Chem: Biological Macromolecules
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Last updated 1:34 PM on 6/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
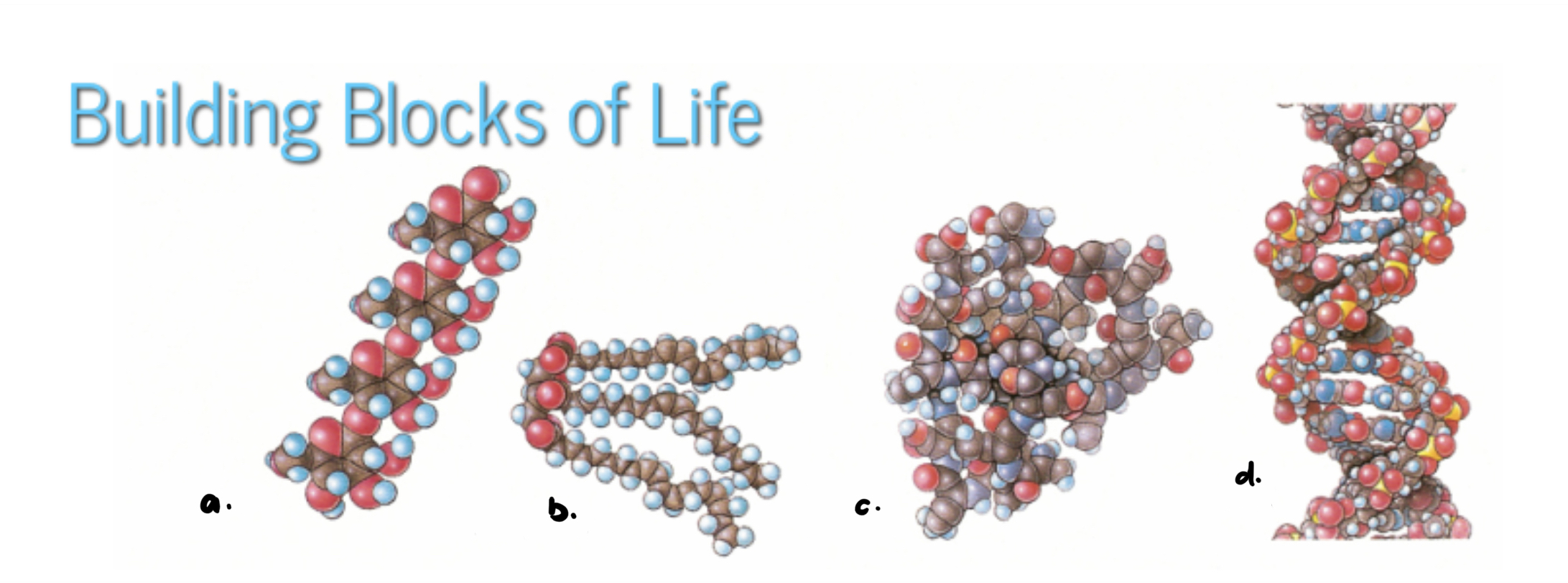
a. Carbohydrates(starch)
b. Lipid(triacylglycerol)
c. Protein(enzyme)
d. Nucleic acid(DNA)
b. Lipid(triacylglycerol)
c. Protein(enzyme)
d. Nucleic acid(DNA)
- All living things are made up of these four classes of biological molecules
- within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules
- within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules
2
New cards
Macromolecules
- are large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms
3
New cards
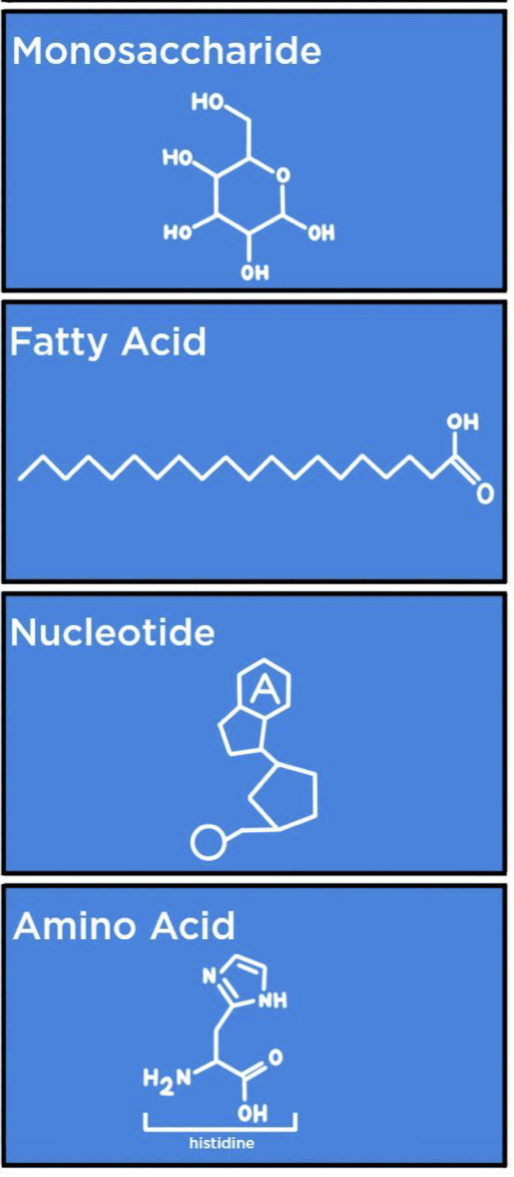
Monomers
- the small building-block molecules to make a polymer
4
New cards
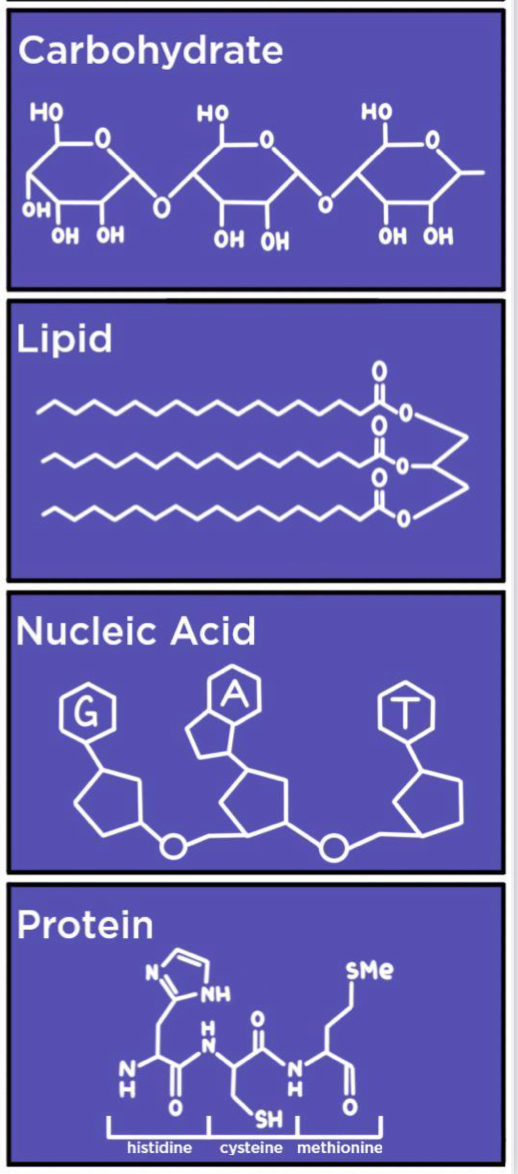
Polymer
- a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
5
New cards
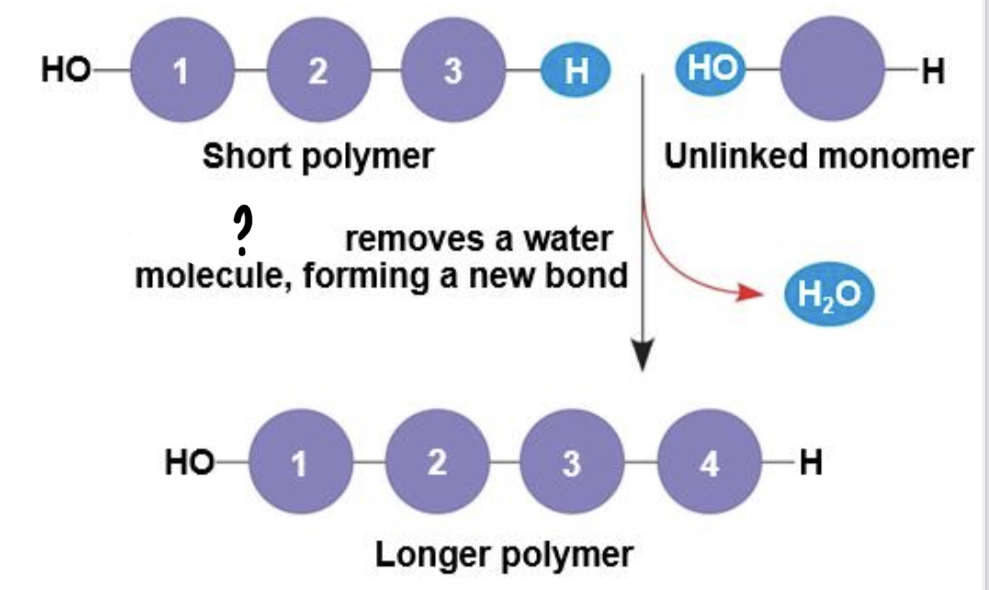
Dehydration reaction/ Condensation reaction
- occurs when two monomer bond together through the loss of a water molecule
6
New cards
Hydrolysis
- process of disassembling polymers to monomers
- a reaction that is essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction
- a reaction that is essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction
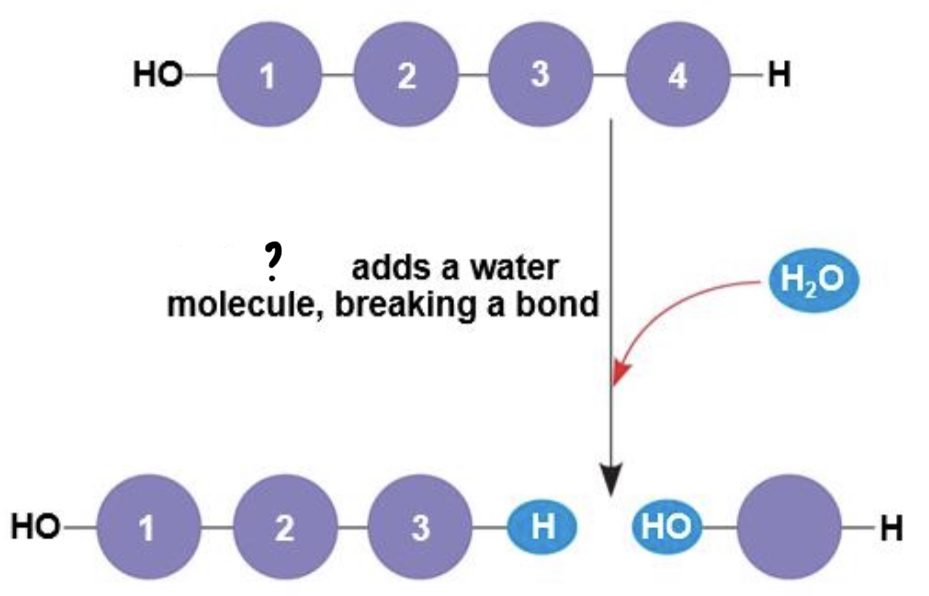
7
New cards
Enzyme
- are macromolecules that speed up the dehydration process
8
New cards
Carbohydrate
- include sugars and the polymers of sugars
9
New cards
Monosaccharides
- also known as simple sugars, the simplest carbohydrates
10
New cards
Polysaccharides
- are carbohydrate macromolecules
- these are polymers composed of many sugar building blocks
- these are polymers composed of many sugar building blocks
11
New cards
Sugars
what carbohydrate has monosaccharides that have molecular formulas that are usually multiples of CH20
12
New cards
Glucose(C6H12O6)
- the most common monosaccharide
13
New cards
Carbonyl group
1. Aldose
2. Ketose
1. Aldose
2. Ketose
• what is highlighted?
1. functions as an aldehyde
2. functions as a ketone
1. functions as an aldehyde
2. functions as a ketone
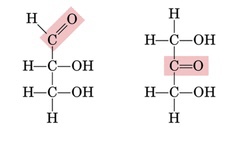
14
New cards
Disaccharide
- formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides
15
New cards
Glycosidic linkage
- the covalent bond that forms disaccharides
16
New cards
Maltose
• Glucose & Glucose
• Glucose & Glucose
- disaccharide used in brewing
• give the two monosaccharides bonded
• give the two monosaccharides bonded
