Acute Care of Injury and Illnesses final
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
Which of the following regulates how any member of a sports medicine team who has health information about an athlete can share that information with others?
- American Academy of Sports Medicine
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- Americans with Disabilities Act
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration
Athletes should shower before receiving treatment in the facility
Which of the following statements is true about the rules and policies of athletic health care facilities?
- Athletes should consume their daily helping of healthy foods within the facility
- Athletes should store game equipment in specific storage units built inside the facility
- Athletes should wear cleated shoes at all times within the facility
- Athletes should shower before receiving treatment in the facility
Different specialized areas related to performance enhancement and injury care
Which of the following definitions best describes the field of "sports medicine"?
- The specialized surgeries that are performed on injured athletes
- Different specialized areas related to performance enhancement and injury care
- An association that includes a few professional organizations
- A team that includes a physician, an athletic trainer and a coach
team physician
In the sports medicine team, the individual who is responsible for compiling medical histories and conducting physical examinations for each athlete is the ____________.
- team physician
- coach
- school nurse
- athletic trainer
sports fans
Who among the following does NOT play a role in an athletes health and safety?
- nutritionists
- biomechanists
- sports fans
- strength and conditioning coaches
Recreational therapists
_________ treat and rehabilitate individuals with specific health conditions, usually in collaboration with physicians, psychologists, social workers, and physical and occupational counselors in acute healthcare settings, using leisure activities such as structured group programs to improve and maintain their clients' general health and well-being.
- Recreational therapists
- Recreational directors
- Activity specialists
- Team supervisors
Psychologist
A team's ________ takes care of the way an injured athlete feels about their injury and how it affects their social, emotional, intellectual, and physical dimensions.
- Podiatrist
- Physician
- Physical trainer
- Psychologist
Identify whether an athlete is at risk before they participate in a sport
The primary purpose of a preparticipation health examination is to:
- satisfy insurance and liability issues
- determine body fat percentages for coaches in a specific sport
- identify whether an athlete is at risk before they participate in a sport
- reveal qualifying conditions
All of these answers are correct
Who among the following is part of the sports medicine team?
- All of these answers are correct
- A certified athletic trainer
- An exercise physiologist
- A coach
Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
Which of the following protects the privacy of students and gives parents certain rights with respect to their children's school records?
- Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
treatment logs
Which of the following types of documentation should be used as a sign-in record for athletes who receive any service in an athletic health care facility?
- injury record forms
- personal information cards
- treatment logs
- injury reports
All of these answers are correct
Athletic training is:
- concerned with the prevention and treatment of injuries related to physical activity
- a major link between sports programs and medical communities
- an area of specialization in sports medicine
- All of these answers are correct
diaphysis
What is the main shaft of the bone known as?
- epiphysis
- periosteum
- diaphysis
- articular cartilage
an avulsion fracture
Identify the type of fracture in which an attached tendon or ligament pulls a small piece of the bone to which it attaches away from the rest of the bone.
- a spiral fracture
- a greenstick fracture
- an avulsion fracture
- an oblique fracture
grade 3 sprain
Which of the following grades of sprain involves total tearing of the ligament, which leads to instability of the joint?
- grade 1 sprain
- grade 2 sprain
- grade 4 sprain
- grade 3 sprain
myositis ossificans
Which of the following complications is a result of repeated blows to the same area?
- crepitus
- DOMS
- myositis ossificans
- neuritis
6 to 8 weeks
How long does the treatment of the hamstring strain commonly take?
- 1 to 2 weeks
- 5 to 7 weeks
- 6 to 8 weeks
- 3 to 4 weeks
DOMS
Which of the following conditions occurs 12 hours after the injury and is most intense after 24 to 48 hours?
- neuritis
- myositis ossificans
- crepitus
- DOMS
resting the injured area to eliminate irritation to the tendon
Which of the following is the key to treating tendinitis
- treating it as tendon degeneration
- injecting the area with a steroid
- resting the injured area to eliminate irritation to the tendon
- stretching to improve the sliding ability of the tendon
They communicate freely and work in close cooperation with both athletic trainers and the team coaches to ensure that the athletes achieve an optimal level of fitness
In the context of the sports medicine team, which of the following is a responsibility of strength and conditioning coaches?
