Biology Lab Final
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sorry this is not going to be finished i already took this exam but uhhhhh if you want me to finish it i will
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
micropipette
tool to obtain precise volumes; NEVER turn the indicator dial beyond the upper or lower volume limits of the micropipette
P1000
measures volumes between 100-1000 μl; 1 μl adjustment
blue
P100
measures volumes between 10-100 μl, 0.1 μl adjustment
yellow
P10
measures volumes between 0.5-10 μl; 0.01 μl adjustment
red
microliter (μl)
most used unit for measuring and dispensing volumes in molecular biology; 1 μl = 10-6 L = 10-3 mL
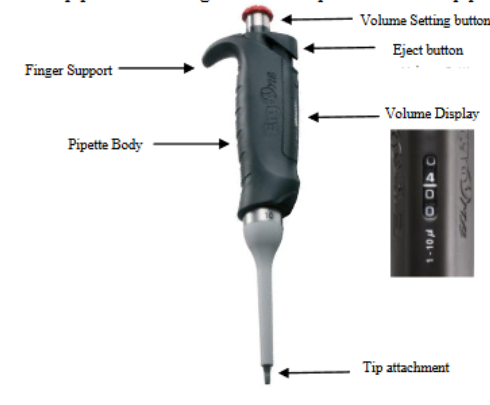
micropipette anatomy
plunger - topmost part of the micropipette which is used to expel and take up the desired amount of liquid into micropipette tip
eject button - used to eject the tip from the micropipette without touching the micropipette tip.
volume display window - adjusted volume is shown
tip attachment - where tips attach

Pipette tips
tips attached to the tip attachment for taking in liquid and then transferring it from one place to another without contaminating the micropipette
first stop (or soft stop)
used to fill the micropipette tip (or release in a gel)
second stop (or hard stop)
used to dispense the contents of the tip (except in a gel)
Accuracy
micropipette delivering the correct volume; giving results near to what is true or expected
Precision
produces reproducible results; low standard deviation
BEST PRACTICES WHEN PIPETTING
Do not withdraw the liquid too quickly into the pipet.
Slowly allow the plunger to return with your thumb.
When collecting your solution, DO NOT push past the “first stop”
Depressing the plunger to the second stop before filling the micropipette tip.
Release plunger slowly
Dispense liquids against the side of the tube or directly into the liquid in order to eject the full volume
Don’t hold the pipette when you’re not pipetting
Bradford assay
colorimetric method used to determine the protein content in a solution based on the formation of a complex between the dye, Coomassie blue, and proteins in solution
Coomassie blue
As proteins bind the dye, there is a change color of from brown to blue; recorded using a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 595nm
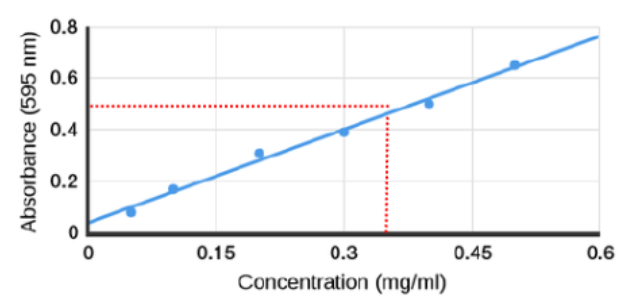
Beer-Lambert law
absorption is proportional to the amount of dye bound and hence the amount of protein in the solution
T = IT/I0
A = -log T
A = ϵbc
spectrophotometer
separates white light into a spectrum of colors (wavelengths) and measures the amount of light absorbed and transmitted by a dissolved chemical; performs Absorbance, % Transmittance, and Concentration measurement
cuvette
contains the sample to be measured; arrow on the front of the cuvette should be oriented in the direction of the light path
