A2.1 origin of cells
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what were the conditions on early (pre-biotic) earth?
very low oxygen levels
absent ozone layer
high CO2 due to volcanic activity
high CH3 due to volcanic activity and meteorite impacts
temperatures higher due to strong greenhouse effect
higher exposure of uv radiation due to lack of ozone
ocean pH predicted to be pH 5-11
how were carbon compounds formed?
Earths early atmospheric components with high surface temperatures and lightning, followed by gradual cooling resulted in the formation of carbon compounds.
what are the functions of life
metabolism, growth, reproduction, response, homeostasis, nutrition, excretion
differences between living and non-living things
can self-sustain and use energy vs cannot do anything and no cells
why are viruses considered to be non-living?
they lack metabolism/homeostasis, cannot reproduce, and are dependent on a host
what is the cell theory?
all organisms are composed of one ore more cells
cells are the smallest units of life
all cells come from pre-existing cells
what is the endosymbiotic theory?
the organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled prokaryotes (big pro + small pro = eu)
what is the spontaneous generation theory and why is it false?
living organisms came from non-organic matter, it was falsified bcs cells form by divion, starting from a zygote
what are the differences between the abiogenesis and biogenesis theory?
abiogenesis: living things came from non living
biogenesis: living things came from pre-existing living things
what are the necessary requirements for the evolution of the first cells?
catalysis: controlled rate of reactions through enzymes
self-replication: essential for the inheritance and evolution of useful characteristics
compartmentalization: membranes to enclose cell contents
self-assembly: carbon compounds form polymers
what was the procedure for the miller and urey experiment?
1.Water was boiled to reflect the high temperatures of prebiotic conditions.
2.Water vapor was mixed with gas (H2, CH4, NH3) to create a reducing atmosphere.
3. The mixture of gases was exposed to “lightning” (electrical charge).
4.The mixture was cooled and condensed - one week later, traces of organic molecules were found.
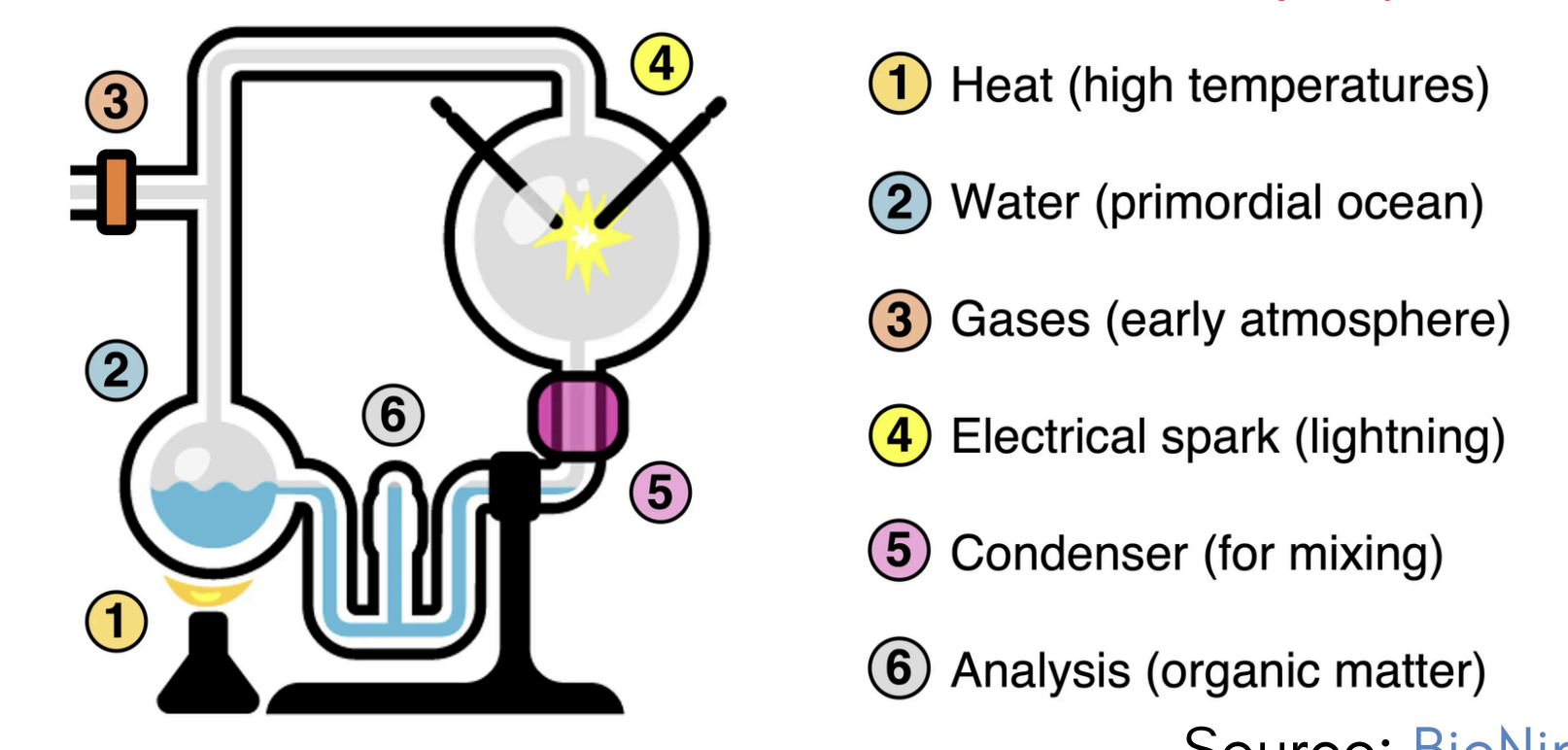