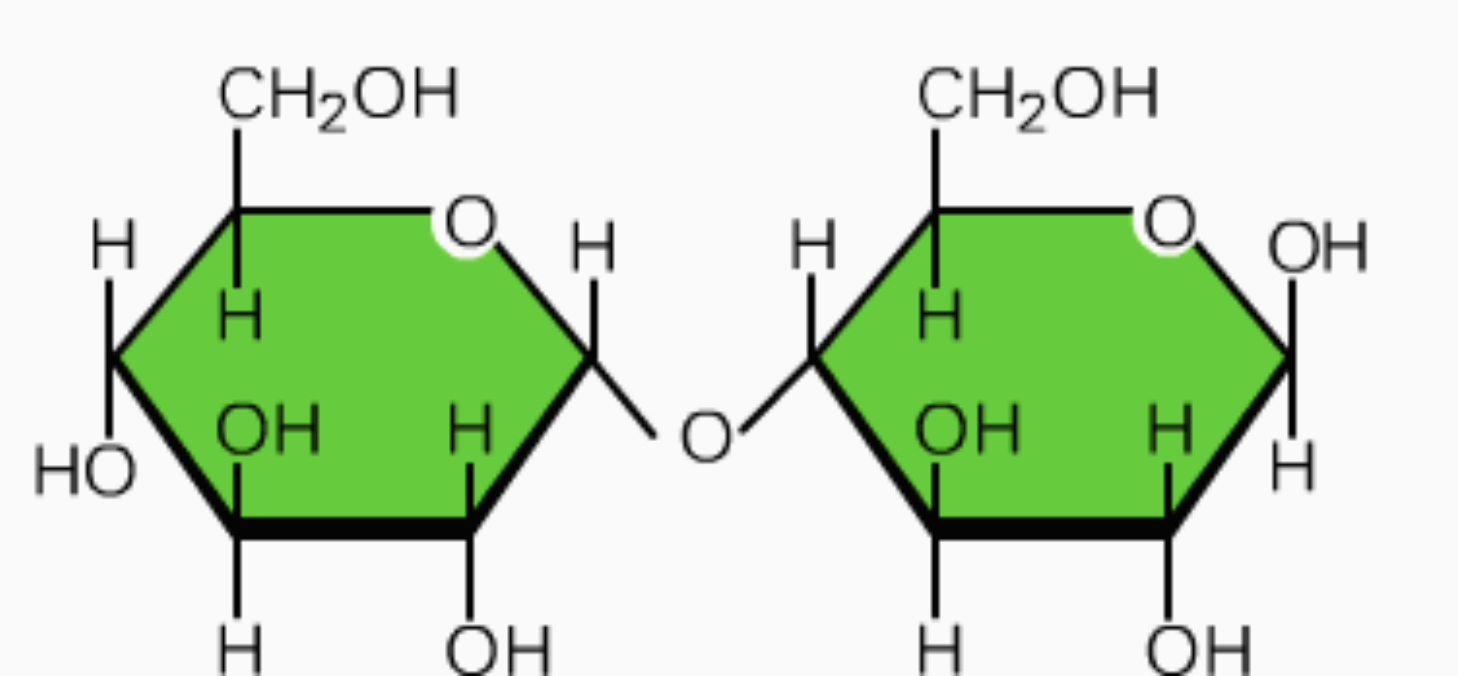
17
New cards
Lactose
• Glucose & Galactose
• Glucose & Galactose
- disaccharide used in transporting the sugar in milk
• give the two monosaccharides bonded
• give the two monosaccharides bonded
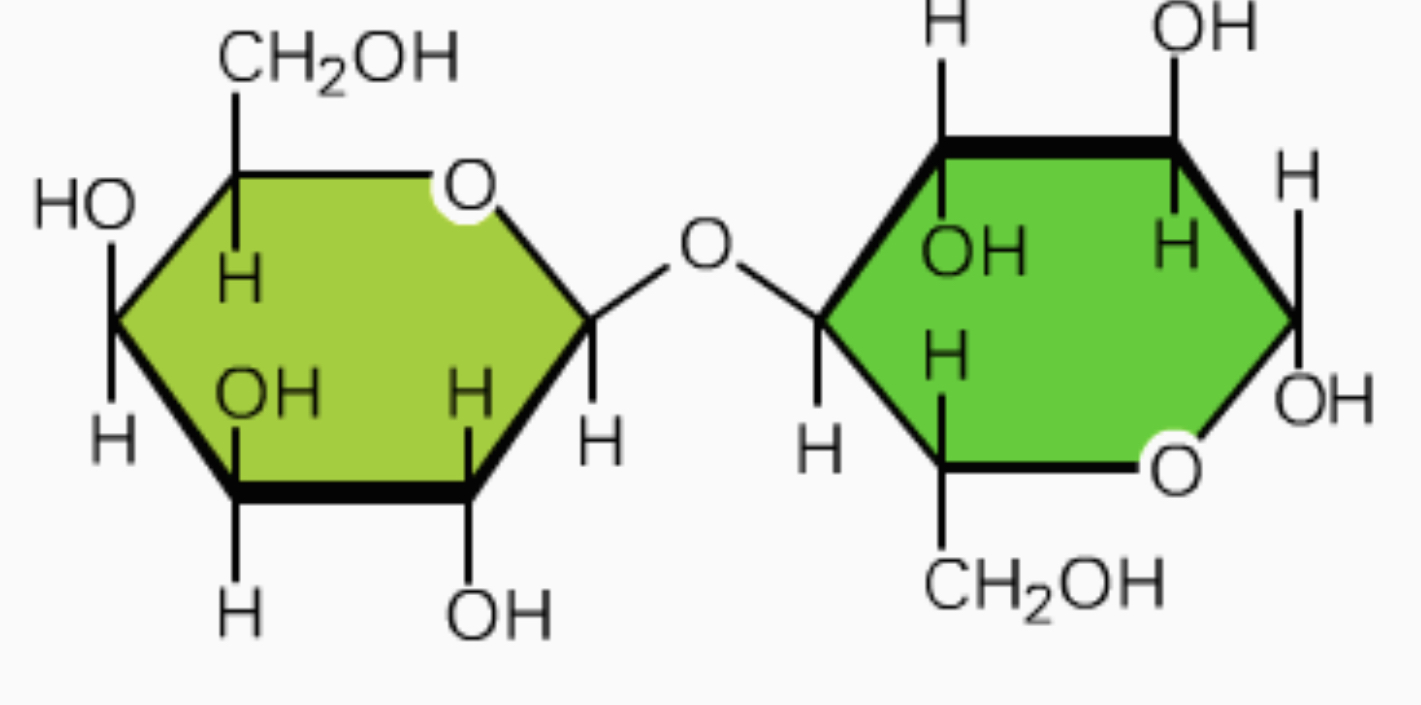
18
New cards
Sucrose
• Glucose & Fructose
• Glucose & Fructose
- disaccharide used in transporting sugar in plants
• give the two monosaccharides bonded
• give the two monosaccharides bonded
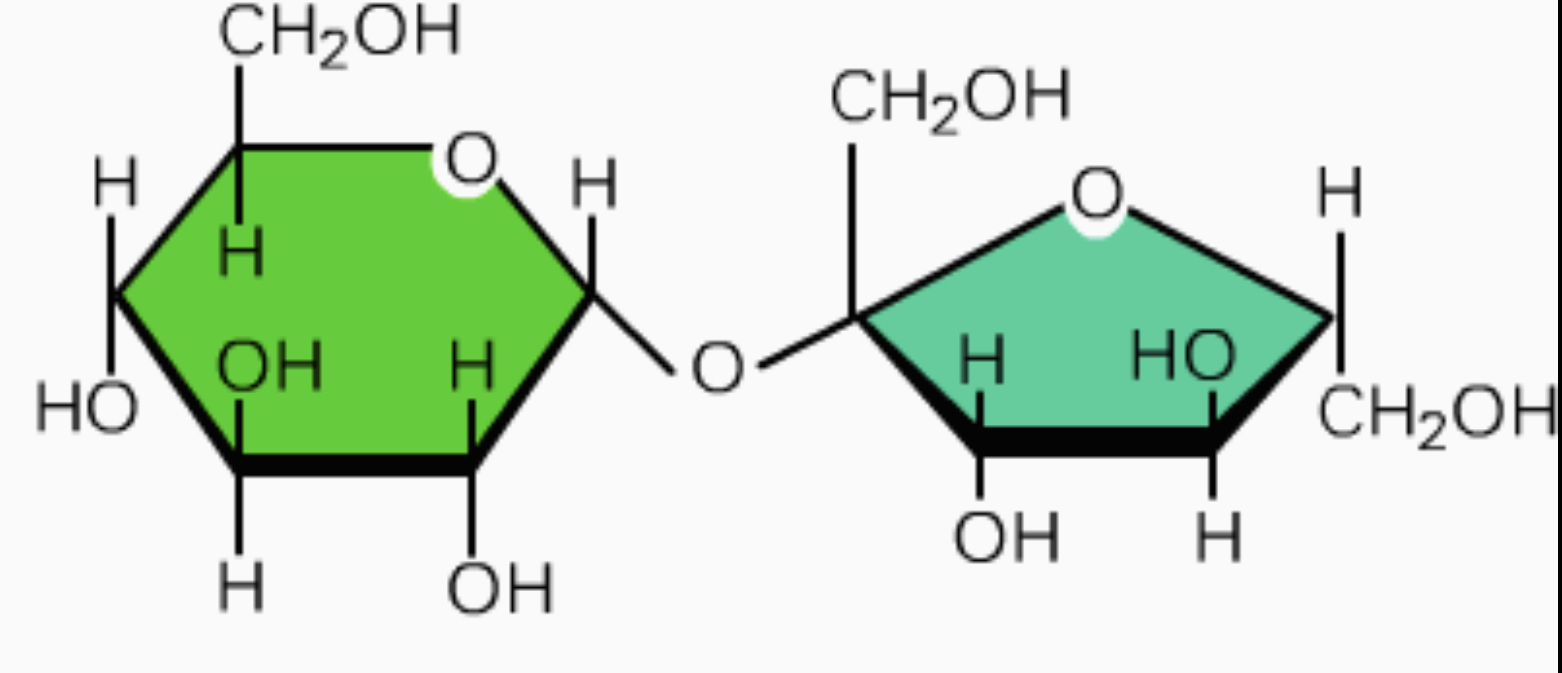
19
New cards
Polysaccharides
- the polymers of sugars, have storage and structural rolls that are determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of glycosidic linkages
20
New cards
Starch
• amylose & amylopectin
• amylose & amylopectin
- a storage polysaccharide of plants, consisting entirely of glucose monomers
- stored in plants as granules within chloroplasts and other plastids
• give the glucose monomers
- stored in plants as granules within chloroplasts and other plastids
• give the glucose monomers
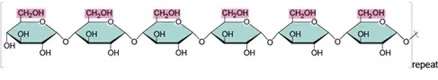
21
New cards
Glycogen
- a storage polysaccharide in animals
- stored mainly in liver and muscle cells of humans and other vertebrates
- stored mainly in liver and muscle cells of humans and other vertebrates
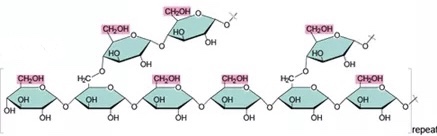
22
New cards
Cellulose
- a structural polysaccharide that is a major component of the tough wall of plant cells
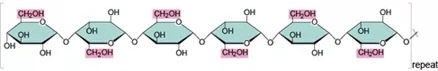
23
New cards
Chitin
- a structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of arthropods
- it also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi
- it also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi
24
New cards
a. Monosaccharide
b. Disaccharide
c. Oligosaccharide
d. Polysaccharide
b. Disaccharide
c. Oligosaccharide
d. Polysaccharide
(c) more than 2
(d) more than 100
(d) more than 100
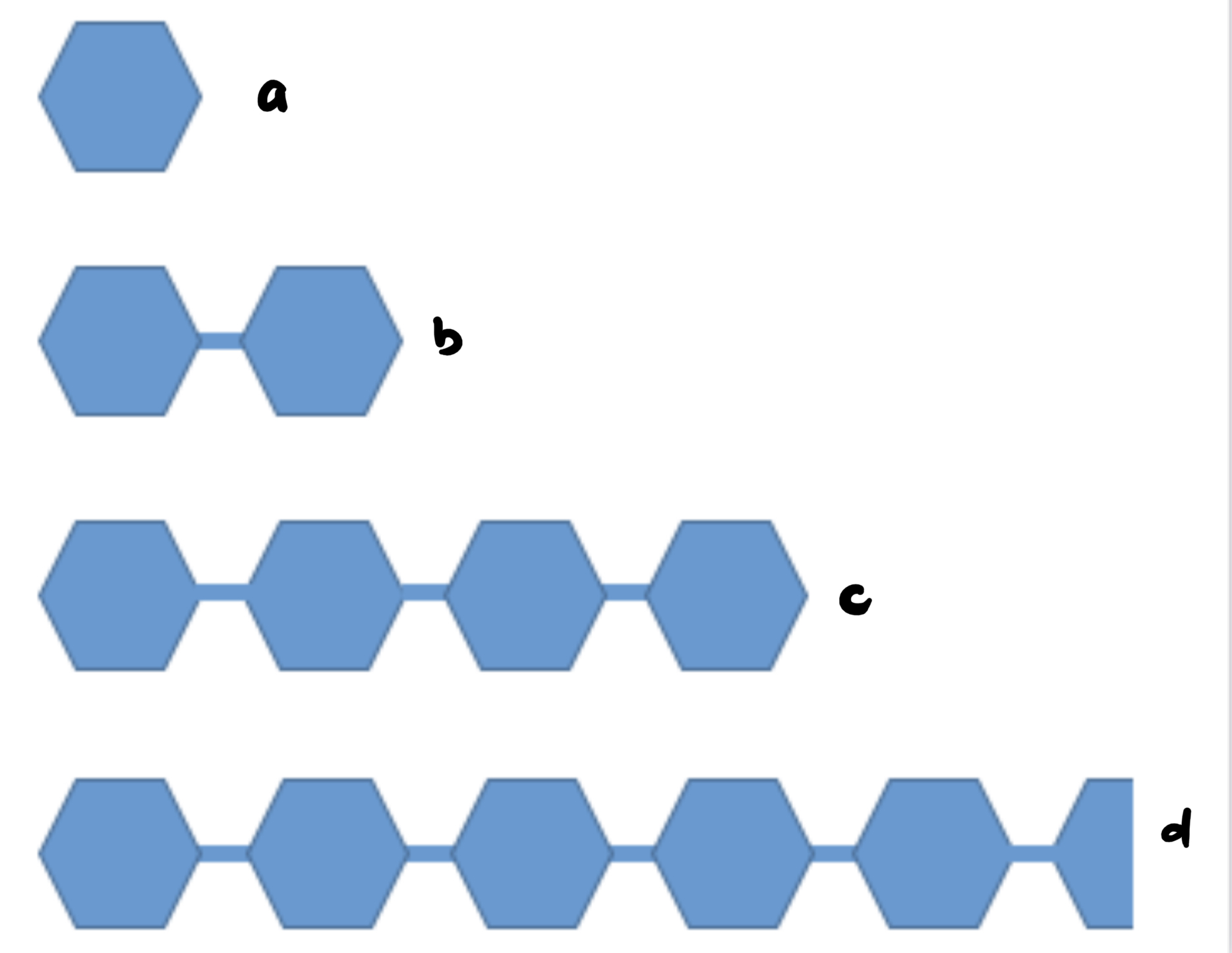
25
New cards
Simple carbohydrates
- also known as sugars, are maid up of shorter chains of molecules and are quicker to digest than complex carbohydrates
26
New cards
Complex carbohydrates
- raises blood glucose levels for longer and produce a more lasting elevation in energy
- provides the body with energy better
- provides the body with energy better
27
New cards
Fiber
- a type of carbohydrate that the body can’t digest
28
New cards
Lipids
- the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers
- are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons which form non-polar covalent bonds
