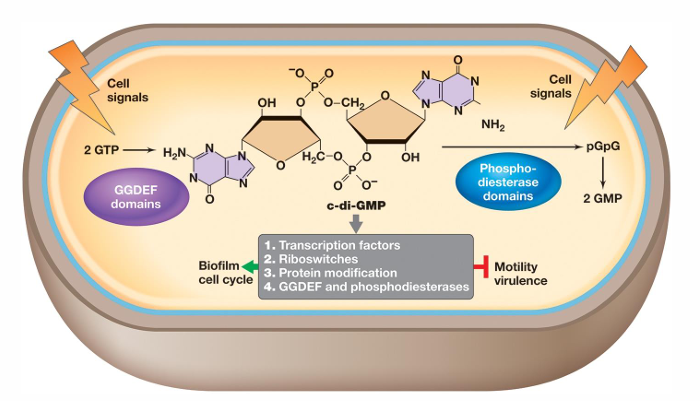
It binds proteins that reduce flagellar motor activity, regulate attachment proteins, and mediate extracellular matrix polysaccharide biosynthesis
What is the primary reservoir of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Soil.
How do Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms increase pathogenicity?
They contain polysaccharides that block antibiotic penetration and enhance bacterial survival.
Which condition is worsened by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in the lungs?
Cystic fibrosis.
What role does quorum sensing play in biofilm formation?
It signals population growth and activates genes for extracellular polysaccharide and c-di-GMP synthesis.
How does elevated c-di-GMP affect Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
It initiates extracellular polysaccharide production and decreases flagellar function, promoting adhesion.
How does DNA contribute to biofilm formation?
DNA released by lysed cells is incorporated into the extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), strengthening biofilms.
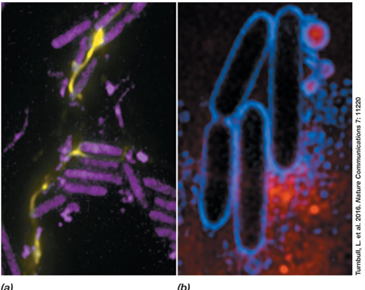
What causes 'explosive death' in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells?
Expression of lysis proteins by inactive prophage in response to stress.
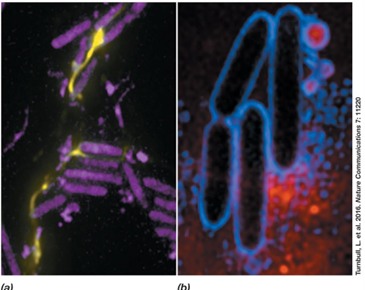
Why does antibiotic treatment sometimes enhance biofilm formation?
It triggers explosive death, releasing DNA that reinforces the biofilm structure.
