Cornell Vet Med Precollege
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
Dorsal
Towards the spine
Ventral
Towards the stomach
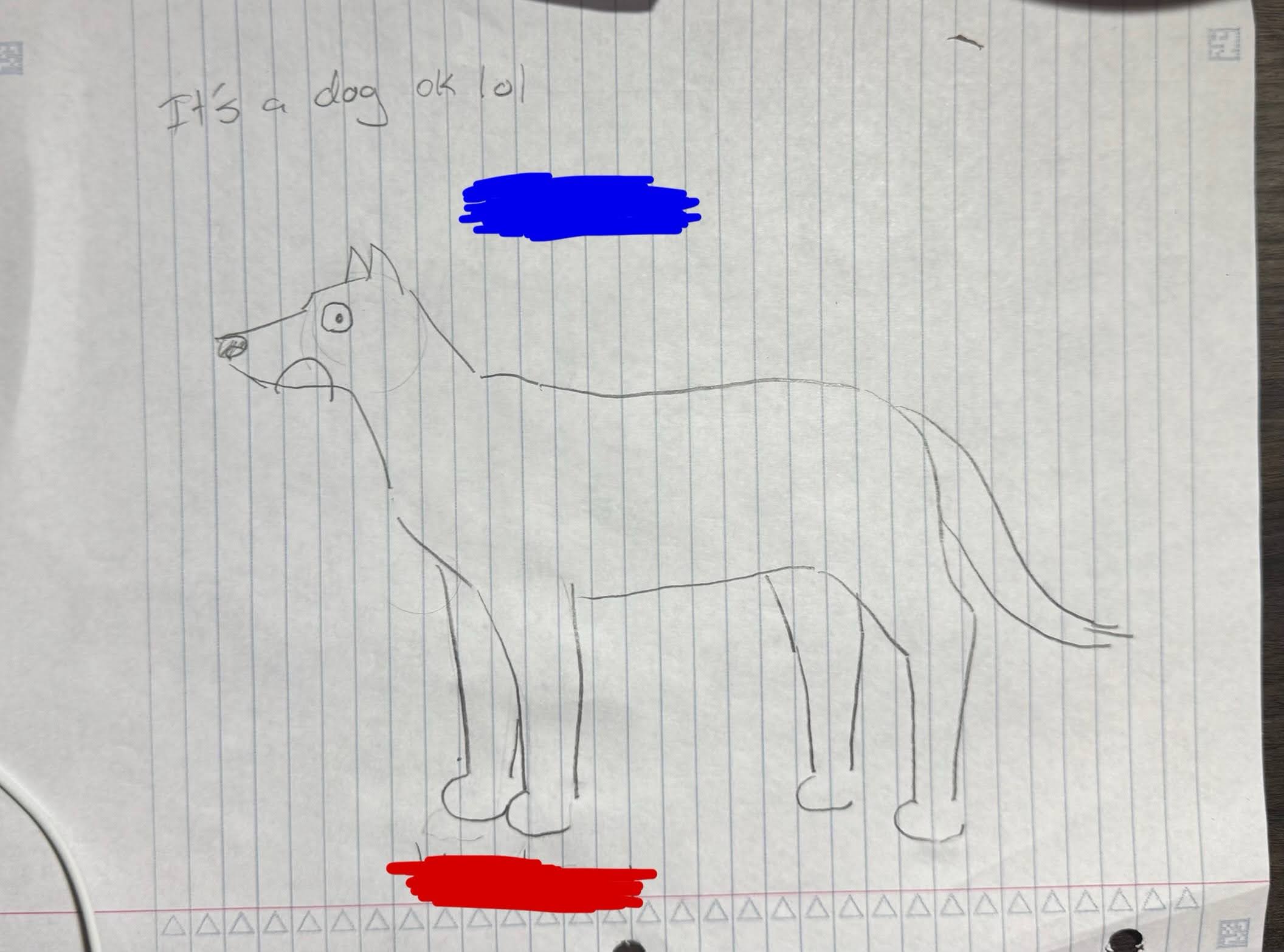

What is the red side?