- are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons which form non-polar covalent bonds
29
New cards
Fats
- lipids that are constructed from 2 types of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids
- separates from water because water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and exclude the fats
- its major function is energy storage
- separates from water because water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and exclude the fats
- its major function is energy storage
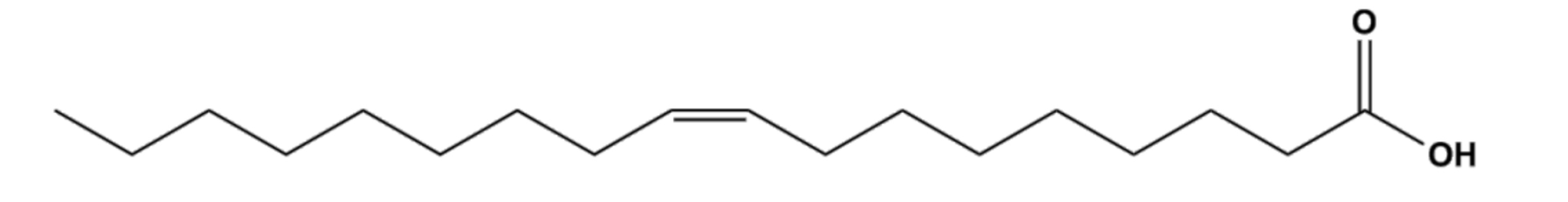
30
New cards
1. Glycerol
2. Fatty Acid
2. Fatty Acid
(1) a three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
(2) consists of carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton; varies in length(number of carbons) and in the number and locations of double bonds
(2) consists of carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton; varies in length(number of carbons) and in the number and locations of double bonds
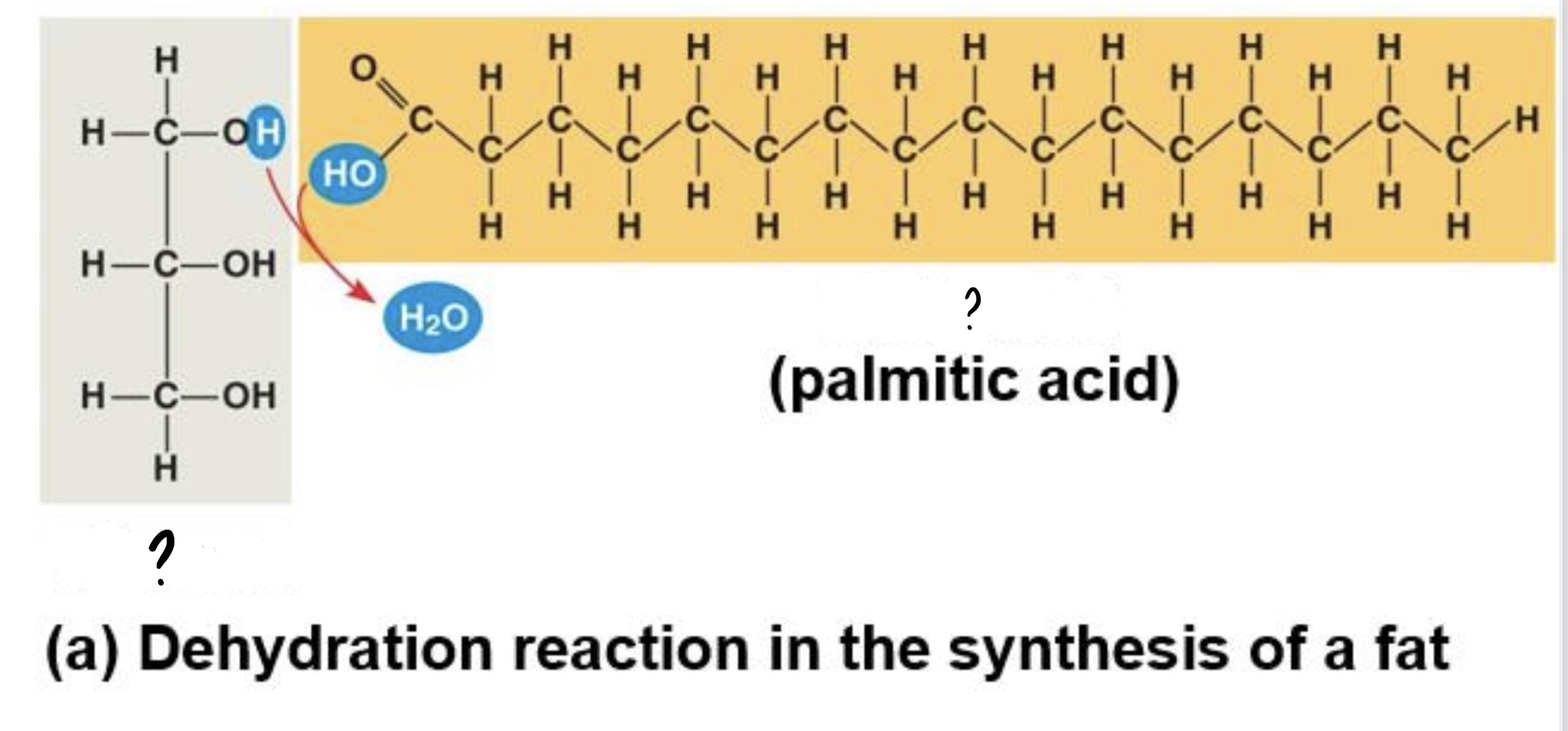
31
New cards
1. Ester linkage
2. Triacylglycerol/triglyceride
2. Triacylglycerol/triglyceride
(1) joins three fatty acids to glycerol
(2) results of (1)
(2) results of (1)
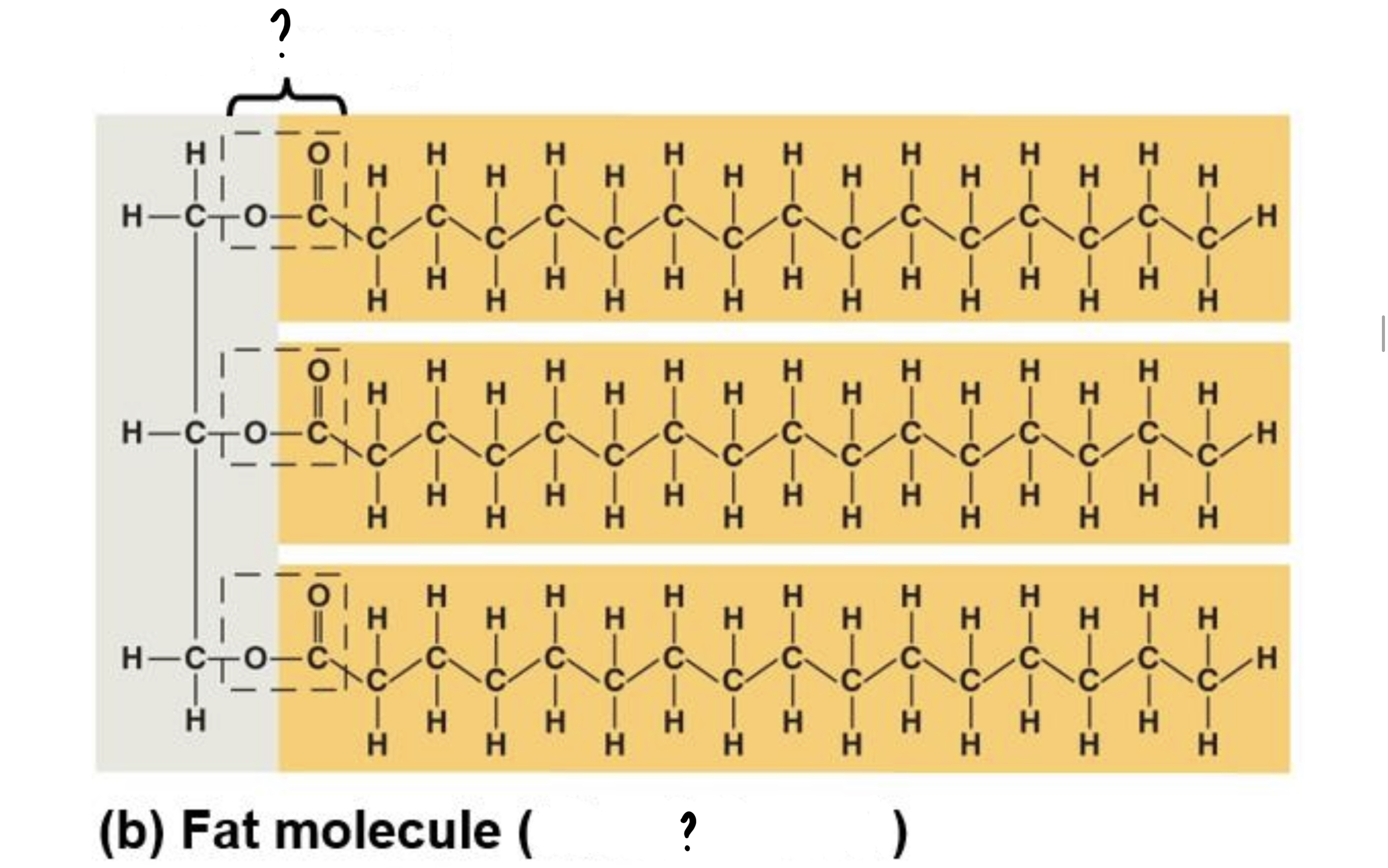
32
New cards
1. Carboxyl group
2. Hydroxyl group
2. Hydroxyl group
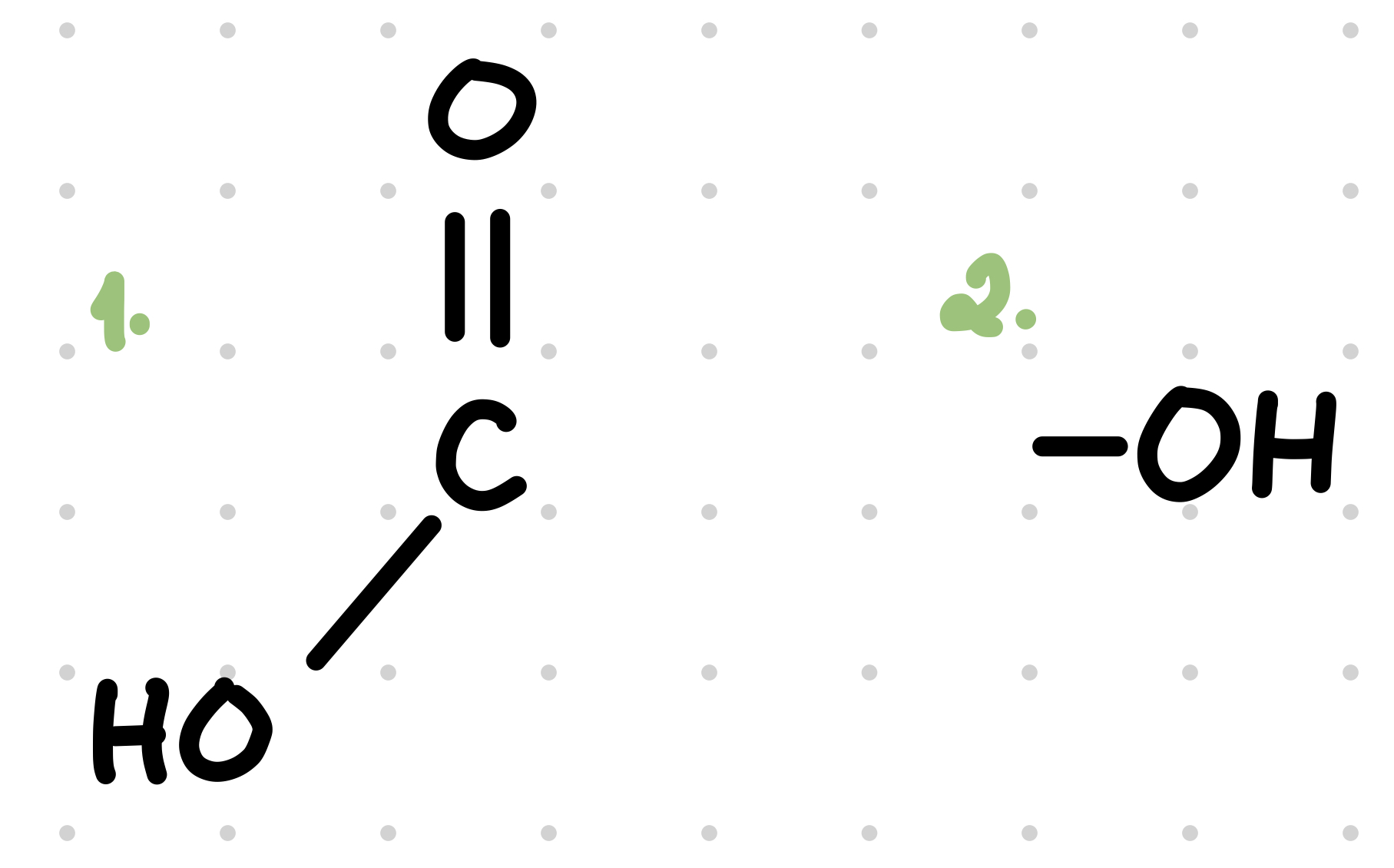
33
New cards
Saturated fatty acids
- fatty acids that have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and NO double bonds
- solid at room temperature
- what most animal fats are
- solid at room temperature
- what most animal fats are
34
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acids
- fatty acids that have one or more double bonds
- liquid at room temperature
- what plant fat and fish fat are
- liquid at room temperature
- what plant fat and fish fat are
35
New cards
a. Cis fat
b. Trans fat
b. Trans fat
• indicate the configuration of the molecule around the double bond
(a) if hydrogen are present in the same plane; causes bending
(b) if the hydrogen atoms are on 2 different planes
(a) if hydrogen are present in the same plane; causes bending
(b) if the hydrogen atoms are on 2 different planes
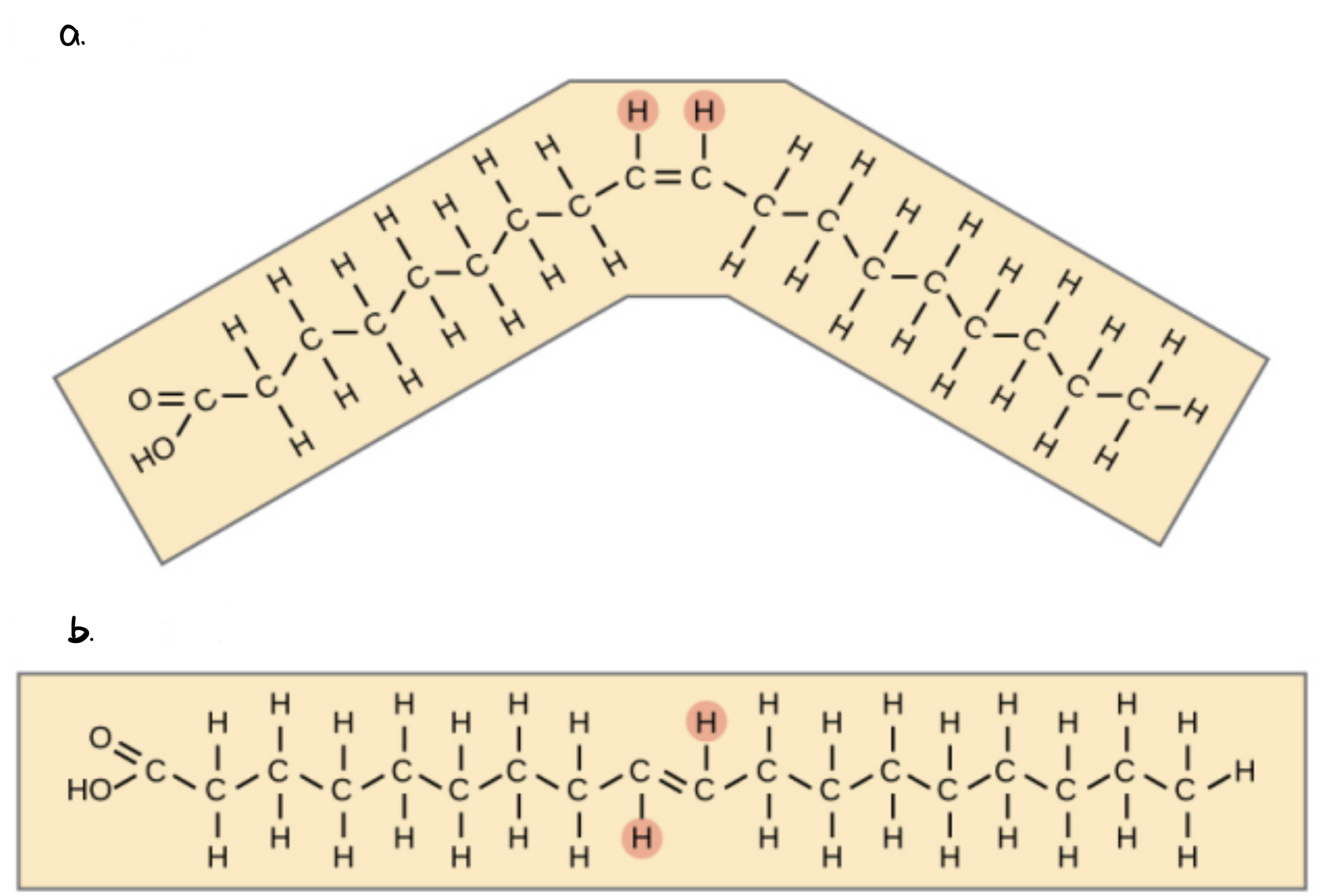
36
New cards
Phospholipids
- where 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group are attached to glycerol
- the major component of all cell membranes
- the major component of all cell membranes
37
New cards
Phospholipid bilayer
a. hydrophobic
b. hydrophilic
a. hydrophobic
b. hydrophilic