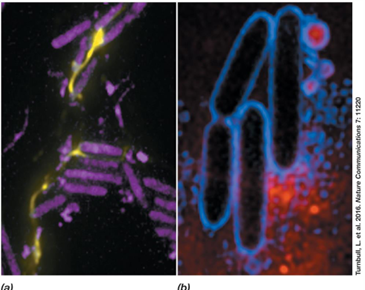
What is the function of acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
They signal population growth and activate biofilm-related genes.
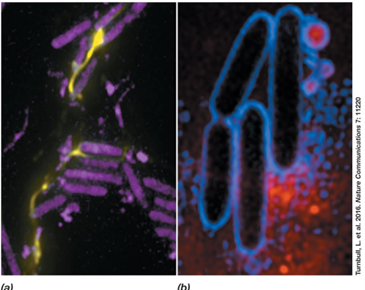
Why is Pseudomonas aeruginosa considered an opportunistic pathogen?
It primarily infects individuals with weakened immune systems.
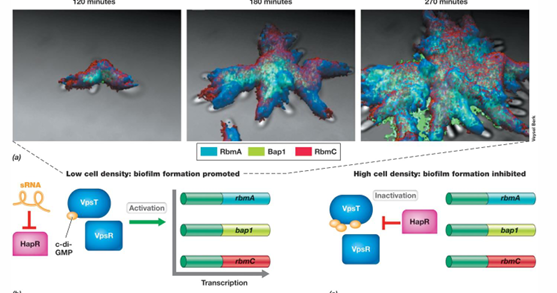
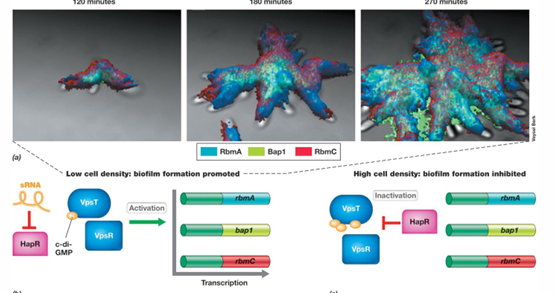
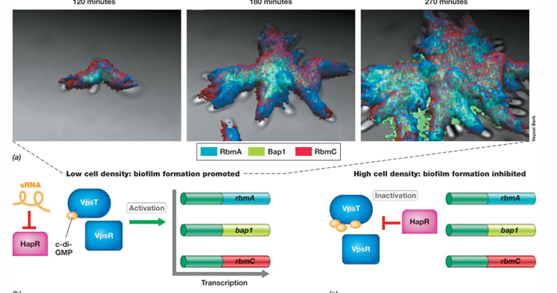
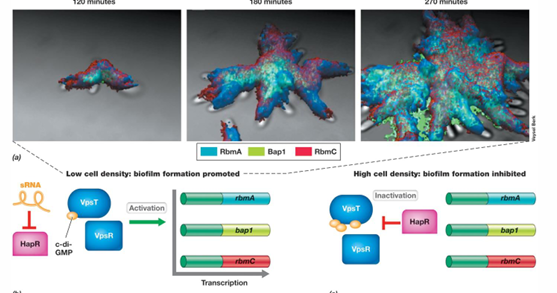
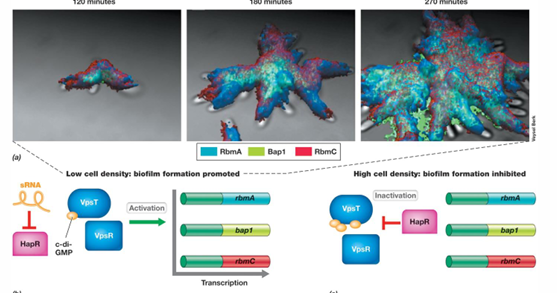
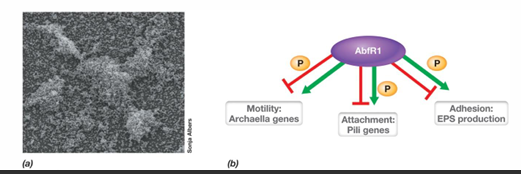
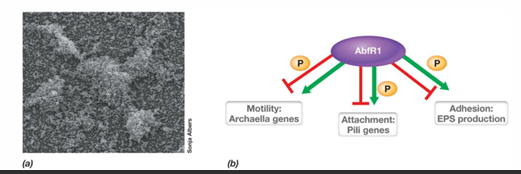
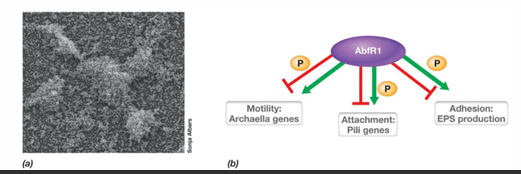
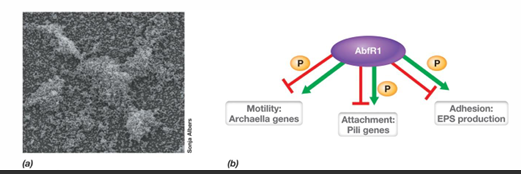
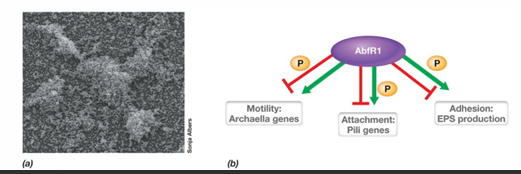
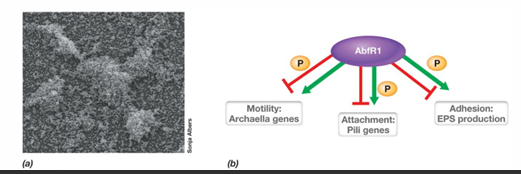
What are some examples of types of biofilms?
Biofilms can be found in natural environments like rivers, lakes, and oceans, as well as in man-made settings such as medical devices, dental implants, and wastewater treatment facilities.
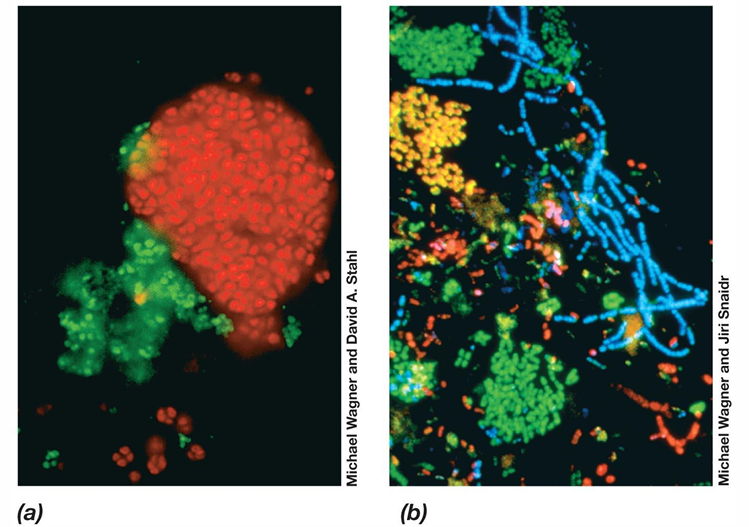
What is this image?
A FISH analysis of an activated sludge from waste water treatment. Each color represents different organisms.wastewater
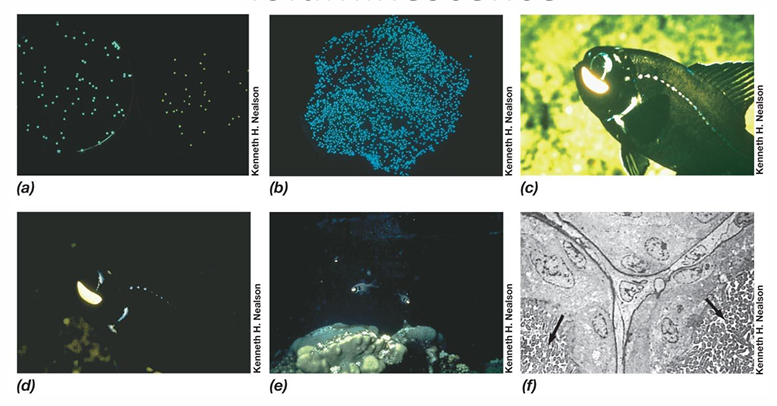
What is Bioluminescence?
natural phenomenon in which living organisms produce light through biochemical reactions, often used for communication, camouflage, or attracting prey.