- They are required to critically review the training and conditioning program designed by the athletic trainers and be very familiar with what is expected of the athletes on a daily basis
- They communicate freely and work in close cooperation with both athletic trainers and the team coaches to ensure that the athletes achieve an optimal level of fitness
- They are responsible for rehabilitating an injured athlete who is undergoing a rehabilitation program.
- They dictate what an injured athlete can or cannot do when engaging in a strength and conditioning program
osetoarthritis
Which of the following conditions results from a wearing down of articular cartilage?
- osetoarthritis
- bursitis
- tendinosis
- tenosynovitis
the maturation-remodeling phase
Which of the following phases of healing features a realignment or remodeling of scar tissues?
- the proliferative endometrium phase
- the maturation-remodeling phase
- the inflammatory response phase
- the fibroblastic phase
osteoblasts
Which cells lay down extra bone formation over a fracture?
- osteocytes
- osteoblasts
- osteomytes
- osteoclasts
dislocation
A________ occurs when at least one bone in a joint is forced completely out of its normal and proper alignment and must be manually or surgically put back into place.
- sprain
- dislocation
- subluxation
- contusion
delayed-onset muscle soreness
Which of the following is characterized by increased muscle tension, swelling, and resistance to stretching following exercise?
- delayed-onset muscle soreness
- myositis ossificans
- tenosynovitis
- acute-onset muscle soreness
subluxation
What type of injury occurs when a bone comes partially out of its normal articulation then goes right back into place?
- subluxation
- dislocation
- stress fracture
- avulsion fracture
return to play after being asymptomatic for 20 minutes
If an athlete shows any sign of a concussion, all the following should occur except
- assessment of concussive injury using SCAT3
- return to play after being asymptomatic for 20 minutes
- rule out cervical injury
- on-site medical evaluation
the pons
Which of the following parts of the brain controls sleep, posture, respiration, swallowing, and the bladder?
- the cerebellum
- the cerebrum
- the medulla oblongata
- the pons
physician
The ______ is ultimately responsible for deciding when an injured athlete is likely to return to full activity.
- physician
- athletic trainer
- coach
- school nurse
The Concussion Recognition Tool 5
Which of the following tests is developed to help non-medically trained individuals identify the signs and symptoms of potential sport-related concussions?
- The Concussion Recognition Tool 5
- The Immediate Post-Concussion Assessment and Cognitive Test
- The Modified Romberg test
- The Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics
amnesia
Which of the following terms describes the inability of an athlete to remember events after the injury has occurred?
- tinnitus
- amnesia
- nystagmus
- concussion
second impact syndrome
Which of the following can occur if an athlete who sustained a concussion previously returns to play prior to resolution of the symptoms and then receives another head injury?
- chondral separation
- cerebral hyperemia
- epistaxis
- second impact syndrome
- Hip moves out of position
- Heel raises from the floor
- Patient opens their eyes
- Moving hands from the hips
Which of the following are examples of errors that are counted in the Balance Error Scoring System (BESS) and modified-Balance Error Scoring (mBESS) tests? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- Hip moves out of position
- Patient cannot count to 20
- Patient fails to hold their breath
- Heel raises from the floor
- Patient opens their eyes
- Moving hands from the hips
healthcare professionals
According to the instructions on the SCAT6, the instrument has been designed to be used by:
- parents
- healthcare professionals
- coaches
- anyone who is trained
- spontaneously resolving signs and symptoms
- usually resolves in 7-10 days
- functional, not structural, injury
- a wide variety of signs and symptoms
A concussion is a very difficult injury to define. Which of the following are components of a concussion? Choose all the correct answers for full credit.
- bleeding in the brain
- spontaneously resolving signs and symptoms
- almost always leads to permanent disability
- usually resolves in 7-10 days
- functional, not structural, injury
- a wide variety of signs and symptoms
baseline testing
Determining an athletes ability to recall words in a list and say the names of the months in reverse order during the pre-participation evaluation is referred to as_______________________.
- post-concussion screening
- pre-concussion screening
- ImPACT testing
- baseline testing
annually
How often are pre-participation evaluations required by the VHSL?
- at the beginning of each sports season
- annually
- monthly
- every two years
to rule out bleeding in the brain
Why do patients who have a concussion often undergo a CT scan?
- to monitor blood flow to the brain
- to determine the severity of the concussion
- to detect injury to the neurons of the brain
- to rule out bleeding in the brain
concussion signs and symptoms persist
Which of the following best describes post concussion syndrome?
