Pathophysiology Exam 3: Inflammation & Healing Study Set
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
**Which two defenses are nonspecific defenses?** **"On Exam"**)
First line and second line of defense
- They are not designed for anything new in nature; they have not been exposed to. Ex: COVID-19 (they have no memory of COVID-19, they are not equipped to fight this off because they know nothing about this)
Example: If you go to a country where there is a new disease, and your body has never been exposed to it. These two defense systems cannot fight off something new because they do not recognize it. They only do generalized protection.
*Innate immunity (First line of defense)*
The immunity you are BORN with... nonspecific defense
Innate protects us from the outside world. They are a physical barrier
**Everything outside of you before it enters your body must go through the first line of defense. The skin and the mucus in your nares and mouth, chemicals in the blood, and immune system are all a part of the first line of defense.
It protects whatever is outside of your body from entering
Refers to nonspecific defense mechanisms that come into play immediately or within hours of an antigen's appearance in the body
*Once a pathogen enters the body, what line of defense does this trigger?*
Second line of defense.
Once it crosses in, it will no longer be the first line of defense
*Once something enters your body that your body does not recognize, it will trigger*
Inflammation
Inflammation is what line of defense?
second line of defense
Inflammation is how your body?
Heals
If the second line defense fails and this is a new disease your body has been exposed to, what defense do you need to protect you?
Third line of defense
**What is the only specific defense?**
Third line of defense
What is the third line of defense?
Adaptive (acquired) (specific) immunity
It has the ability to create antibodies (antigens) using B-cells. They also have T-cells that will attack that new virus that came in.
The third line of defense job is to understand this new pathogen in your body, create memory for it, and suppress it all at the same time.
Why do infants have a weak immune system?
They do not have a strong third line of defense, and they do not have the ability to fight it. The T-cells and B-cells have not been well developed.
Why do the elderly have a weak immune system?
The B-cells and the thymus glands get smaller as we age so it is not as effective. Nature sets us up to DIE. The immune system weakens as you get older.
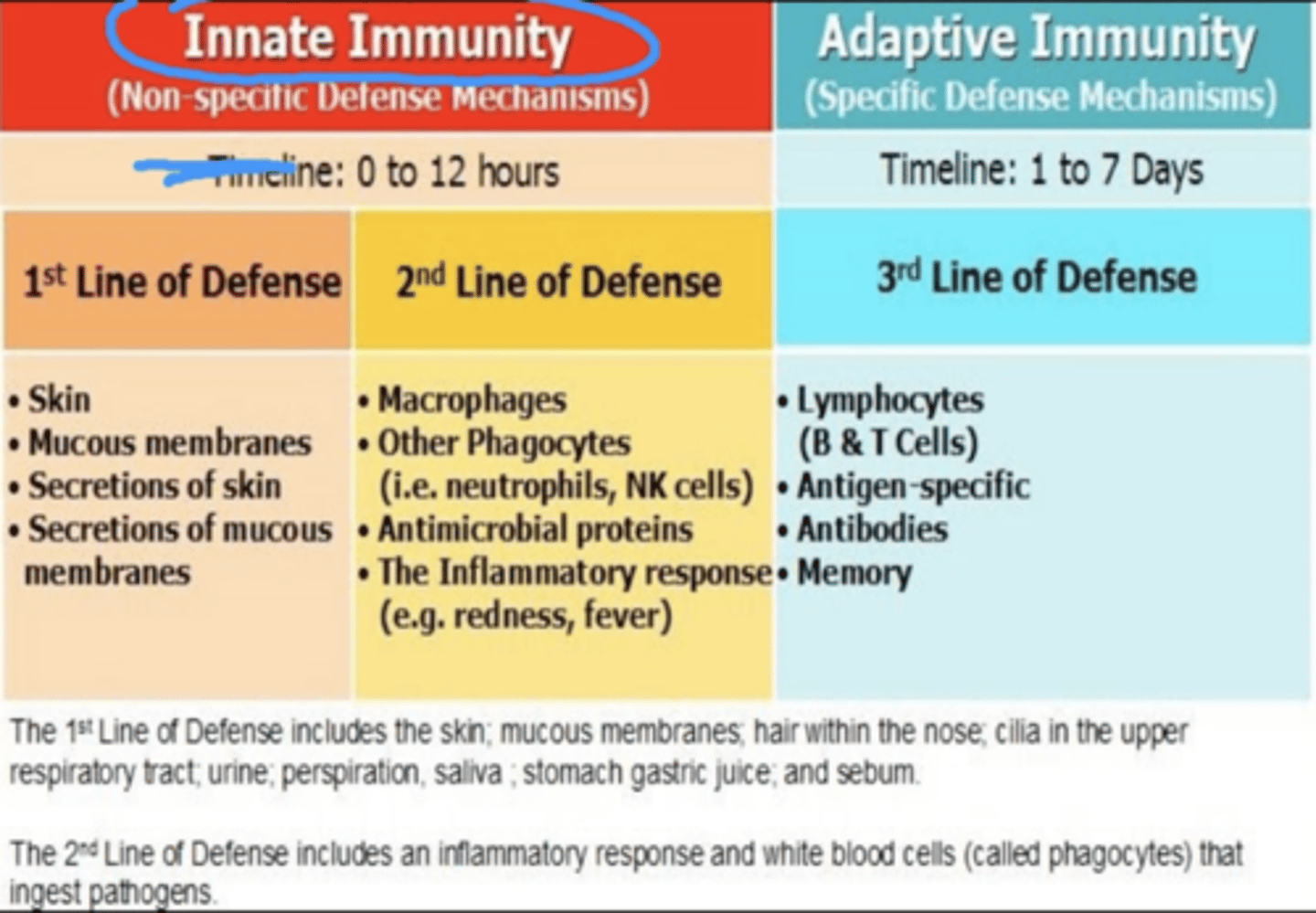
What does the innate immune system include? (**"Make sure to go over"**)
First line - Physical barriers (skin, mucous membranes, chemicals)... protects from outside
Second line - Cell-derived defenses (phagocytes, complement proteins, interferons, inflammation, fever)... components of inflammation - when something ENTERS the body
*What do the non-specific defenses in our body make up? What do they protect from?*
They make up the innate immune system. They are not SPECIFICALLY direct against any one pathogen; they provide a guard against all infections (generalized)
What is the most important nonspecific defense/ physical barrier of the human body?
