USMLE: Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
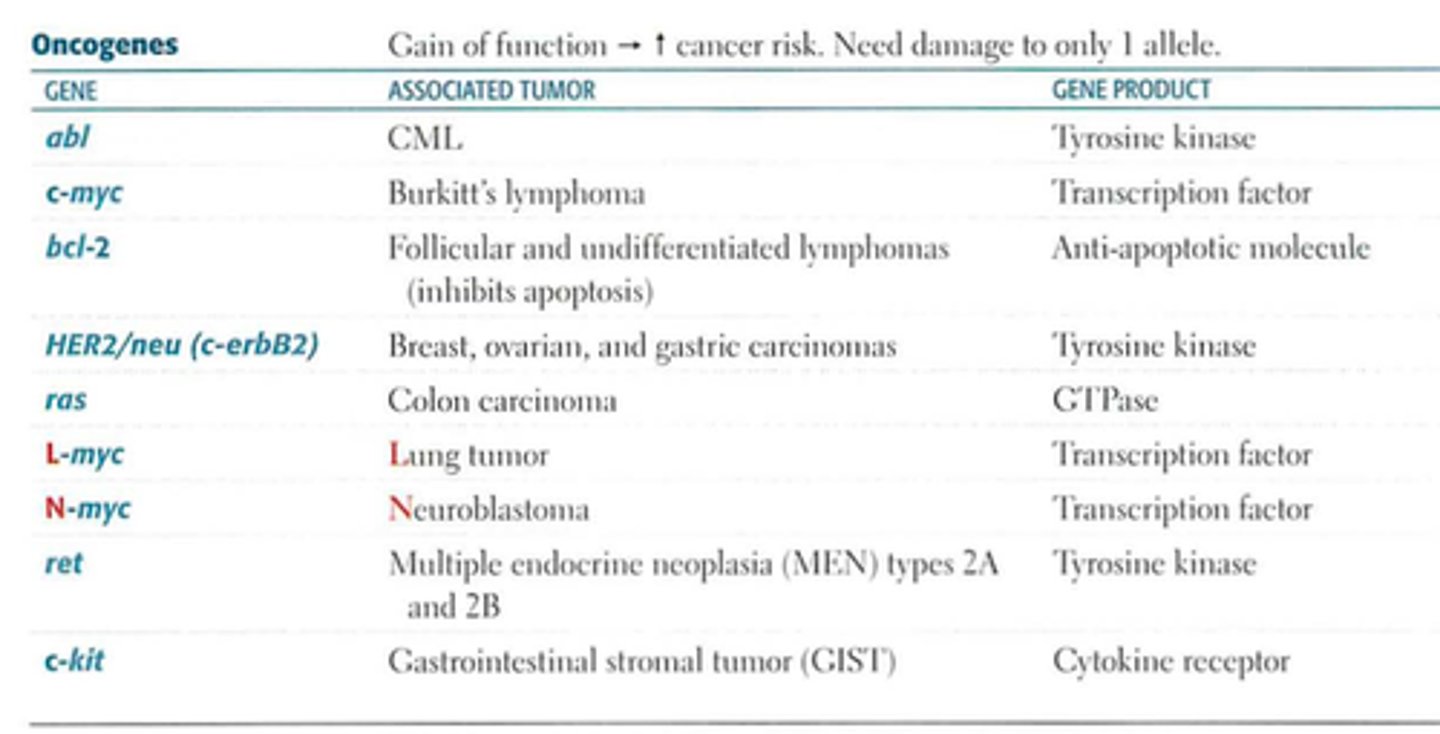
Oncogenes
Gain of function ➡️ Increase cancer risk.
Only need damage to 1 allele.
ALK
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
Lung Adenocarcinoma
HER2/neu (ERB-B2)
Growth Factor receptors
Tyrosine kinase
Overexpression of growth factor receptors that are amplified in breast cancer.