- result from the structure of phospholipids found in cell membranes
(a) the 2 fatty acid tails in a phospholipid; points toward the interior when phospholipids are added to water
(b) the phosphate group in a phospholipid and its attachment
(a) the 2 fatty acid tails in a phospholipid; points toward the interior when phospholipids are added to water
(b) the phosphate group in a phospholipid and its attachment
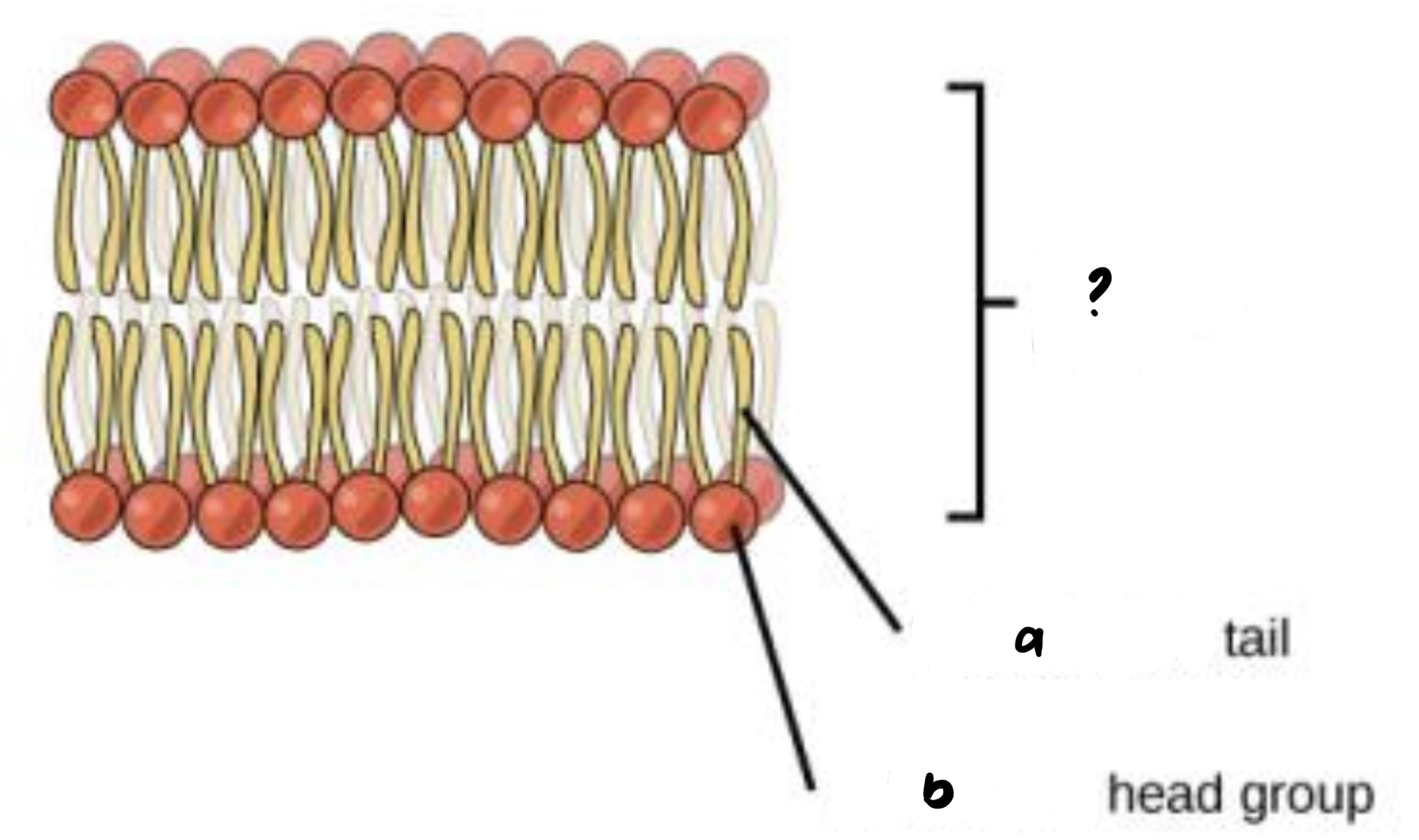
38
New cards
Steroids
- lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
39
New cards
Cholesterol
- an important steroid, is a component in animal cell membranes
- essential in animals but high levels in blood may contribute to cardiovascular disease
- essential in animals but high levels in blood may contribute to cardiovascular disease
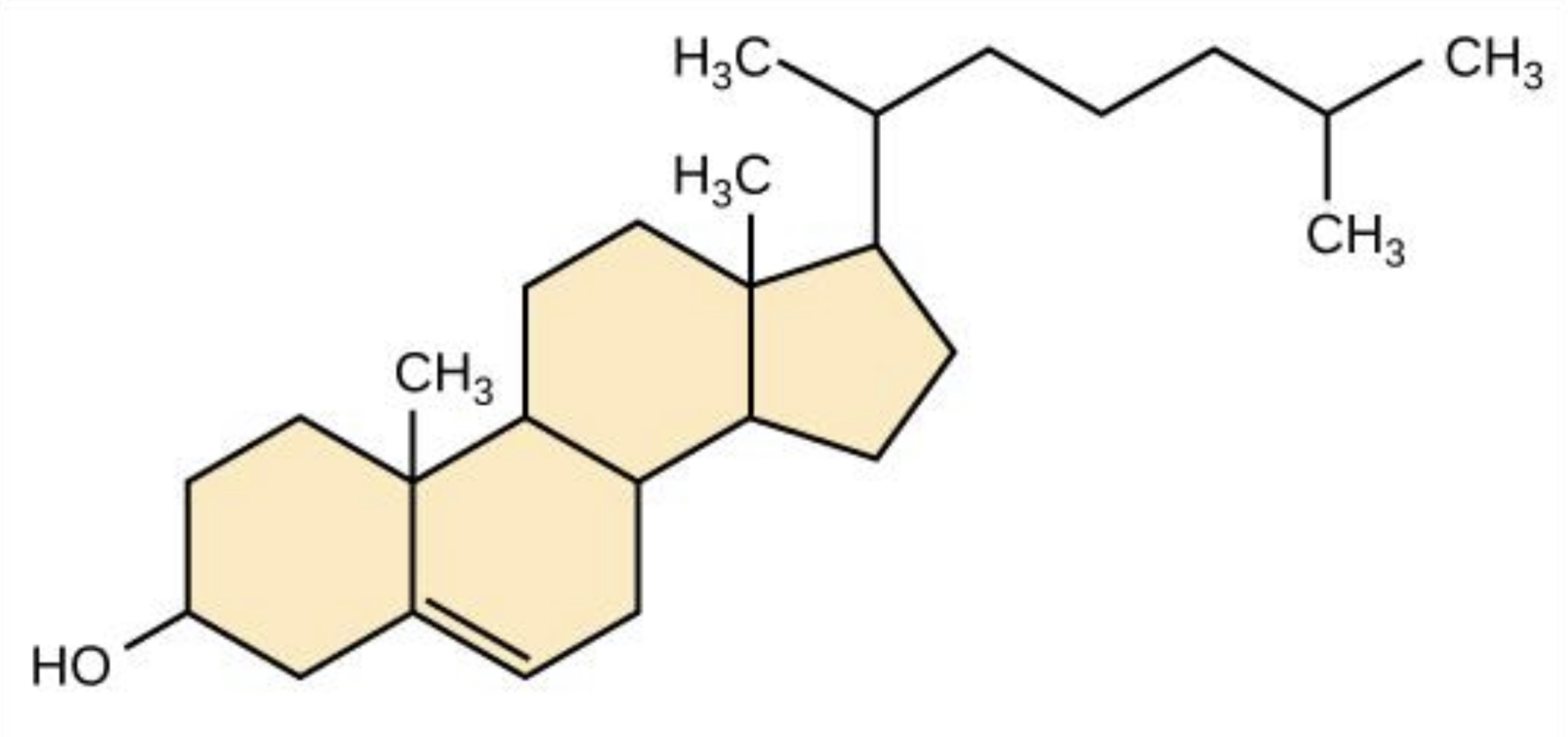
40
New cards
Cortisol
- a steroid hormone that when released, raised your cholesterol level
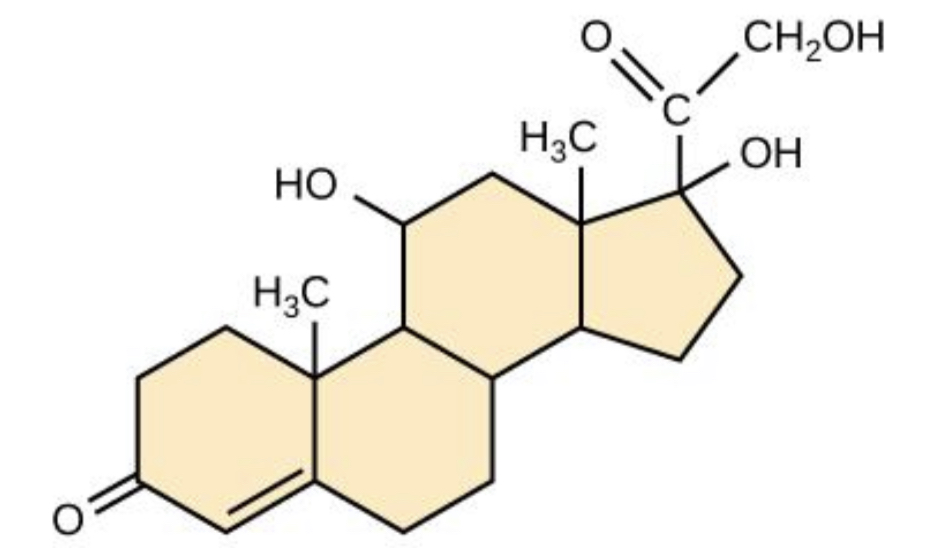
41
New cards
a. cortisol b. corticosterone c. aldosterone d. progesterone e. Beta-estradiol f. testosterone
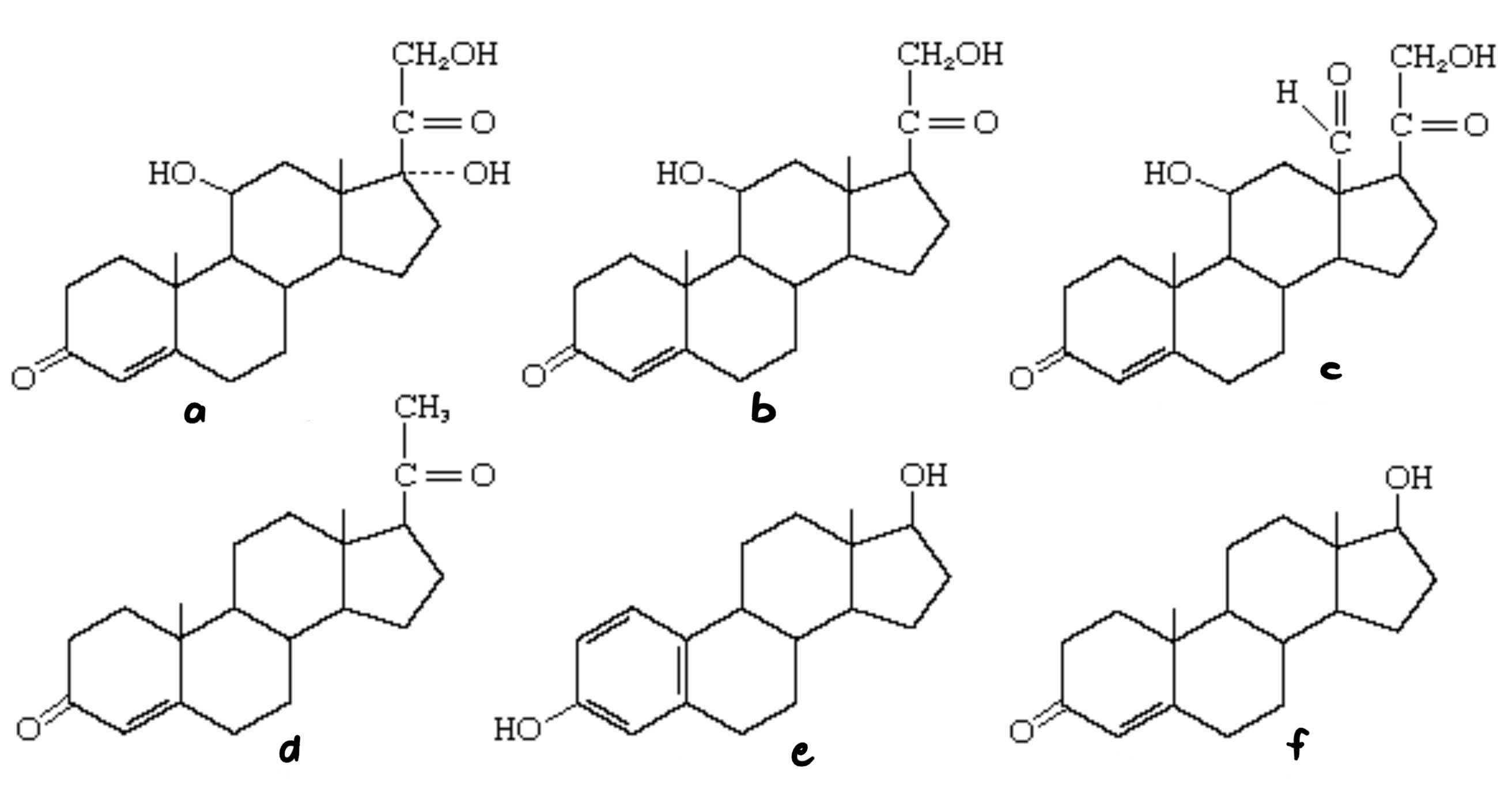
42
New cards
Glycolipids
- a type of complex lipids comprising carbohydrates, fatty acids, sphingolipids or a glycerol group
- mainly describe any compound containing one or more monosaccharides residues bound by glycosidic linkage
- found on the leaflet of cellular membranes
- maintains membrane stability & facilitates cell-cell communication
- mainly describe any compound containing one or more monosaccharides residues bound by glycosidic linkage
- found on the leaflet of cellular membranes
- maintains membrane stability & facilitates cell-cell communication
43
New cards
Proteins
• Hemoglobin
• Hemoglobin
- account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells
• give the protein that helps in the transfer of oxygen in blood
• give the protein that helps in the transfer of oxygen in blood
44
New cards
Enzymatic proteins
Function: selective acceleration of chemical reactions
Example: Digestive ________ catalyze the hydrolysis of bonds in food molecules
Example: Digestive ________ catalyze the hydrolysis of bonds in food molecules
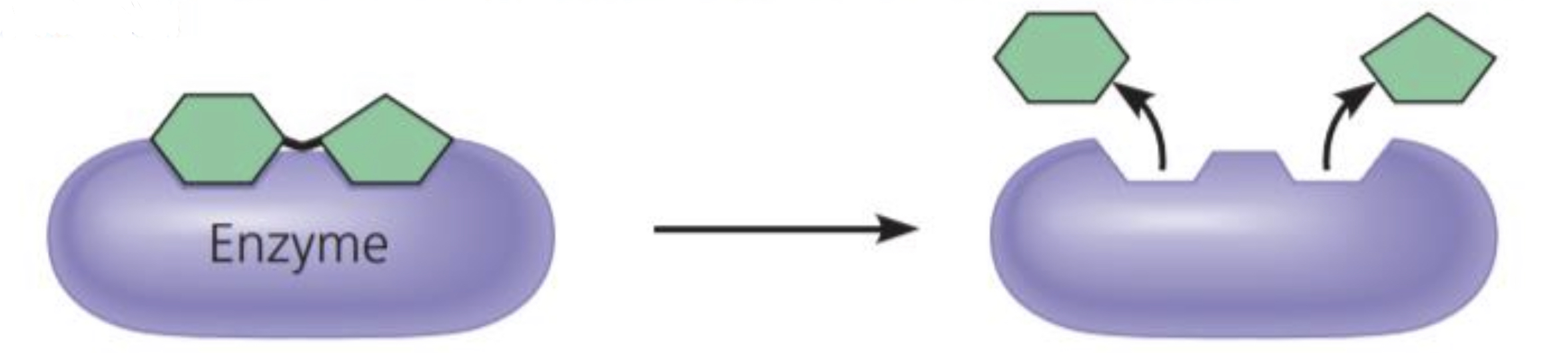
45
New cards
Storage proteins
Function: Storage of amino acids
Examples: CASEIN, the protein of milk, is the major source of amino acids for baby mammals. Plants have storage proteins in their seeds. OVALBUIM is the protein of egg white
Examples: CASEIN, the protein of milk, is the major source of amino acids for baby mammals. Plants have storage proteins in their seeds. OVALBUIM is the protein of egg white