- bleeding in the brain that carries a 50% chance of death
- additional injury to the brain after the initial concussion
- concussion signs and symptoms persist longer than expected
- concussion signs and symptoms do not fully resolve ever
an injury to the brain that occurs after sustaining a concussion
Which of the following best describes second impact syndrome?
- signs and symptoms of concussion persist longer than expected
- signs and symptoms of concussion never fully resolve
- an injury to the brain that occurs after sustaining a concussion
- a spinal cord injury that results in permanent paralysis
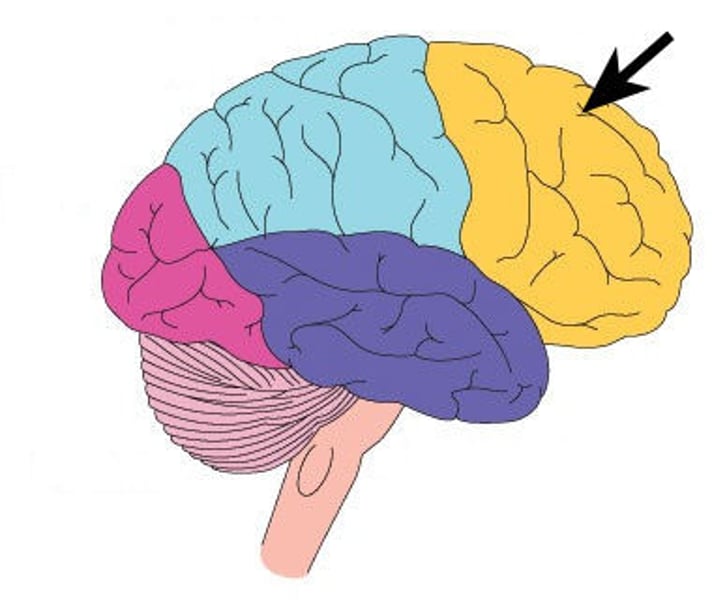
frontal lobe
What is the arrow pointing to in this image?
- occipital lobe
- frontal lobe
- cerebellum
- parietal lobe
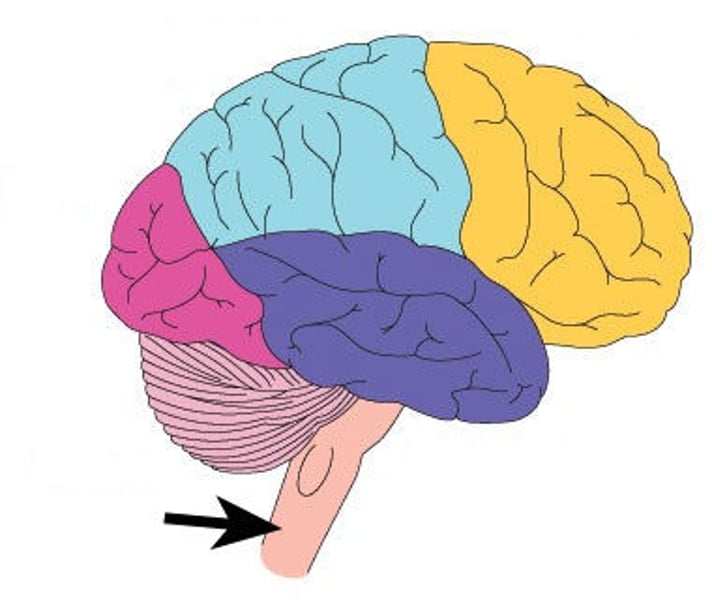
brain stem
What is the arrow pointing to in this image?