Breast, ovarian and gastric carcinoma
JAK2
Tyrosine Kinase
Chronic Myeloproliferative disorders
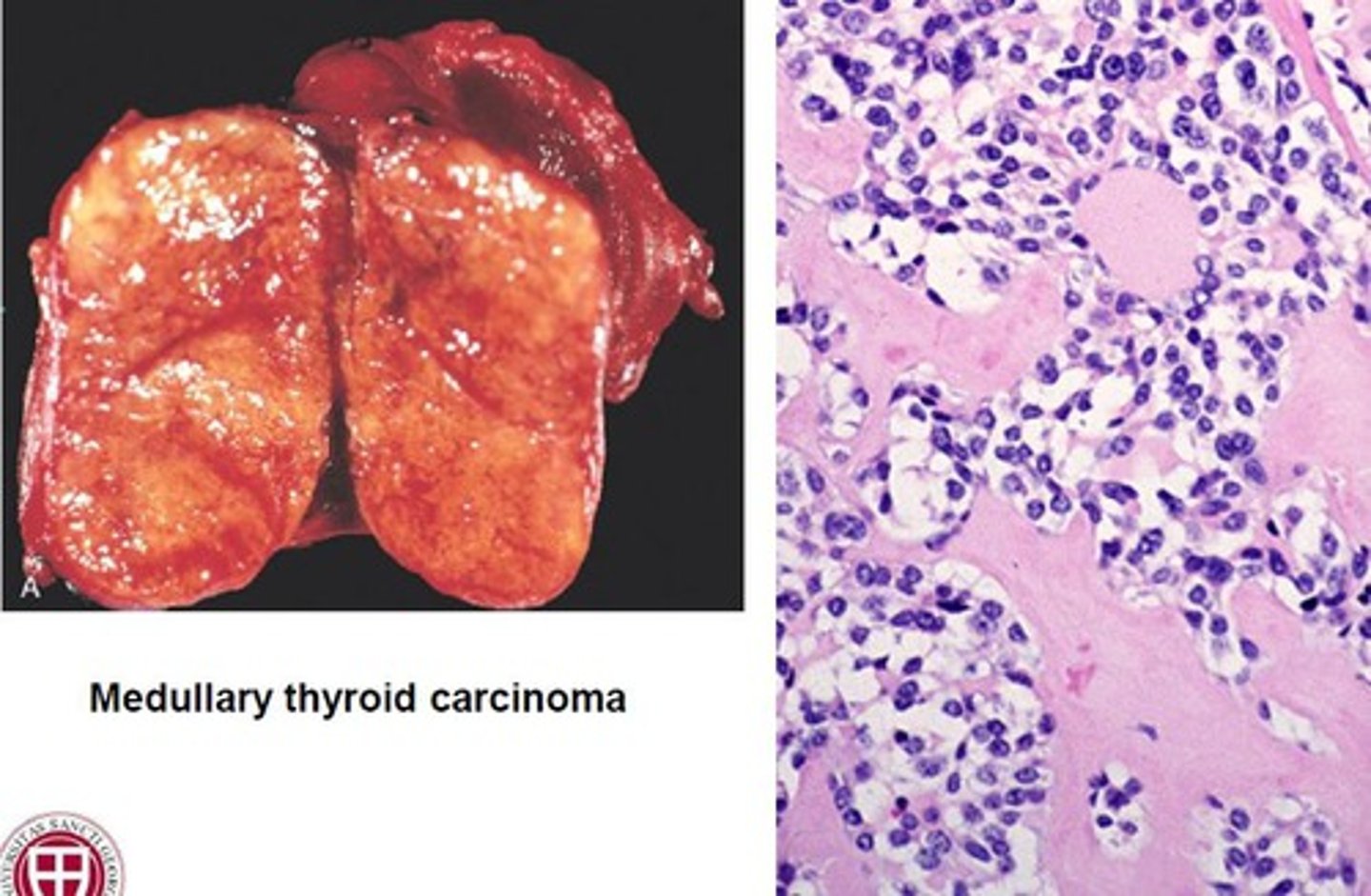
RET
Growth Factor Receptor
Tyrosine kinase
MEN 2A and B
Medullary Carcinoma of the thyroid
c-kit
Growth Factor Receptor
Cytokine receptor
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
RAS (70% of human tumors)
KRAS
Signal Transducer
GTPase ➡️ When growth factor binds to the receptor, GDP ➡️ GTP and a message is sent to the nucleus.
RAS & GTPase have the ability to dephosphorylate GTP ➡️ GDP which turns off the signal.
