Ch. 2: Overview of the Labour Market
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Market
Interaction of buyers and sellers
Buyers demand products
Sellers supplu products
Workers are selling their labour for businesses to buy
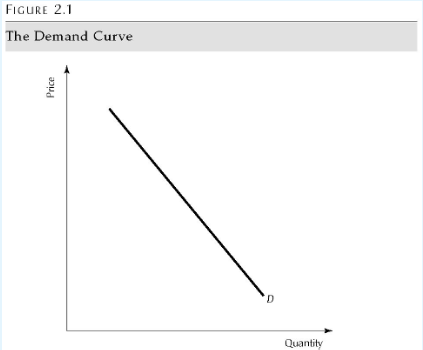
Demand Curve
Schedule
Downwards sloping
Inverse relationship between price and quanitity
Income Effect
Lower prices mean consumers buying more
Feeling like they have more money
Substitution Effect
Buying the cheaper product in place of the more expensive original
Factors that make Demand Increase or Decrease
Price of related products or services
Substitutes and compliements
Income levels of consumers
Consumer or employer expectations
Tastes and preferences (for workers)
Number of buyers (employers)
Supply Curve
Schedule
For normal prod.
Upward sloping, direct relationship betwen price and quanitity
Higher price means suppliers are willing to prove more labour
Short run: Unit cost increases (needing sleep)
Law of diminishing return: Labour is not 24/7
Factors Affecting Supply (Shifts)
Production costs
Prcies of related prod. or services
How much you are paid for a different job
Expected future prices
State of tech.
Number of suppliers (workers)
Govt. regulations
Weather conditions
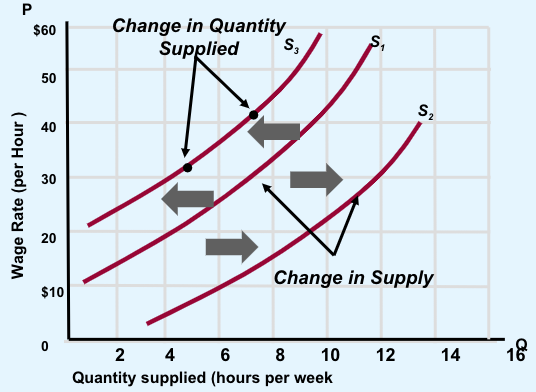
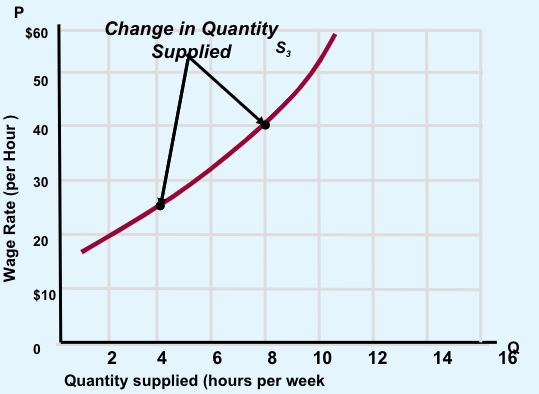
Factors Affecting Quantity Supplied
Point on the supply curve corresponding to a specific price
Changes in the price of the product or service indicates a movemenet along the supply curve
Three Factors that Influence Price Elasticity of Demand?
Number of subistitutes
Luxury vs necessity
Percentage of income spent on the prod.
AI + Globalization
Opportunity to increase labour productivity
Growth of foreign trade/investment
Reduction of trade labour
Difference in labour standards
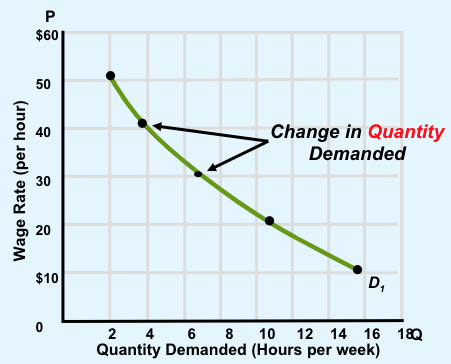
Quanity Demand
Is a point on the demand curve corresponding to a specific price
Movement along the curve, but does not shift the curve
A change in demand means a shift in the entire curve
Price Determinatio/ Equilibrium
Market prices are determined by the intersection of demand and supply
Disequilibrium
Shortage: When prices are too low
Surplus: When prices are too high
Elasticity Coefficent
The responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price
= % change in the quantity demand / % change in price
elastic= > 1 (greater)
inelastic= < 1 (lesser)
Four Difference Between the Labour Market and Markets for Other Products
Labour services are inseparable from people
Employment relations last longer
Workers and jobs are highly diverse
Labour markets are highly fragmented
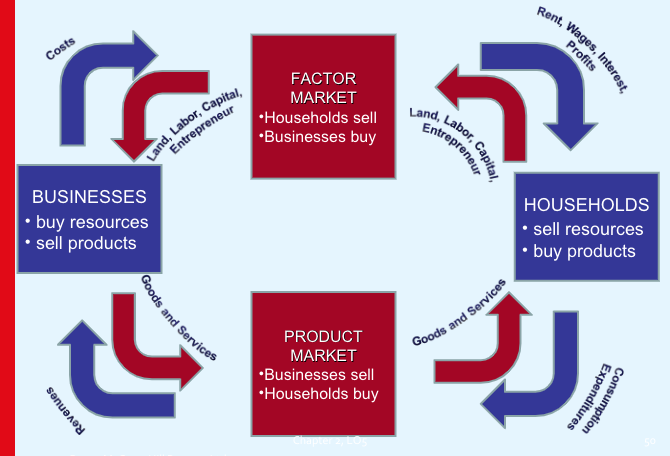
Circular Flow Model
Simple rep. of the relationship between firms and households
Money flows
Prod. markets and factor markets are included
Equality of income and output in an economy