Key Events and Legislation in the Civil Rights Movement
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
13th Amendment
Abolished slavery in the United States (1865).
14th Amendment
Granted citizenship and equal protection (1868).
15th Amendment
Granted voting rights to former male slaves (1870).
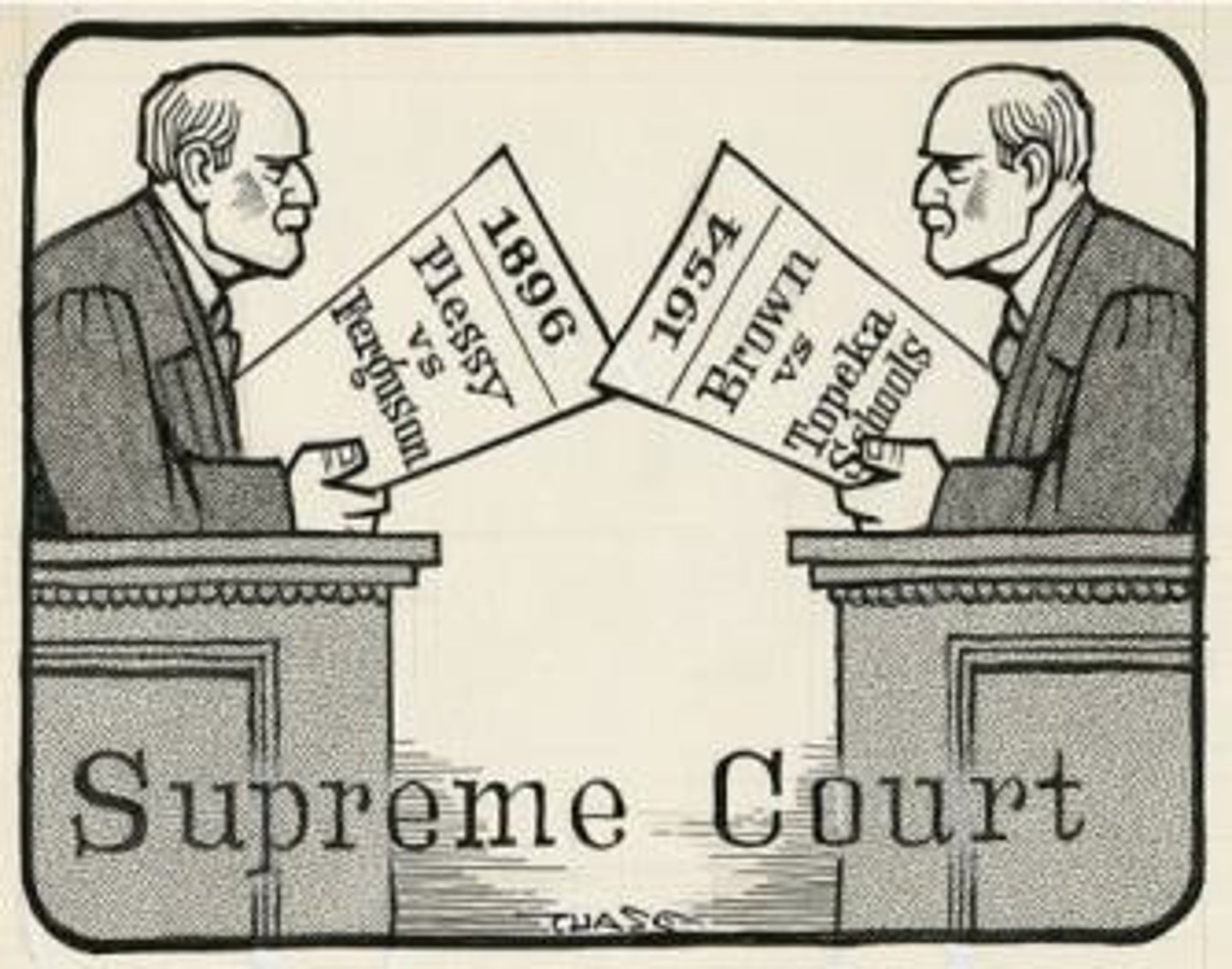
Plessy v. Ferguson
Established 'separate but equal' doctrine (1896).
Jackie Robinson
First African American in Major League Baseball (1947).
Desegregation of Military
Truman's order ending military segregation (1948).
Sweatt v. Painter
NAACP case for African American law school access (1950).
Brown v. Board of Education
Declared school segregation unconstitutional (1954).