- forebrain
- midbrain
- diencephalon
- brain stem
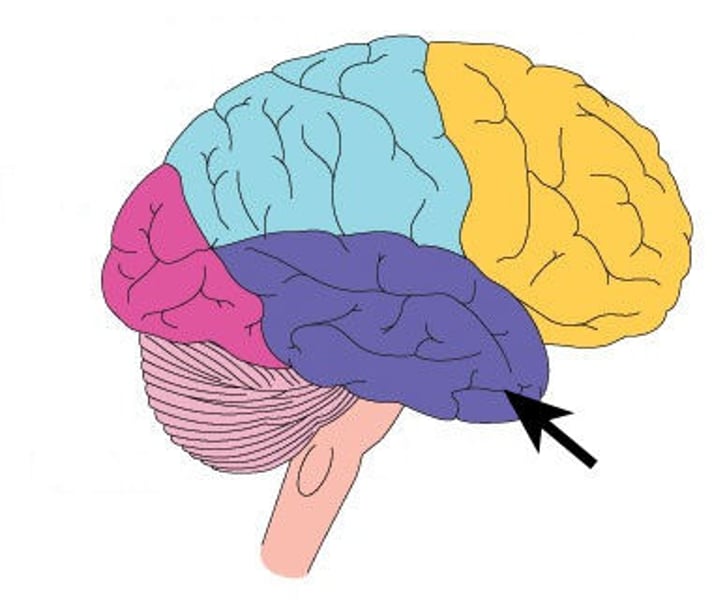
temporal lobe
What is the arrow pointing to in this image?
- cerebellum
- pons
- frontal lobe
- temporal lobe
10-14 days
Most concussions heal within what time frame?
- 10-14 days
- 5-7 days
- 4-6 weeks
- 1-2 months
- patient must be able to complete a 5-step return to play protocol
- patient must be symptom-free
- patient must return to school without accommodations
Which of the following must occur before a patient with concussion can return to play? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- patient must be able to recite the months of the year in reverse order
- patient must be able to complete a 5-step return to play protocol
- patient must complete a 10-step protocol that gradually reintroduces physical exertion
- patient must be symptom-free
- patient must return to school without accommodations
physical and cognitive rest
The most important rehabilitation for a concussion is _________
- range of motion exercises
- eye coordination exercises
- physical and cognitive rest
- balance exercises
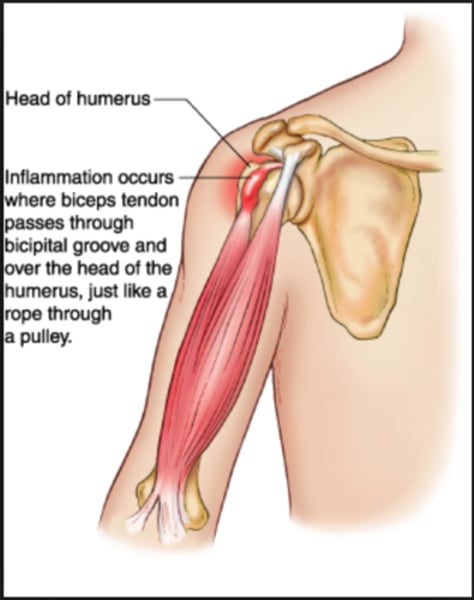
tendonitis
What injury do you suspect for this patient?
- Patient is 32-year old male
- Plays pickleball 4 times per week
- Complains of right lateral elbow pain that is worse in the morning, better in the afternoon. Pain increases after playing pickleball.
- Reports pain is 4/10 at rest and 8/10 after playing.
- Pain is located on the right distal lateral humerus and extensor muscle belly
- sprain
- strain
- macrotrauma
- tendonitis
epidural hematoma
Which of the following injuries are immediately life-threatening? Choose all answers for full credit.
- epidural hematoma
- second-impact syndrome
- bursitis
- concussion
- subdural hematoma
- tarsals
- metatarsals
- phalanges
What are the three groups of bones in the foot? Choose only the three correct responses for full credit.
- anterior compartment
- posterior compartment
- tarsals
- metatarsals
- phalanges
- carpals
- metacarpals
anterior inferior iliac spine
What is the origin of the rectus femoris muscle?
pes cavus
What foot type is characterized by its high arch?
- pes cavus
- pes planus
- mortons toe
- plantar fascitis
hallux valgus
Which condition of the foot causes a bunion to form at the first metatarsalphalangeal joint?
- hallux valgus
- digitorum valgus
- sesamoiditis
- bunions do not form at the 1st MTP
5
There are ______ metatarsals in the foot.
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
fifth
A jones fracture involves a fracture of the neck of the _____ metatarsal.
- first
- third
- fourth
- fifth
four
In the lower leg, there are how many separate compartments containing muscles, tendons, blood vessels and nerves?
- two
- three
- four
- five
False
Mortons toe is a condition in which the first metatarsal is abnormally long. True or False
pes planus
What is another name for flat feet?