Ventral
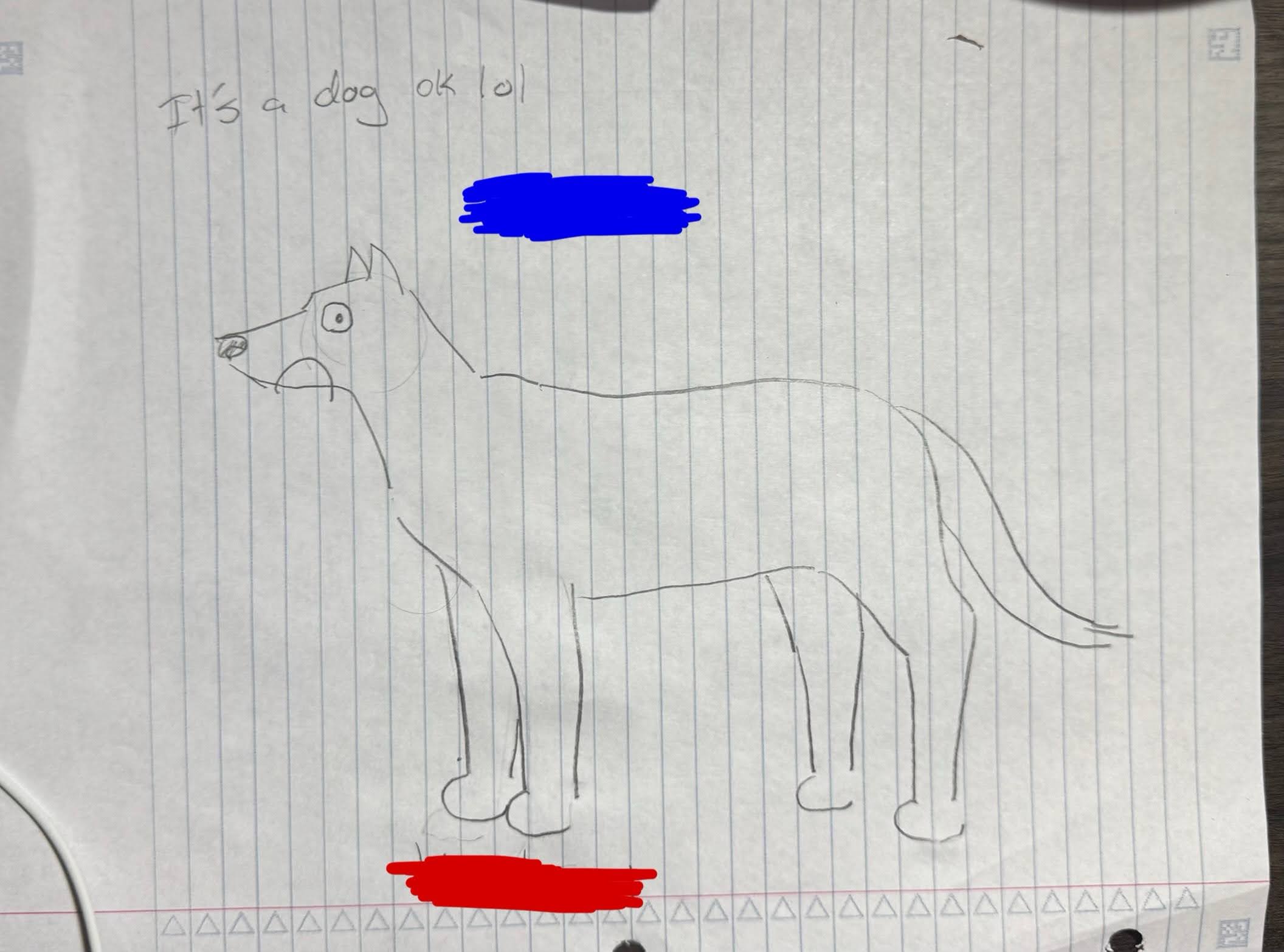

What is the blue side?
