Lecture 19: Slime molds
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
Plasmodial slime molds
Myxomycetes (Amoebozoa)
2
New cards
Myxomycetes
• ~500 described species
• phagotrophic nutrition
• four life-cycle stages:
• phagotrophic nutrition
• four life-cycle stages:
3
New cards
four life-cycle stages of myxomycetes
1. three types of uninucleate single cells:
spore, myxamoeba, swarm cell
2. multinucleate somatic phase - plasmodium
--moves and exhibits a reversible cytoplasmic streaming
3. resistant stage consisting of a sclerotium
4. reproductive phase: stationary sporophores containing
walled spores
spore, myxamoeba, swarm cell
2. multinucleate somatic phase - plasmodium
--moves and exhibits a reversible cytoplasmic streaming
3. resistant stage consisting of a sclerotium
4. reproductive phase: stationary sporophores containing
walled spores
4
New cards
Spores
• haploid, resistant to unfavorable conditions
• germinate in rain water
• germination results in one or more myxamoebae or
swarm cells
• germinate in rain water
• germination results in one or more myxamoebae or
swarm cells
5
New cards
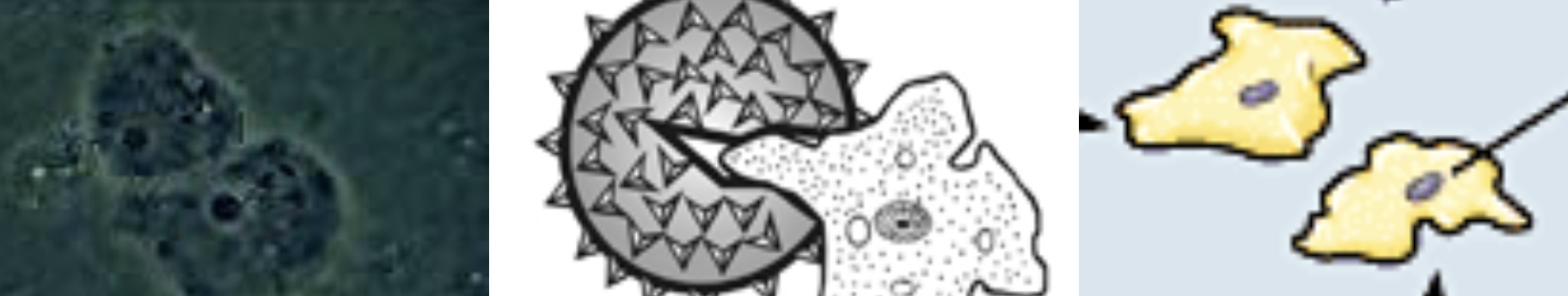
Myxamoebae
are the basic unit of structure of slime
molds and are uninucleate, naked, haploid amoeba
molds and are uninucleate, naked, haploid amoeba
6
New cards
Swarm cells
are unicellular motile cells of the
Myxomycetes that possess from 1 to 4 anteriorly
attached whiplash flagella
Myxomycetes that possess from 1 to 4 anteriorly
attached whiplash flagella
7
New cards
Swarm cells
• Mxamoebae may convert into swarm cells - reversible
• Absorb dissolved food material or ingest fungi &
bacteria
• Swarm cell can withdraw flagella and transform into a
myxamoeba
• Absorb dissolved food material or ingest fungi &
bacteria
• Swarm cell can withdraw flagella and transform into a
myxamoeba
8
New cards
Formation of Zygotes and Plasmodia
• Swarm cells and myxamoeba can both function as
gametes - fuse to form a zygote
• Zygote is initially flagellated, swims, retracts flagella
and transforms into an amoeba-like cell
• Zygote grows; its nucleus undergoes successive
mitotic divisions without cytokinesis -- becomes
transformed into a multinucleate plasmodium
gametes - fuse to form a zygote
• Zygote is initially flagellated, swims, retracts flagella
and transforms into an amoeba-like cell
• Zygote grows; its nucleus undergoes successive
mitotic divisions without cytokinesis -- becomes
transformed into a multinucleate plasmodium
9
New cards
Plasmodium
• No cell wall
• Enveloped by a gelatinous slime sheath
• Inside the slime sheath is the plasma membrane
• Feed on bacteria, spores of fungi and plants, protozoa
and decaying organic matter
• Enveloped by a gelatinous slime sheath
• Inside the slime sheath is the plasma membrane
• Feed on bacteria, spores of fungi and plants, protozoa
and decaying organic matter
10
New cards
Sclerotium
a hardened structure composed of tissue
that resists unfavorable conditions.
