GB1- Chapter 2 Voab
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
element
substance that can’t be broken down into other substances through chemical reactions
makes up matter
compound
substances consisting two or more elements in a fixed ratio
essential elements
20-25% of 92 natural elements
required for life
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen make up 96% of living matter (CHON)
4% is composed of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur (CapKS)
trace elements
elements that are only required in minute quantities
atom
smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element
makes up element
atomic composition
atomic nucleus- neutrons and protons
electrons forming cloud of negative charge
neutron mass = proton mass/ measured in daltons
electrons aren’t calculated in atom’s total mass
atomic number
number of protons
mass number
number of protons and neutrons
atomic mass
atom’s total mass
isotopes
atoms of an element that varies in neutron numbers
radioactive isotopes
decay spotaneously, giving off particles and energy
radiometric dating
determines how old a rock or fossil is by measuring the ratios of different isotopes and calculates the number of half lives have passed since its formation
half-life
the fixed rate a parent isotope decays into daughter isotope
can vary from seconds to billions of years
energy
the capacity to cause change
potential energy
energy that matter posesses because of its location or structure
matter has natural tendancy to be at lowest possible potential energy state
electron shells
shells with different energy levels and average distance
valence electrons
in the outermost shell, valence shell
determines chemical behavior of the atom
elements with full valence shells are chemically inert
orbital
3D space where electrons are found 90% of the time
each orbital can have 2 electrons max
atoms interact to complete their valence shells = stability
chemical bonds
formed by the transfer or sharing of valence electrons
covalent bond
equal sharing of a electron pair between atoms
the shared electrons are counted as a part of both atom’s valence shells
molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
valence
atom’s bonding capacity
electronegativity
atom’s attraction for electrons in a covalent bond
the more electronegative it is, the stronger it pulls shared electrons toward itself
nonpolar covalent bond
equal electron sharing
polar covalent bond
one atom is more electronegative than the other= resulting in an unfair sharing of electrons
unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial charge
ions
charged atoms
cation
positively charged ion
anion
negatively charged ion
ionic bond
anion and cation’s attraction for each other
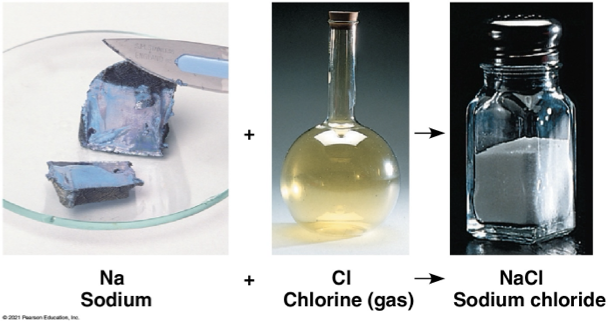
ionic compounds/ salts
formed by ionic bonds
NaCl
dissociate easily in water
hydrogen bond
hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom like nitrogen or oxygen
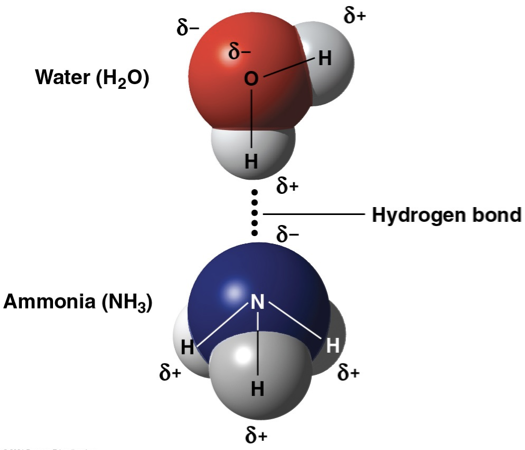
van der waals interactions
weak bonds formed between molecules due to uneven distribution of electrons
strong collectively
molecule’s shape
determined by orbital positions
covalent bond may cause s and p orbitals to hybridize, creating specific molecular shapes
crucial to molecule function
reactants
starting molecules of a chemical reaction
chemical reactions
making and breaking of chemical bonds
all chemical reactions are reversible
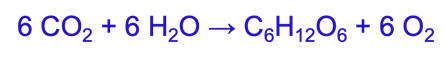
photosynthesis
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
products
resulting molecules of a chemical reaction
chemical equilibrium
forward and reverse reactions happening at the same rate
the relative concentration of reactants and products do not change