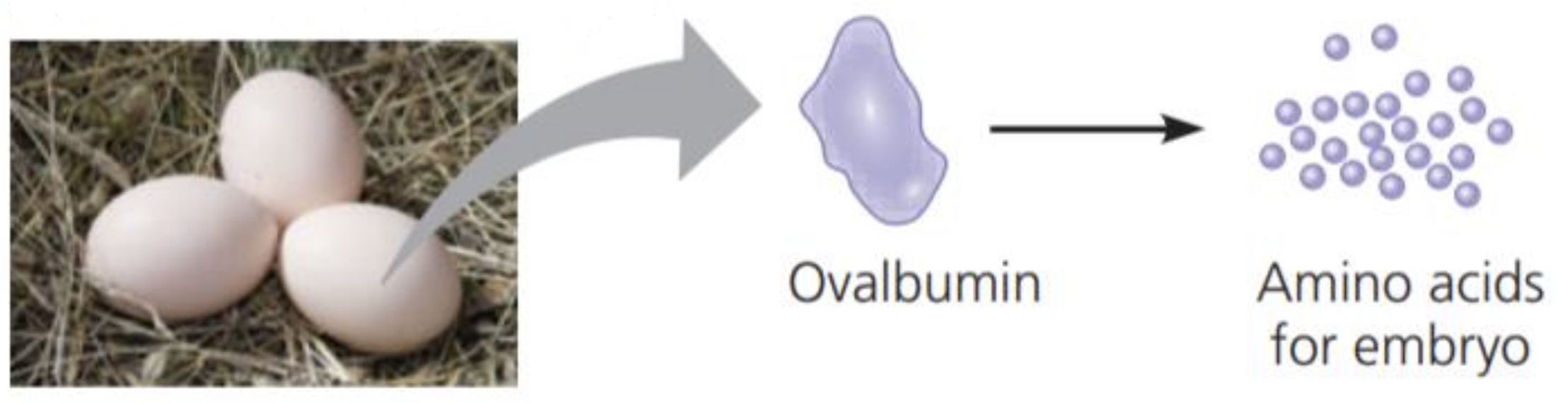
46
New cards
Defensive proteins
Function: protection against disease
Example: Antibodies inactivate and help destroy viruses and bacteria
Example: Antibodies inactivate and help destroy viruses and bacteria
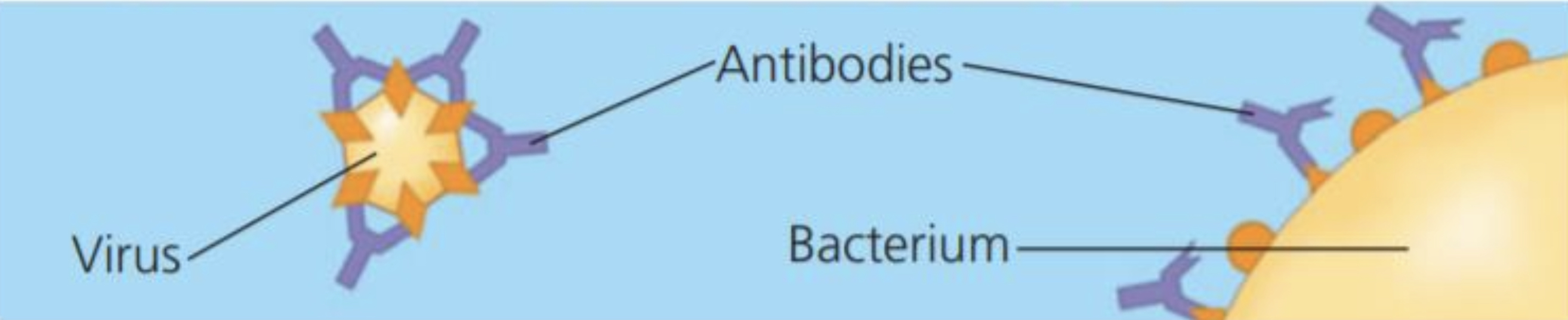
47
New cards
Transport proteins
Function: transport of substances
Example: HEMOGLOBIN, the iron-containing protein of vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body
Example: HEMOGLOBIN, the iron-containing protein of vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body
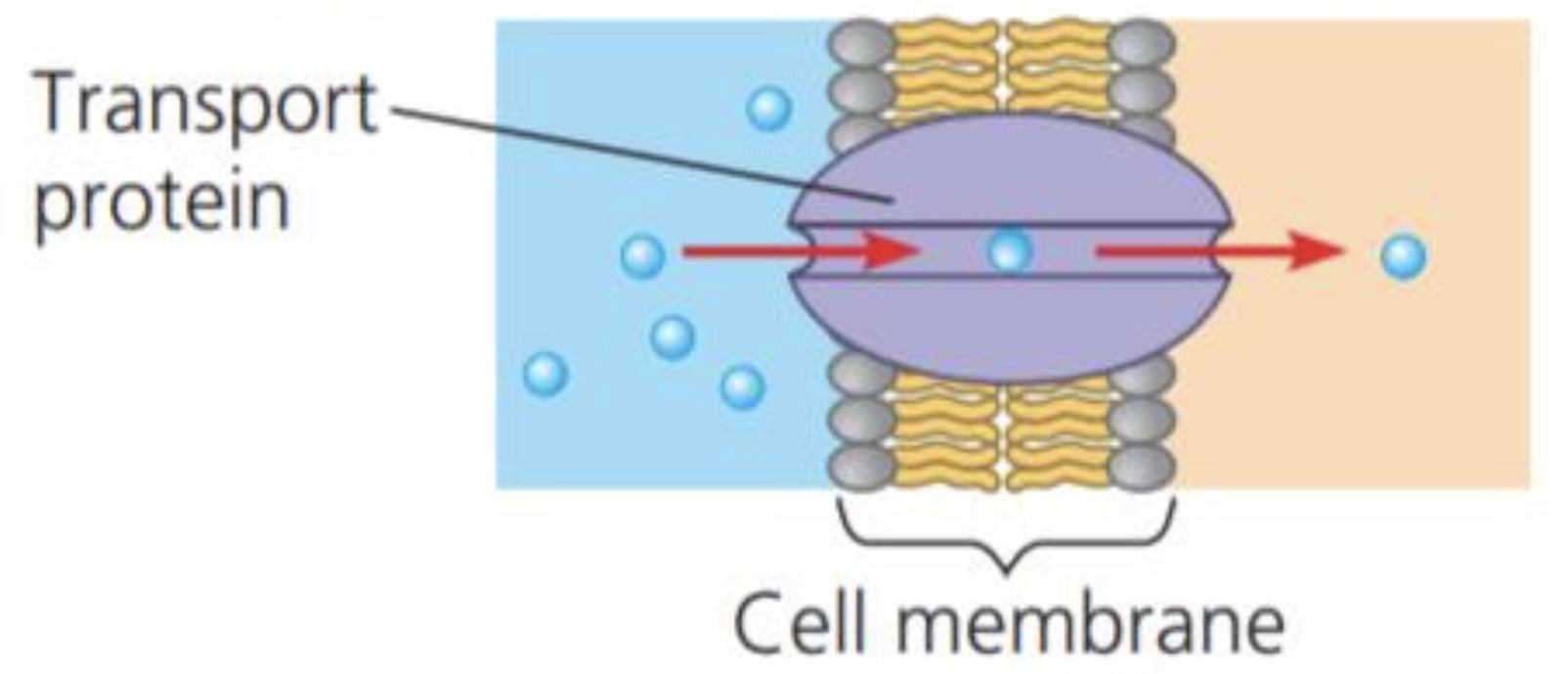
48
New cards
Hormonal proteins
Function: coordination of an organism’s activities
Example: INSULIN, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, causes other tissues to take up glucose, thus regulating blood sugar concentration
Example: INSULIN, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, causes other tissues to take up glucose, thus regulating blood sugar concentration
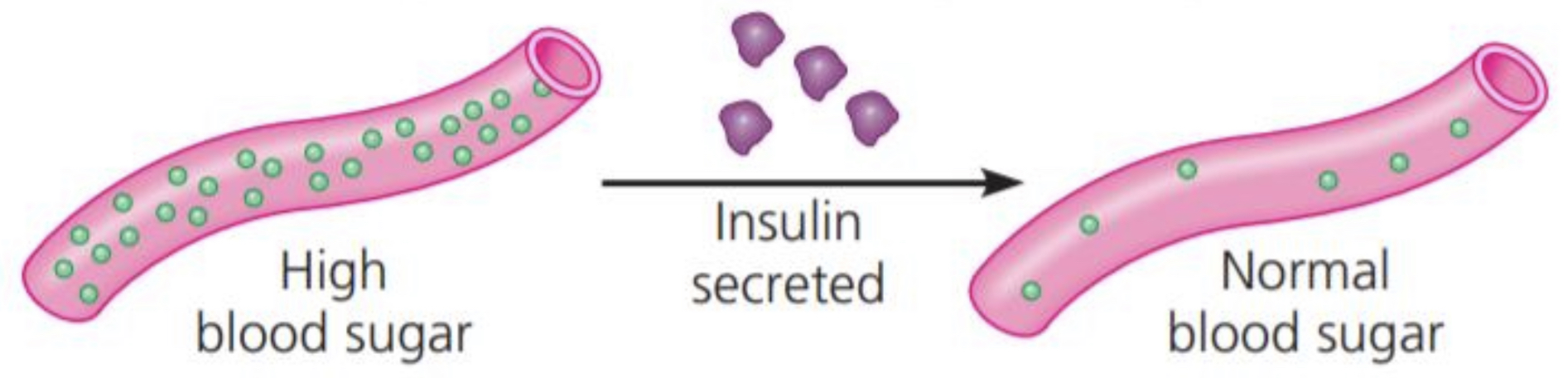
49
New cards
Receptor protein
Function: response of cell to chemical stimuli
Example: receptors built into the membrane of a nerve cell detect signaling molecules released by other nerve cells
Example: receptors built into the membrane of a nerve cell detect signaling molecules released by other nerve cells
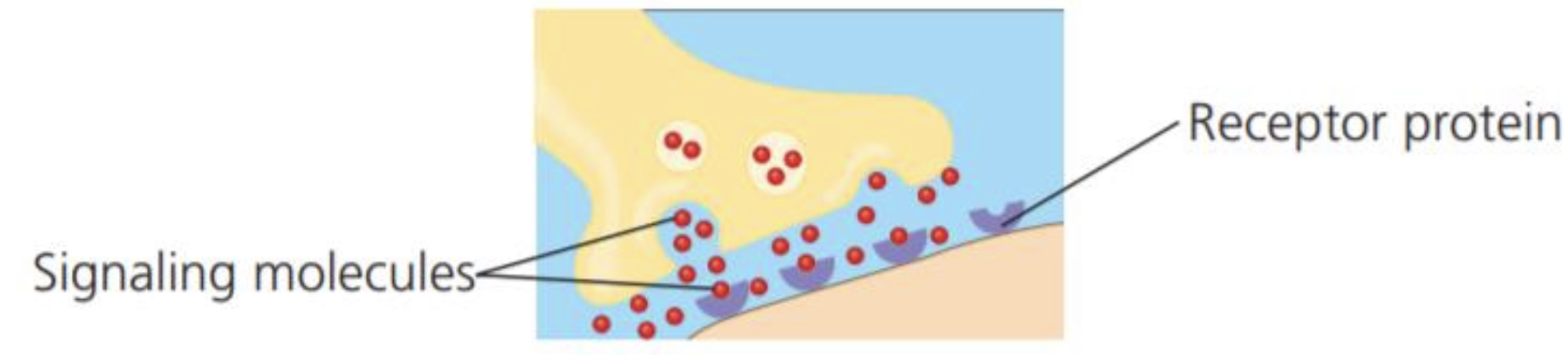
50
New cards
Structural proteins
Function: support
Examples: KERATIN is the protein of hair, horns, feather and other skin appendages. COLLAGEN and ELASTIN proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues
Examples: KERATIN is the protein of hair, horns, feather and other skin appendages. COLLAGEN and ELASTIN proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues
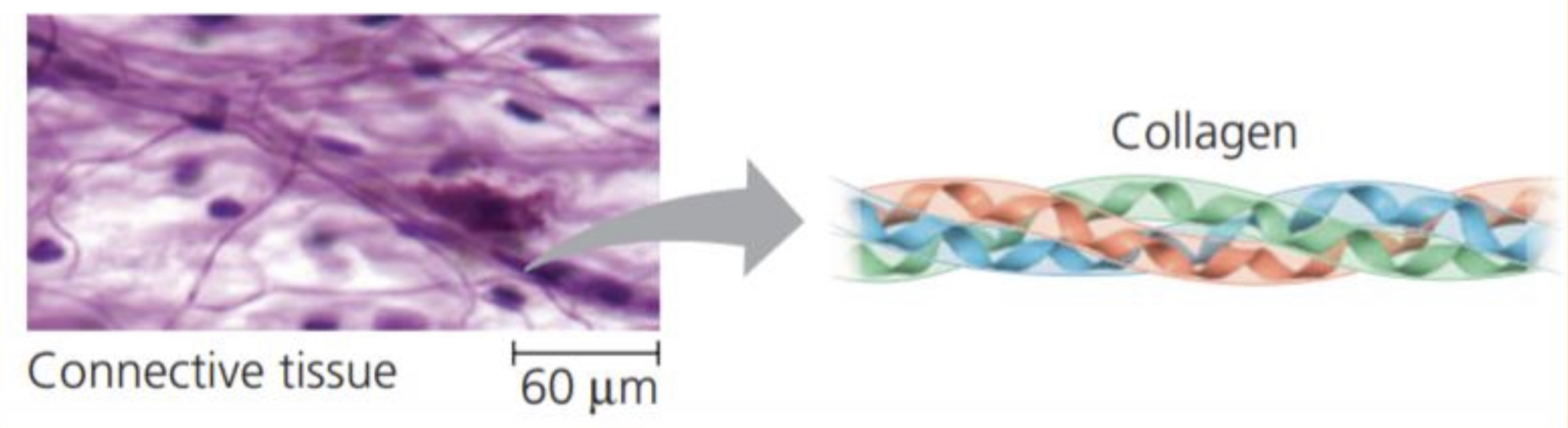
51
New cards
Contractile & motor proteins
Functions: movement
Examples: Motor proteins are responsible for the undulations of cilia and flagella ACTIN and MYOSIN proteins are responsible for the contraction of muscles
Examples: Motor proteins are responsible for the undulations of cilia and flagella ACTIN and MYOSIN proteins are responsible for the contraction of muscles
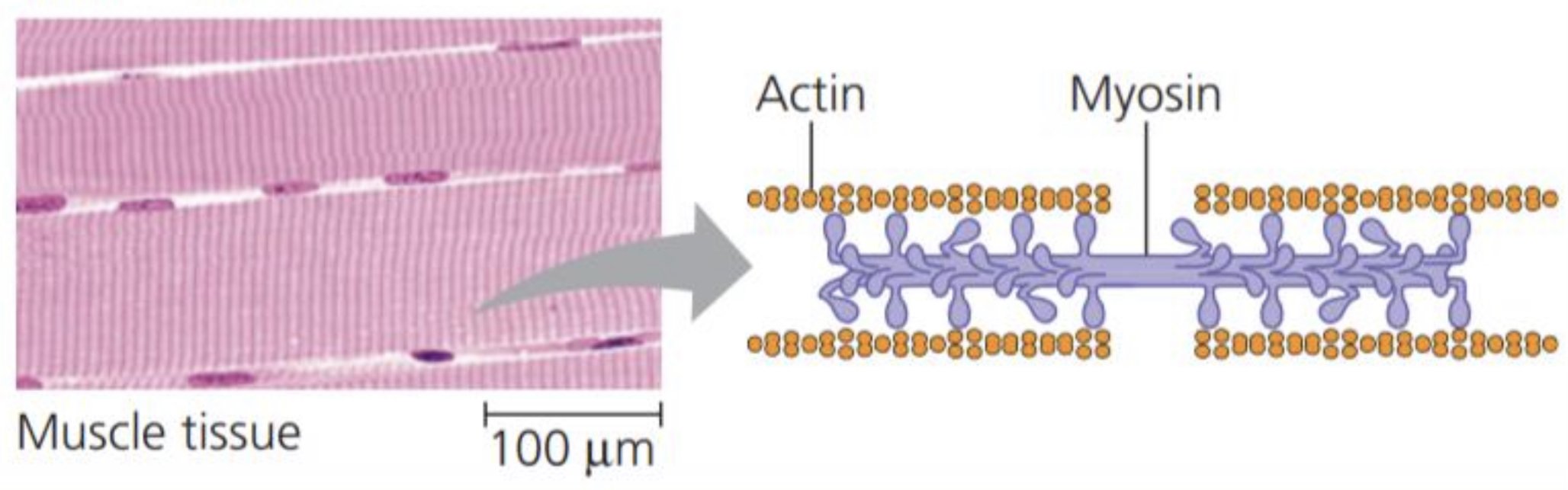
52
New cards
Gene Regulatory proteins
- Bind to DNA in particular locations and determine whether or not certain genes will be read.
- Allows cell to becomes specialized for different functions and respond to changes in their surroundings
