physics magnetism
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
magnetically soft material is…
easy to magnetise
easily to lose magnetism
temporarily magnetised
magnetically hard material is…
hard to magnetise
hard to lose magnetism
permanently magnetised
magnetic field is…
the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet/on magnetic material e.g. iron, steel, cobalt, nickel
strength of magnetic field is shown by…
spacing of magnetic field lines
if closer together, field is strong
if far apart, field is weak
magnetic materials are…
materials which are always attracted by magnets, regardless of the pole
they do not have to be magnets themselves
magnetic metals:
iron
cobalt
nickel
steel (alloy containing iron)
test for magnet:
if it can be repelled by known magnet
if it can only be attracted, not repelled, it is magnetic material
permanent magnets
made out of permanent magnetic materials
will produce its own magnetic field
will not lose magnetism
induced magnets
magnetism induced when magnetic material placed in magnetic field
will lose most/all magnetism once removed from field
experiment investigating magnetic field pattern
place permanent magnet on piece of paper
draw dot at one end of magnet near corner (north pole)
place plotting compass next to dot, so that one end of the needle of the compass points away from the dot
use pencil to draw new dot at other side of compass needle
move compass so it points away from new dot, repeat process
keep repeating until there is a chain of dots going from one end of the magnet to the other
remove the compass, link the dots using a smooth curve - this is the magnetic field line
repeat the whole process several times to create other field lines
repeat whole process for two bar magnets placed 5cm apart first facing the same pole, then facing opposite poles
magnetic field is produced (around a wire) when…
a current flows through a conducting wire
right hand thumb rule
used to work out direction of magnetic field
thumb points along direction of current, other fingers give direction
factors affecting field strength
size of current
distance from long straight conductor e.g wire - greater dist = weaker magnetic field
motor effect:
occurs when a wire with current flowing through is placed in a magnetic field and experiences a force
effect = result of two interacting magnetic fields
result = wire will experience a force
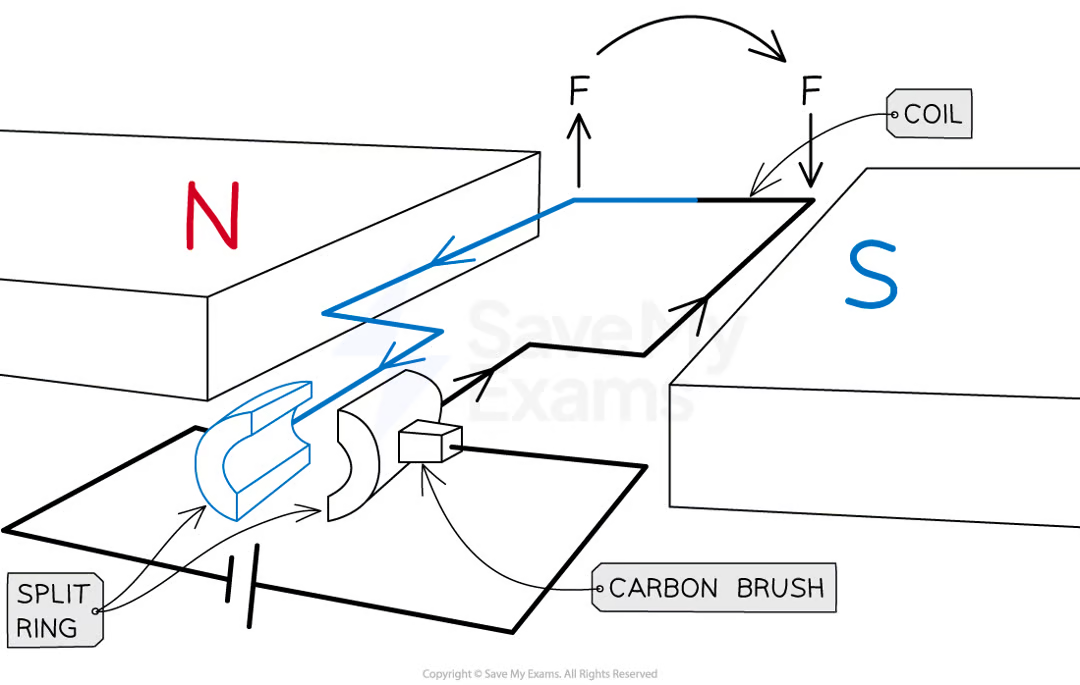
DC motor
force on a current carrying coil is used to make it rotate in a single direction
consists of:
coil of wire (free to rotate) - positioned in uniform magnetic field
when horizontal, wire forms complete circuit with a cell
coil attached to split-ring (circular tube of metal split in two)
split right connected in a circuit with cell via contact with conducting carbon brushes
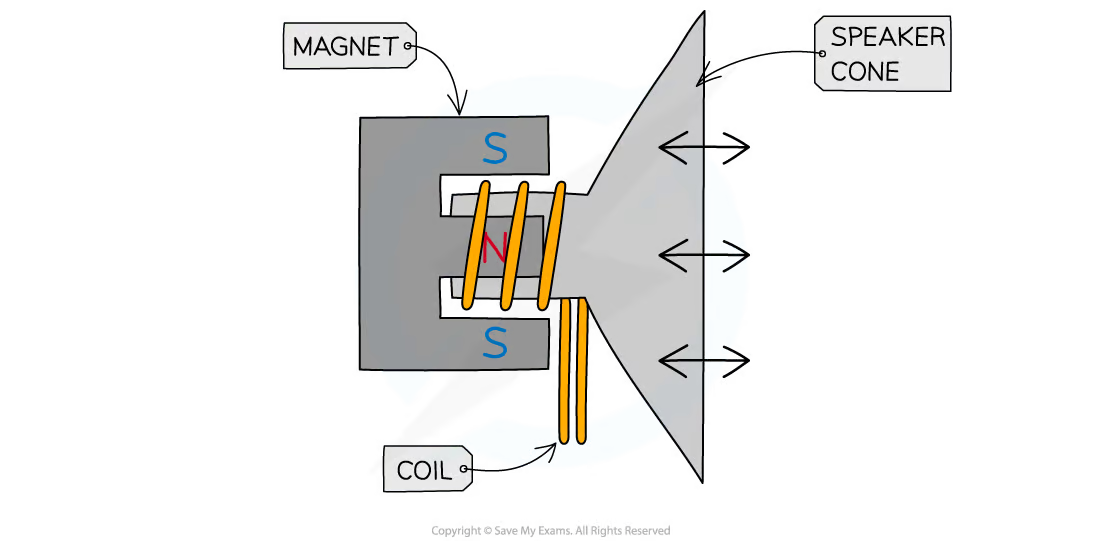
loudspeaker:
converts electrical signals into sound
consists of coil of wire wrapped around one pole of a permanent magnet
1. AC passes through coil, creating changing magnetic field around coil
direction of magnetic field constantly changing with current
magnetic field produced around coil interacts with field of permanent magnet
interacting fields exert force on coil
force exerted on coil constantly changing direction, making coil oscillate
oscillating coil causes speaker cone to oscillate, making air oscillate, creating sound waves
factors affecting magnetic force
use stronger magnets
increase amount of current flowing through wire
place wire at 90 degrees to direction of pole’s magnetic field lines (maximum interaction bewteen fields)
Fleming’s LH rule
thumb - thrust/force
first finger - field line direction
second finger - current direction
electromagnet:
ONLY WHEN CURRENT IS FLOWING THRU WIRE
EM induction
A voltage is induced in a conductor or a coil when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it