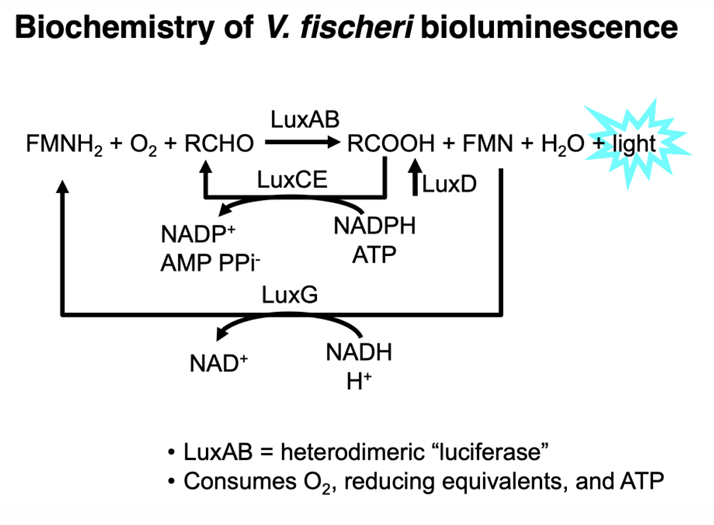
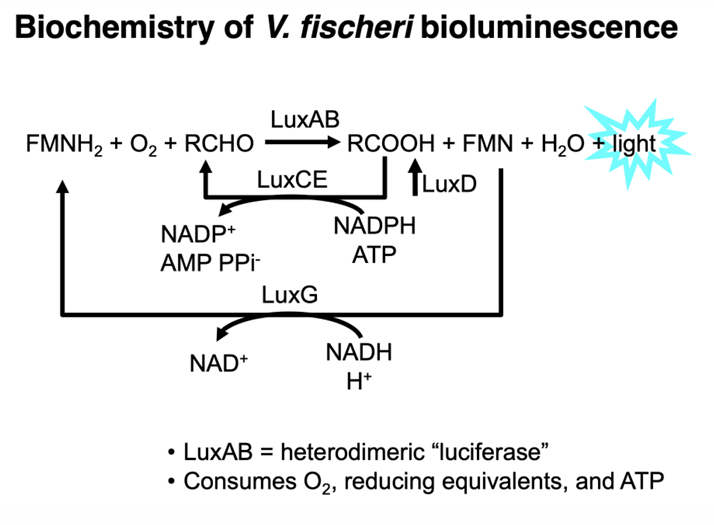
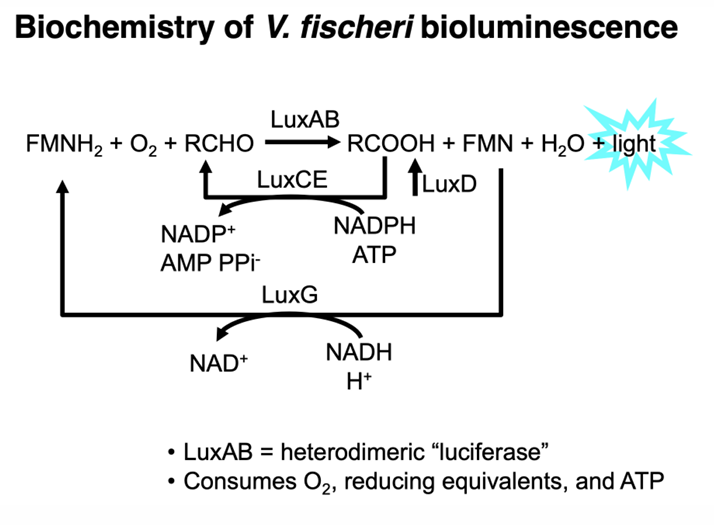
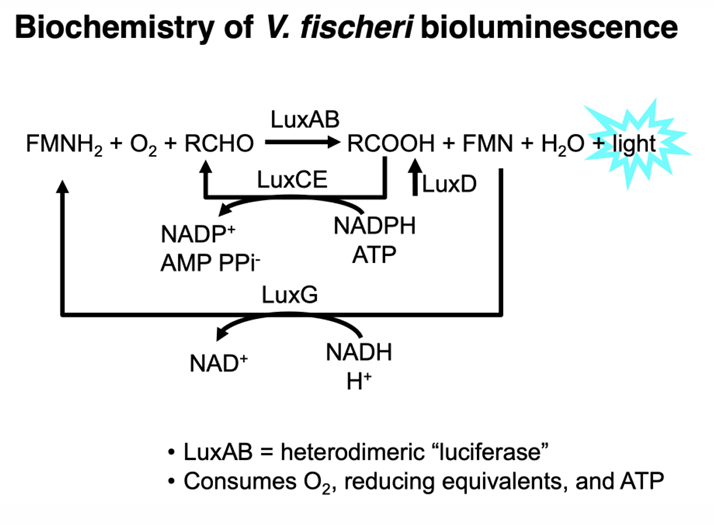
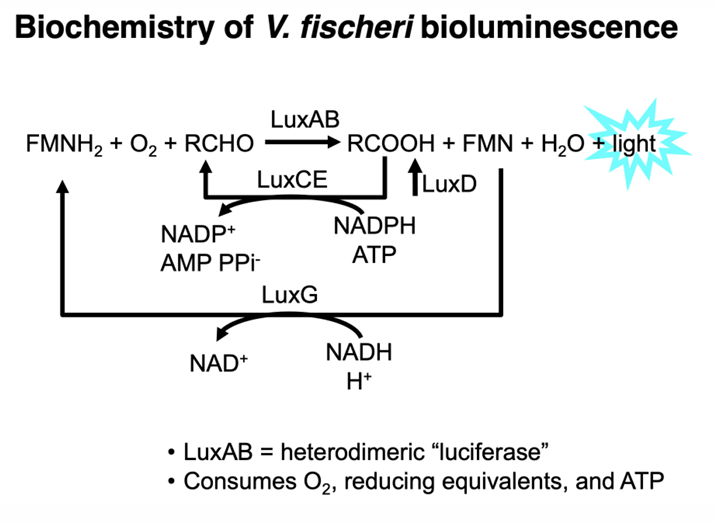