Point Mutation
Colon cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer
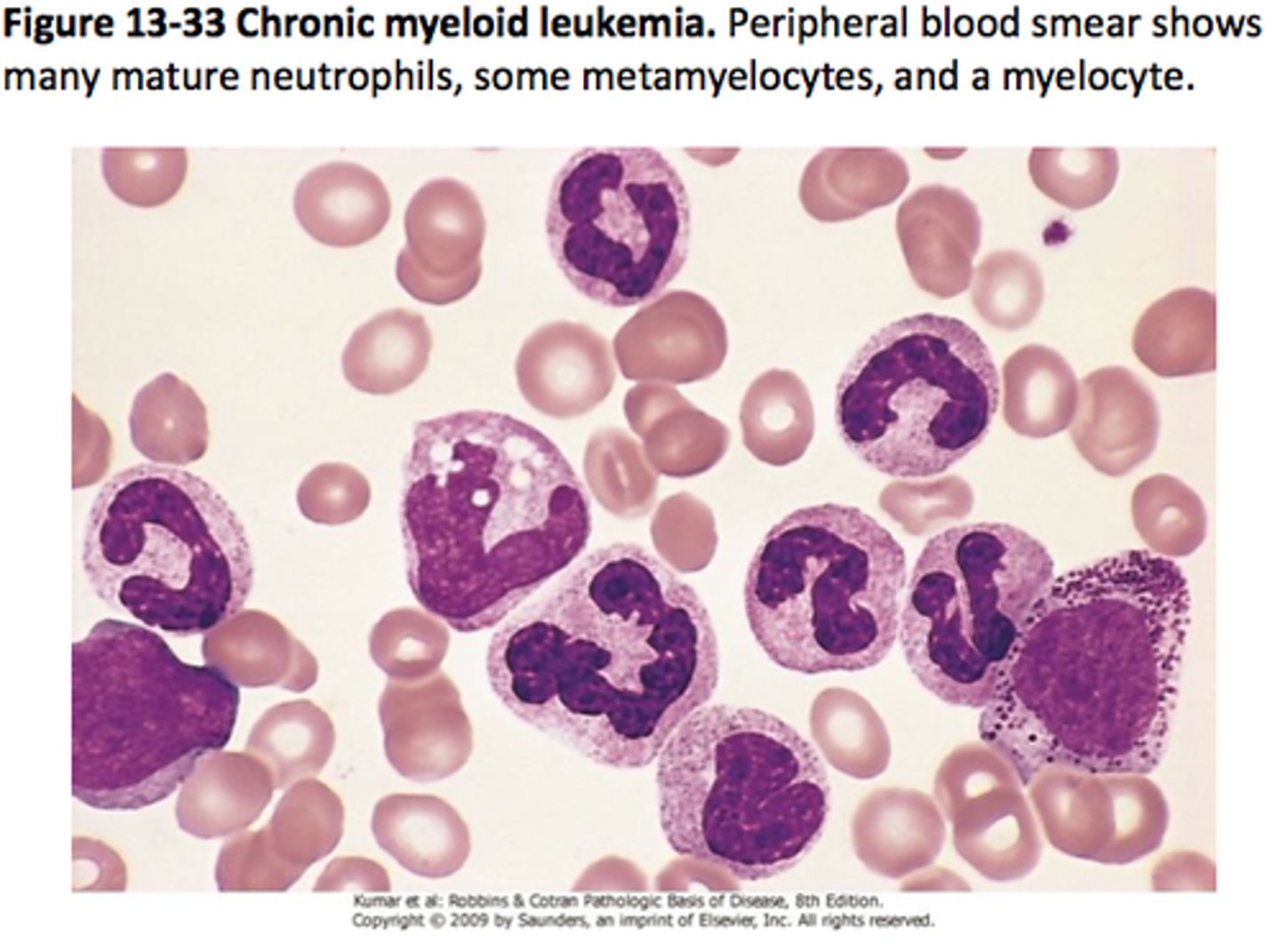
BCR-ABL
Tyrosine kinase
CML, ALL
c-myc
Nuclear Regulator
Transcription factor
Burkitt lymphoma (8,14): Lymphoma of B-Cells with myc being translated to the heavy chain region in B-Cells (Chromosome 14).
Starry sky appearance. Blue represents the cancer cells, the white represents macrophages.
N-myc
Nuclear Regulator
Transcription factor
Neuroblastoma
Small cell carcinoma of the lung
L-myc
Nuclear Regulator
Transcription factor
Lung tumor
Cyclin and CDK's
Cell cycle regulators
Cyclin and CDK forms a complex that phosphorylates the retinoblastoma protein, which promotes progression through the G1 ➡️ S phase.