Skin
What does the first line of defense also include that you may not think would be first line of defense?
Linings of the gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and respiratory tracts (mucus and cilia trap microorganisms are filters)
Expelled through coughing/sneezing, urination, vomiting/defecation
Secrete saliva, tears ( when something gets in your eye, you get teary-eyed to protect us) , earwax, sweat, and mucus

*On Exam*
If a patient coughs, if they have mucus buildup, urination, vomiting
They will get rid of it. This is all a part of the first line of defense
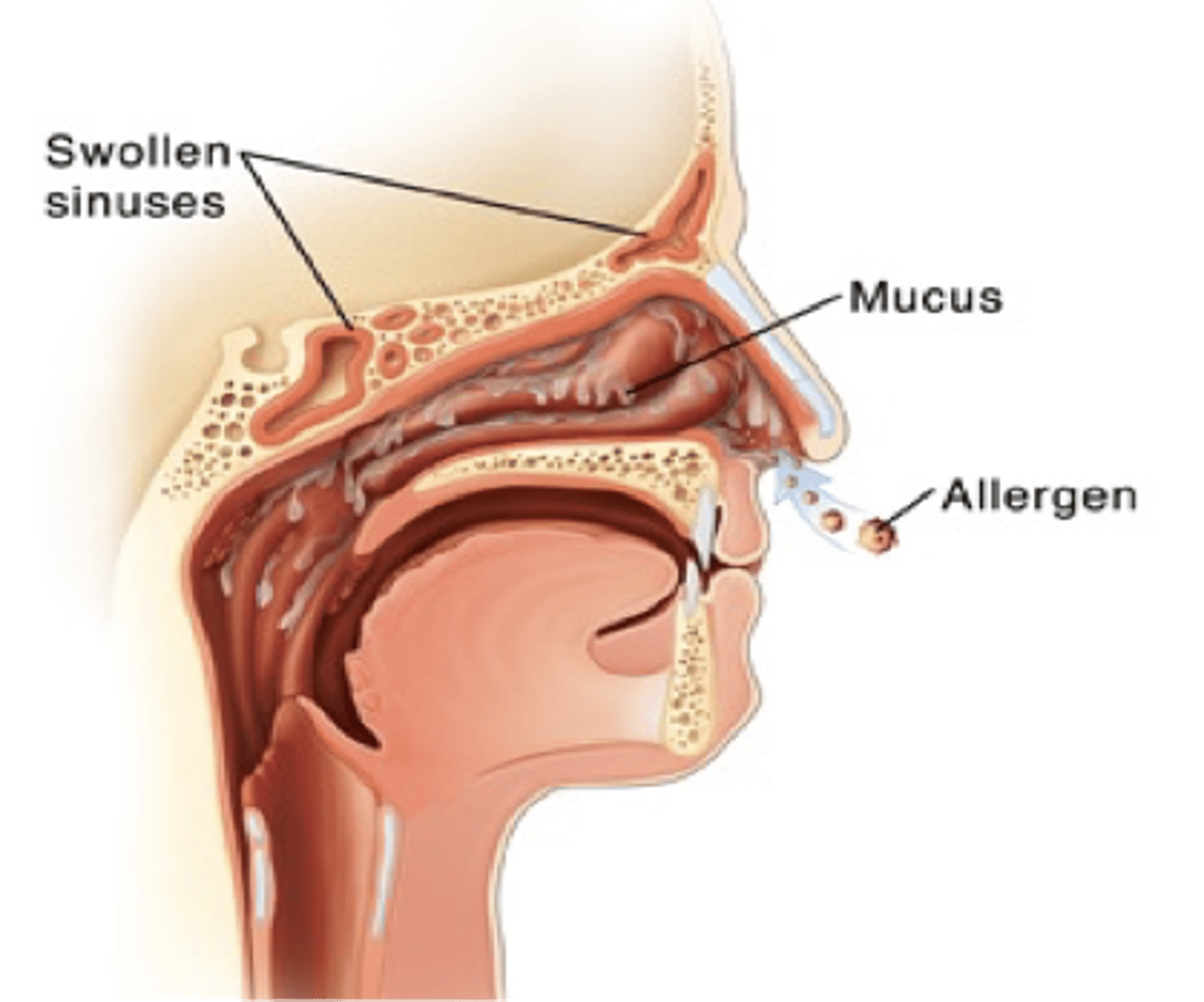
Mucus and Cilia
Once an allergen enters, the allergen will trigger us to have extra mucus
First Line of Defense (2 of 2)
•Lysozymes attack bacteria
•Lysozyme is a naturally occurring enzyme found in bodily secretions such as tears, saliva, and milk. It functions as an antimicrobial agent.
•Antimicrobial peptides kill bacteria, fungi, viruses
•Defensins and collectins
•Defensins are members of a large family of cationic antimicrobial peptides that form an essential element of innate immunity.
Collectins can interact with receptors on host cells. Binding of collectins to microorganisms may facilitate microbial clearance
*Interferons* (Important)
Group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells (a living cell in which a virus multiplies) in response to the presence of several viruses
Once something foreign comes in, it will signal all of the proteins that are a part of the immune system to be activated. They are letting it be known something is WRONG
**The first line of Defense (Select All that Apply)**
a. Nonspecific
b. Mechanical barrier
c. Unbroken skin and mucous membranes
d. Secretions such as tear and gastric juices
**The second line of defense (Select All that Apply)**
a. Nonspecific
b. Phagocytosis
c. Inflammation
**What is phagocytosis?**
The process by which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles.
