Honors Biology: Cumulative Assessment 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What do all living things have in common?
made up of cells
contain DNA
grow and develop
need food for energy
reproduce
respond to stimuli
populations evolve
What are the 8 life processes and what they are?
Cellular Respiration: process that releases energy from food (w & w/o O2)
Excretion: removal of toxic waste
Regulation: communication between systems that helps maintain homeostasis
Reproduction: continues species (sexually & asexually)
Transport: movement of materials throughout organism
Synthesis: combination of simple substances to form more complex substances
Growth & Development: increase in size/number of cells in organism
Nutrition: process of taking in/making organic nutrients and then breaking them down for energy
What is homeostasis?
maintaining stable internal conditions through a systems of both positive and negative feedback systems
What does “metabolism” mean?
refers to all the chemical reactions that occur in an organism
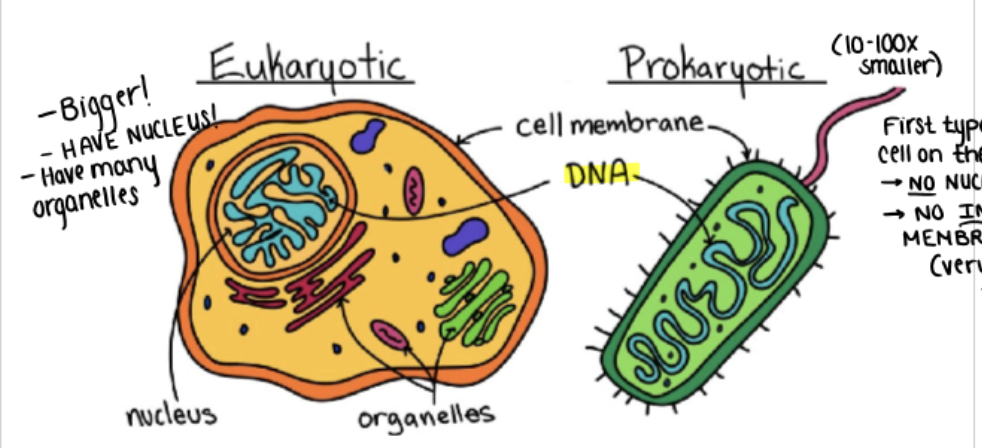
(1) Prokaryotic vs. (2) Eukaryotic
simple structure, no internal membranes, few organelles, and no nuclei
complex structure, many organelles, nucleus w/ DNA
What is the difference between (1) positive and (2) negative feedback?
enhances the stimuli or effects of until the event is over
reduces the original effect of stimuli until it reaches its ideal value or set point
What is the fight or flight response? What causes it and why is it important?
innate and automatic response to when body is in immediate or prolonged situations/danger
Caused by sympathetic nervous system who responds to stress
We would die if we didn’t have one → helps us get out of immediate danger fast
Define hydrogen bonds
electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen atom bound to a highly electronegative atom experiences attraction to some other nearby polar molecule
Define cohesion
attraction between the same molecules due to hydrogen bonding
Define adhesion
attraction between 2 dissimilar surfaces/molecules to one another because of hydrogen bonding
Define monomer
single unit/building block of a biomolecule
Define polymer
many units/building blocks of a biomolecule
Define dehydration synthesis
reaction involving the removal of water into order to bond something
Define hydrolysis
reaction involving the addition of water in order to break a bond
What are the properties of water? Why are they important for living things?
cohesion → high surface tension →
cohesion → high heat of vaporization → temperature stabilizer through sweating (a lot of heat is absorbed from body before evaporating from skin)
cohesion → high specific heat → acts as a temperature stabilizer (absorbs a lot of heat, but slowly)
cohesion → less dense as a solid → during winter prevents further freezing of water sources
adhesion & cohesion → capillary action → helpful in fluid transport in plants & animals
adhesion → versatility as a solvent → allows for all our chemical rxns to occur because the necessity of an aqueous environment
What are the elements in CARBS?