Dorsal
Cranial
Towards the head
Caudal
Towards the tail
Rostral
Towards the muzzle
Proximal
Closer to the body mass
Distal
Further from the body mass
Superficial
Surface of the body mass
Deep
Center of the body mass
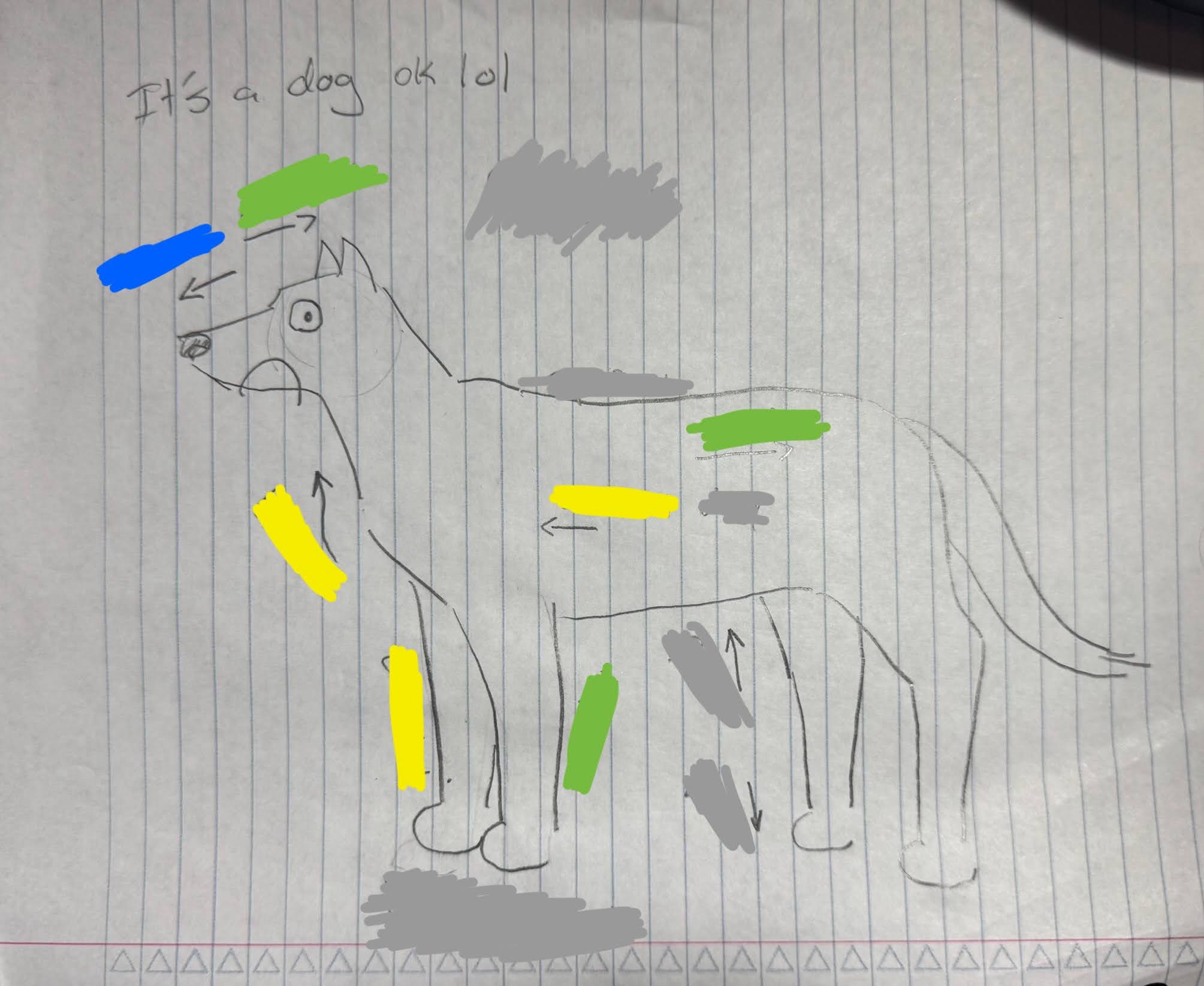

What is the green color?