WBC, macrophages, neutrophils that engulf the actually pathogens
**Third line of defense** (Ding, DIng, DIng)
Specific defense
Production of specific antibodies or cell-mediated immunity
**What makes up the third line of defense?**
lymphocytes
- T-lymphocytes
- B-lymphocytes
Lymphocytes (**must know**)
A type of white blood cell found in the blood or lymph nodes
**Made by bone marrow**
Example: If you have leukemia, nine times out of ten, you will die because that type of cancer suppresses the bone marrow. If the bone marrow is suppressed, you will be unable to produce T-cells and B-cells.
Reverse precautions for this patient. You will have to wear the mask because they have a weak immune system so we are a danger to them (3rd line defense suppressed, cancer in the bone marrow)
T-Lymphocytes (**Must know**)
Recognize antigens on pathogens and either attack them directly or coordinate the activity of other cells of the immune system
Cell mediated immunity... attack directly
DO NOT DEVELOP ANTIBODIES... role is to ATTACKWHat
On exam
Which lymphocyte attacks the cell directly? (cell-mediated)
T-lymphocytes/T-cells
On exam
Which lymphocyte creates antibodies?
B-lymphocytes/B-cells
When T-cells attack the cell
B-cells attach and download the information
B-lymphocytes (**Must know**)
Produce antibodies (having the disease)
Recognize antigens and produce special chemicals called antibodies
They tag antigens and formulate a "memory" for the body to know how to attack the antigen again in the future
If you are given a vaccine this means you have the
virus
On the Exam
The answer for fever is
systemic
3 lines of defense summary
On Exam
First Lines of Defense
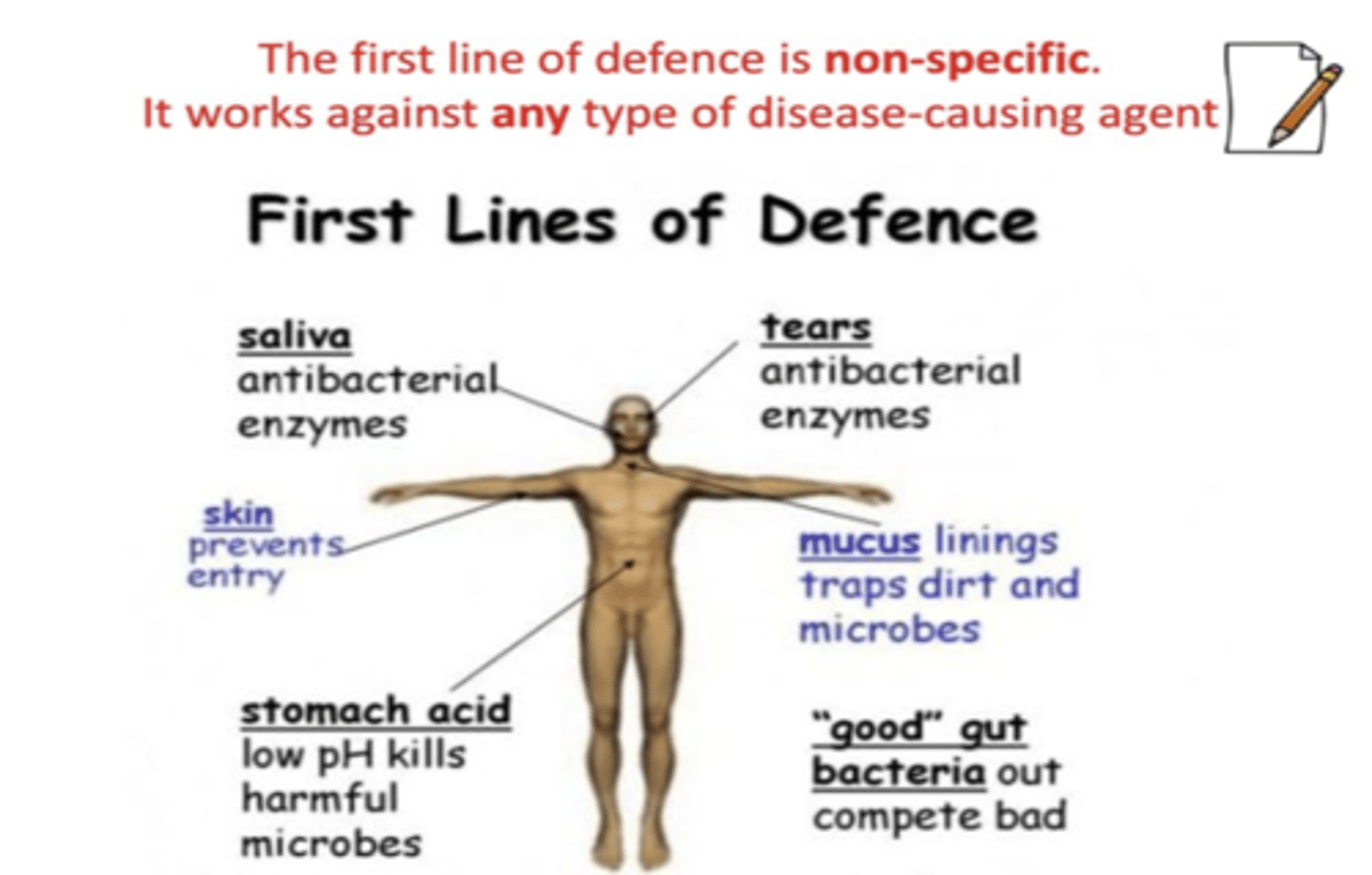
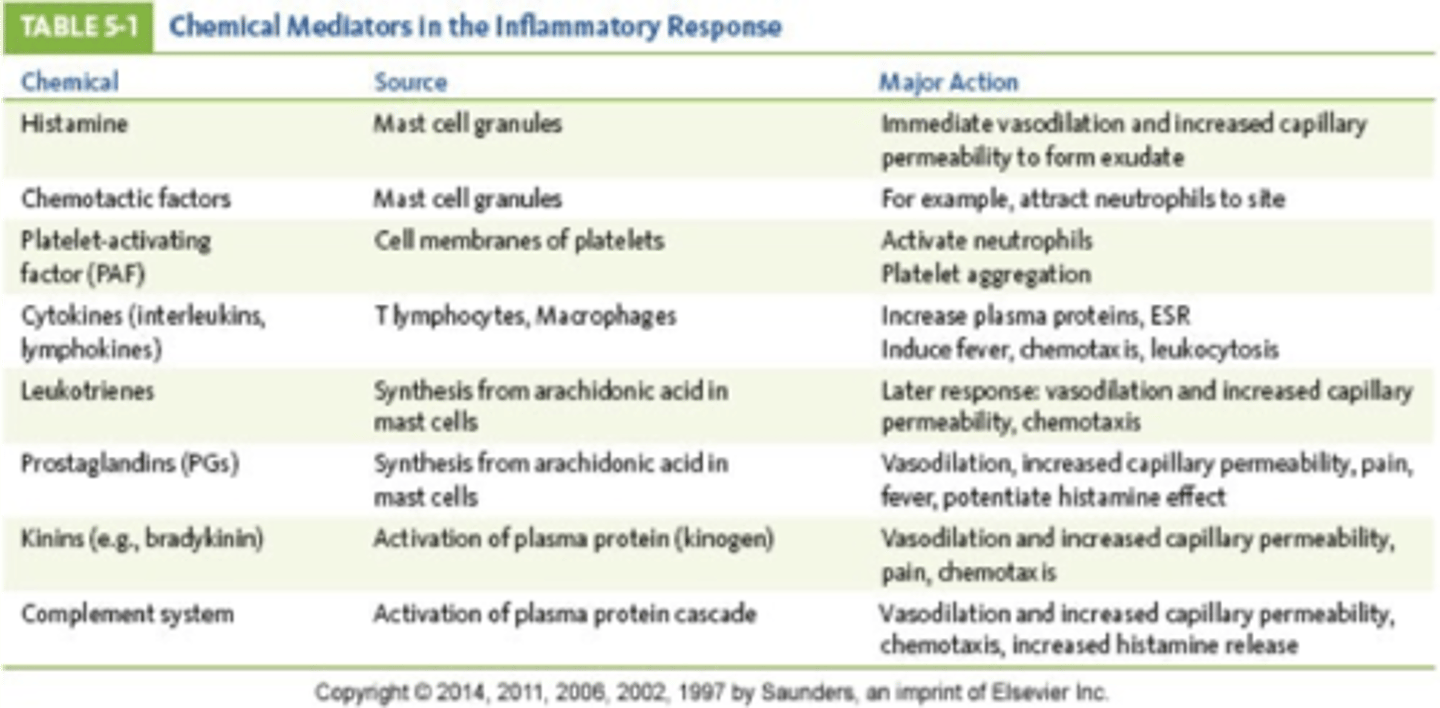
How do histamines affect blood vessels?
**Vasodilate**
Increased capillary permeability (edema)(want WBC to come out of blood vessels to go to the site of injury). It opens up so everything comes out so we can fight off the infection.
Ding Ding Ding
Histamine is part of the inflammatory response. If you took an anti-histamine it will stop the whole inflammatory response.
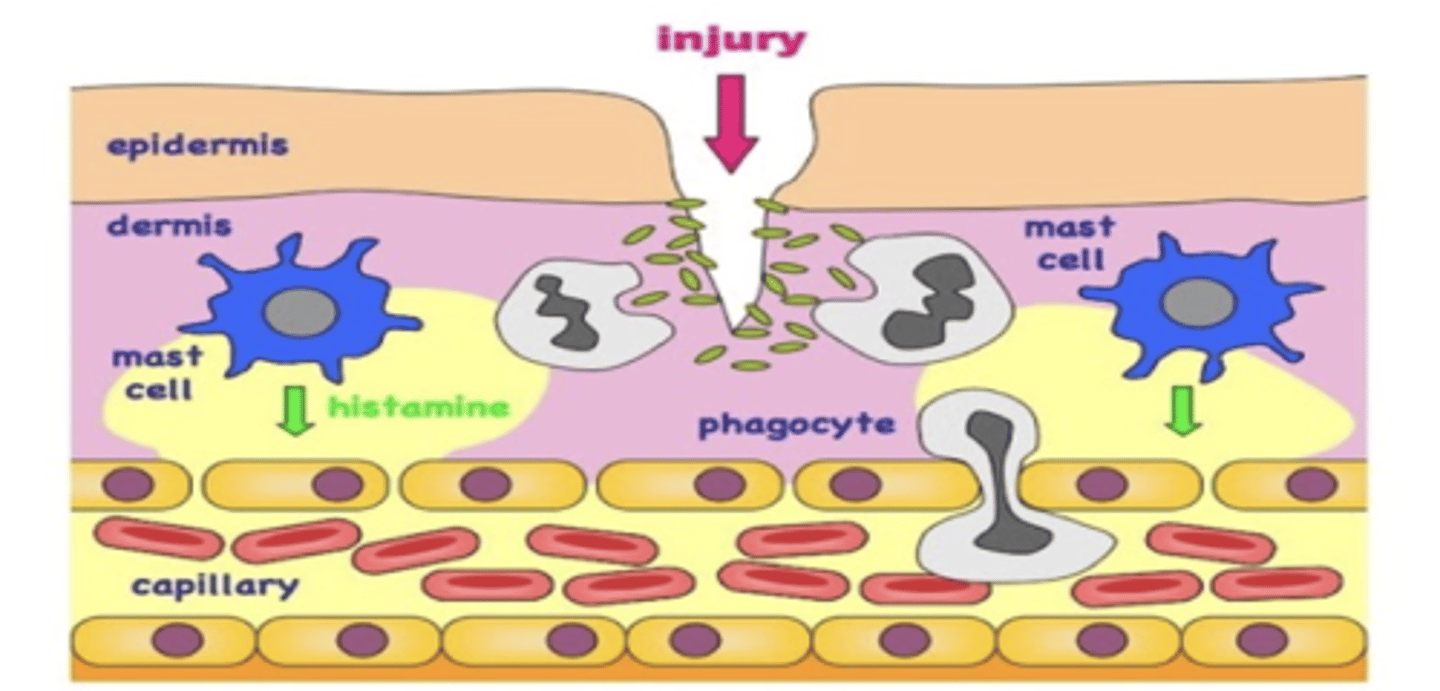
What is extravasation?