- pes planus
- pes equins
- pes cavus
- hallux rigidus
14
How many phalanges are in the foot?
- 9
- 10
- 14
- 15
- Sartorius
- semitendinosus
- gracilis
What muscles attach to the pes anserine? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- Sartorius
- vastus lateralis
- biceps femoris
- semitendinosus
- gracilis
- semimembranosus
superior medial tibia
Where is the pes anserine located?
Plantarflexion
Which of the following is the mechanism of injury for an Achilles tendon rupture?
- Plantarflexion
- Inversion
- Dorsiflexion
- Eversion
- Dorsiflexion
- Plantarflexion
- Inversion
- Eversion
The ankle joint is capable of what movements? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- Dorsiflexion
- Plantarflexion
- Inversion
- Eversion
- Medial rotation
during deceleration with the knee in valgus and the tibia internally rotated
When is the anterior cruciate ligament most often injured?
- during the deceleration with the knee in varus and the tibia internally rotated
- during acceleration with the knee in varus and the tibia externally rotated
- during deceleration with the knee in valgus and the tibia internally rotated
- during acceleration with the knee in valgus and the tibia externally rotated
- vastus lateralis
- vastus medialis
Which two muscles have a proximal attachment to the linea aspera? Choose both correct answers for full credit.
- iliopsoas
- vastus lateralis
- vastus medialis
- rectus femoris
inversion
A(n)______ ankle sprain is most common and often result in injury to the lateral ligaments.
- eversion
- inversion
- dorsiflexion
- plantarflexion
- Anterior talofibular
What is the most commonly sprained ligament in the ankle?
- Anterior tibiofibular
- Anterior talofibular
- Deltoid
- Posterior talofibular
fibula
The lateral malleolus is part of what bone?
- tibia
- navicular
- fibula
- calcaneus
functional tests
Running, jogging and sprinting are examples of
- the Lachman's test.
- varus stress tests.
- functional tests.
- the Apley's compression test.
the deep infrapatellar bursa
Which of the following is the bursa that commonly becomes inflamed from the overuse of the patellar tendon?
- the prepatellar bursa
- the superficial infrapatellar bursa
- the suprapatellar bursa
- the deep infrapatellar bursa
ligaments
Which of the following are the main sources of stability in the knee?
- menisci
- ligaments
- bones
- cartilage
lateral
A patella usually dislocates in what direction?
- lateral
- medial
- anterior
- posterior
peroneus brevis
What muscle is this?
- posterior tibialis
- peroneus brevis
- peroneus longus
- anterior tibialis
- tibialis anterior
- flexor hallucis longus
Which of the following muscles assists with the inversion of the ankle? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- tibialis anterior
- flexor hallucis longus
- peroneus longus
- peroneus brevis
- peroneus tertius
subtalar joint
True inversion and eversion occur at the ______ joint.
- metatarsophalangeal joint
- subtalar joint
- talocrural joint
- midtarsal articulation
2nd metatarsal and 2nd proximal phalange
What two bones form the 2nd metatarsophalangeal joint in the foot?
- 2nd and 2nd cuneiform
- 2nd distal phalange and 2nd middle phalange
- 2nd metatarsal and 2nd proximal phalange
- 2nd metatarsal and 2nd distal phalange
lateral to the tibial crest
The belly of the anterior tibialis muscle is located:
- posterior to the tibial crest
- superior to the tibial crest
- lateral to the tibial crest
- medial to the tibial crest
- flexor hallucis longus
- flexor digitorum longus
- posterior tibialis
Which of the following muscles are located in the deep posterior compartment? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- flexor hallucis longus
- flexor digitorum longus
- posterior tibialis
- gastrocnemius
- soleus
- extensor hallucis longus
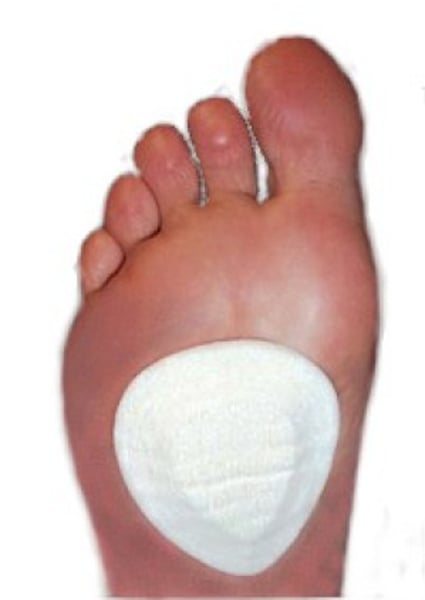
metatarsal arch
What structure is above the white?