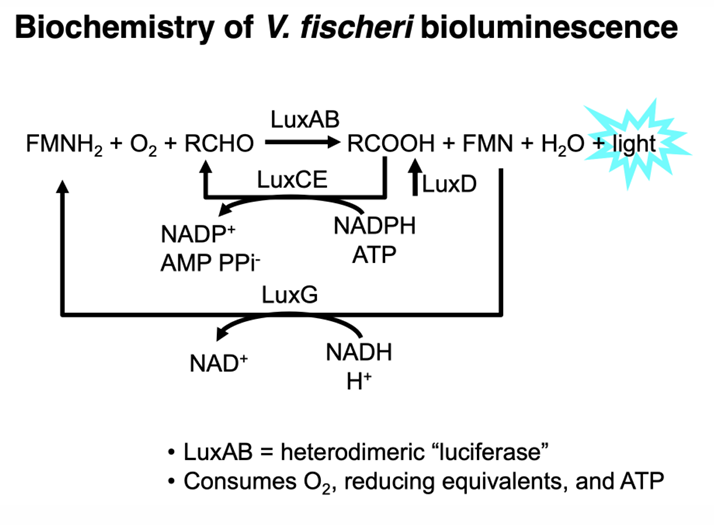
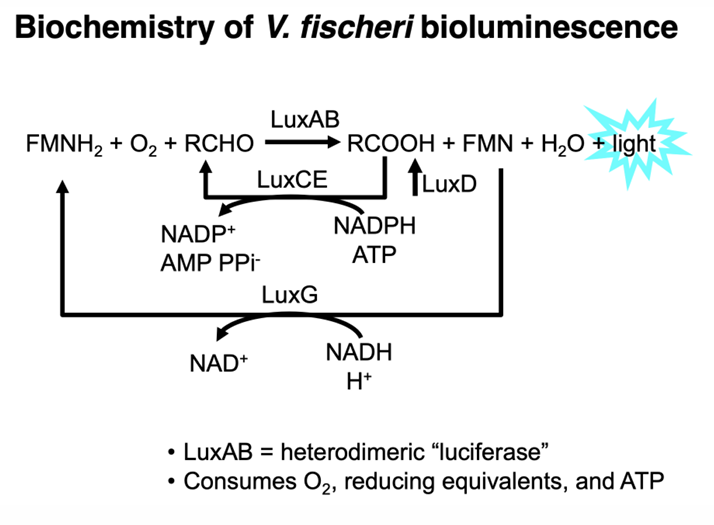
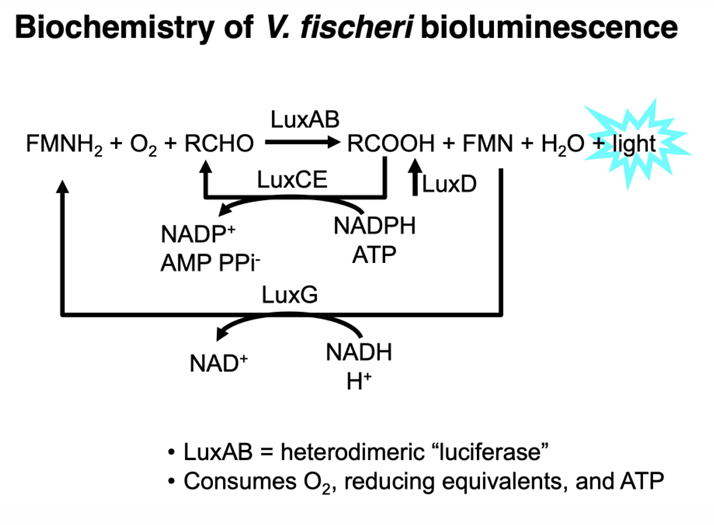
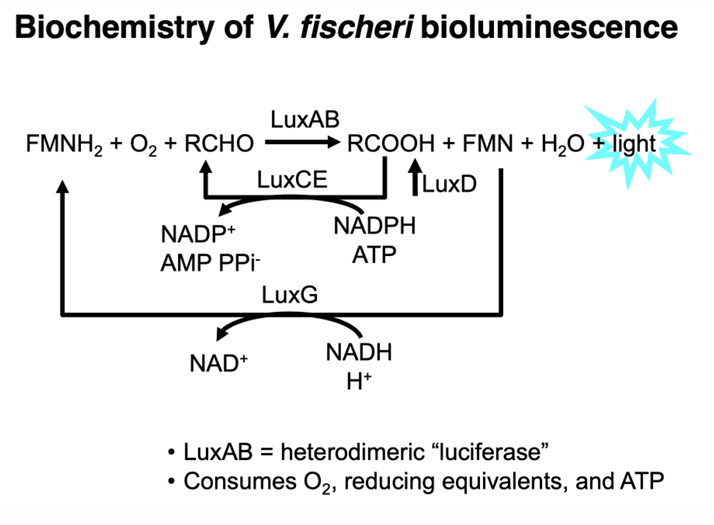
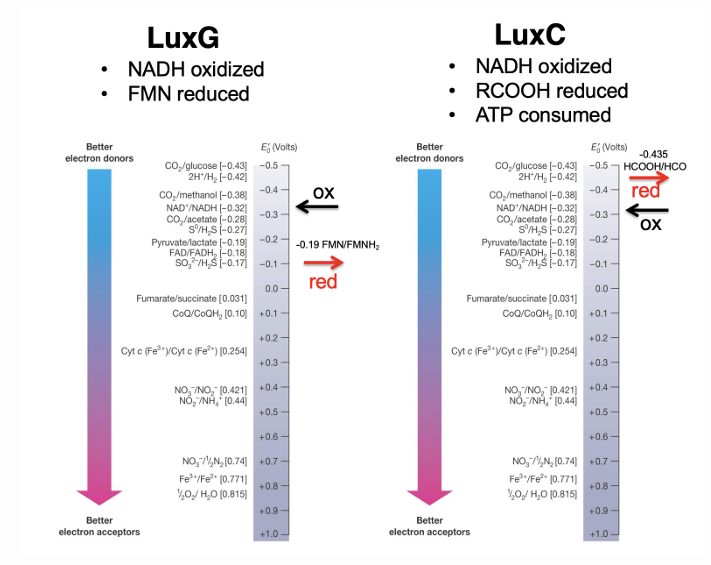