Caudal
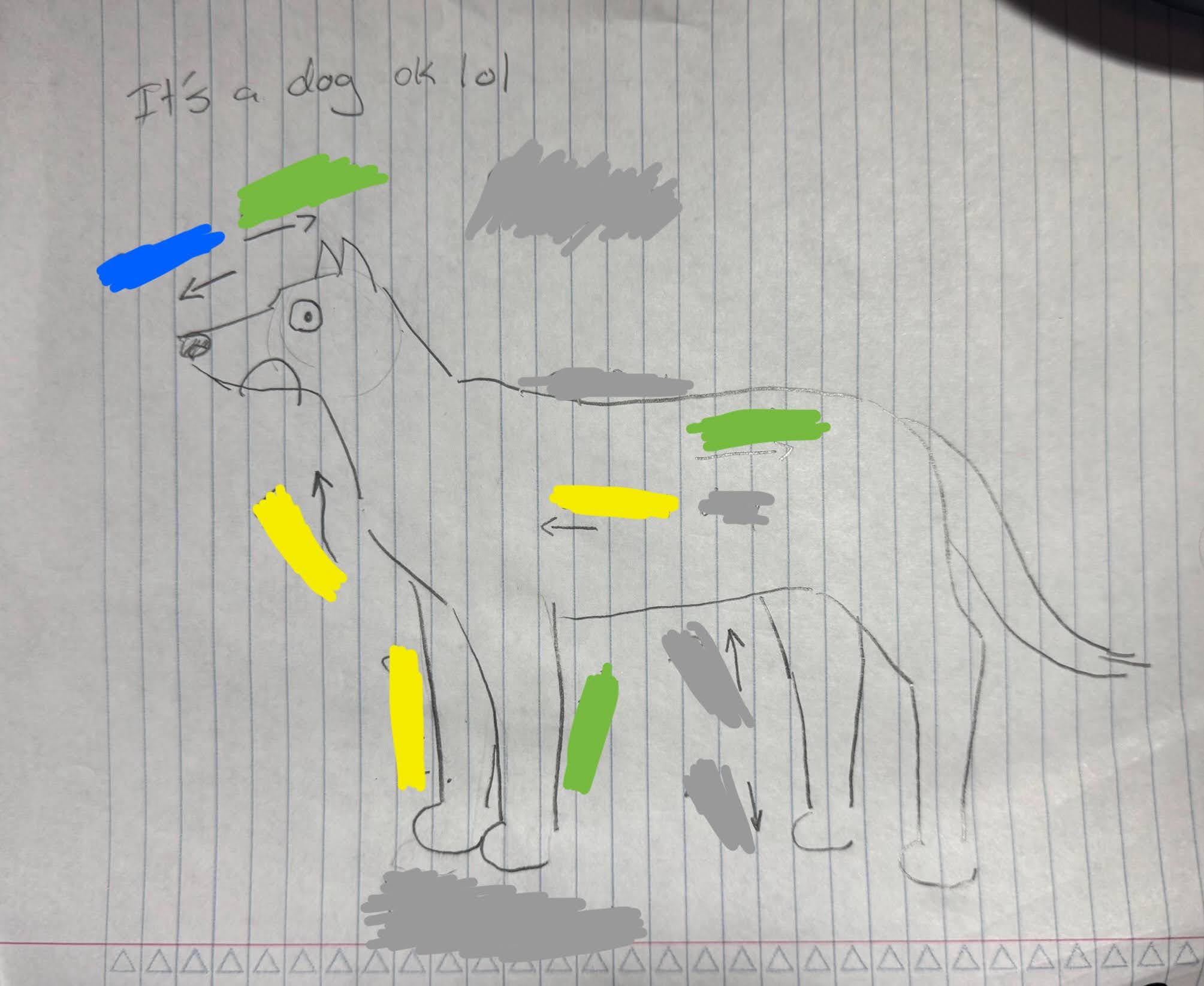

What is the blue color?