- Allows cell to becomes specialized for different functions and respond to changes in their surroundings
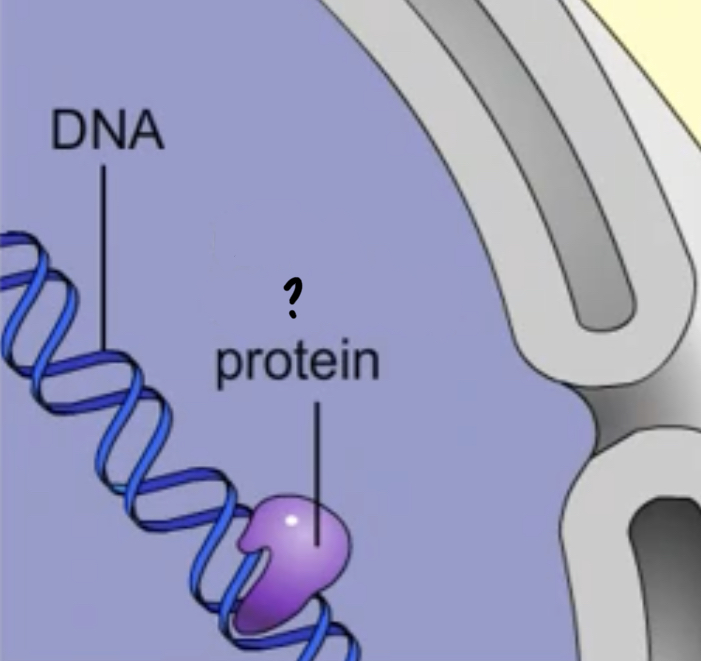
53
New cards
Sensory proteins
- detect environmental changes like light and respond by emitting or producing signals that call for a response
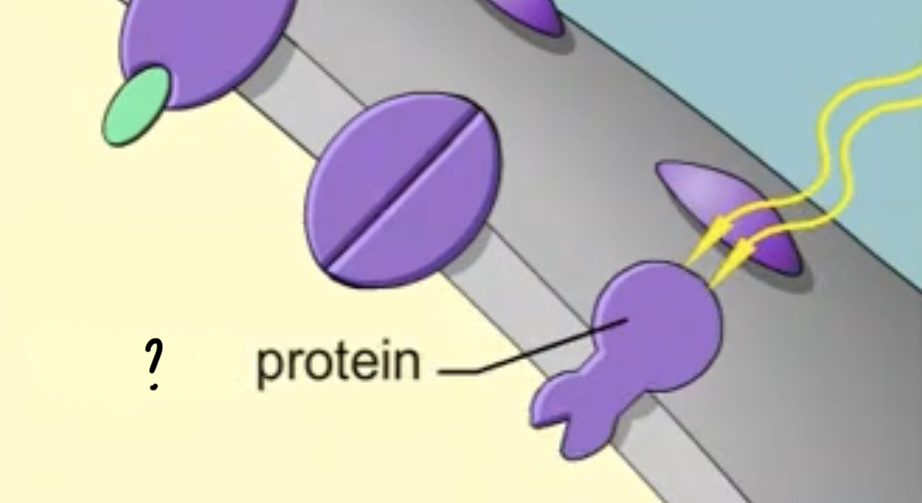
54
New cards
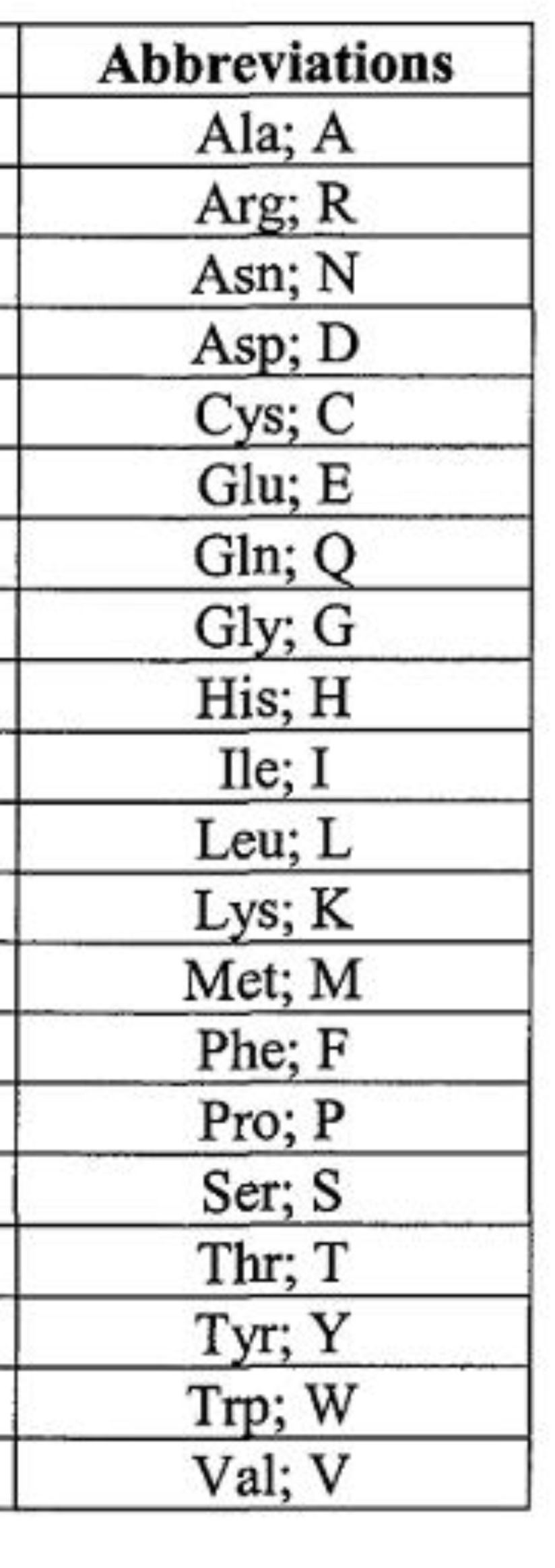
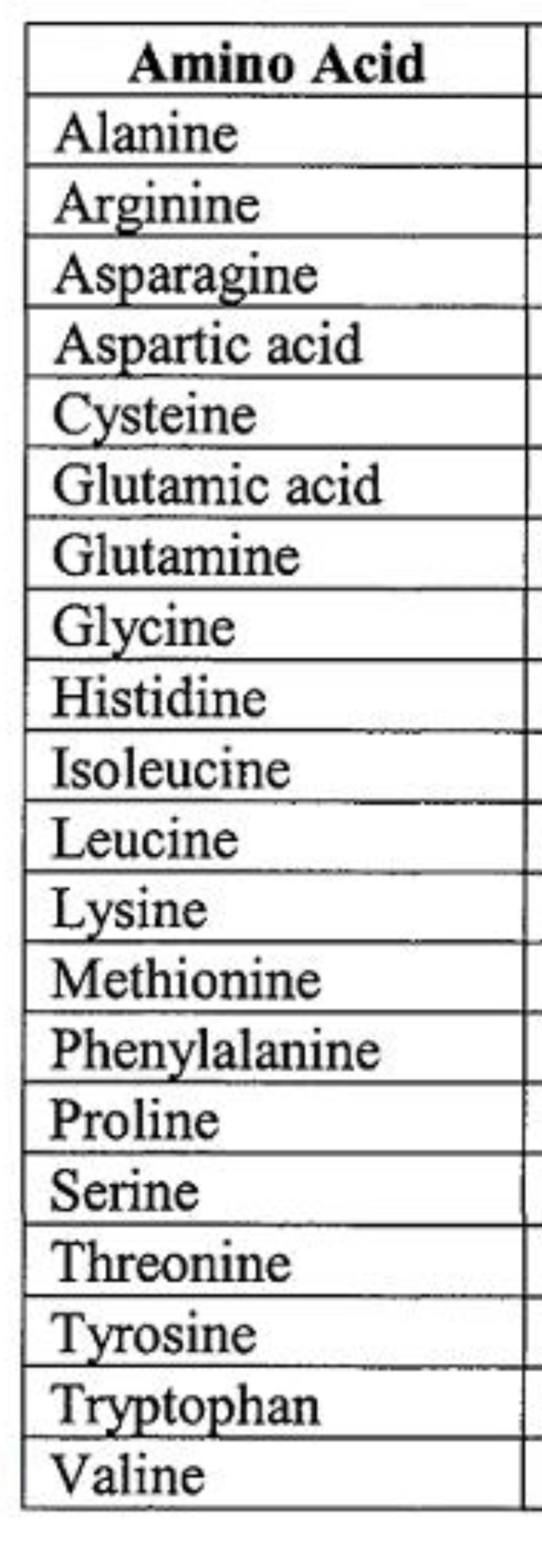
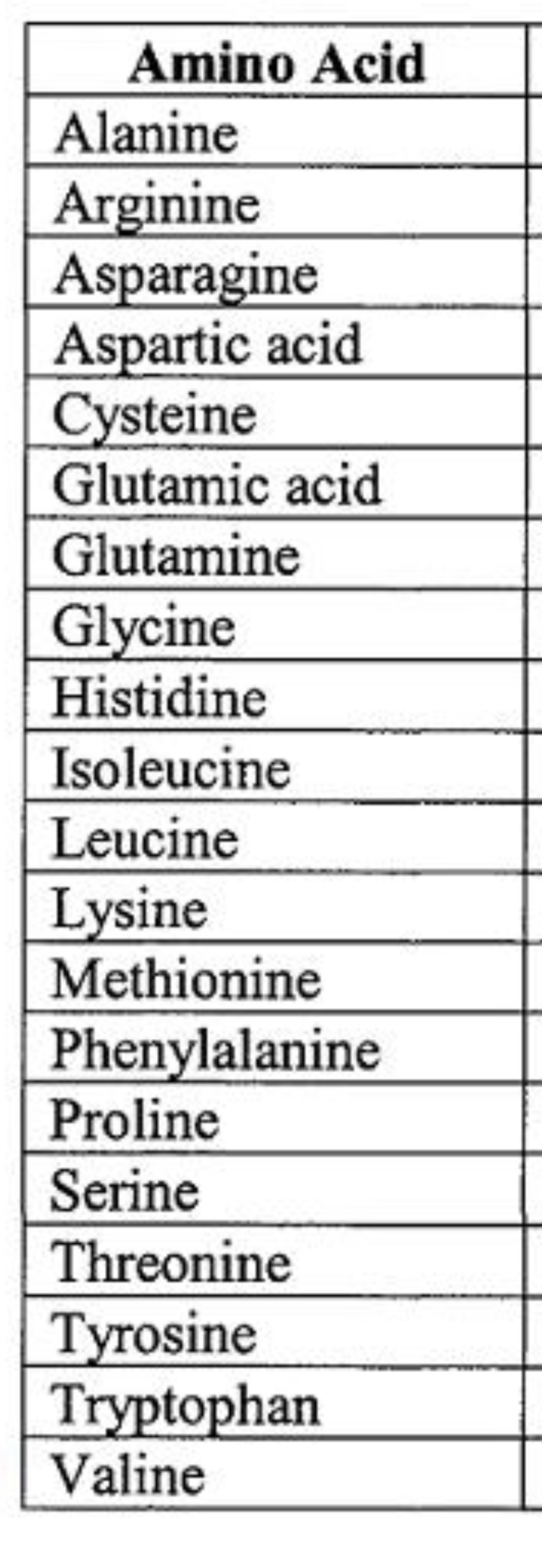
a. Amino acids
b. Polypeptide
c. Protein
b. Polypeptide
c. Protein
(a) Are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
(b) polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids
(c) consist of one or more polypeptides
(b) polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids
(c) consist of one or more polypeptides
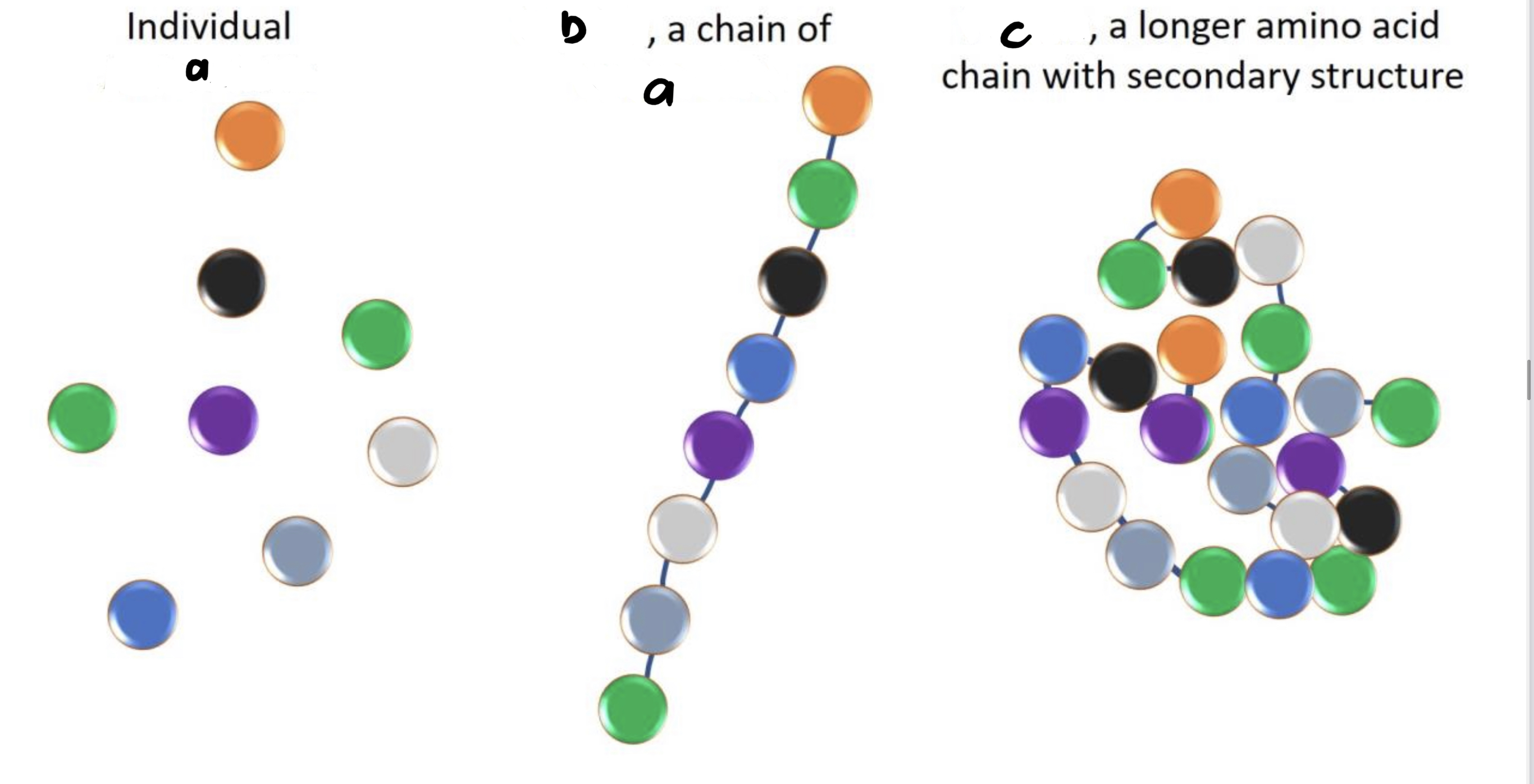
55
New cards
Amino group

56
New cards
R groups
- the differing chains that differ the properties of amino acids
57
New cards
58
New cards
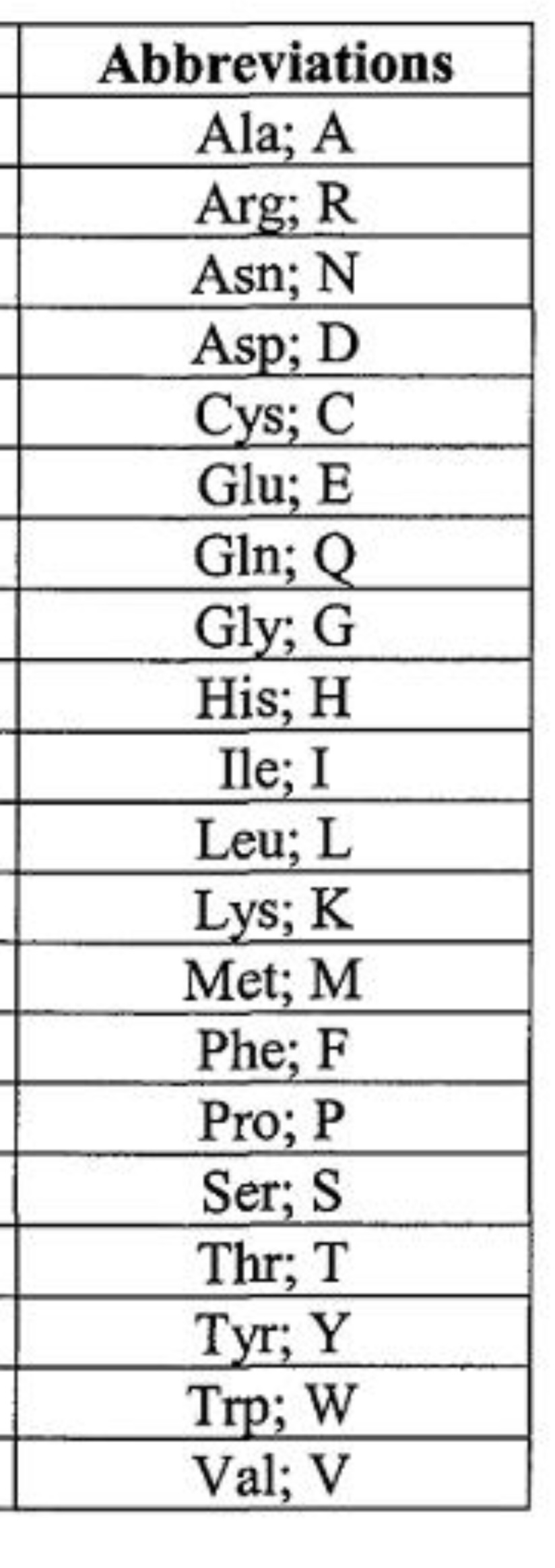
59
New cards
Glycine (Gly/G)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
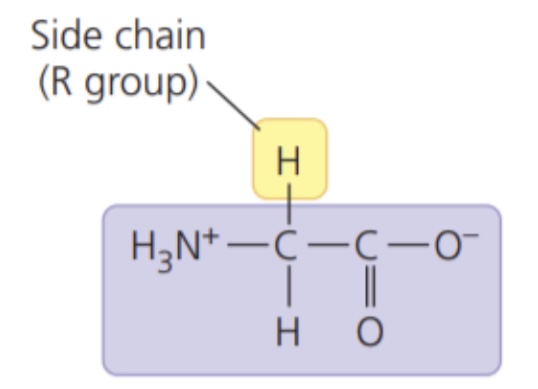
60
New cards
Alanine (Ala/A)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
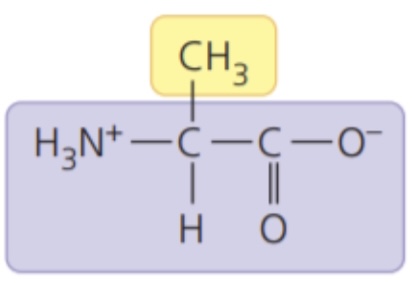
61
New cards
Valine (Val/V)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
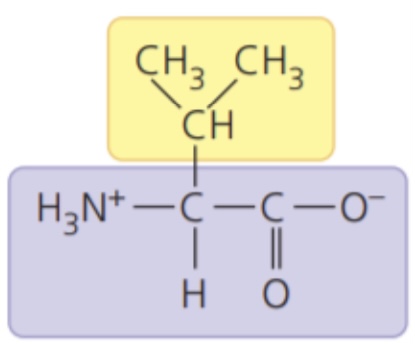
62
New cards
Leucine (Leu/L)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
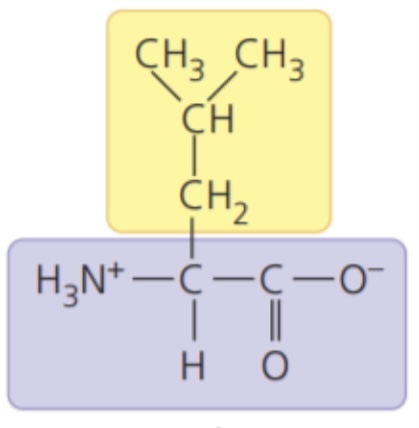
63
New cards
Isoleucine (Ile/I)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
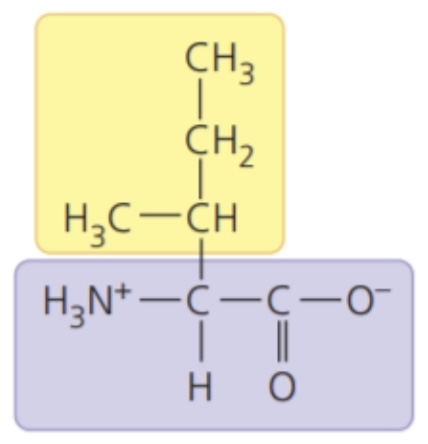
64
New cards
Methionine (Met/M)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
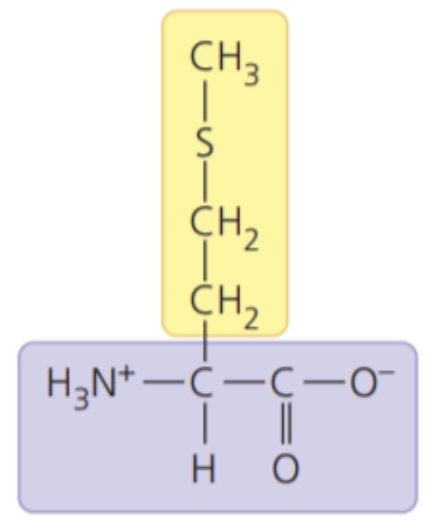
65
New cards
Phenylalanine (Phe/F)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
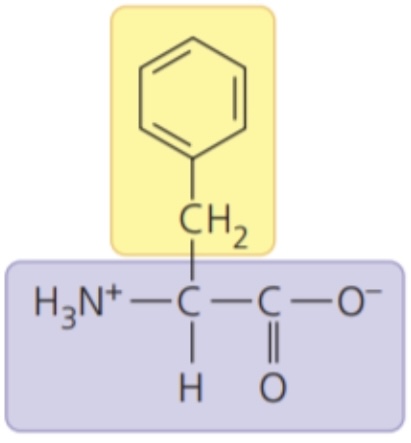
66
New cards
Tryptophan (Trp/W)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
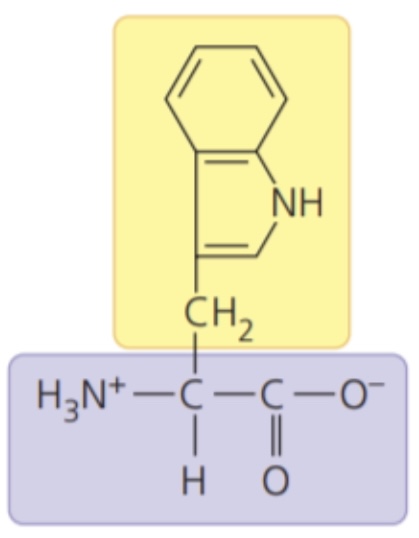
67
New cards
Proline (Pro/P)
- nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic
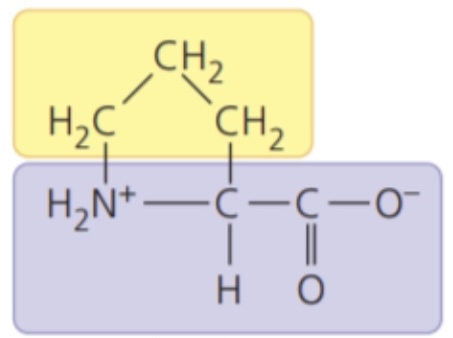
68
New cards
Serine (Ser/S)
- polar side chains; hydrophilic
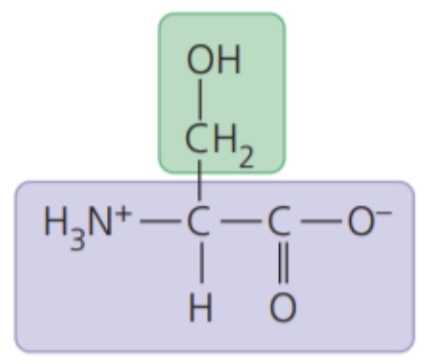
69
New cards
Threonine (Thr/T)
- polar side chains; hydrophilic
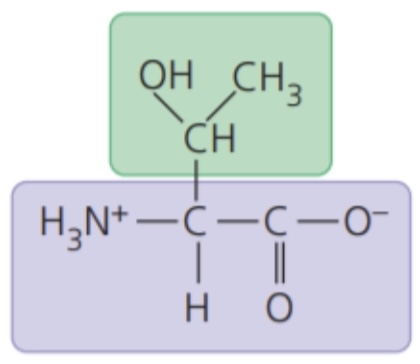
70
New cards
Cysteine (Cys/C)
- polar side chains; hydrophilic
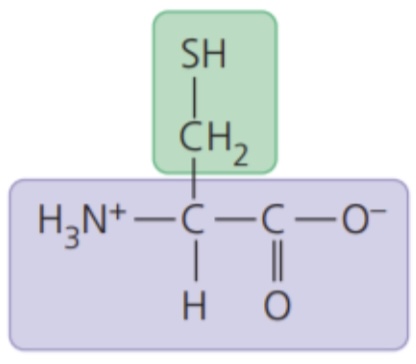
71
New cards
Tyrosine (Tyr/Y)
- polar side chains; hydrophilic