What is its function?
What is its monomer?
What is its polymer?
C, H, O
Acts as (1) immediate energy w/ monosaccharides able to be delivered straight to cells directly for respirating out ATP (2) stored energy for later (3) structural support
Cellulose in plant cell walls/Chitin in fungi cell walls
Monosaccharide (2:1 H to O ratio)
Polysaccharide
What are the elements in LIPIDS?
What is its function?
What is its monomer(s)?
What is its polymer(s)?
C, H, O
Triglyceride → stored energy, heat insulation, padding
Phospholipid → in all cell membranes to provide membrane structure
Waxes → protective coating from water and from dehydration
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
Triglycerides, phospholipids, steriods
What are the elements in PROTEINS?
What is its function?
What is its monomer?
What is its polymer?
C, H, O, N, maybe sometimes some S (whats up chons)
Enzymes, contractile proteins, immune defense, transporting, structure, storage, hormones for signaling
amino acids
polypeptide
What are the elements in NUCLEIC ACIDS?
What is its function?
What is its monomer?
What is its polymer?
C, H, O, N, P
DNA that contains all genetic code for all inherited traits while RNA reads the genes, which is code, on DNA and synthesizes proteins
Nucleotide
Polynucleotide
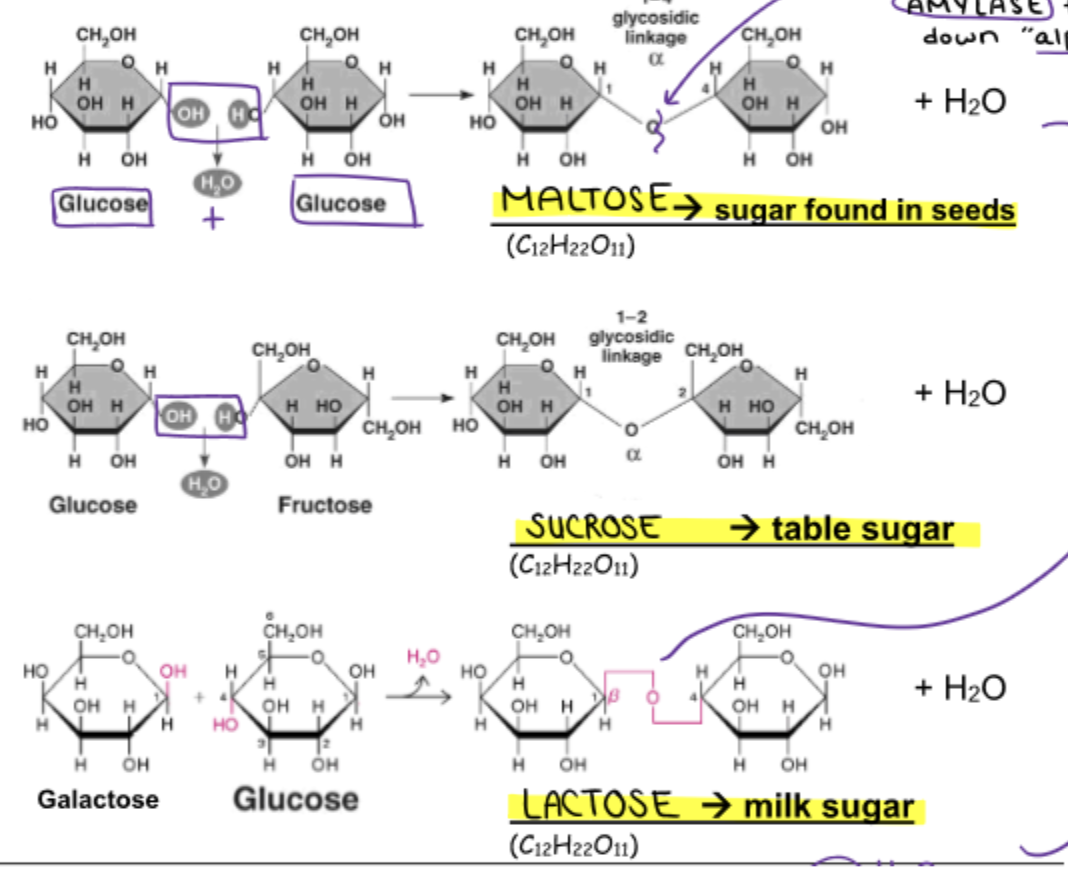
General structure of carbs and its monomer
5-6 sided rings bonded by removal of water
General structure of lipids and its monomers
1 glyceride + 3 fatty acids branching off → triglyceride
General structure of proteins and its monomer
amino group on left and carboxyl group (-cooh) on right
top is R group bottom with have hydrogen
General structure of nucleic acids and its monomers
in rows of 2 nucleotides going down
monomer = 1 phosphate group, 1 5-carbon sugar either being ribose or deoxyribose, then a nitrogenous base
What is the relationship between nucleic acids and proteins?