Rostral
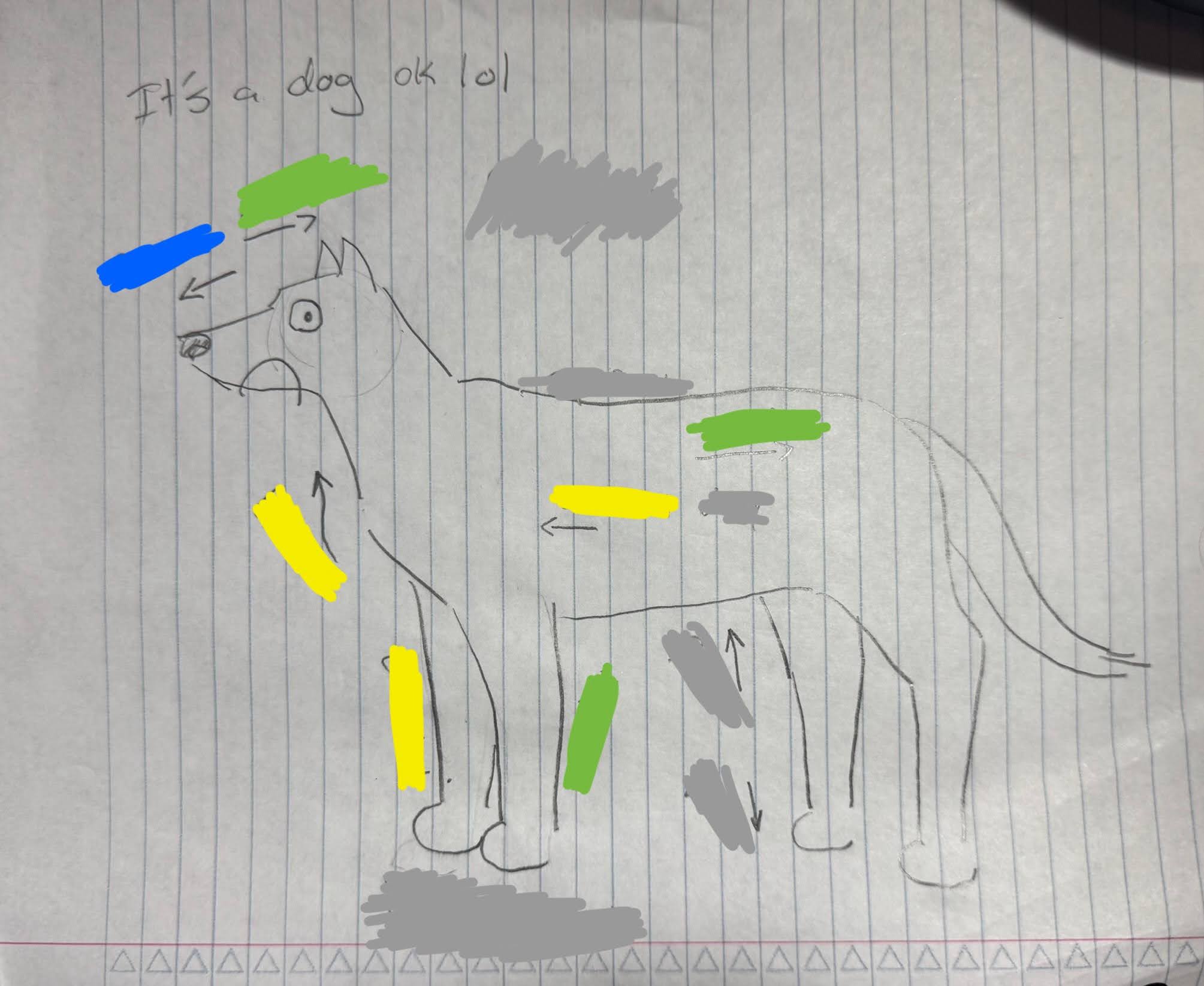

What is the yellow color?
Cranial
Anatomy
The form, disposition, and structure of tissues and organs that comprise the body
Physiology
The function of anatomy. How systems in the body structure and function in the whole being.