- medial longitudinal arch
- metatarsal arch
- lateral longitudinal arch
- medial calcaneal tuberacle
- the patient moving the joint by contracting the muscles around the joint
Assessment of active range of motion involves:
- the patient moving the joint by contracting the muscles around the joint
- the clinician moves the patients joint while the patient remains relaxed
- the clinician provides resistance as the patient moves the joint by contracting the muscles around the joint
- an isometric contraction
lateral
The anterior compartment is located _____ to the tibial crest.
- superior
- medial
- lateral
- inferior
Deltoid ligament
All of these provide stability to the lateral aspect of the talocrural joint except for:
- Anterior talofibular ligament
- Calcaneofibular ligament
- Posterior talofibular ligament
- Deltoid ligament
eversion
The main action of the muscles located in the lateral compartment is:
- plantarflexion
- dorsiflexion
- eversion
- inversion
anterior translation of the talus
The anterior talofibular ligament controls:
- posterior translation of the talus
- plantarflexion of the subtalar joint
- anterior translation of the talus
- dorsiflexion of the talocrural joint
- dorsiflexion of the talocrucal joint
- anterior tibiotalar
- posterior tibiotalar
- tibiocalcaneal
- tibionavicular
The deltoid ligament is composed of four ligaments. Which of the following are parts of the deltoid ligament? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- talocrural
- anterior tibiotalar
- posterior tibiotalar
- tibiocalcaneal
- tibionavicular
- anterior talofibular
- calcaneofibular
extensor hallucis longus
The name of the muscle that moves the first toe into extension is:
- extensor digitorum longus
- extensor hallucis longus
- flexor hallucis longus
- flexor digitorum longus
abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body is called______.
- flexion
- extension
- rotation
- abduction
compare to the contralateral (opposite) side
How can we determine if a patient has normal range of motion at a particular joint?
- consult our ROM manual
- ask the patient if that is as far as the joint moves
- compare to the contralateral (opposite) side
- palpate the joint
- none of the above
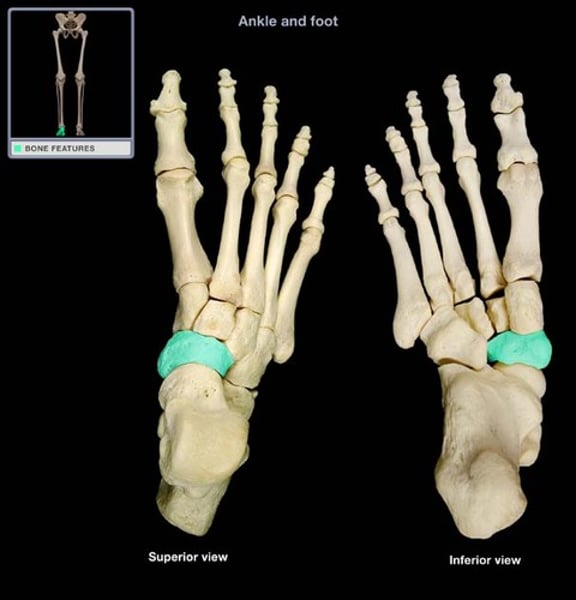
Navicular
What is the highlighted structure?
- Navicular
- cuboid
- talus
- cuneiform
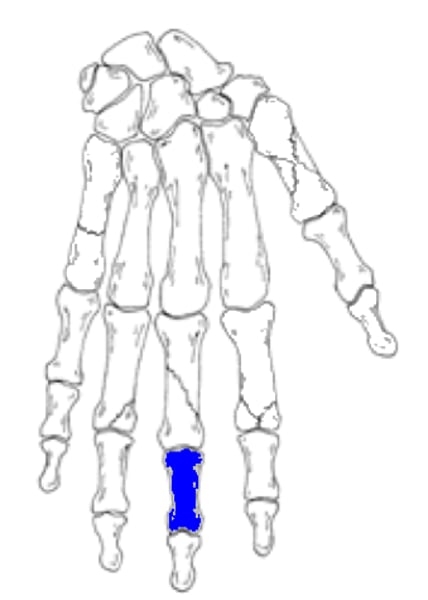
3rd middle phalange
What is the highlighted structure?