DNA codes for proteins and in order to synthesize the protein, RNA will “read” DNA’s code (genetic information) and make it
What is transcription? Where does it occur in a cell?
process where a segment of DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA)
occurs in the nucleus
Which molecules are involved in transcription?
DNA helicase
RNA polymerase
Free RNA nucleotides
mRNA
What are exons? What are introns? How is mRNA edited?
coded regions that are spliced together
uncoded regions that are cut out
Final mRNA transcript will only consist of extrons
What is translation? Where does the process occur in a cell?
process of “reading” the mRNA codons and putting together the correct sequence of amino acids
in the cytoplasm and on a ribosome
How are mRNA, tRNA, involved in translation?
mRNA carries the copied and coded genetic information to the cytoplasm and onto the ribosome
tRNA will then use its anticodons to match up to the mRNA’s codons, bringing over a corresponding amino acid
What is a gene mutation?
a change in the order of nucleotides in the DNA
What is ATP? How is it used to do work in cells?
Adenosine Triphosphate → unstable molecule with high energy
When ATP hydrolyzes and breaks off a phosphate group, energy is released that can be used to do work in the cells
What is an enzyme? Why are they important in living things?
a catalyst made up of special proteins that is required to start and speed up all chemical reactions in an organism by lowering activation energy
it makes biochemical reactions happen faster when otherwise the reactions would just not occur or would occur at too slow of a rate to sustain life
How do enzymes work?
Induced fit model → when substrate enters onto an enzyme’s active site, it will change shape and grip the substrate, bringing the substrate into a position that will enhance their ability to catalyze the reaction
Substrate enters active site and enzyme grips (enzyme-substrate complex w/ highest energy)
Enzyme’s active site lowers activation energy and speeds the reaction up
Substrates are converted into products
products are released
What factors affect the rate of enzyme action?
Anything that causes a change in the active site shape (denaturing) by distributing interactions between amino acids
Temperature
pH levels
Salts
Most enzymes function optimally at…
37 oC (body temp)
~7 but stomach enzymes ~2
~1-2%
Inhibitors
Competitive inhibition: inhibitor competes with substrate to the same active site to block it from entering so no more rxns continue
Noncompetitive inhibition: inhibitor attaches to an allosteric site of enzyme and changes the shape of the active site so substrate cant fit, so no rxns will continue
Feedback inhibition: the end product of a biochemical pathway will attach itself to an allosteric site of the first enzyme apart of the pathway to change the shape of its active site so the biochemical pathway will not continue when there is a sufficient amount of product, the rxn will resume when more end product is needed
enzyme action will increase when the substrate amount increases until the rxn rate reaches the Vmax (maximum rate of reaction) where all enzymes are in use so adding extra substrate would no longer increase the reaction rate since there is no enzyme to facilitate the reaction
what does it mean if a protein is denatured?
when a protein has changed shape and can no longer function
what causes proteins to denature?
Temperature
Changes in pH
Salts