Ex. electrical conduction, muscle constraction
Gross anatomy
Anatomy of things you can touch and/or see with an unaided eye
ex. organs
Microscopic anatomy
(Histology) The anatomy of things that cannot be seen with an unaided eye
ex. tissues and cells
cells, structure of cells, and how they form together
Developmental anatomy
How an organism develops from the fetal state
Clinical anatomy
Anatomy pertaining to surgical procedures, exams, and the drawing of blood
Radiographic anatomy
Anatomy visualized using radiograph and imaging techniques
Applied anatomy
Application of anatomical knowledge to diagnose and treat
Head and neck
Important things to think about:
Pathway of food and air
What can be palpated?
What diagnostic tools can be used for the patient?
Ex. Muscles, nerves, blood vessels, lymph nodes, salivary glands
Thorax
Important things to think about:
What can be heard with a stethoscope?
What diagnostic tools can be used for the patient?
Ex. Heart, lungs, blood vessels, nerves
Abdomen
Important things to think about:
Spatial relationship
What can be palpated
What diagnostic tools can be used for the patient?
Pathway of food?
Ex. organs
Limbs
Important things to think about:
What can be palpated?
Important things to think about:
Ex. bones, joints muscles, nerves, blood vessels
Anterior
To the front (especially for the head)
Posterior
To the back (especially for the head)
Inferior
To the bottom (especially for the head)
Superior
To the top (especially for the head)
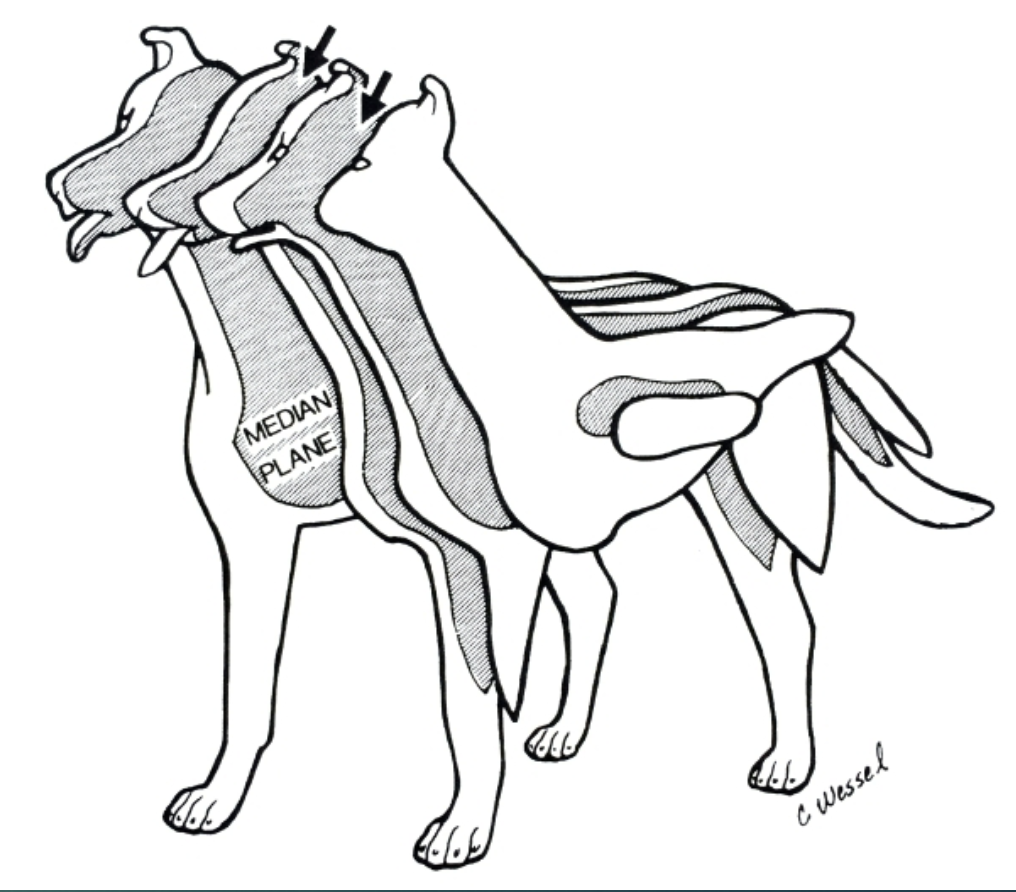
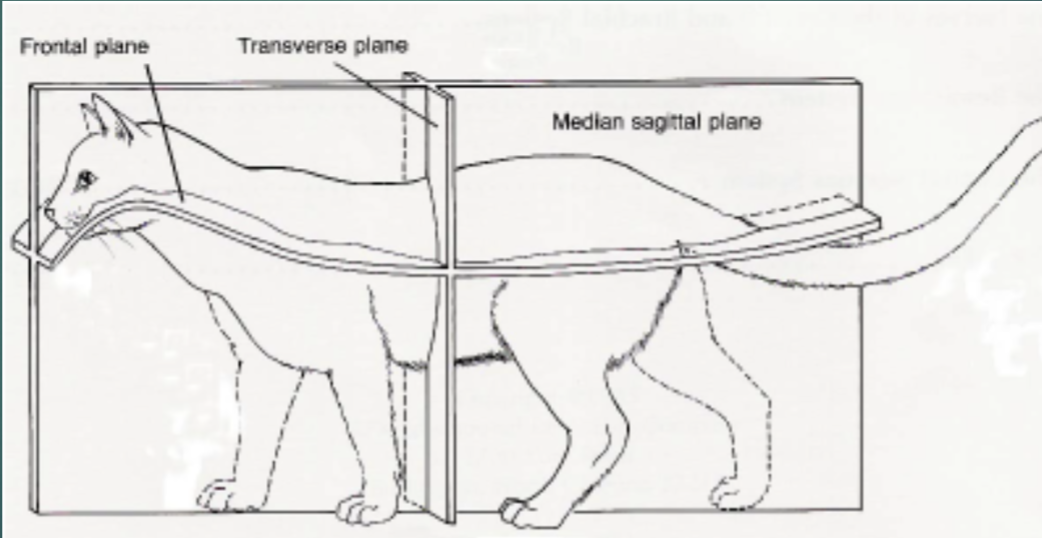
Sagittal plane
Division of an animal into left and right parts
Medial
Towards the middle (sagittal plane)
Lateral
Away from middle (sagittal plane)
This is a…?
Sagittal plane
This is a…?
Transverse plane
Division of an animal into cranial/rostral and caudal parts
Transverse plane
The four tissue types