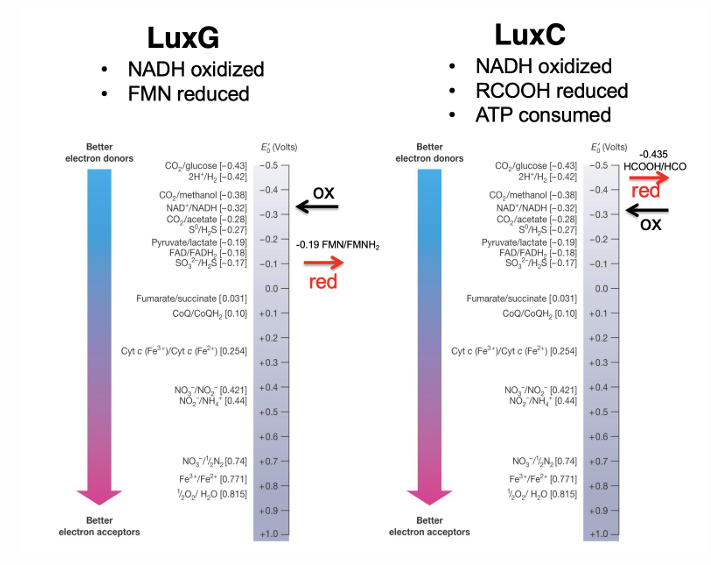
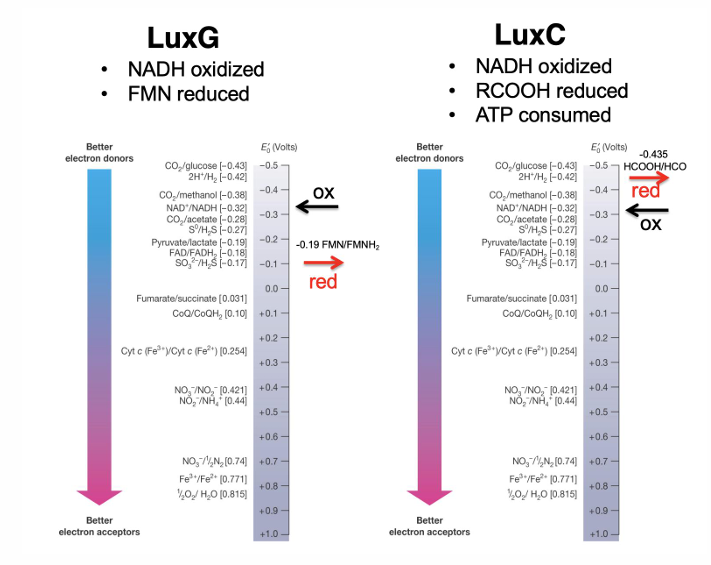
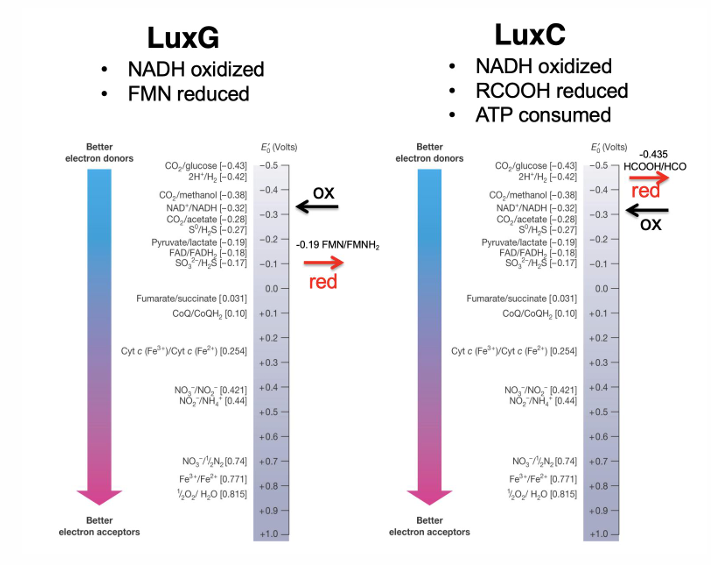
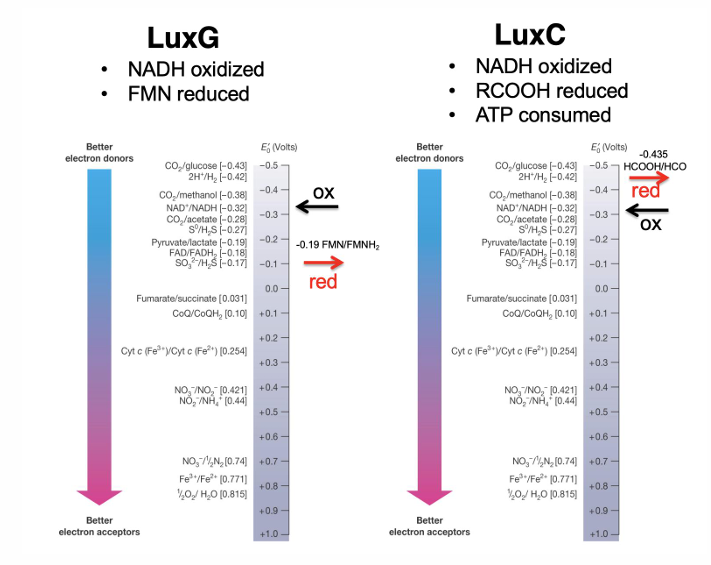