Dilution
process of decreasing the concentration of a solute in a solution; mixing it with more solvent like adding more water
direct dilution
adding solvent once to get desired concentration; split up DF into multiple factors of dilution
serial dilution
multiple additions of solvent to get to desired concentration
dilution factor (DF)
Final concentration / Initial concentration
standard curve
plot of absorbance vs. a varying amount of some known concentration of proteins
scientific method
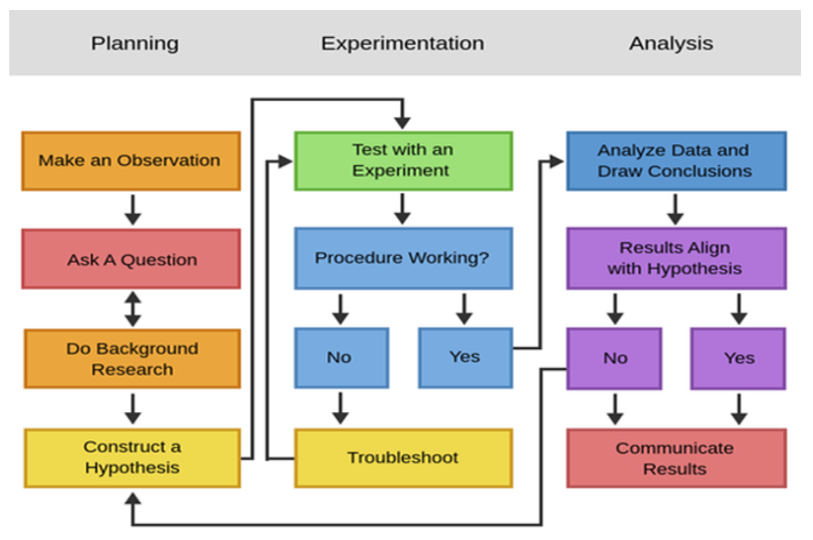
framework used to accurately investigate the world and explain natural phenomena
hypothesis
proposed explanation for a phenomenon based on observations and existing knowledge; leads to experimental predictions
Predictions
often written as "If X then Y" statements
Experiment
procedure designed to test a hypothesis; must be reproducible and reliable, include a control, and use well-designed variables
independent variables
changed by the researcher; 1 per experiment
dependent variables
affected by the independent variable and that is measured; no limit to how many
controlled variables
held constant during the experiment
controls
will not receive the treatment (neutral condition or receive placebo)
experimental group (Test group)
receive the treatment/change in independent variable
Positive controls
groups where the condition guarantees a positive result
Negative controls
produce a negative outcome
Reproducibility
Anyone should be able to replicate the experiment and get similar result
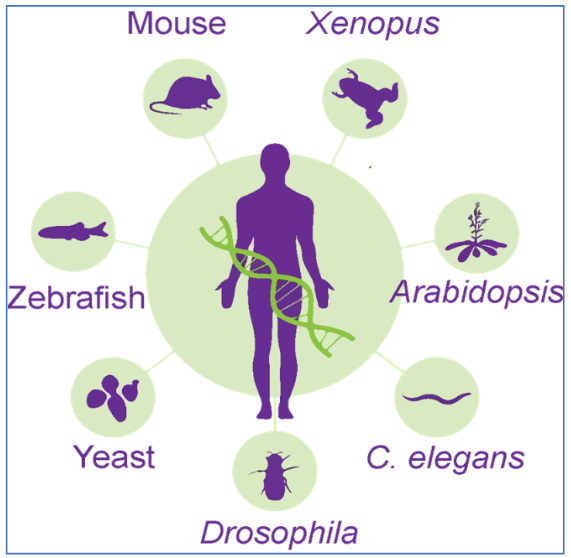
Model organisms
species that are used to study certain aspects of biology
Easy to breed and maintain in a laboratory setup
Short generation times
Large number of offspring
Well studied genome
Can be manipulated easily
Decreased complexity compared to humans
Efficient manipulation of genomes
Less ethical concerns compared to research on human
levels of biological organization
Biosphere > ecosystem > community > population > organisms > Organs > tissues > cell > organelles > molecule
enzyme
macromolecule that acts as a catalyst; affected by temperature and pH
catecholase (or catechol oxidase)
common in plants; fruit browning reaction; forms benzoquinone and water from catechol; stored in vesicles in undamaged cells
transgenesis or genetic transformation
universality of the genetic code allows genes from one species to be transplanted into the genetic code of another
transformation
host into which DNA can be inserted (E. coli)
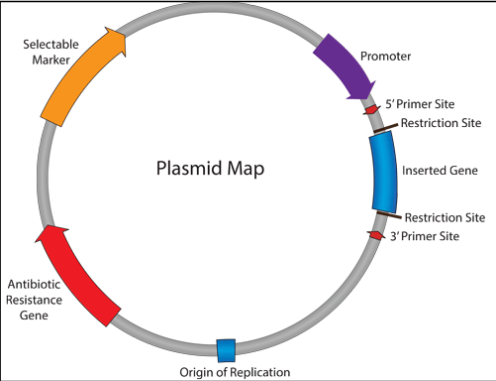
Vector (plasmid)
Selection method or selecting and isolating the successfully transformed organisms (ampicilin/blacklight)
Vector
means of carrying the DNA into the host
Origin of replication (ori) - allows the plasmid to be recognized by the replicating machinery of the bacteria. This will allow the plasmid to replicate in the host.
