Chapter 6: Dermis, Lines of Cleavage and Strech Marks, Subcutaneous Layer
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms

What is the dermis?
Deep to epidermis
composed of CT proper
other structures present: blood vessels, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles, nail roots, sensory nerve endings, arrector pili, motile dendritic cells
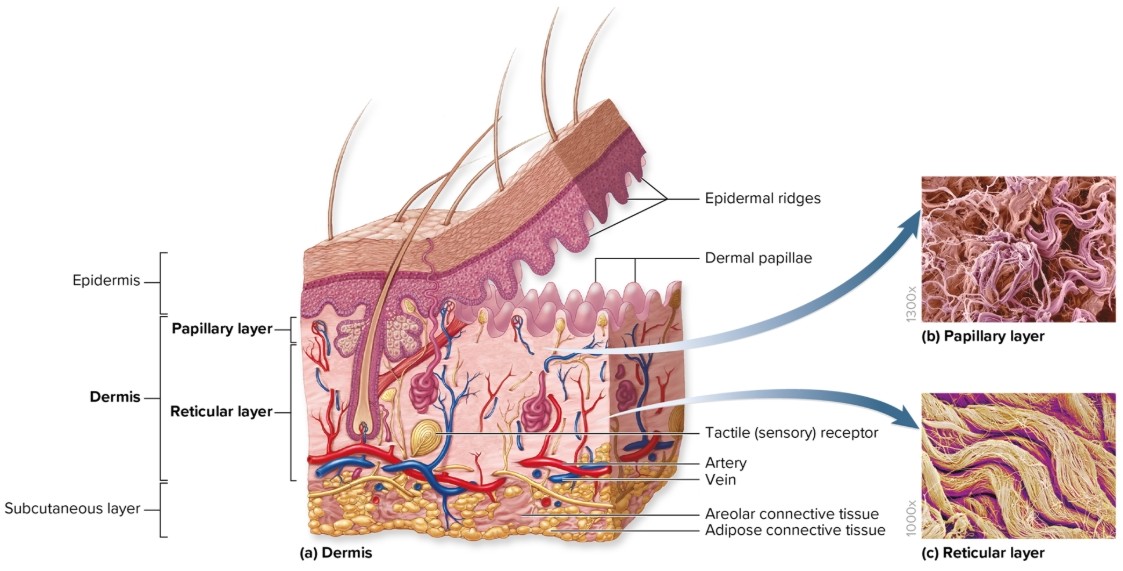
What is the papillary layer of the dermis?
superficial region of dermis (named for projections of dermis)
deep to epidermis
areolar connective tissue
dermal papillae
interlock with epidermal ridges to increase area of contact between layers
What is the reticular layer of the dermis?
deeper
major portion of dermis
dense irregular connective tissue

What are lines of cleavage?
collagen and elastic fibers oriented in parallel bundles at specific locations
Bundles function to resist stress during routine movement
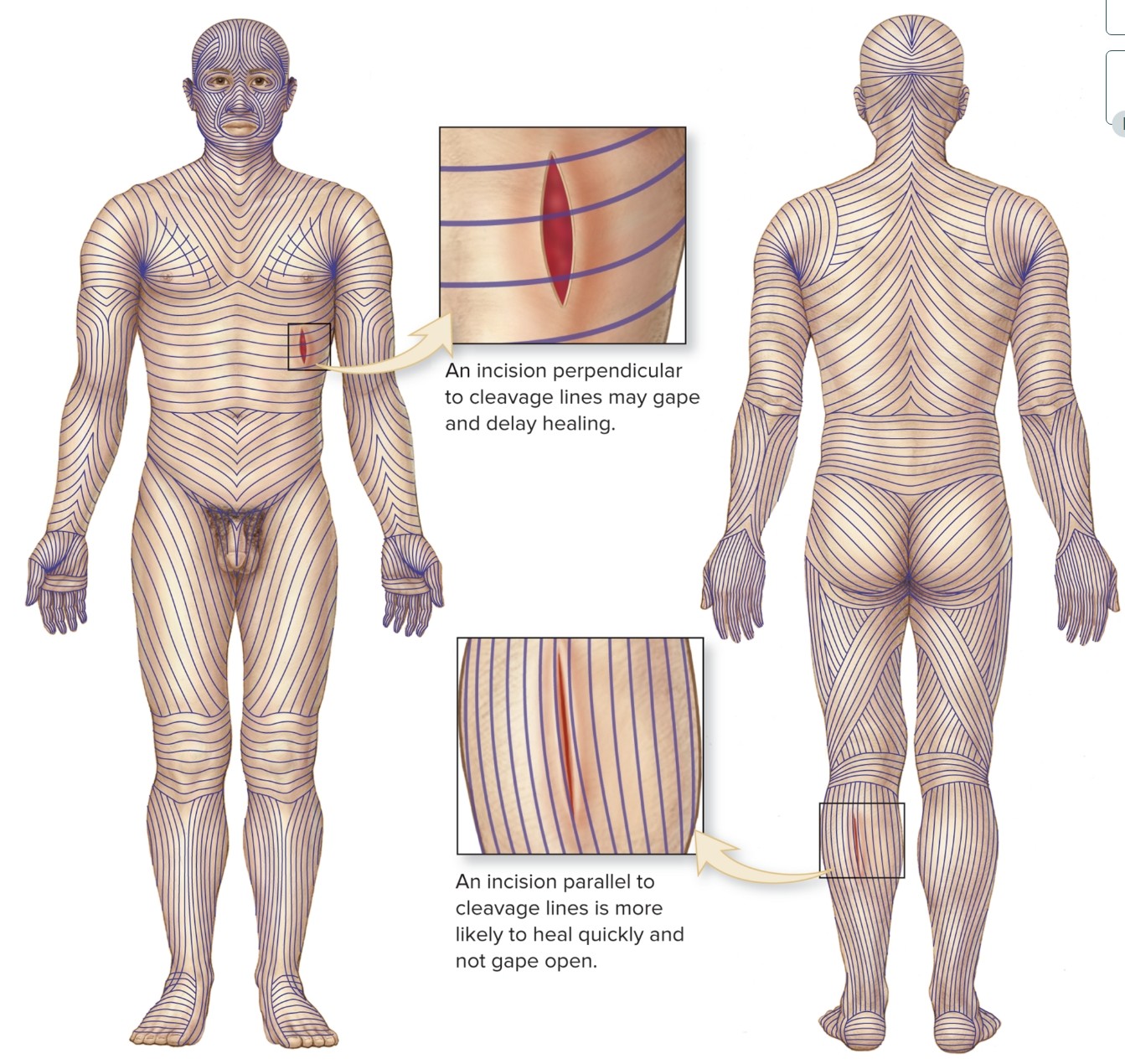
What is the orientation indicated by lines of cleavage?
incisions parallel to cleavage lines more likely to heal quickly
incisions perpendicular to cleavage lines are more likely to open due to cut elastic fibers
What causes stretch marks?
skin is stretched beyond its capabilities, results in striae
some collagen fibers torn
What is the subcutaneous layer?
hypodermis, superficial fascia
Not part of integument, areolar and adipose CT
F: protection, energy storage, and insulation, common drug injection site, extensive vascular network promotes rapid absorption, thickness/distribution influenced by sex hormones