Is the leakage of a fluid from its container into the surrounding area, especially blood or blood cells from vessels. In the case of inflammation, it refers to the movement of white blood cells from the capillaries to the tissues surrounding them.
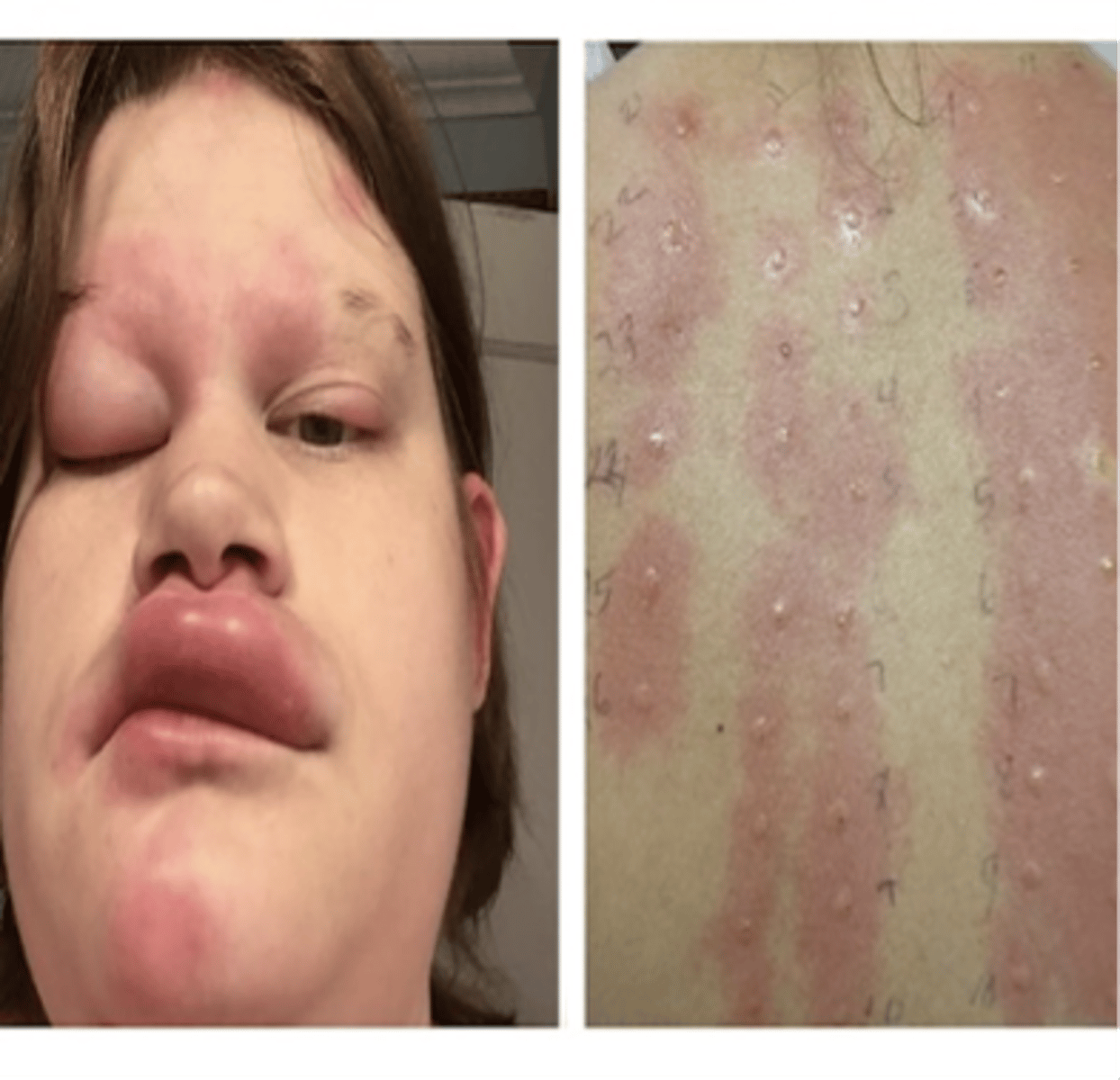
What are the five hallmark signs of inflammation - second line of defense? (**on exam**)(select all that apply)
1. Heat (capillary widening - increased blood flow)(in vasodilation the blood pressure drops)
2. Redness
3. Swelling (Increased permeability (muscle walls loosen) - fluid release into tissues)(Protein leaves which should not be going out because it pulls water with it)(Edema)
4. Tenderness (fluid build up is putting pressure on nervous system around site of injury)
5. Pain (tenderness and pressure)
What is inflammation?
Wide variety of physiologic and pathologic responses intended to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury (tissue injury), remove the damaged tissue, and generate new tissue
How the body responds to cell injury and how the body removes damage tissue
Inflammation can be healthy. It is only unhealthy if it is excessive.
Inflammation process sets the stage for...
The events that will eventually heal the damaged tissue.
Thus, inflammation is intimately interwoven with the repair processes that replace damaged tissue or fill in the residual defects with fibrous scar tissue
Antivirals only work on
Viruses
Antibiotics only work on
Bacterial
Anything ending with -itis... (**on exam**)
Means that that part of the body is going through the inflammatory process
EX: appendicitis, pericarditis, neuritis, pancreatitis
Causes of Inflammation
•Direct physical damage
•Examples: cut, sprain
•Caustic chemicals
•Examples: acid, drain cleaner
•Ischemia (reduced blood flow) or infarction
•Allergic reactions
•Extremes of heat or cold
•Foreign bodies
•Examples: splinter, glass
•Infection
Steps of inflammation (**on exam**)
1. Transient Vasoconstriction
2a. Release of bradykinin from injured cells
2b. Activation of pain receptors by bradykinin
3. Mast cells and basophils release histamine
4. Capillary dilation
5. Increased blood flow
6. Capillary permeability
7a. Neutrophil and monocytes come to injury site
7b. Neutrophils
8. Neutrophils phagocytize bacteria
9. Macrophages leave bloodstream for phagocytosis of microbes
First step of inflammation (**on exam**)
Transient vasoconstriction
Body vasoconstricts because it doesn't know if the body is actively bleeding or not. The body automatically does this in case you are bleeding to stop it.