Restriction enzyme sites – allows ligation of the DNA fragment (gene of interest) into the
plasmid.
Antibiotic resistance - allows the identification of a positive transformant
competence
natural ability to alter their genetics by taking up extracellular ("naked") DNA from their environment; promoted by heat shock or electroporation
CaCl2 (calcium chloride) in transformation
eutralizes the repulsive negative charges of the phosphate backbone of the DNA and the phospholipids of the cell membrane is used to allow the DNA to enter the cell; increases cellular competencyhe
heatshock
chemically competent cells are mixed with plasmid DNA in ice, briefly (25-45 sec) exposed to an elevated temperature (usually 42oC), then immediately returned to ice (0°C) for ≥2 minute. The rapid temperature change creates a thermal imbalance on either side of the cell membrane, creating pores that moves the plasmid into a small percentage of cells
Aseptic technique
designed to provide a barrier between the microorganisms in the environment and the sterile cell culture
Before and after use, your work surface should be disinfected thoroughly.
Always keep the lid on your plates, except when performing manipulations.
When transferring bacteria, sterilize the loop or you are use a sterile disposable loop.
Avoid touching the pipette tip to anything non-sterile, including the outside edge of the bottle
colony
visible mass of cells usually resulting from the division of a single cell and the number of cells in a single colony can exceed one billion (109); growing very close to each other fuse into lawn
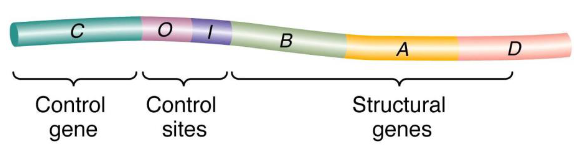
promoter
where RNA polymerase binds and begins transcription of the gene
inducible promoter
can be switched from an OFF to an ON state
operons
clusters of genes controlled by a single promoter
Gene green fluorescent protein (GFP)
reporter gene from jellyfish
central dogma
DNA➜RNA➜PROTEIN➜TRAIT
phenylthiocarbamide (PTC)
bitter tasting chemical similar to those found in vegetables
PTC taster allele
dominant
PAV (ProAlaVal)
cut by restriction enzymes
PTC nontaster allele
recessive
AVI (AlaValIle)
not cut by restriction enzymes
Genomic or chromosomal DNA (gDNA)
full-length DNA sequence, including coding (exons) and non-coding (introns) DNA; majority of DNA in a cell is found in the nucleus, with a much smaller amount in the chloroplasts and mitochondria; typically more mitochondria per cell than nuclei per cell so one finds more molar equivalents of DNA in the mitochondria than in the nucleus; can be harvested from any sample containing eukaryotic cells apart from a pure sample of mature red blood cells
Mitochondrial DNA (mDNA)
found inside the mitochondria of cells and differs from the nuclear DNA in that it comes from the mother only
Complementary DNA (cDNA)
not found inside cells but is created by reverse transcription of RNA in a test tube
centrifugation
technique that helps to separate mixtures by applying centrifugal force; substances separate according to their density; ALWAYS BALANCE THE CENTRIFUGE with hinges out
pellet
solid particles at the bottom of centrifuge tube
supernatant
remaining solution in centrifuge tube
Lysis Buffer
Detergent (such as SDS or Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate) will lyse the cells by solubilizing (breaks apart) the phospholipid cell membrane and nuclear membranes, allowing the DNA to be released
buffering agent (Tris) to maintain the pH of the solution so that the DNA stays stable
Protease (usually proteinase K), an enzyme that digests proteins removes proteins bound to the DNA (such as histones) and destroys cellular enzymes that would digest the DNA
incubated at 50 -55°C, the optimum temperature for protease activity
Salt solution (NaCl)
added to help precipitate proteins and cellular debris clump together
Alcohol (isopropyl/ethanol)
isolate concentrated DNA (Precipitation); esp. cold
TE (Tris -EDTA) buffer
TRIS, pH 8.0 (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane is a buffering agent used to maintain pH.