Cyclin D1 (CCND1)
Cell cycle regulator
Cyclin
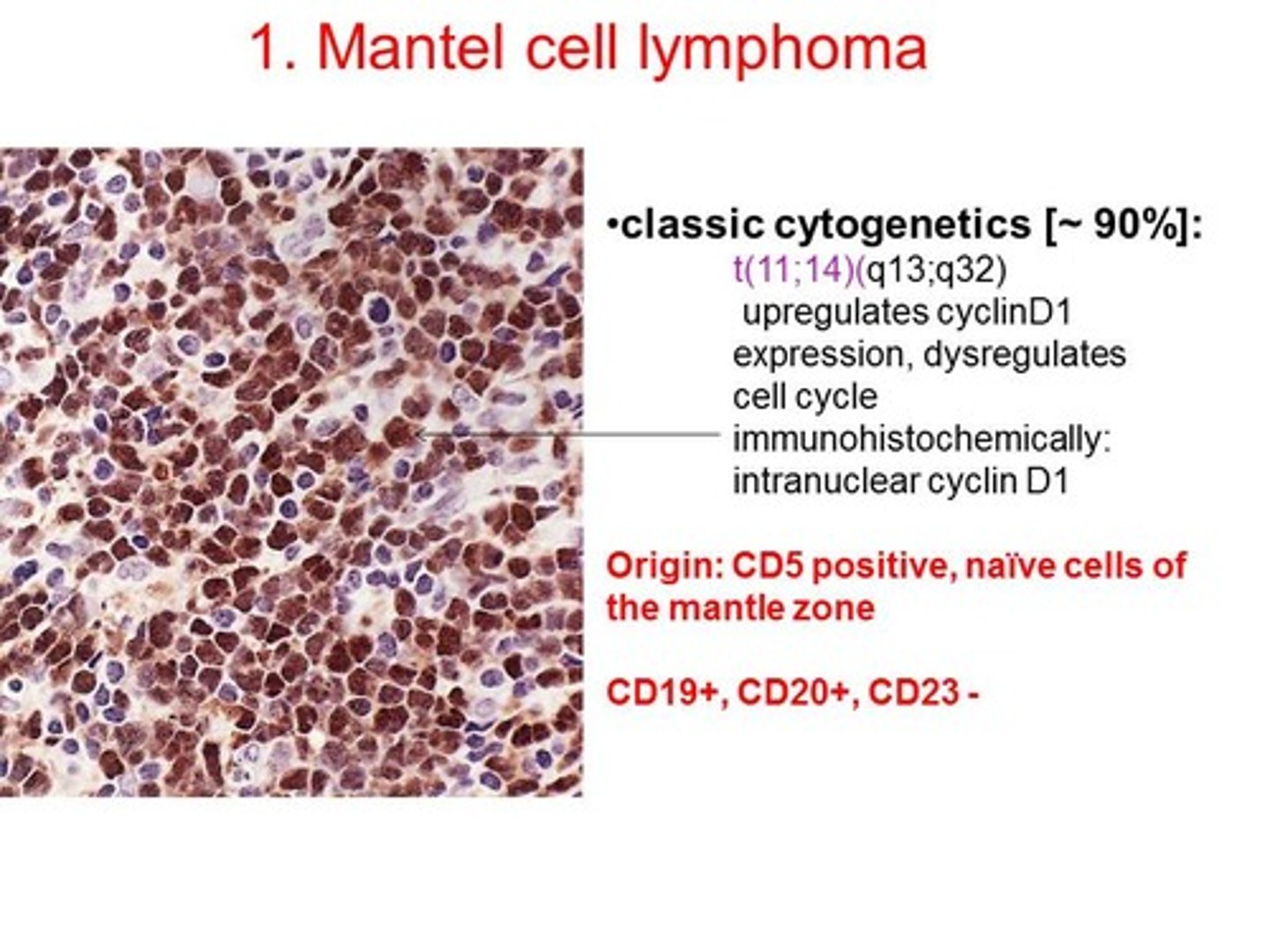
Mantle Cell Lymphoma t(11,14): B-Cell lymphoma. Cyclin D is translated to Chromosome 14, allows the cell to go from G1 ➡️ S phase.
Expansion of the mantle, which is right outside of the follicle.