Step 2a of inflammation (**on exam**)
Release of bradykinin from injured cells
Bradykinin is a vasodilator and a mild diuretic (lowers BP)
(**Ding, DIng, DIng, DIng**)
It increases capillary permeability and is also involved in the mechanism of pain.
On Exam
During inflammation which WBC will arrive first
Neutrophils
Macrophages follow neutrophils is to make sure it gets it out of the body
On Exam
The steps of inflammation answer choice *This was stated during lecture, she will review the answer during tutoring*
vasoconstriction-->vasodilation-->hyperemia
What is vascular permeability?
the capacity of a blood vessel wall to allow for the flow of small molecules (drugs, nutrients, water, ions) or even whole cells (lymphocytes on their way to the site of inflammation) in and out of the vessel.
Step 2b of inflammation
Activation of pain receptors of bradykinin
Bradykinin triggers pain receptors because the body wants you to pay attention
Step 3 of inflammation (**on exam**)
Mast cells and basophils release histamine (**must know**)
Histamine (*on exam*)
Produces the dilation of blood vessels, which increases permeability and lowers BP within an immune response
Central role as a mediatory of itching
Also causes bronchial constriction while vasodilating... can be very dangerous if uncontrolled
Step 4 of Inflammation
Capillary dilation (bradykinin and histamine)
Step 5 of inflammation (*on exam*)
Increased blood flow (hyperemia)
Step 6 of Inflammation
Capillary permeability
- Fluid leaks out and we get edema
Neutrophil (step 7a of inflammation) (**on exam**)
The first cells to arrive on the scene when we experience a bacterial infection
They are a type of WBC.
Is a phagocyte
Is the primary phagocyte that arrives early at the site of inflammation, usually within 90 min of injury
On Exam
If you are working in the ER and the patient has a reaction and you suspect they have an infection. What lab values are the most important to look at?
WBC, specifically neutrophils. The body produces more neutrophils to fight off the infection
What are the main types of phagocytes
a. Monocytes
b. macrophages
c. neutrophils,
d. tissue dendritic cells, and
e. mast cells
Step 7b of inflammation (neutrophils)
Able to generate oxygen (hydrogen peroxide) and nitrogen products (nitric oxide [NO]) that assist in destroying the engulfed debris
The neutrophil count in the blood often increases (**on exam**) greatly during an inflammatory process, especially with bacterial infections.... It requires an increase in circulating WBCs, a condition called **leukocytosis**) which is frequently elevated with bacterial infections and tissue injury
Test Question- Patient Scenario
The patient is really sick and the WBC count is really high. What does the patient have?
Answer: Leukocytosis
Monocytes
A type of leukocyte, or WBC
Adaptive immunity is an immunity that occurs after exposure to an antigen either from a pathogen or a vaccination (activated when the innate immune response is insufficient)
This part of the immune system is activated when the innate immune response is insufficient to control an infection.
Macrophages (Step 9 of inflammation) (**very important**)
Special cells involved in the detection, phagocytosis and destruction of bacteria and other harmful organisms
Step 8 Inflammation
Neutrophils phagocytize bacteria
Adaptive immunity is what type of defense?
Third line defense]
NOT INNATE
Phagocytosis (step 9 of inflammation)
The process by which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles
Phagosome (step 9 of inflammation)
A vesicle formed around a particle engulfed by a phagocyte via phagocytosis
*What does vascular permeability lead to?*
Edema
Proteins leak out... protein loss... decreased osmotic pressure, increases interstitial osmotic pressure (intravascular-->intracellular space)
Fluid fills up in the third spacing
Exam Question
What is the cause of edema?
It is due to vascular permeability
Vascular changes with inflammation
Begin soon after injury and are characterized by vasodilation, changes in blood flow, increased vascular permeability, and leakage of fluid into the extravascular tissues.
What changes blood flow?
-Vasodilation
**Vascular changes when tissue is first injured**
The small blood vessels in the damaged area constrict momentarily (vasoconstriction).
