Neurodevelopment
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Name the main aspects of neuroanatomy
spinal cord
brain stem
cerebellum
diencephalon
cerebral cortex
Name the parts of brain stem
medulla
pons
midbrain
Name the parts of diencephalon
thalamus
basal ganglia
hypothalamus
Name the parts of the cerebral cortex
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital lobes
State areas in the anatomy of a neuron
cell body
dendrite
axon
synapse
What is the organiser in neural induction
specialised region to induce the nervous system
What does the ectoderm give rise to in neural induction
The neural plate
What is the neural plate
the precursor of the central and peripheral nervous systems
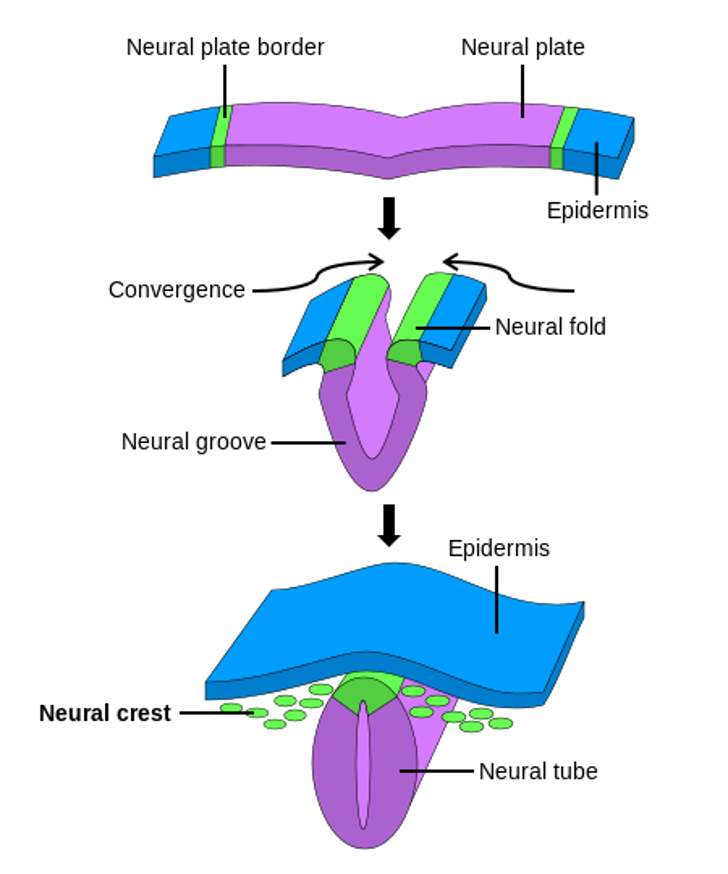
state the order of neural induction structures
neural plate → neural groove → neural tube
What is spemanns organiser
A specific region to induce a nervous system
a phD work by Hilda Mangold led to a Nobel
Name the key molecules in underlying molecular mechanisms
BMP (bone morphogenetic protein)
BMP inhibitors
chordin
noggin
follistantin
What does BMP result in according to molecular logic
BMP → epidermis
BMP inhibitors from the organiser → neural induction
What does BMP inhibitors from the organiser result in according to molecular logic
BMP inhibitors from the organiser → neural induction
Name the different types of patterning of the nervous system
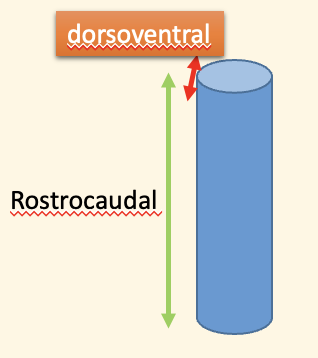
rostrocaudal patterning
dorsoventral patterning
forebrain patterning
What is dorsoventral patterning associated with
spinal cord development
Name the regions in rostrocaudal patterning
forebrain
midbrain
hindbrain
spinal cord
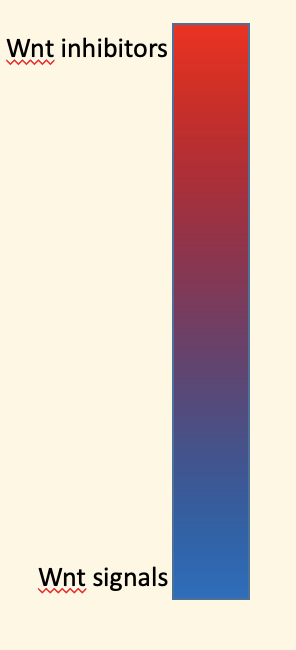
Label for rostrocaudal molecules


Label for rostrocaudal molecules
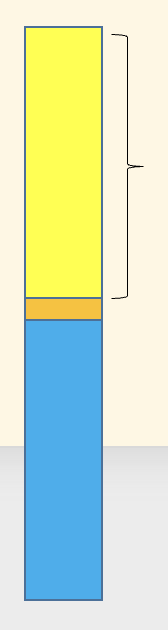
Label for rostrocaudal molecules
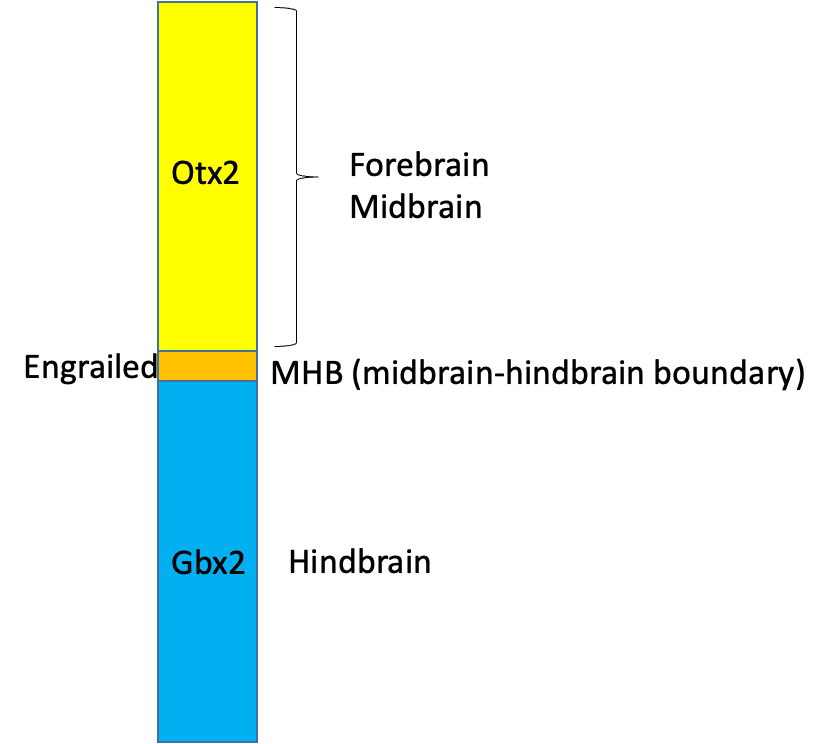

label the patterning
What is the ventral neural tube patterned by in dorsoventral patterning