BRAF
Serine/threonine kinase
Melanoma
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
papillary thyroid carcinoma
CDK4
Cyclin-dependent kinase
Melanoma
S100+, Neural Crest derived
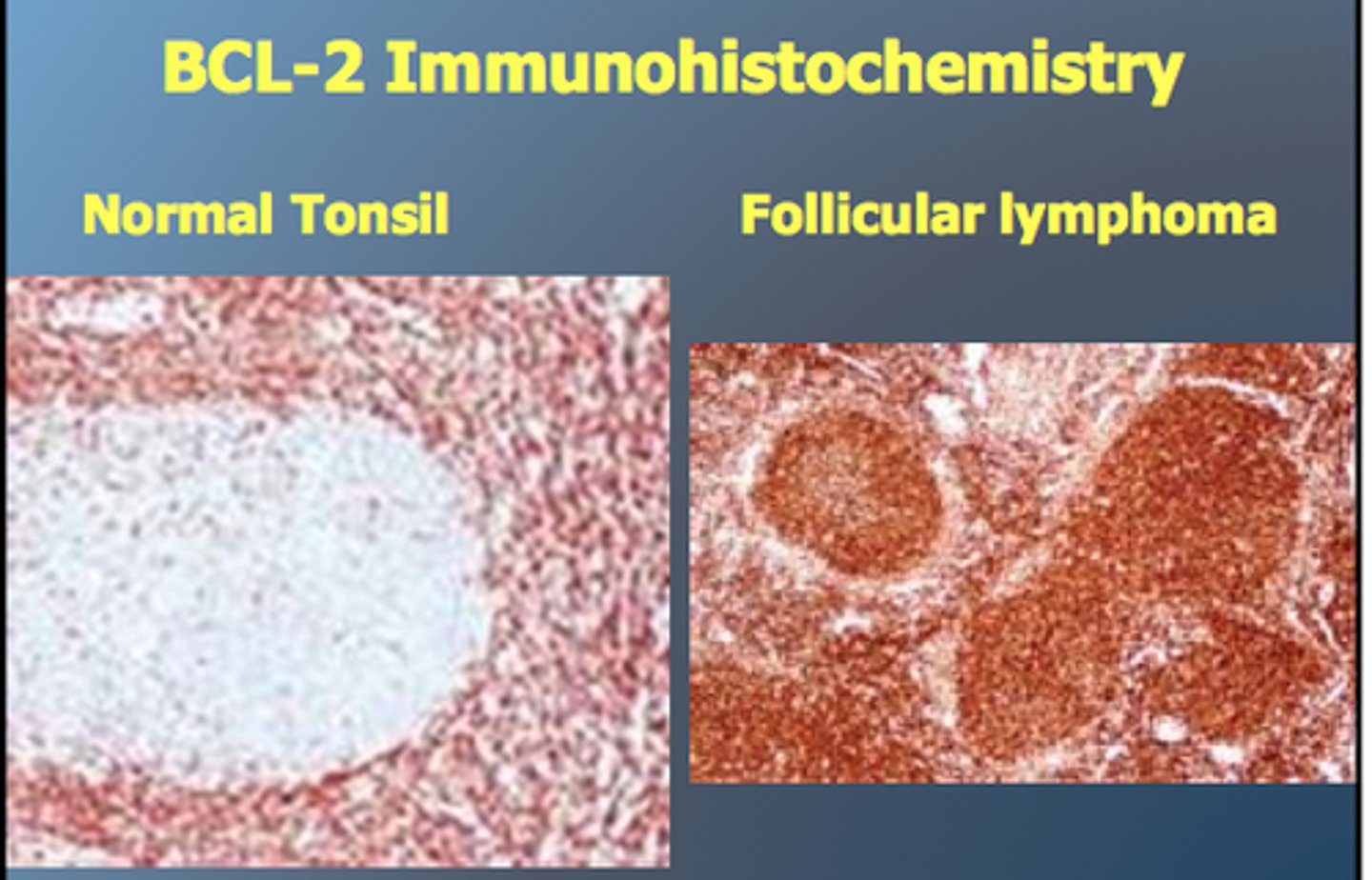
bcl-2
Inhibits apoptosis (antiapoptotic molecule)
Follicular and DLBC lymphomas
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Loss of function ➡️ Increases cancer risk; both alleles must be lost for expression of disease.