Following this transient event, which is believed to be of little importance to the inflammatory response, the blood vessels dilate which increases blood flow to the area
Erythema (*on exam*)
Redness caused by congestion in the area after vasodilation and warmth associated with acute inflammation
Difference between neutrophils and macrophages
Neutrophil is a type of )(a) WBC, (b) granulocyte, and (c) phagocyte =Inflammatory Response
Neutrophils supplement macrophages with molecules that enhance macrophage antimicrobial capacities
Neutrophils transfer to macrophages intracellular pathogens
(**on test**) neutrophils show up first and macrophages follow
Cortisol effect on the immune system (**on exam**)
*Ding, Ding, Ding**
a. Primary stress hormone
Suppresses the immune system by suppressing the Th-1 cell activity (T1 helper cells) (part of the adaptive immune system-3rd line of defense)
Increases glucose

**Cardinal signs of Inflammation** (Will be on the exam in different ways) (**on exam**)
a. Heat
b. Redness (Rubor)
c. Swelling
d. Tenderness
e. Loss of function (make sure to choose this answer; students often miss this answer choice)
Pain
What are the chemical mediators that vasodilate and increase capillary permeability?(**Must know**) (**on exam**)
a. Histamine
b. prostaglandins
c. bradykinin (kinin)
Vascular changes (Vasodilation) that happen with inflammation
1. An immediate transient response (minor injury)(immediate injury=vasoconstrict)
2. An immediate, sustained response (Occurs with more serious injury and continues for several days and damages the vessels in the area)
3. A delayed hemodynamic response (involves an increase in capillary permeability that occurs 4-24 hours after injury)
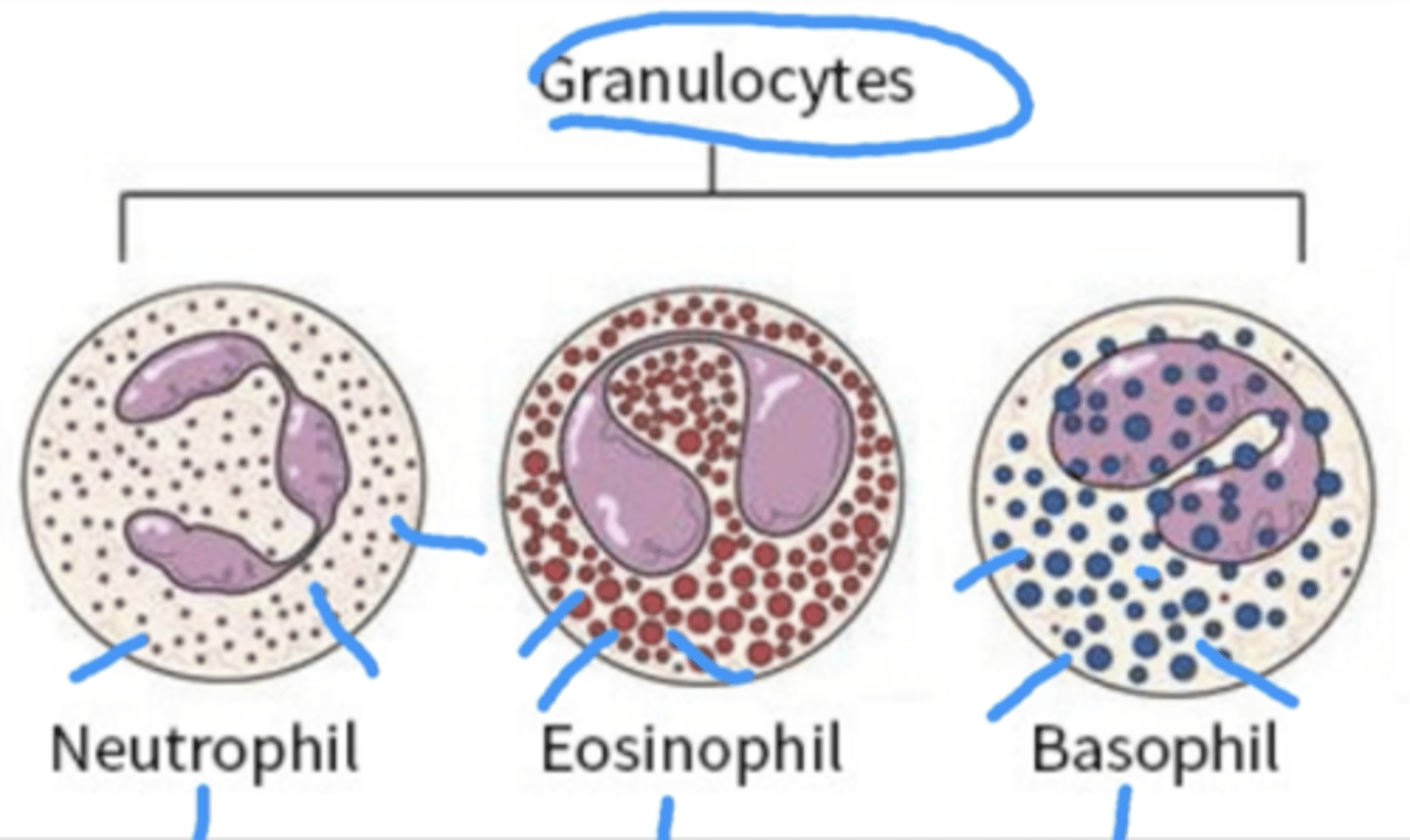
What are the two types of leukocytes participate in the acute inflammatory response?** (**on exam**)
Granulocytes
Monocytes (the largest of the WBCs)
**What is a granulocyte? What are the three types of granulocytes?** (**on exam**)
Type of WBC that has small granules (that contain proteins). The granules help release peroxide onto the pathogen to kill them.
basophils, Eosinophils, Neutrophils,
Remember it has BEN)
**What are monocytes?** (**on exam**)
largest white blood cells
Monocytes can turn into macrophages
When are eosinophils triggered? (**on exam**)
alerted in allergic reactions or fighting off parasitic infection
Contain a protein that is highly toxic to large parasitic worms that cannot be phagocytized
Granules are red
Basophils (**on exam**)
Contain histamines
Blue granules
Come from your bone/bone marrow and circulates in the blood
**Essential for the inflammatory response**
HIGHER LEVELS ARE PRESENT DURING INFLAMMATION BECAUSE THEY CONTAIN HISTAMINE
Binding of IgE triggers release of histamine and vasoactive agents from the basophil granules
**Basophils and mast cells bind to what antibody?** (**on exam**)
Immunoglobulin E (This is an antibody) (immunoglobulin E helps fight off infections and allergic reactions and will triffer histamine
Mast cells
Derive from same hematopoietic stem cells (are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells) and **do not develop until they leave the circulation and lodge in tissue sites** (whatever site they are sent to fo injury that is where they actually develop
A resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin
Activation of mast cells mediates inflammatory responses such as hypersensitivity (overreaction) and allergic reactions.
Which of the following molecules will induce endothelial cell retraction?
A. Omega-3 fatty acids
B. Leukotrienes
C. Histamine
D. VCAM
C. Histamine
Rationale: Histamine is the primary activator of endothelial retraction and increased permeability of the vessels
**What is serous exudate?** (**on exam**)
Watery, thin and colorless exudate
**What is purulent exudate?** (**on exam**)
Thick, yellow-green (opaque), contains more leukocytes (WBCs), cell debris, and microorganisms (such as bacteria)
An abscess... localized pocket of purulent exudate in solid tissue. Inside of this abscess it will have fluid.