- 3rd middle phalange
- 2nd middle phalange
- 3rd distal phalange
soleus
All of these are located in the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg except for:
- posterior tibialis
- flexor hallucis longus
- soleus
- flexor digitorum longus
passive
Which of the following types of Range of Motion (ROM) requires the examiner to move the joint for the patient?
- active
- passive
- resistive
- manual
- all of the above
Palpation
When determining the areas that the patient is most point tender during the evaluation, you are actively engaging in what portion of the evaluation?
- History
- Observation
- Palpation
- Special Testing
passive
Which of the following types of range of motion requires the examiner to move the joint for the patient?
- active
- passive
- resistive
- manual
to determine what care is required, such as calling 911
What are the two main purposes of the musculoskeletal evaluation?
- to determine the diagnosis of the injury
- to determine what care is required, such as calling 911
- to determine how strong a patient is in a particular joint or joints
- to determine how much pain the patient is in
- peripheral nerves
- capillaries
- arteries
What types of structures are being tested during the neurovascular exam? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- peripheral nerves
- capillaries
- arteries
- lymph nodes
- muscles
- bones
- tibiofemoral joint
- patellofemoral joint
- proximal tibiofibular joint
Which of the following are articulations in the knee? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- tibiofemoral joint
- patellofemoral joint
- proximal tibiofibular joint
- distal tibiofibular joint
- adductor tubercle
- tibial condyle
- femoral condyle
Which of the following structures are located on the medial aspect of the knee? Check all correct answers for full credit.
- Gerdy's tubercle
- adductor tubercle
- tibial condyle
- femoral condyle
- fibular head
- Pain description, including rating
- Mechanism of injury
- Previous history
- Timing of injury
- Activities of daily living
- Medications
(ALL)
What are the categories of questions the athletic trainer should ask during the history phase of a musculoskeletal evaluation? Choose all correct answers for full credit.
- Pain description, including rating
- Mechanism of injury
- Previous history
- Timing of injury
- Activities of daily living
- Medications
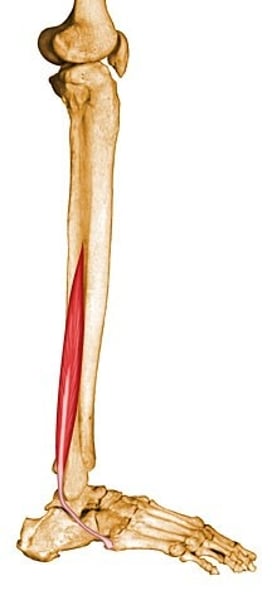
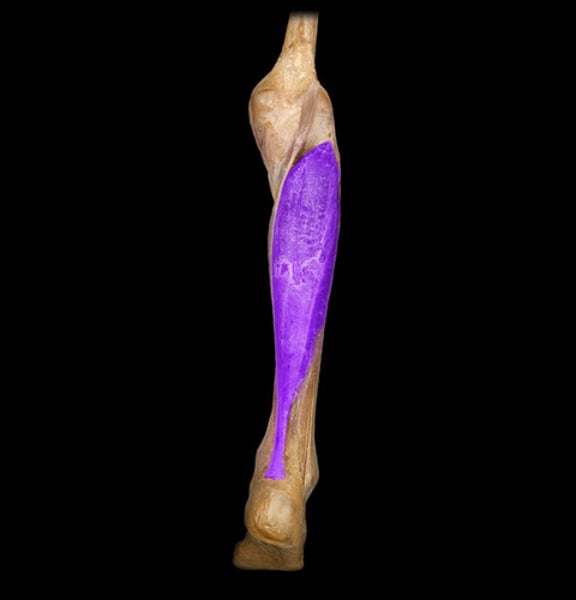
Soleus
What muscle is this?
- tibialis posterior
- extensor digitorum longus
- gastrocnemius
- soleus
- tibia, fibula and calcaneus
The talocrural joint is comprised of which bones?
- talus, calcaneus and fibula
- tibia, fibula and calcaneus
- talus, tibia and fibia
- talus, fibula and tibia