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
What type of tissue is blood?
Specialized connective tissue
Definition of connective tissue
Cells suspended in a tissue specific extracellular matrix
Functions of blood
Transportation - move oxygen/carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, and waste products
Protection - fight infection, clot blood, coagulation
Regulation - PH balance, temp, electrolyte balance
What are the components of blood?
Plasma, red blood cells, and the buffy coat
Plasma in blood
~55% of blood
Components:
water (90%)
dissolved substances (10%)
proteins (albumin, globulin)
waste products (urea, creatinine, bilirubin)
Salts, minerals
Red blood cells in blood
~45% of blood
Buffy coat in blood
~1% of blood
white blood cells, platelets
Serum
Liquid remaining after blood clots naturally
no clotting factor
plasma - clotting factor = serum
Plasma
Liquid portion of blood treated with an anticoagulant
Contains clotting factors (fibrinogen)
Blood clots contain..
fibrinogen
Red blood cells are also called
Erythrocytes
Erythrocytes function to…
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
Principally made of hemoglobin
Each molecule carries oxygen
Live for 2-4 months
Mature in bone marrow from reticulocytes (larger and less contained hemoglobin)
Erythrocytes appearance
Anucleate - spit out the nucleus as they develop
Biconcave disc
Central pallor - pale area in center
An increase erythrocyte is called
Erythrocytosis
overproduction by the bone marrow
Compensation for chronic hypoxia (low oxygen) or high altitude
A decrease of erythrocyte is called
Anemia
Regenerative anemia
Hemorrhage (loss of RBC)
Hemolysis (destruction of RBCs)
Non-regenerative anemia (decreased production)
White blood cells are also called..?
Leukocytes
Leukocytes functions
The defense of the body against infection
Less numerous than erythrocytes
What are the two types of leukocytes?