• capable of long periods of dormancy
that resists unfavorable conditions.
• capable of long periods of dormancy
11
New cards
Sclerotia
• Under unfavorable environmental conditions a
plasmodium can become converted into a sclerotium
• When conditions are favorable, a plasmodium emerges
plasmodium can become converted into a sclerotium
• When conditions are favorable, a plasmodium emerges
12
New cards
Cellular slime molds
Dictyostelia (Amoebozoa)
13
New cards
Dictyostelia
• ~350 spp. described
• Grow as unicellular amoebae and aggregates
• Myxamoebae are the basic unit of structure of slime
molds and are uninucleate, naked, haploid amoeba
• Fructifications are inconspicuous, delicate and
ephemeral
• Terrestrial – soil, leaf litter
• Nutrition: consume bacteria
• Grow as unicellular amoebae and aggregates
• Myxamoebae are the basic unit of structure of slime
molds and are uninucleate, naked, haploid amoeba
• Fructifications are inconspicuous, delicate and
ephemeral
• Terrestrial – soil, leaf litter
• Nutrition: consume bacteria
14
New cards
Amoeba growth
• Typically uninucleate
• Unicellular (exc. aggregations)
• Lacking a cell wall
• Pseudopods
• Lacking a definite form
• mobile
• Unicellular (exc. aggregations)
• Lacking a cell wall
• Pseudopods
• Lacking a definite form
• mobile
15
New cards
pseudoplasmodium
is a structure formed by the
massing of separate myxamoebae.
massing of separate myxamoebae.
16
New cards
Pseudoplasmodial growth
A pseudoplasmodium is a structure formed by the
massing of separate myxamoebae.
Separate myxamoebae do not fuse.
massing of separate myxamoebae.
Separate myxamoebae do not fuse.
17
New cards
“Slimy” or aggregate parts of the life cycle
• Component amoebae do not fuse
• Retain their individuality while cooperating as members
of the pseudoplasmodium
• Acrasin (e.g. cyclic AMP): pheromone responsible for
aggregation of myxamoebae to form a mound stage
• Retain their individuality while cooperating as members
of the pseudoplasmodium
• Acrasin (e.g. cyclic AMP): pheromone responsible for
aggregation of myxamoebae to form a mound stage
18
New cards
Acrasins
• Chemical messengers in slime
molds
• Edmund Spenser’s epic poem
“The Faerie Queen” 1590
• Acrasia seduced men against their
will and then transformed them
into beasts
molds
• Edmund Spenser’s epic poem
“The Faerie Queen” 1590
• Acrasia seduced men against their
will and then transformed them
into beasts
19
New cards
“Slimy” or aggregate parts of the life cycle
• The mound stage of the pseudoplasmodium
transforms into the mobile slug, or grex stage
• 10 to 50,000 individual amoebae make up a single slug
• Grex results in the differentiation of myxamoebae –
stalk and spore mass
• Amoebae in the stalk will die and their genetic
information won’t be passed on
transforms into the mobile slug, or grex stage
• 10 to 50,000 individual amoebae make up a single slug
• Grex results in the differentiation of myxamoebae –
stalk and spore mass
• Amoebae in the stalk will die and their genetic
information won’t be passed on
20
New cards
Farming
Bacterial prey dispersed with spores of Dictyostelium
21
New cards
Model Organism
Dictyostelium discoideum
Dictyostelium discoideum
A model for studying:
-cytokinesis
-signaling (e.g. cAMP)
-chemotaxis
-phagocytosis
-motility
-cell sorting
-cell differentiation
-cytokinesis
-signaling (e.g. cAMP)
-chemotaxis
-phagocytosis
-motility
-cell sorting
-cell differentiation