Two-hit hypothesis
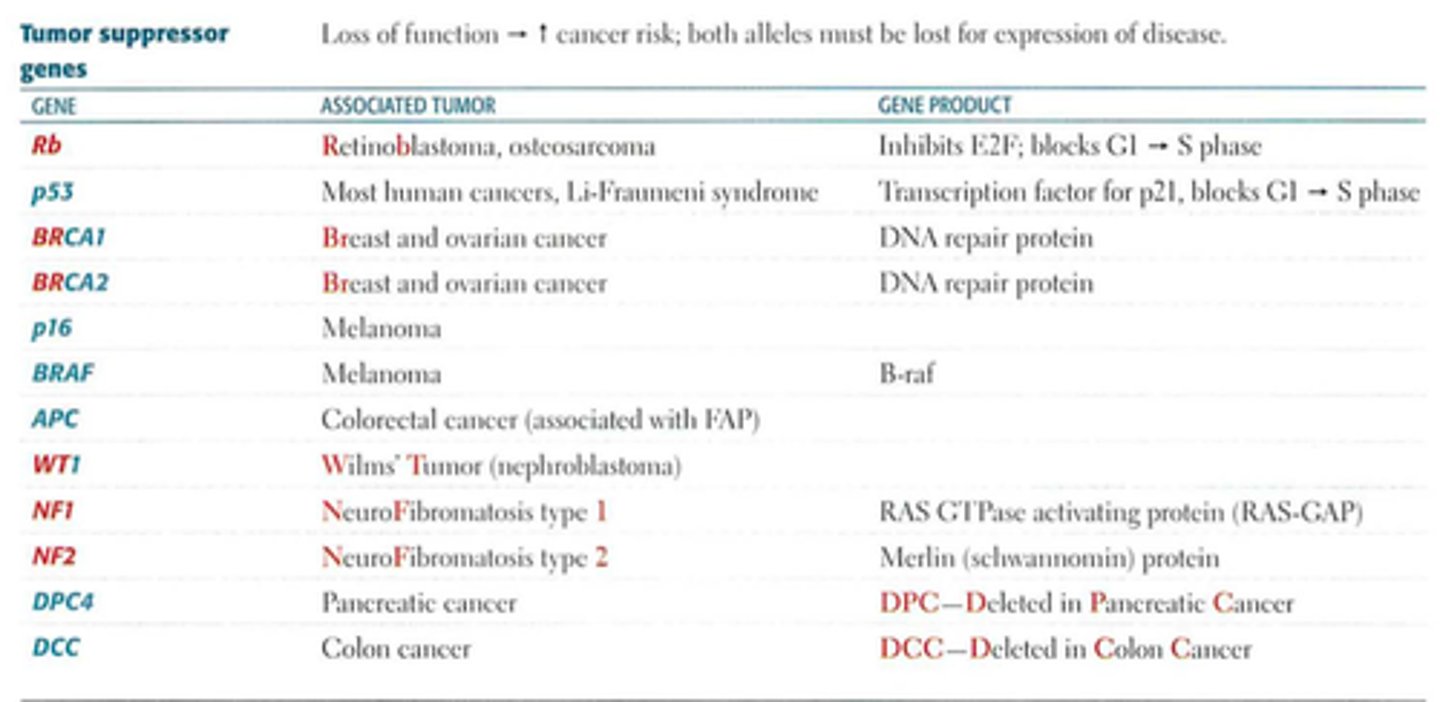
p53
Regulates the progression of the cell cycle from G1 ➡️ S phase.
In response to DNA damage, p53 slows the cell cycle and upregulates DNA repair enzymes. If DNA repair is not possible, p53 induces apoptosis by upregulating BAX (proapoptotic) and downregulating BCL-2 (antiapoptotic), cytochrome C leaks out of the mitochondria. Both copies of p53 must be knocked out for tumor formation (Knudson's two-hit hypothesis)
Germline mutation results in Li-Fraumeni Syndrome (2nd hit is somatic) ➡️ Develop multiple types of carcinomas and sarcomas.
SBLA syndrome: Sarcoma, Breast, Leukemia, Adrenal
Rb
Inhibits E2F; blocks G₁➡️ S phase
When Rb is phosphorylated by the cyclin/CDK complex, E2F is released and the cell is able to progress through G1 ➡️ S phase.
If Rb is mutated, E2F is constitutively free = uncontrollable growth. Both copies must be mutated. Sporadic mutation (both hits are somatic) = Unilateral Retinoblastoma.