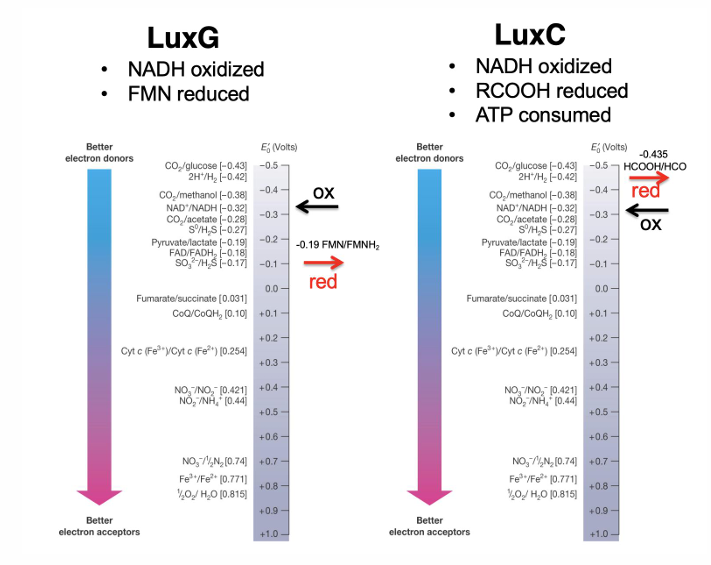
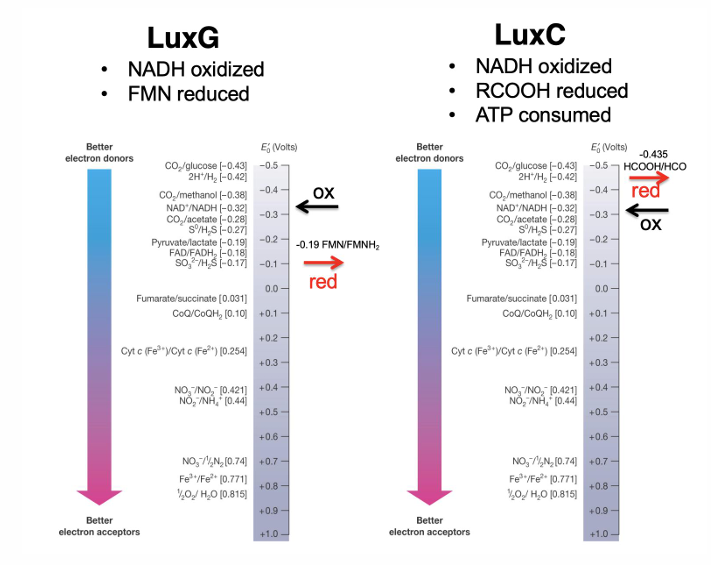
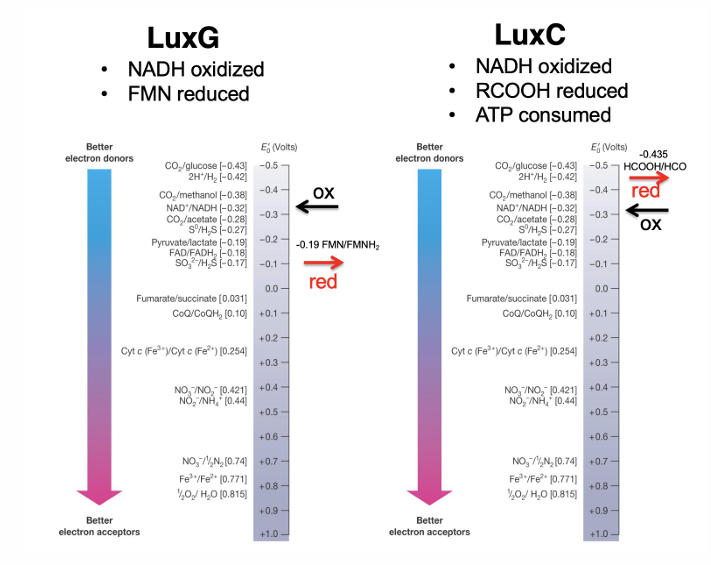
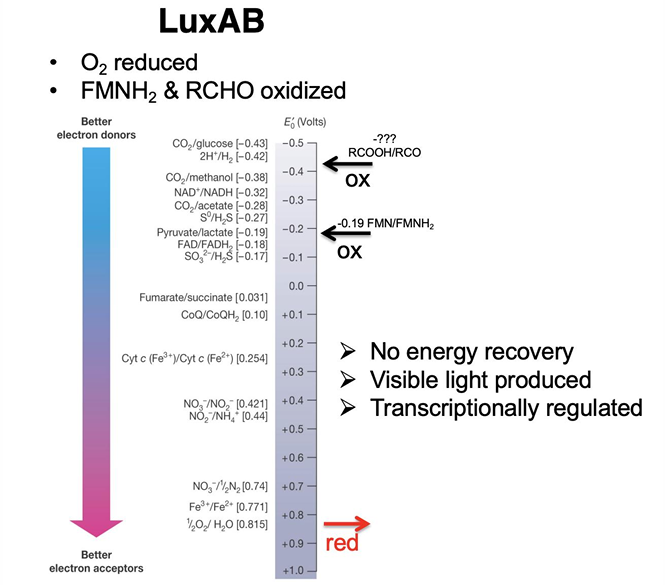
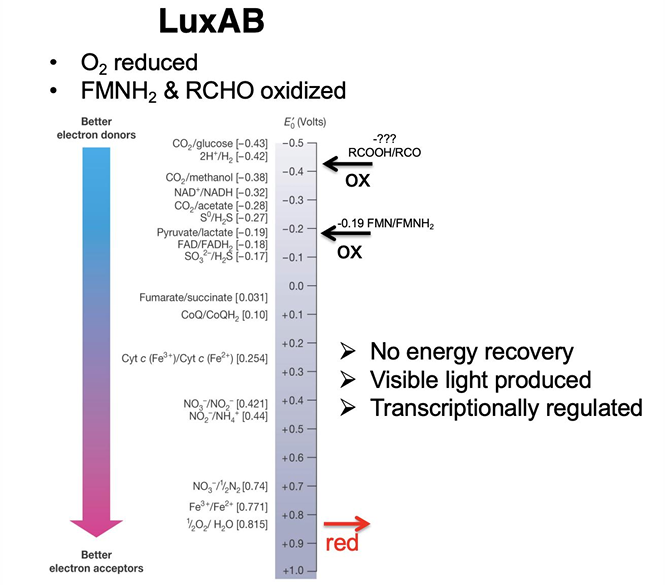