EDTA (Ethylene Diamino Tetra-acetic Acid) chelates any divalent cations like Ca2+ or Mg2+ preventing the activity of DNase (nucleases which require these ions to be active)
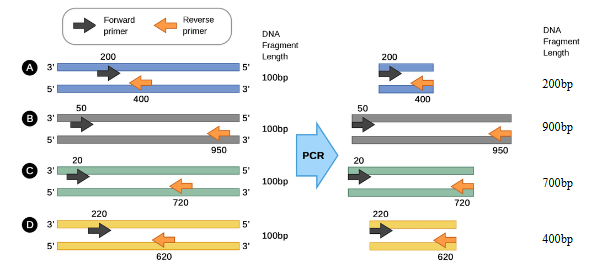
POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR)
used to replicate DNA of a specified length in vitro
Primers (forward (
5' to 3') and reverse (3’ to 5’))Nucleotides
DNA polymerase
DNA template
Extra care with contaminations
A thermocycler
Primers
bind at a specific DNA sequence and mark the beginning of the DNA amplification
Taq polymerase
active at temperatures up to 95oC; multiple cycles of PCR can be performed in a single continuous event, and no additional polymerase is required
PCR Reaction
Denaturation (melting the double stranded DNA into two separate strands) >94oC
Annealing (primer binding) at 50oC to 65oC
Elongation. (DNA synthesis) at 72oC
copies of replicated DNA
2^n - 2n
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) analysis
enzyme digestion followed by electrophoresis
gel electrophoresis
process that separates molecules using an electric current
Semi-solid, porous gel matrix
DNA or RNA sample
Loading buffer
Dye
Molecular weight standard samples or "ladders”
TASTE TEST
phenotype testing
evolution
Change in allele frequency over time
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
No gene mutations may occur and therefore allele changes do not occur.
There must be no migration of individuals either into or out of the population.
Random mating must occur, meaning individuals mate by chance.
No genetic drift, a chance change in allele frequency, may occur.
No natural selection, a change in allele frequency due to environment, may occur

Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)
a small, free-living, nematode worm (round worm) that is currently used as a genetic model; feeds on microbes such as bacteria; Most of these nematodes are self-fertilizing hermaphrodite and a few are male
C. elegans development
4 days; Juvenile worms progress through four larval stages (L1-L4) over the next two days, increasing in size with each stage. After the fourth larval molt (L4), the worms are reproductively mature, meaning that they can be used for further genetic studies. Adults will live for 2-3 weeks, over which time they gradually age and lose vigor
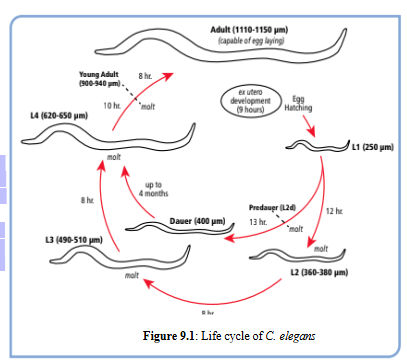
C. elegans as model organism
a simple and complete genome, a fast generation time, and are easy and inexpensive to maintain; 35% of worm genes have human homologs; extensive nervous system
SEXING of C. Elegans
Hermaphrodite - sharp tail, visible embryos in center
Male - spade tail, no eggs
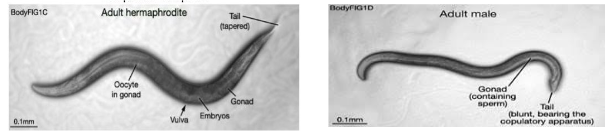
mating of C. elegans
s. Males arise by spontaneous X chro mosome nondisjunctionat a frequency of ∼0.1%
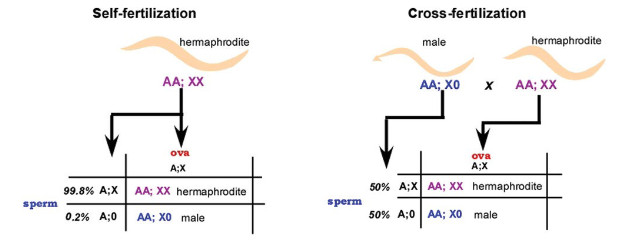
C. elegans mutations
Him-5 - increased rate of X-chromosome nondisjunction, leading to a higher proportion of male progeny (Up to 30% vs. 0.1% wildtype incidence)
Rol (rolling) - rolls around in crcles aimlessly
hbl (hunchback) - bent on dorsal side
Dpy (dumpy) - short and stout
bli (blister) - balloon like blisters on head and body
adr-2 - no ADAR activity and have lower protein diversity so aplastic and unadpative
Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome
mutations in the ADAR gene in humans; early onset
childhood disease characterized by microcephaly, seizures, glaucoma, skin lesions, and general abnormal
neurology
Exposures to heavy metal
common and dangerous environmental health issue.
The fast metabolic rates and limited self-repair abilities of nerve cells, as well as the large number of chemical messengers used in interneuron communication, make the nervous system particularly vulnerable to these chemicals