Germline Mutation = familial retinoblastoma (2nd hit is somatic) = bilateral retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma.
Retinoblastoma, Osteosarcoma, & HPV (16, 18)
APC
Negative regulator of beta-catenin/WNT pathway
Colorectal cancer associated with FAP
BRCA1 and 2
DNA repair protein
Breast cancer
Ovarian cancer
Pancreatic cancer
MEN1
MEN1, produces Menin
MEN type 1
Pituitary
Parathyroid
Pancreas
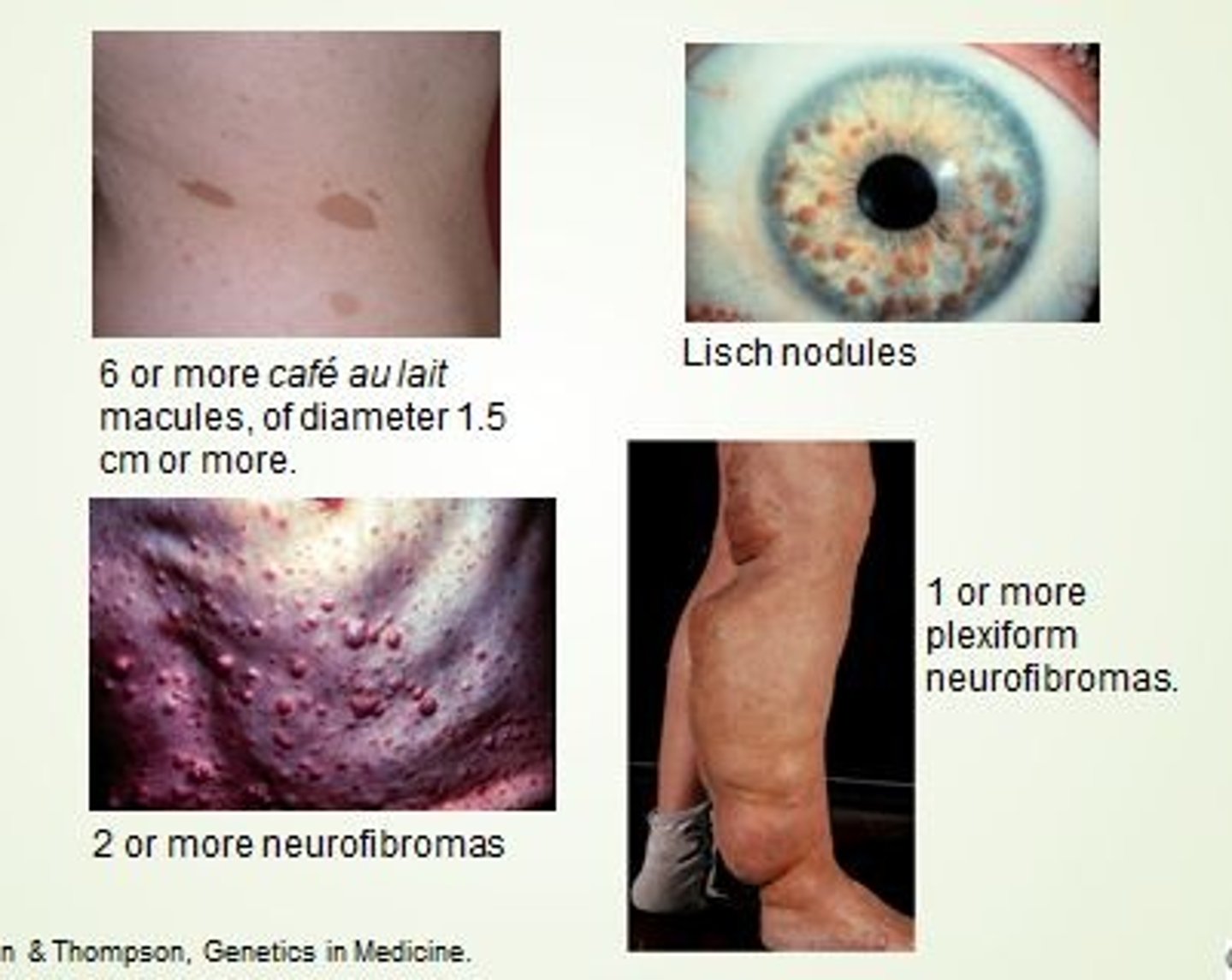
NF1
Ras GTPase activating protein (Neurofibromin) .