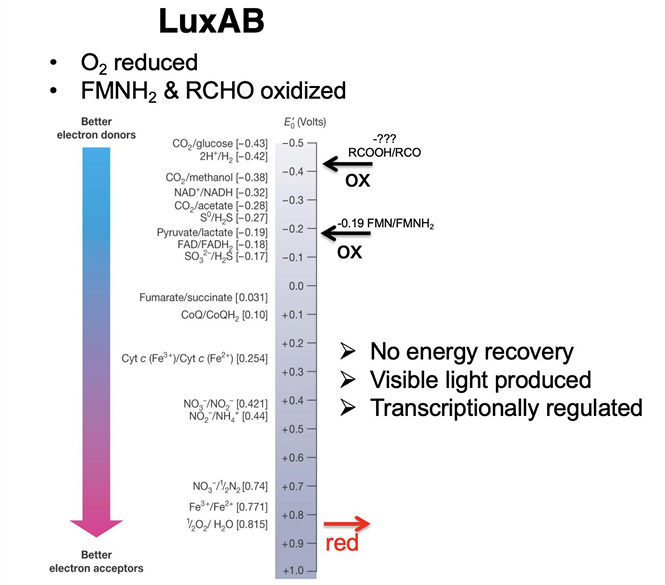
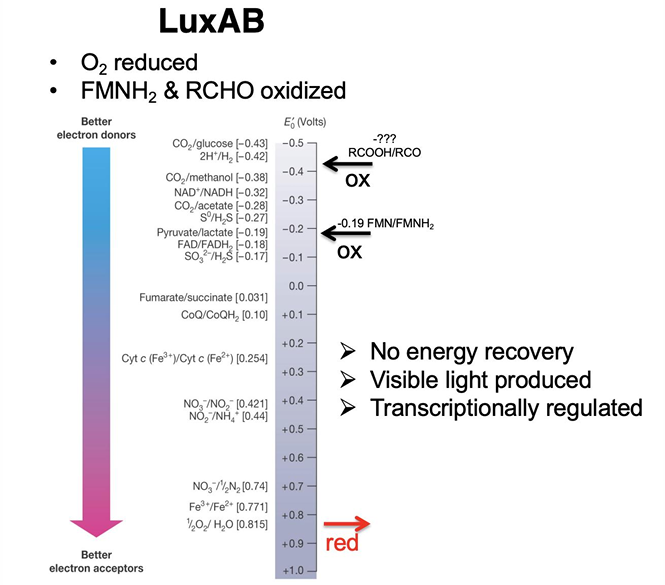
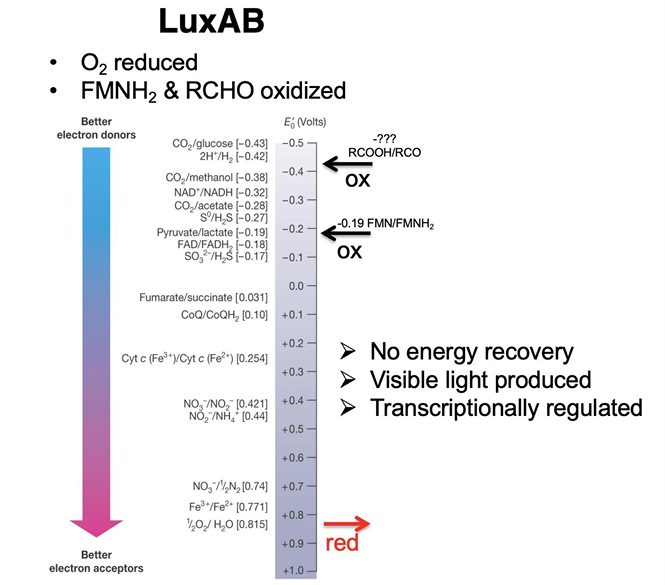
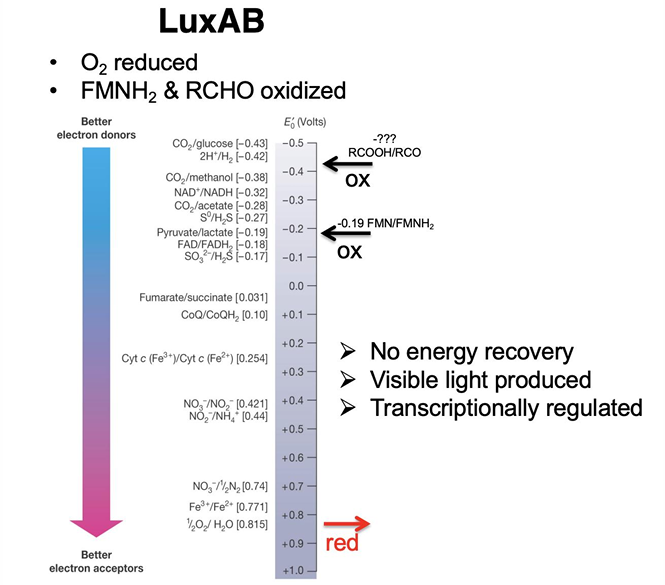
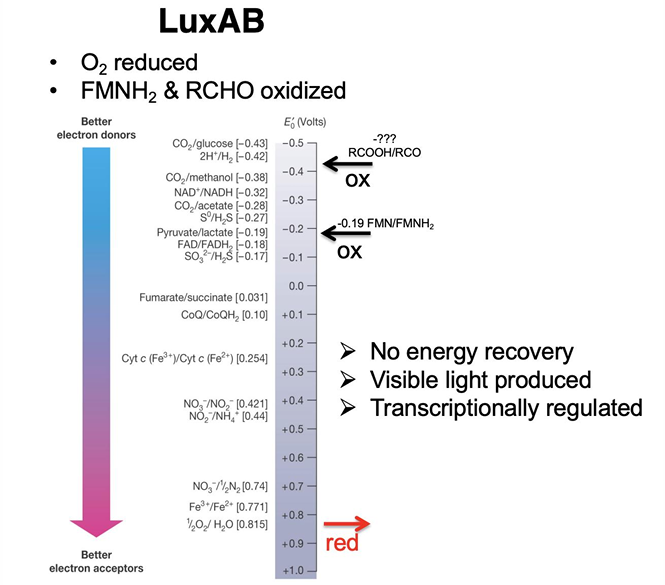