Thurgood Marshall
First African American Supreme Court Justice (1967).
Emmett Till
Murdered boy whose death sparked civil rights activism.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
Protest against bus segregation initiated by Rosa Parks.
Rosa Parks
Civil rights activist known for bus refusal (1955).
E.D. Nixon
Local leader in organizing Montgomery Bus Boycott.
Jo Ann Robinson
Key figure in planning the Montgomery Bus Boycott.
Civil Rights Movement
Social movement for racial equality in the U.S.
NAACP
National Association for the Advancement of Colored People.
Separate but Equal
Doctrine allowing racial segregation if facilities are equal.
Civil Rights Legislation
Laws aimed at ending discrimination and segregation.
Public Facilities
Government-owned spaces subject to segregation laws.
Economic Pressure
Strategy to influence change through financial means.
Segregated Bus
Public transportation system divided by race.
Open Casket Funeral
Funeral style that displayed Till's disfigured body.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
381-day protest against bus segregation in Montgomery.
Browder v. Gayle
Supreme Court ruling declaring segregated buses unconstitutional.
Martin Luther King Jr.
Leader advocating civil disobedience against unjust laws.
Civil Rights Act (1957)
Legislation aimed to increase African American voting rights.
Jim Crow Laws
State laws enforcing racial segregation in the South.
Civil Rights Commission
Federal body created to register African American voters.
Little Rock Nine
Group of nine students integrating Central High School.
Orval Fabus
Arkansas Governor who opposed school desegregation.
Daisy Bates
NAACP leader and mentor to Little Rock Nine.
Elizabeth Eckford
First student of Little Rock Nine to face hostility.
Ernest Green
First African American to graduate from Central High.
Ruby Bridges
First African American child at William Frantz Elementary.
Barbara Henry
Ruby Bridges' teacher who supported her education.
Sit-ins (1960)
Nonviolent protests at segregated lunch counters.
Greensboro Four
Students who initiated the sit-in movement at Woolworth's.
SNCC
Student-led organization promoting nonviolent protests.
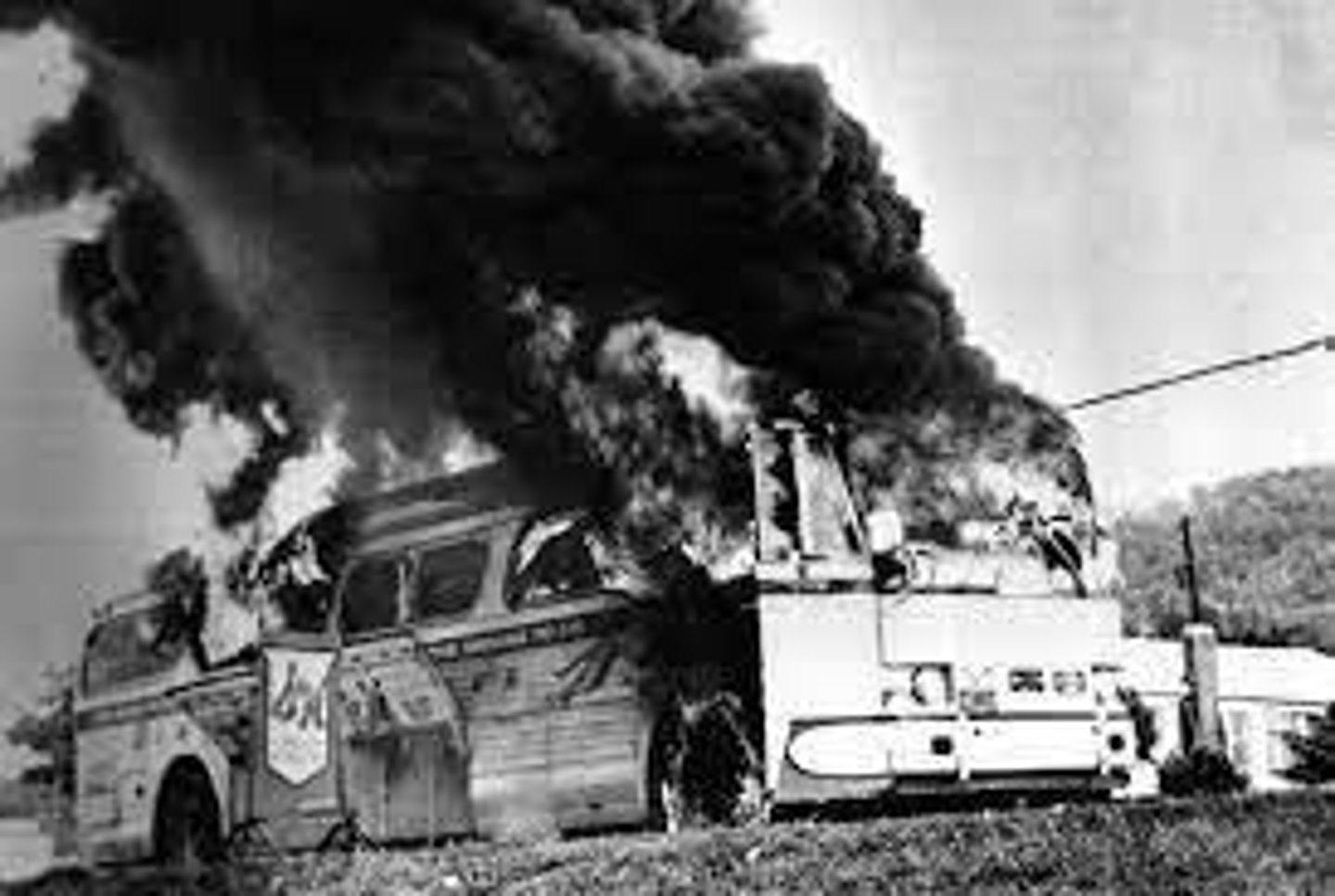
Freedom Rides
Interracial bus rides challenging segregation in the South.
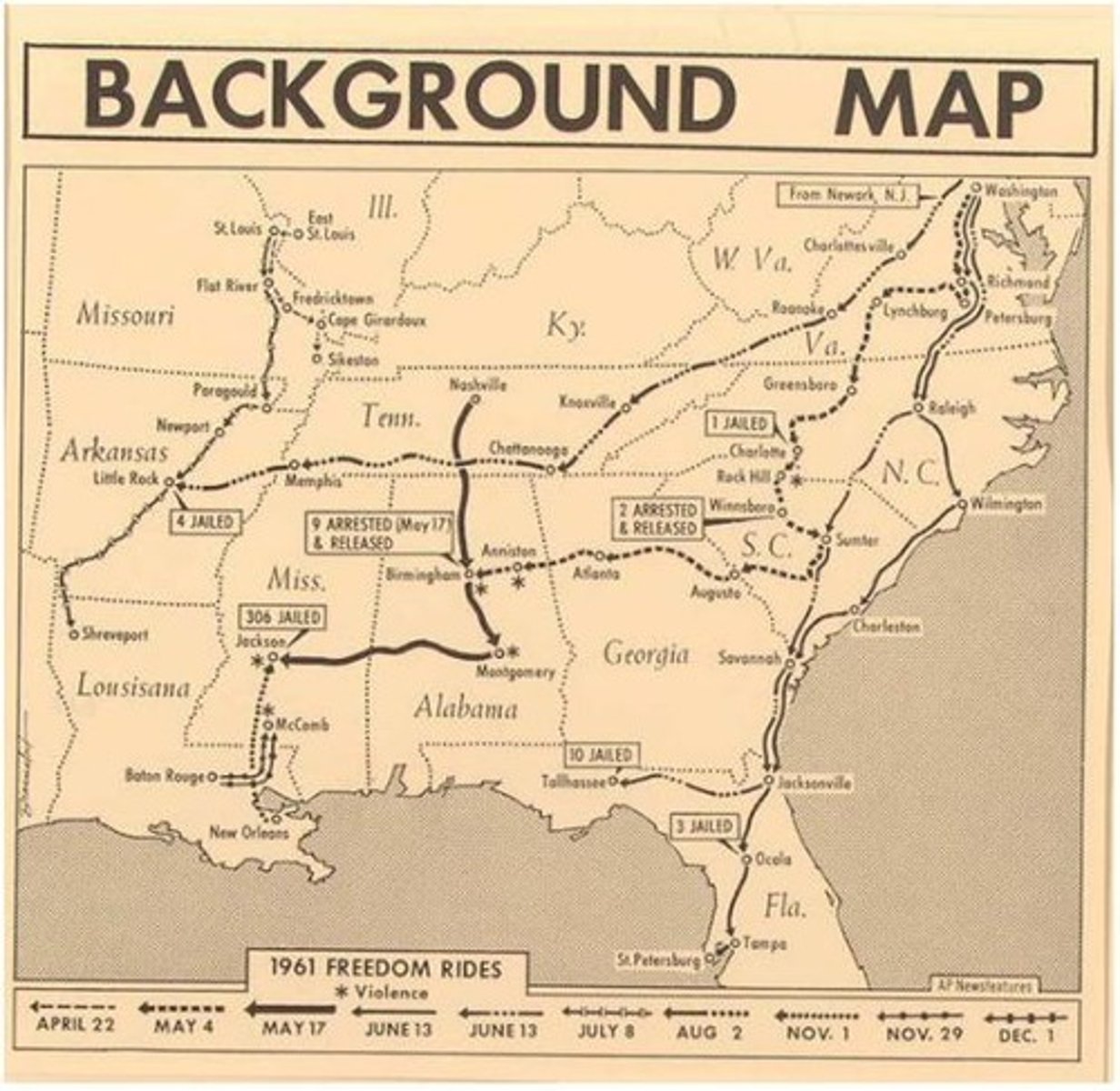
CORE
Congress of Racial Equality, organized Freedom Rides.