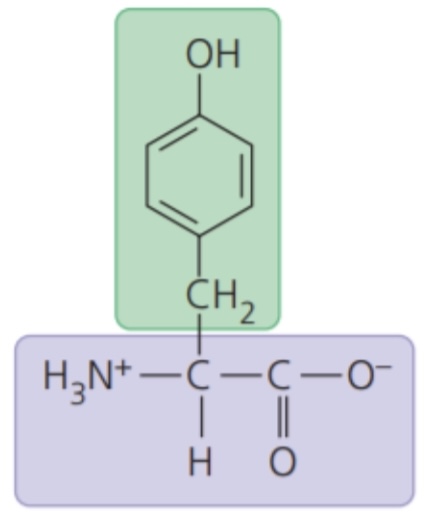
72
New cards
Asparagine (Asn/N)
- polar side chains; hydrophilic
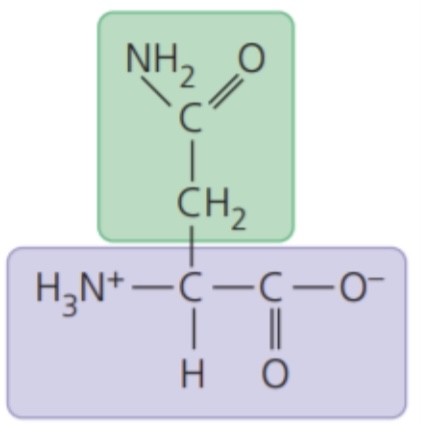
73
New cards
Glutamine (Gln/Q)
- polar side chains; hydrophilic
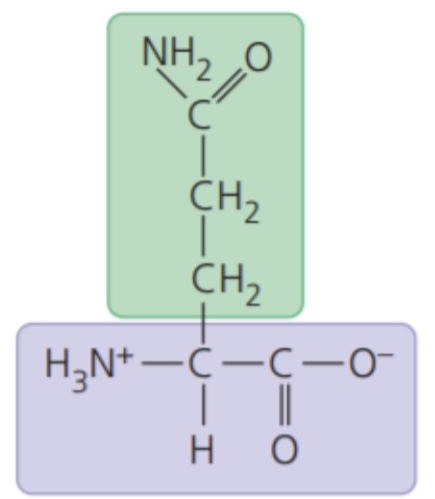
74
New cards
Asparitic acid (Asp/D)
- electrically charged side chains; hydrophilic
- Acidic(negatively charged)
- Acidic(negatively charged)
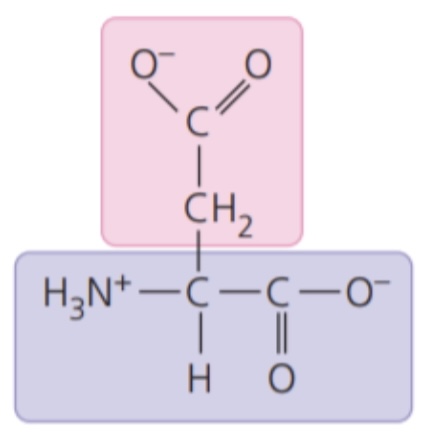
75
New cards
Glutamic acid (Glu/E)
- electrically charged side chains; hydrophilic
- Acidic(negatively charged)
- Acidic(negatively charged)
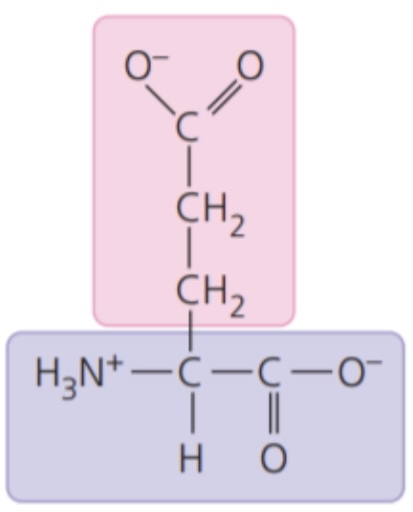
76
New cards
Lysine (Lys/K)
- electrically charged side chains; hydrophilic
- Basic (positively charged)
- Basic (positively charged)
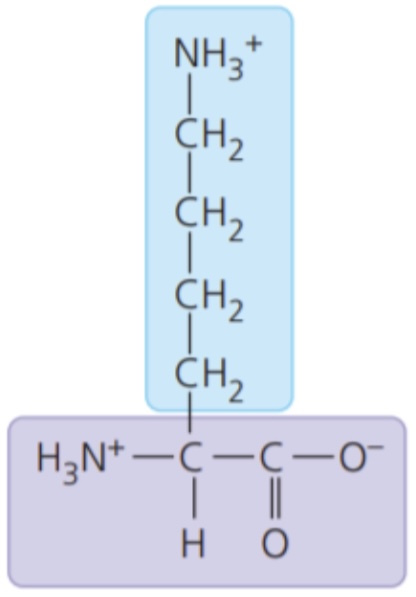
77
New cards
Arginine (Arg/R)
- electrically charged side chains; hydrophilic
- Basic (positively charged)
- Basic (positively charged)
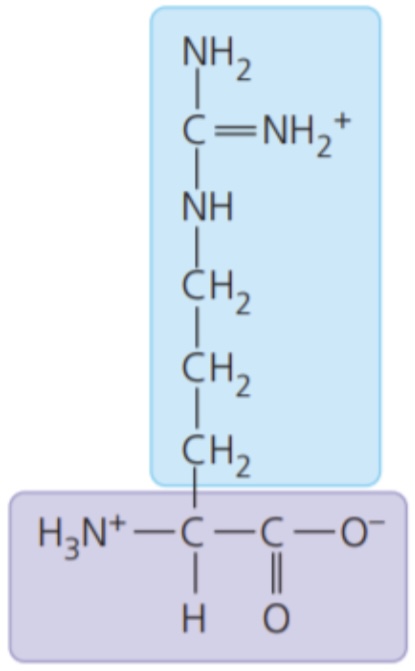
78
New cards
Histidine (His/H)
- electrically charged side chains; hydrophilic
- Basic (positively charged)
- Basic (positively charged)
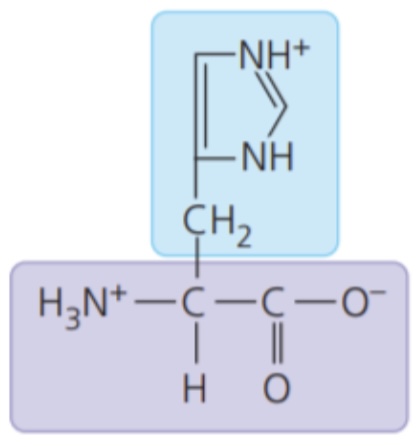
79
New cards
Peptide bonds
- links amino acids
80
New cards
Polypeptide
- a polymer of amino acids
- range in length from a few to more than a thousand monomers
- has a unique linear sequence of amino acids
- range in length from a few to more than a thousand monomers
- has a unique linear sequence of amino acids
81
New cards
a. Amino end
b. Carboxyl end
b. Carboxyl end
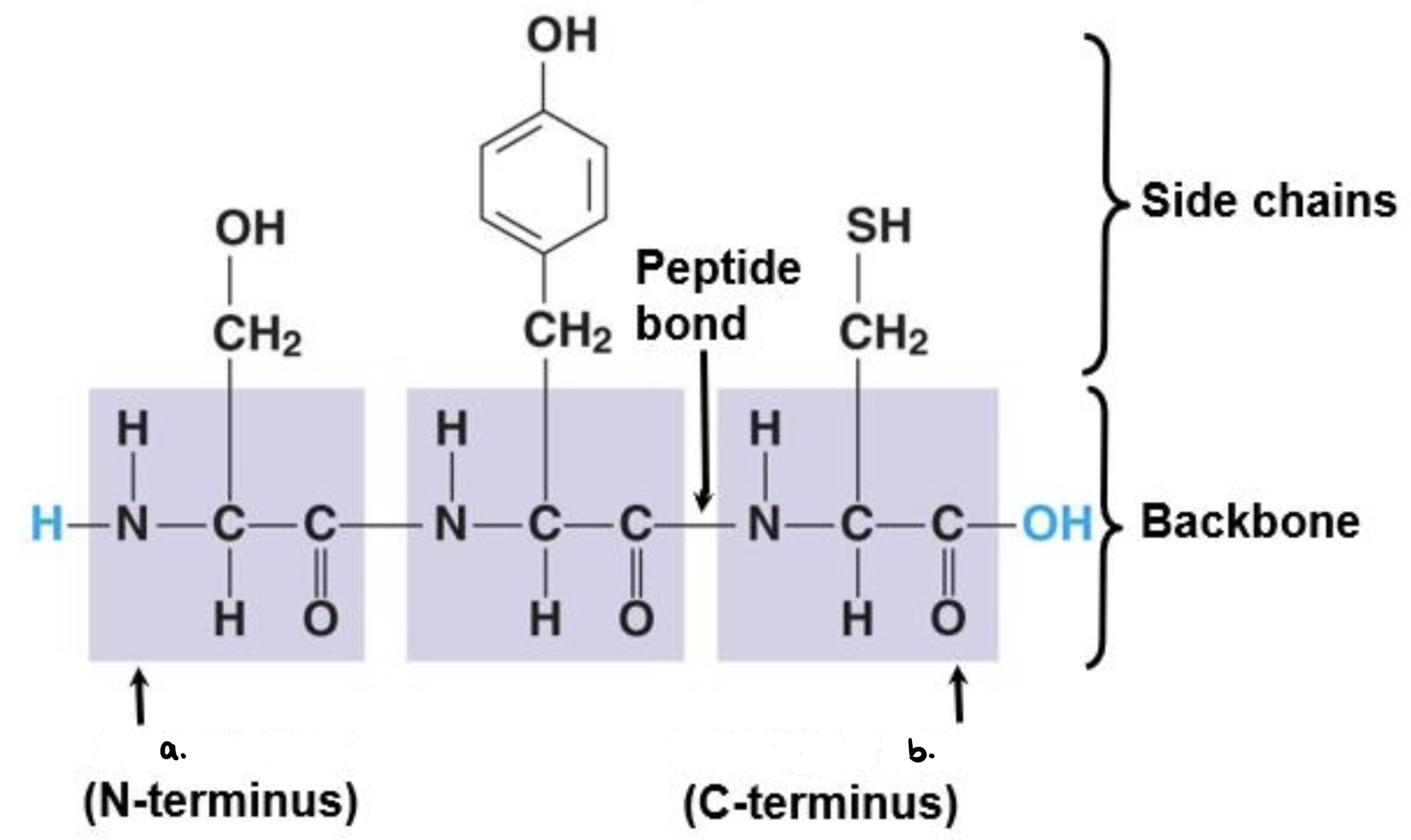
82
New cards
Primary structure
- the sequence of amino acids in a protein, is like the order of letter in a long word
- determined by inherited genetic information
- determined by inherited genetic information
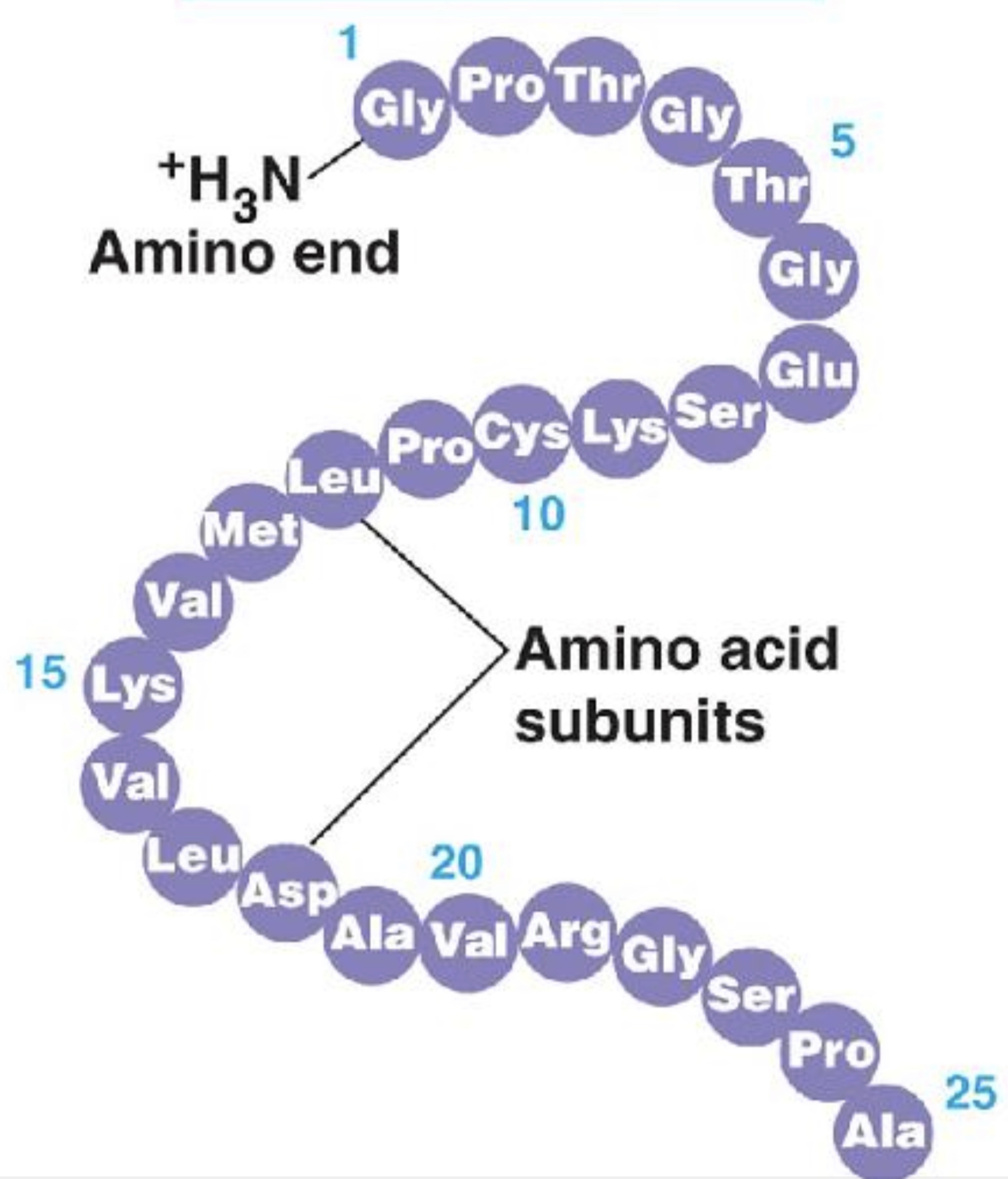
83
New cards
Secondary Structure
a. Alpha helix
b. Beta-pleated sheets
a. Alpha helix
b. Beta-pleated sheets
- its coils and folds result from hydrogen bond between repeating constituents of the polypeptide backbone
(a) a coil structure
(b) folded structure
(a) a coil structure
(b) folded structure
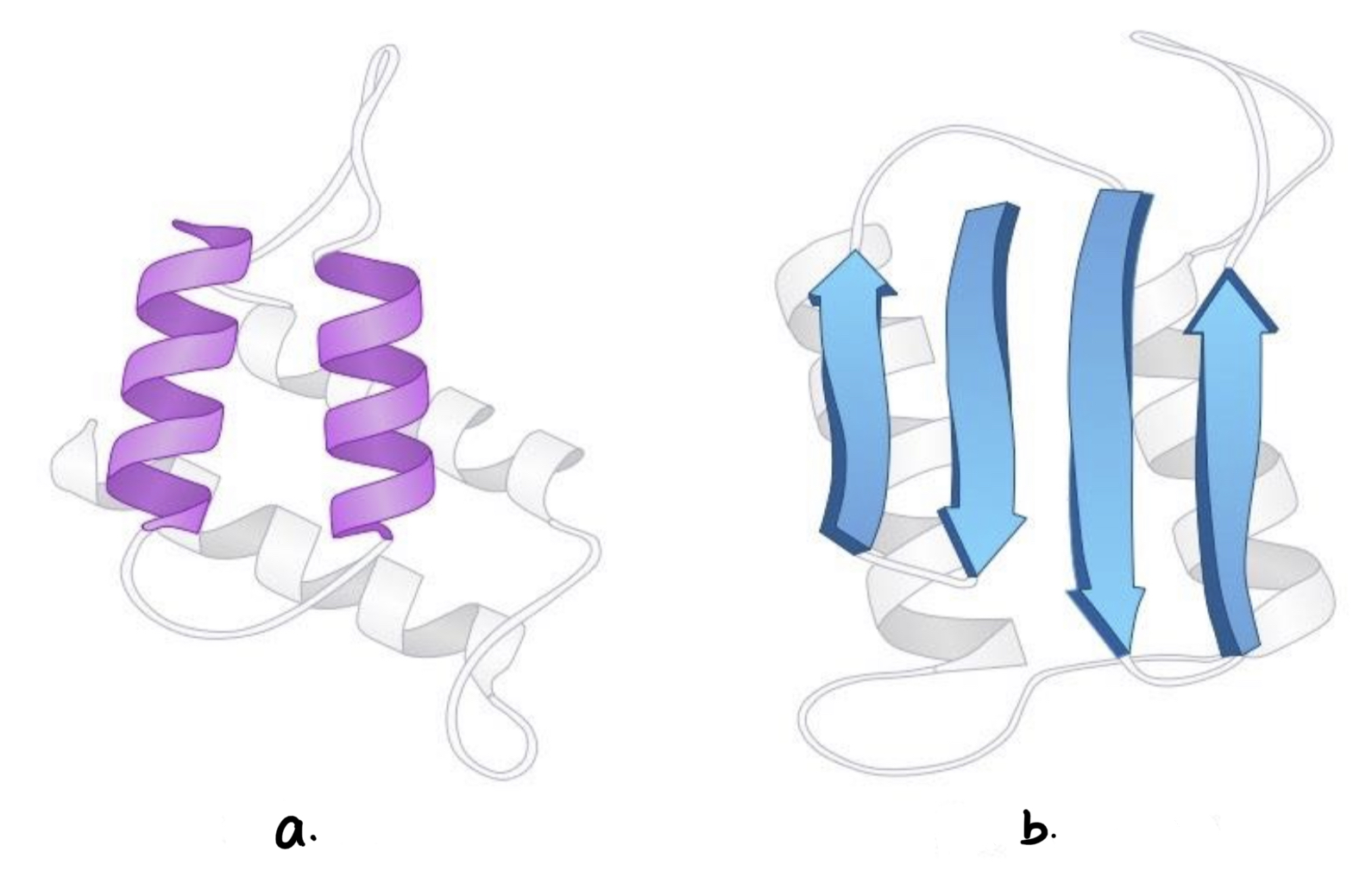
84
New cards
Tertiary structure
- determined by interactions between R groups, rather than interaction between backbone constituents
85
New cards
Hydrogen bond
- can form between the different amino acids
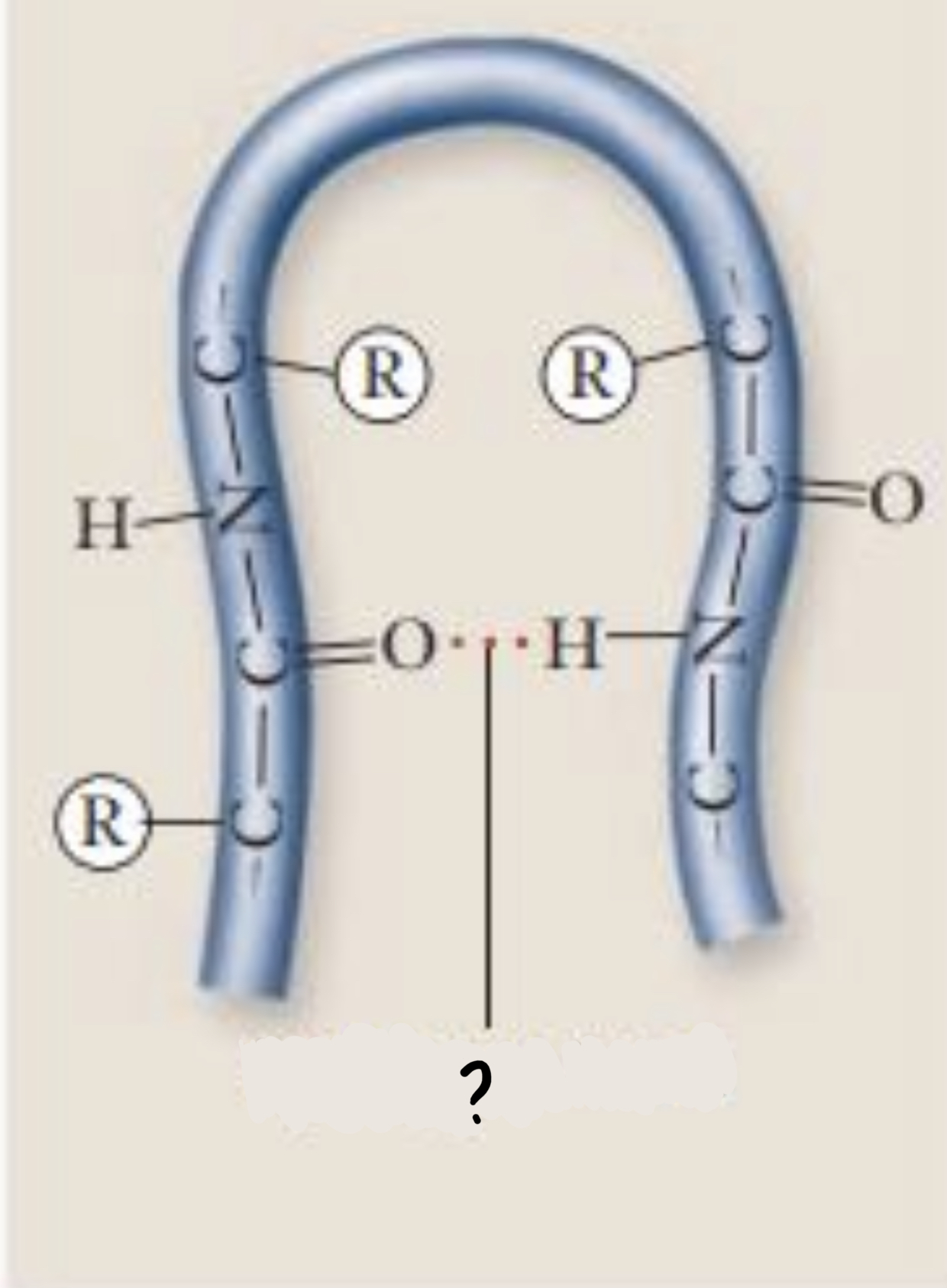
86
New cards
Disulfide bridge
- can form between 2 cysteine side chains
- are strong covalent bonds that may reinforce the protein’s structure