The ventral neural tube is patterned by sonic hedgehog protein secreted from the notochord floor plate.
What is the dorsal neural tube patterned by in dorsoventral patterning
The dorsal neural tube is patterned by bone morphogenetic proteins
What is the role of FGF8 in forebrain patterning
establish the rostrocaudal pattern of the cerebral cortex
What is the role of Pax6 and Emx2 in forebrain patterning
mutually represent each others expression
Give examples of progenitor cells
neurons
glia
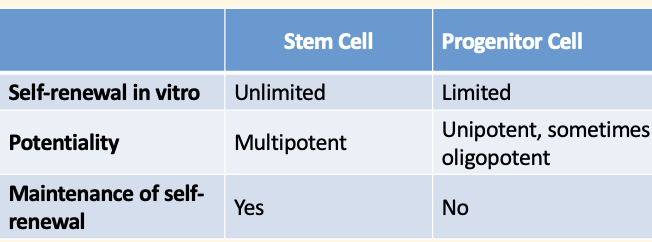
fill in blanks
Name the types of proliferation
asymmteric and symmetric
What is meant by oligopotent
Progenitor cells can be several different cell types
Describe differentiation in cortical development
neural stem cells
radial glial cells
progenitor cells
glias (astrocytes)
neurons
molecules
delta-notch signalling
basic helix-loop helix transcription factors
What pattern does neural migration of cortical cells follow
cortical cells follow inside-first outside-last pattern of migration (inside-out)
What takes place in the ganglionic eminence (GE)
Tangential migration during neural migration of cortical cells.
inhibitory neurons migrate into the cortex
Describe survival in neurons
not all neurons are destined to survive
apoptosis (programmed cell death)
what are neurotrophins
nerve growth factors
BDNF , NT-3
receptors of neurotrophins
TrkA (tyrosine kinase)
receptors of BDNF , NT-3
TrkB, C, p75
Name the stages of synapse formation
establishing neuronal polarity
axon guidance
synaptogenesis
refining neural circuits
What is synaptic plasticity
the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity
What are 2 types of brain disorders
neurological diseases
neuropsychiatric diseases
What are neurological diseases caused by
loss of neurons
what are neuropsychiatric diseases caused by
changes in neural circuits
give examples of neurological diseases
alzeimers
parkinsons
stroke
give examples of neuropsychiatric diseases
schizoprenia
depression
anxiety
autism