John Lewis
Iconic civil rights leader and Freedom Rider.
James Zwerg
White Freedom Rider beaten in Montgomery for desegregation.
Diane Nash
Key organizer of Freedom Rides and SNCC leader.
Warren Hudgins
White participant in Freedom Rides, faced violence.
Martin Luther King Jr.
Leader of the civil rights movement, advocate for nonviolence.
Letter from a Birmingham Jail
MLK's letter explaining urgency for civil rights.
Children's March
SCLC-organized march involving children under 18.
Eugene 'Bull' Connor
Birmingham Police Chief known for violent repression.
Civil Rights Act of 1964
Legislation prohibiting discrimination in public accommodations.
March on Washington
1963 demonstration for jobs and freedom, 200,000 participants.
I Have a Dream
MLK's famous speech advocating for racial equality.
Lyndon B. Johnson
President who advanced civil rights legislation post-Kennedy.
Freedom Summer
1964 initiative to increase voter registration in Mississippi.
Congress on Racial Equality (CORE)
Civil rights organization focused on nonviolent protests.
Student Non-Violent Coordinating Committee (SNCC)
Youth-led organization advocating for civil rights.
Mississippi Burning
Murder of civil rights workers Chaney, Goodman, Schwerner.
Ku Klux Klan (KKK)
White supremacist group involved in violent attacks.

Malcolm X
Spokesman for Nation of Islam, advocate for Black Power.
Black Power
Movement emphasizing racial pride and self-defense.
Black Panthers
Militant group advocating for African American rights.
Birmingham Jail
Location where MLK wrote his influential letter.
Gaston Motel
Site firebombed by KKK during Birmingham protests.
Federal troops
Military forces called to restore order in Birmingham.
Civil rights activists
Individuals fighting for racial equality and justice.
Violent attacks
Systematic violence against civil rights workers in Mississippi.
JFK assassination
Event that led to LBJ's presidency and civil rights push.
Black Panther Party
Advocated for immediate change in civil rights.
Bloody Sunday
1965 march violence at Edmund Pettus Bridge.
Voting Rights Act of 1965
Legislation ensuring voting rights for minorities.
Affirmative Action
Policies to increase minority representation in workplaces.
Regents of the University of California v. Bakke
Supreme Court case on affirmative action in admissions.
Mendez V. Westminster School District
1947 ruling against segregation of Mexican American children.
Delgado V. Bastrop ISD
1948 case making segregation illegal in Texas.
Hernandez V. Texas
1954 ruling for jury inclusion of Mexican Americans.
White V. Regester
1973 ruling for fair voting district representation.
Edgewood ISD V. Kirby
1984 case mandating equitable school funding.
Selma to Montgomery March
1965 march advocating for voting rights.
Martin Luther King Jr.
Leader of non-violent civil rights movement.
SCLC
Southern Christian Leadership Conference, civil rights organization.
SNCC
Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee, youth civil rights group.
LBJ
Lyndon B. Johnson, President who signed civil rights legislation.
Ghettos
Inner-city slums where African Americans were forced to live.
Billy Graham
Christian leader supporting civil rights and desegregation.
Reverse Discrimination
Claim that affirmative action discriminates against majority groups.
Urban Poverty
Economic hardship affecting inner-city African American communities.
Civil Rights Movement
Struggle for social justice and equality for minorities.
March 7, 1965
Date of the first Selma to Montgomery march.
3,200 Marchers
Number of participants in the second Selma march.
54 Miles
Distance from Selma to Montgomery during the marches.