- are strong covalent bonds that may reinforce the protein’s structure
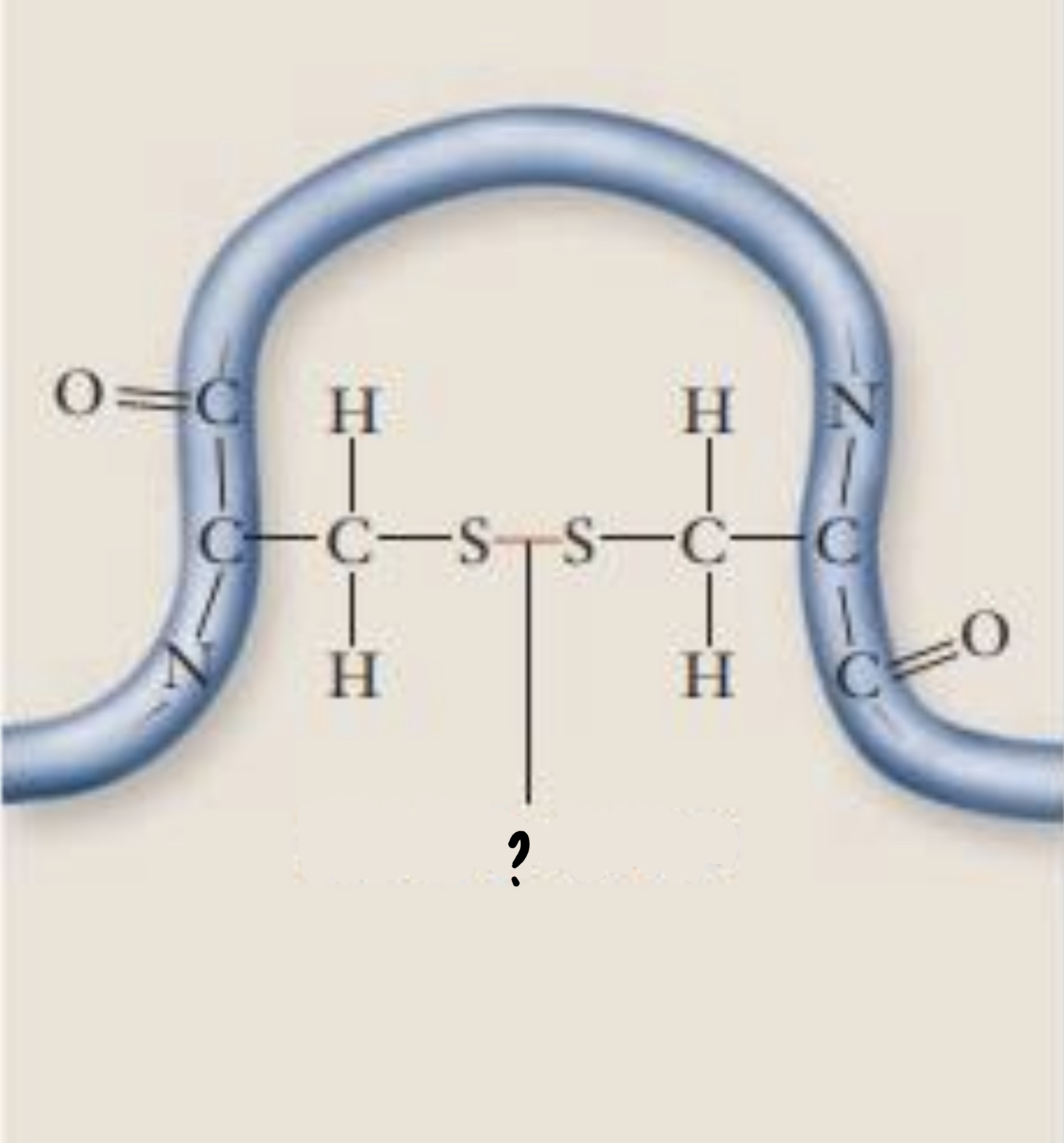
87
New cards
Ionic bond
- can form between groups with opposite charge
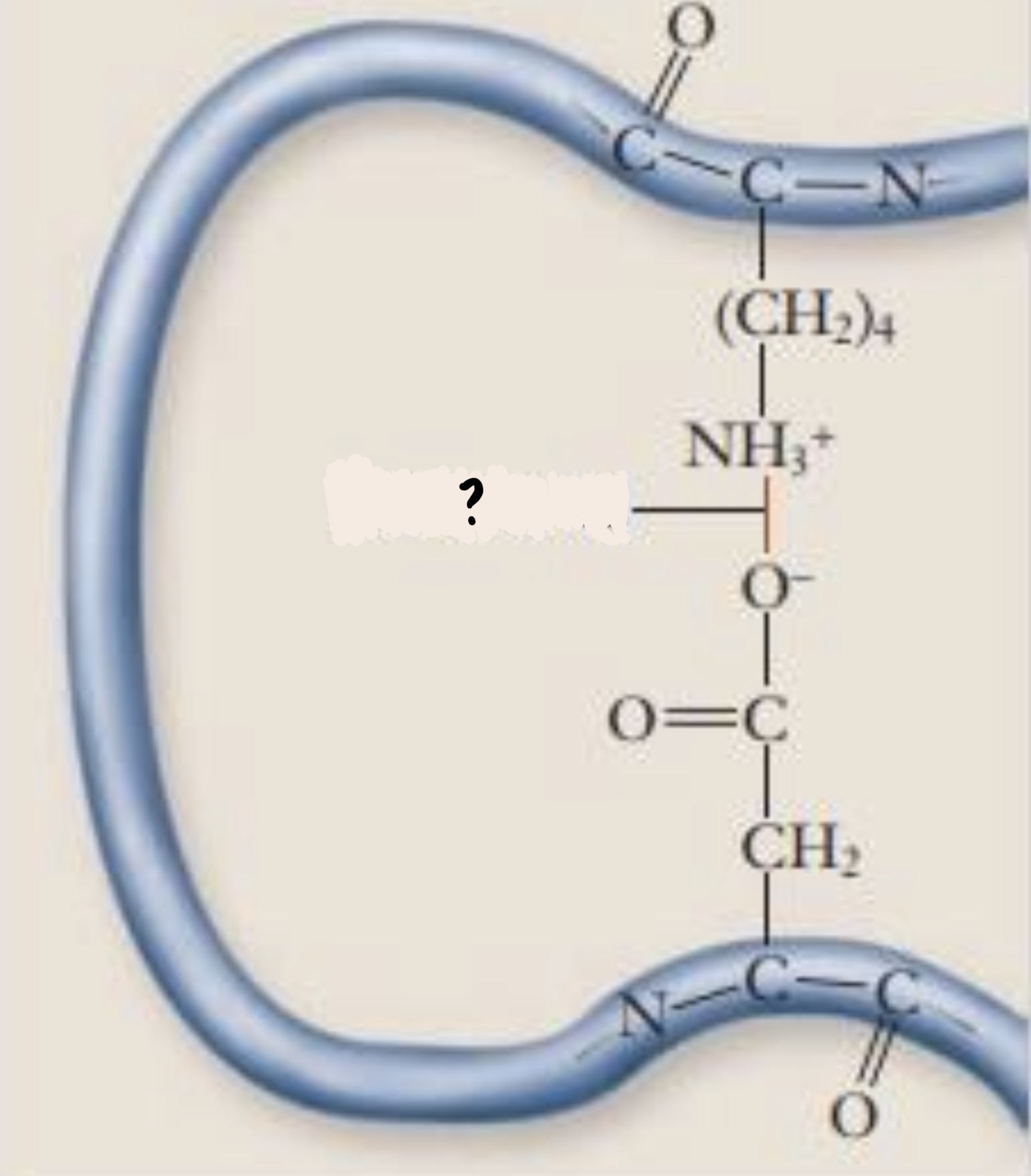
88
New cards
van der Waals attraction
- weak attractions between atoms due to oppositely polarized electron clouds
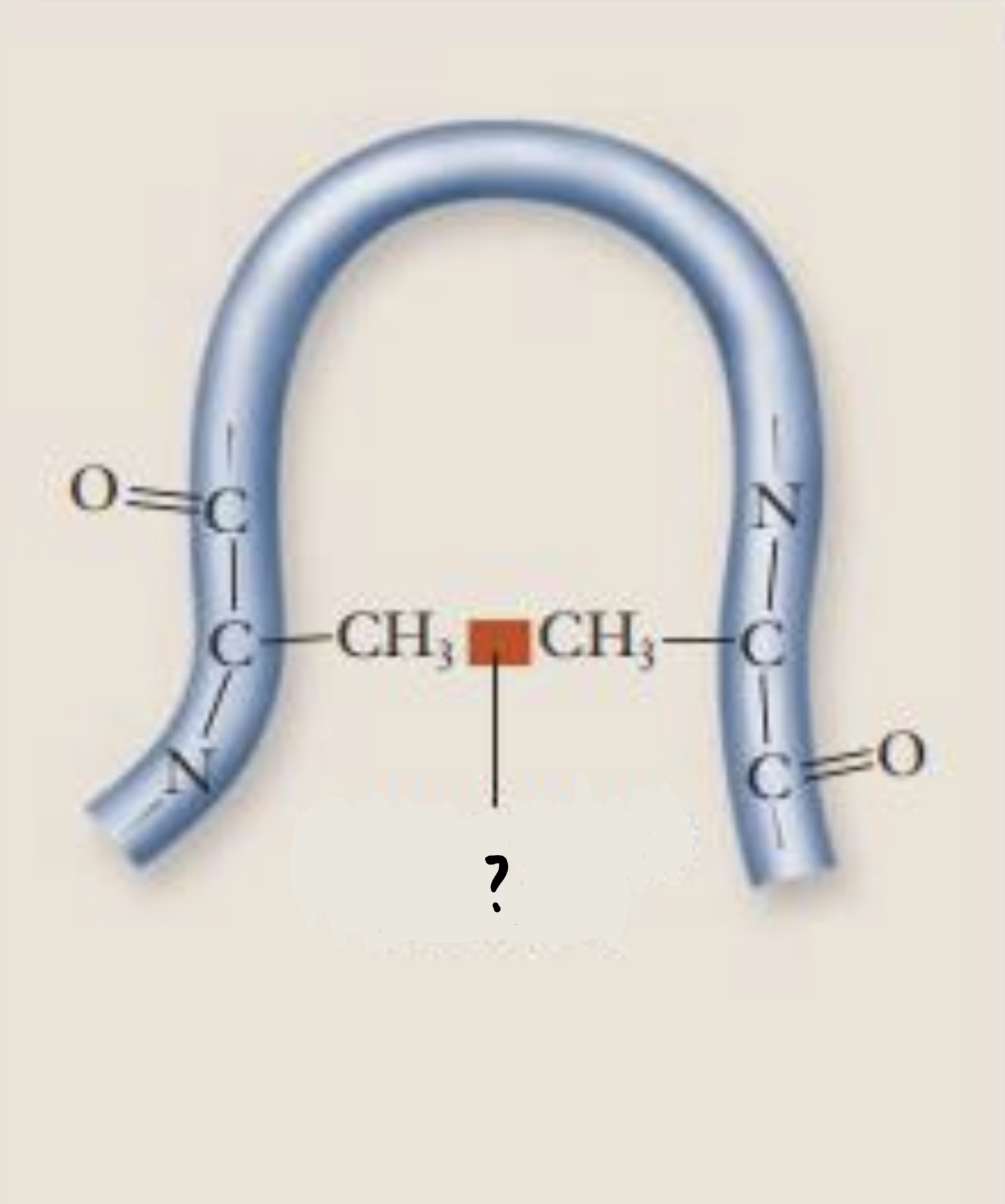
89
New cards
Hydrophobic exclusion
- the tendency of the multiple oil droplets that are present in water to coalesce into fewer and larger droplets.
90
New cards
Quaternary structure
- results when 2 or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecule
91
New cards
Denaturation
- altercations in secondary to quaternary structure without altering the primary structure
- the loss of a protein’s naive structure due to alterations in pH, salt concentration, temperature or other environmental factors
- this kind of protein is biologically inactive
- the loss of a protein’s naive structure due to alterations in pH, salt concentration, temperature or other environmental factors
- this kind of protein is biologically inactive
92
New cards
Chaperonins
- are protein molecules that assist the proper folding of other proteins
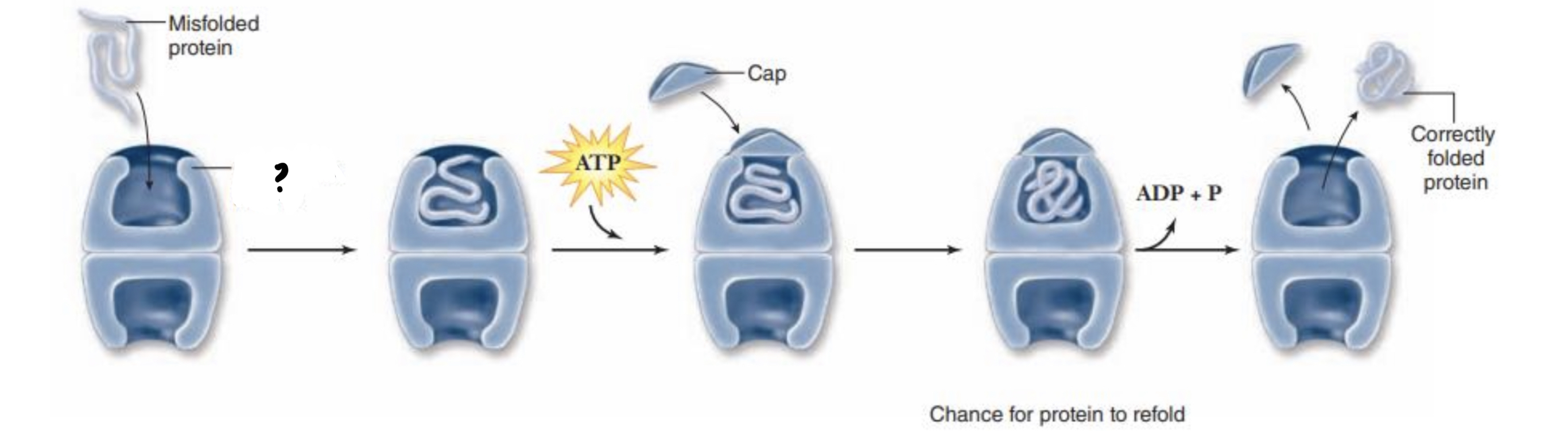
93
New cards
X-ray crystallography
- determines a protein’s structure
94
New cards
Nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR) spectroscopy
- determines a protein’s structure which does not require protein crystallization
95
New cards
Bioinformatics
- uses computer programs to predict protein structure from amino acid sequences
96
New cards
Gene
- a unit of inheritance that programs the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
- made of DNA
- made of DNA
97
New cards
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- type of nucleic acid
- provides directions for its own replication
- direct synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) and through mRN, controls protein synthesis
- provides directions for its own replication
- direct synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) and through mRN, controls protein synthesis
98
New cards
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- type of nucleic acid
99
New cards
Protein synthesis
• Transcription
• Translation
• Transcription
• Translation
- occurs in the ribosomes; has 2 stages
1. DNA is copied to RNA
2. RNA is used to produce proteins
1. DNA is copied to RNA
2. RNA is used to produce proteins
100
New cards
Polynucleotides
- polymers of nucleic acids