what are strenghts and weaknesses of the miller and urey experiment?
Strengths: Repeatable - other experiments also showed similar results
Limitations: Some conditions are likely incorrect (ex., ratio of gases in the atmosphere)
how were vesicles made and what do they do?
Fatty acids naturally form micelles in water, with the hydrophilic parts facing the water, creating vesicles. The formation of vesicles allows the internal chemistry to be different from the external environment, making it essential for the development of cells.
why is RNA thought to be the first genetic material?
able to store genetic information
self-replicate
RNA can catalyze reactions (ribozymes)
Some still use RNA as genetic material
Ribosomes still rely on RNA to catalyze protein synthesis, showing RNA’s ancient role
what is evidence that there is a last universal common ancestor (LUCA)?
all living things use a universal, genetic, 4 letter code made of 64 codons specific to the same amino acids (have the same meaning)
shared genes across organisms
similar cell structures (ribosomes, DNA/RNA enzymes, protein families, etc.)
was a different genetic code and other forms of life possible?
it is likely that other forms of life evolved, but they may have gone extinct due to competition from LUCA or species that evolved from it in the process of natural selection
how did fossils estimate the dates of the first living cells and LUCA?
fossilized stromatolites in rocks in Western Australia show that life existed 3.42 billion years ago
how did isotopes in rocks indicate the dates of the first living cells and LUCA?
living things prefer lighter carbon isotopes (¹²C)
a lower ¹³C/¹²C ratio in ancient rocks suggests biological activity
rocks from Greenland (3.8 Gya/billion years ago) and zircon from Australia (4.1 Gya) show these ratios → evidence of early life
how does genomic information help estimate the dates of the first cells and LUCA?
DNA mutates at a steady rate = molecular clock.
more genetic differences → species split longer ago
comparing genomes of all organisms suggests a LUCA, approx 4.5 Gya.
what are evidences for the evolution of the LUCA in hydrothermal vents?
355 shared genes found in modern bacteria and archaea match survival without oxygen and CO₂ fixation
hydrothermal vents that follow earths prebiotic conditions provide the right energy-rich chemicals to evolve the genes (the LUCA)