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (Neurofibromas are derived from Schwann Cells = Neural Crest)
NF2
Merlin (schwannomin) protein
Neurofibromatosis type 2
DPC4/SMAD
DPC (Deleted in Pancreatic Cancer)
Pancreatic cancer
DCC
DCC (Deleted in Colon Cancer)
Colon cancer
p16
Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A
Melanoma
PTEN
Tyrosine Phosphatase of PIP3 (PKB-AKT activation)
Breast cancer
Prostate cancer
Endometrial cancer
TSC1
Hamartin protein
Tuberous Sclerosis
TSC2
Tuberin protein (Twoberin)
Tuberous Sclerosis

ERB-B1
Proto-oncogene
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the lung
VHL
Inhibits hypoxia inducible factor 1a
von-Hippel-Lindau & RCC
WT1/WT2
Transcription Factor that regulates urogenital development
Wilms Tumor (nephroblastoma)
Does NOT cross the midline (vs. Neuroblastoma)
"Wilms is a whimp... Never crosses the line."
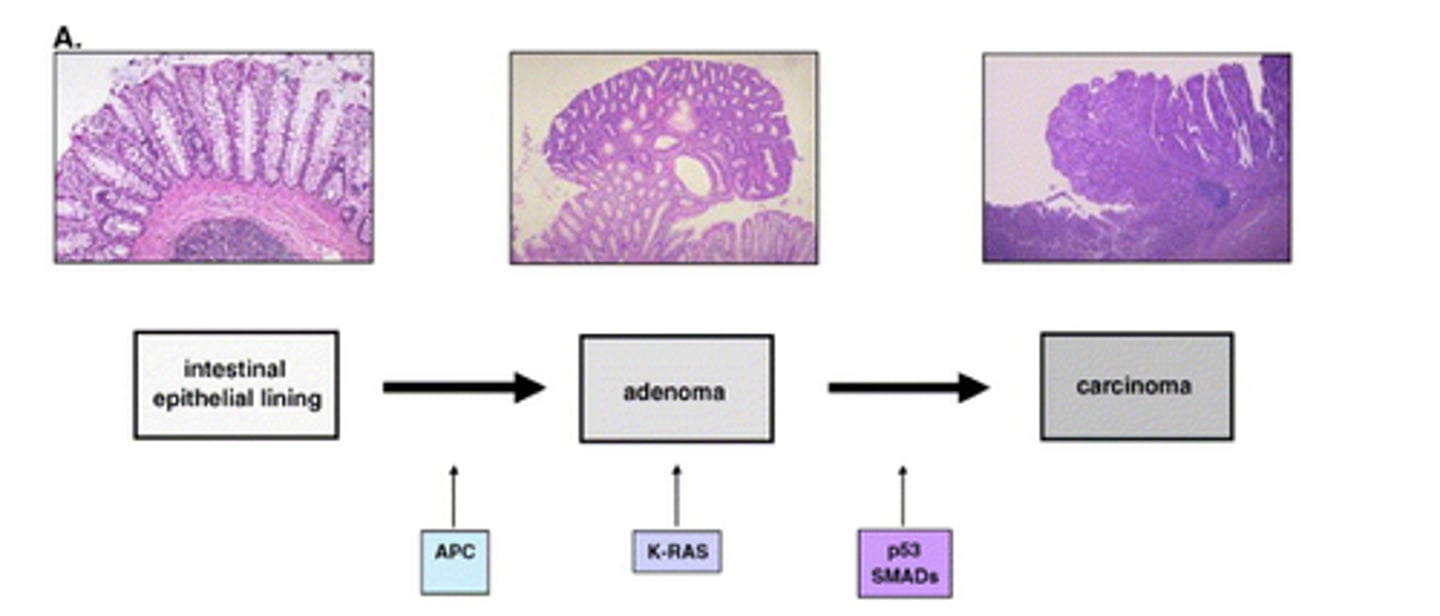
What is the adenoma-to-carcinoma sequence?
Normal Epithelium ➡️1⃣ Early Adenoma ➡️2⃣ Late Adenoma ➡️3⃣ Adenocarcinoma
1⃣APC = Progression from normal mucosa to small polyp.
2⃣K-RAS = Increase in the size of the polyp. K-RAS is a protooncogene.
3⃣P53 = Malignant transformation requires mutations in both P53 & DCC