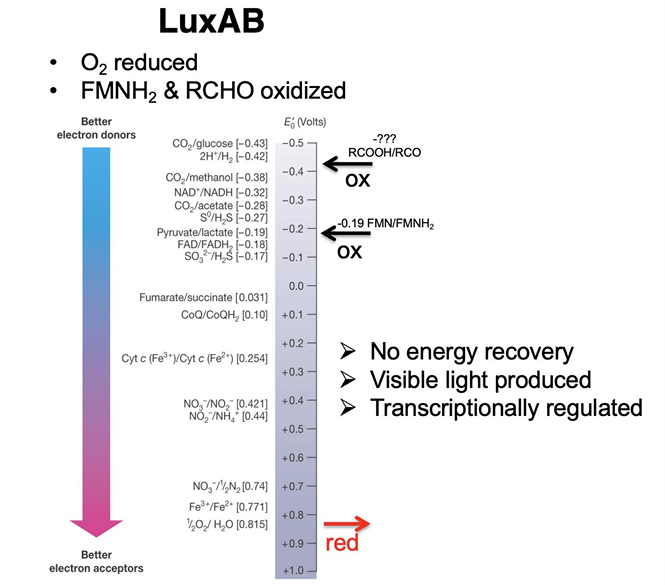
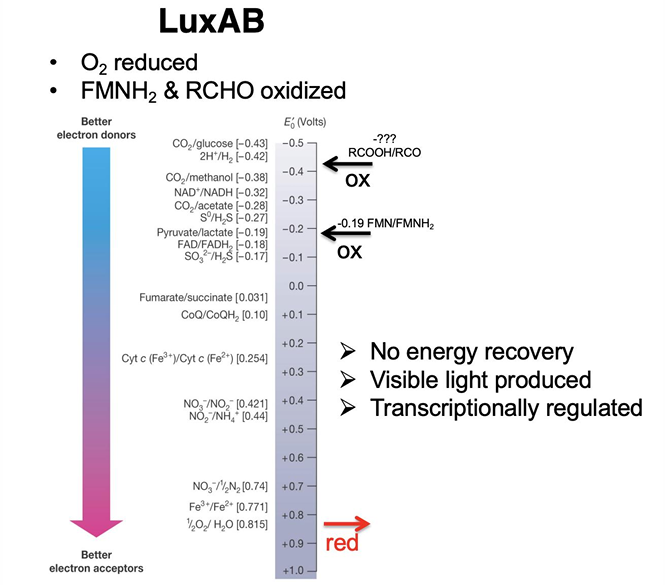
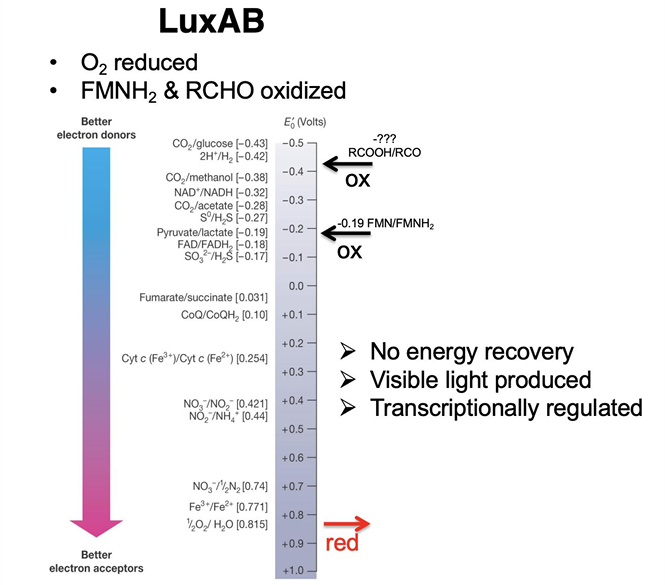
Are biofilms and bioluminescence based on density-dependent behavior?
yes