**What is hemorrhagic exudate?** (**on exam**)
present when blood vessels are damaged
Any time you see puss...
Rich with WBCs
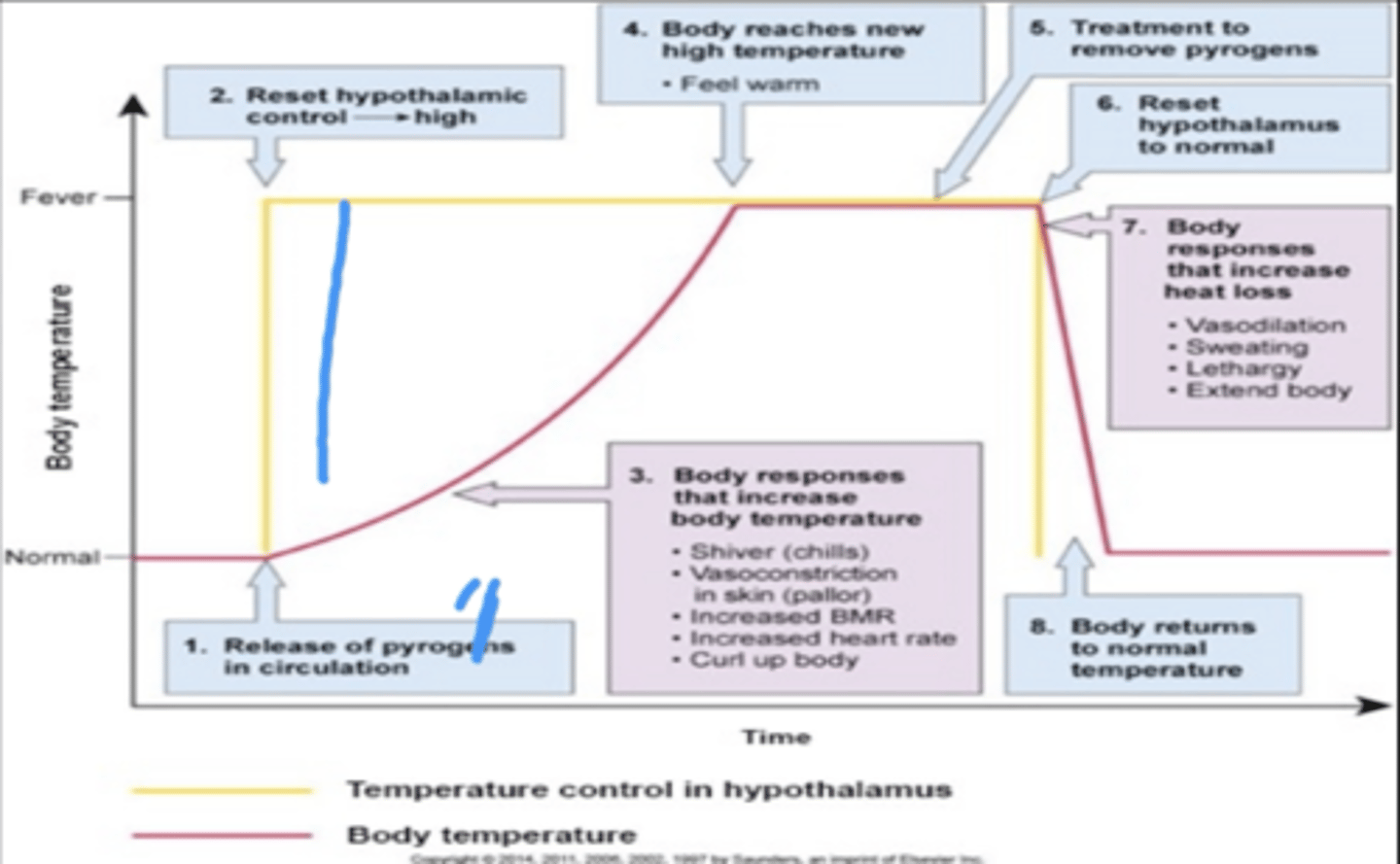
Mild fever (pyrexia) leads to...
Release of pyrogens (destroy the cells of the body and systemically you will have an inflammatory response)
pyrogens: Released either from bacteria or viruses or from destroyed cells of the body, are capable of raising the thermostat and causing a rise in body temperature
Pyrogens are substances that can produce fever
Are fevers local or systemic? (**on exam**)
Systemic
Local injury DOES NOT CAUSE A FEVER
One of the systemic effects of inflammation is a? (**on exam**)
Fever
Systemic effects of inflammation
1. mild fever (pyrexia)
2. Malaise (feeling unwell)
3. Fatigue
4. Headache
5. Anorexia
Normal core body temperature (**on exam**)
97.0-99.5
Low grade fever temperature range
100.4-102.2
this is a low-grade fever
DO NOT CALL A DOCTOR ABOUT A LOW-GRADE FEVER
Nursing intervention: monitor and give Tylenol
*Do fever increase or decrease the body temperature?*
Fevers increase body temperature and the core body temperature is stored in the hypothalamus
What are exogenous pyrogens?
Induce host cells to produce fever-producing mediators called endogenous pyrogens (once fever is caused, we call them endogenous pyrogens)
What happens after phagocytic cells of the immune system engulf the bacterial products?
Pyrogenic cytokines are released into the bloodstream for transport to the hypothalamus, where they exert their actio.
These cytokines induce prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)
What induces fever in the body? (**on exam**)
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) acts on the brain (hypothalamus) to induce fever (it tells the body to reset the temperature)
The hypothalamus then initiates shivering and vasoconstriction that raise the body's core temperature to the new set point, and fever is established
What is endogenous pyrogens?
Fever-producing actions
Inflammatory mediators that produce other signs of inflammation such as leukocytosis (increased levels of leukocytes in the blood), anorexia, and malaise
What is the role of Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)?(**on exam**)
This triggers the increase in the core body temperatures because during a fever, your body is hot.
Vasoconstriction happens
The course of a fever process