Granulocytes: contains granules
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils
Agranulocytes: lacks granules
lymphocytes, monocytes
Leukocyte abnormalities
Increase:
Leukocytosis
Decrease:
Leukopenia
What are granules?
Little vesicles with different proteins, enzymes etc that help with immune function of the cells. Each cell has granules with different content depending on function
Neutrophil function
Granulocyte
Most abundant
Fights against disease
Engulf invading bacteria and cellular debris through phagocytosis
Lifespan: 5-10 hours
Abnormalities:
Neutrophilia - increase
Neutropenia - decrease
Left shift - increased banding
Neutrophil appearance
Lobulated nucleus with granulated cytoplasm
Mature -segmented nucleus
Immature - “band” nucleus
Basophil function
Granulocyte
Last line of parasite defense
Regulates allergic reactions (releases histamine, pro-inflammatory)
Lifespan: ~6 hours
Abnormalities
Increase: Basophilia
Decrease: Basopenia
Basophil appearance
Lobulated nucleus with basophilic (purple) granules
Eosinophil function
Granulocyte
Parasite defense
Regulates allergic reactions
Enzymes inactivate histamine (balances basophils)
Lifespan: minutes to hours
Abnormalities:
Defense: eosinophilia
Increase - eosinopenia
Eosinophil appearance
Lobulated nucleus with eosinophilic (pink) granules
Monocyte function
Agranulocyte
Largest of leukocytes
Phagocytic cells kill microorganisms, ingest foreign materials, and remove dead cells
Lifespan: 12 - 24 hours
Migrate into tissues (similar to neutrophils) and mature to macrophages or dendritic cells
Abnormalities:
increase: monocytosis
decrease: monocytopenia
Monocyte appearance
Varies
Horseshoe shape
Bubble vacuoles
Nucleus +/-1 lobules
Cytoplasm +/-1 vacuoles
Lymphocyte
Agranulocyte
Second most common type of leukocyte
Main cell type of the immune system(B and T cells)
Lifespan: hours to years
B cells:
matures in plasma cells, antibody production
T cells:
cytotoxic T cells kill infected cells
helper T cells recognize infected cells and recruit other cells
Abnormalities:
Increase: Lymphocytosis
decrease: Lymphopenia
Plasma is a type of…
Lymphocyte
Lymphocyte appearance
Round nucleus, little cytoplasm
What are platelets also known as
Thrombocytes
Platelets function
Formation of blood clots
Prevent bleeding after vessel injury
Form platelet plug at injury
Lifespan: 1 - 2 weeks
Produced in bone marrow
Abnormalities:
increase: Thrombocytosis
Decrease: Thrombocytopenia
Can lead to increased bleeding and bruising
For this course platelets…
are their own category of cell, NOT a white blood cell
Platelet appearance
Very small, disc shaped
Anucleated cell fragments
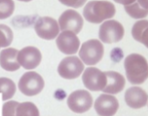
These are…
Red blood cells (erythrocyte)
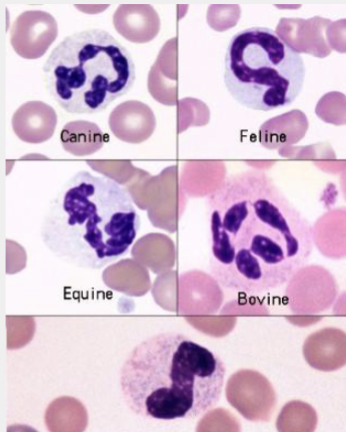
These are…
Neutrophils
Lobulated nucleus
Granulated
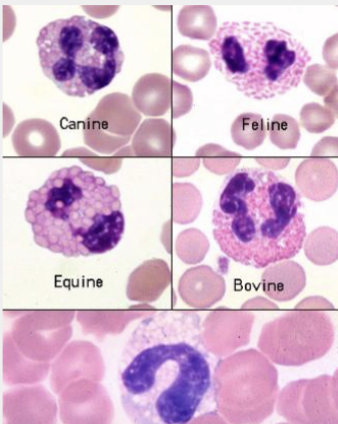
These are…
Eosinophils
Pink
Bubbly
Granulated
Lobulated nucleus
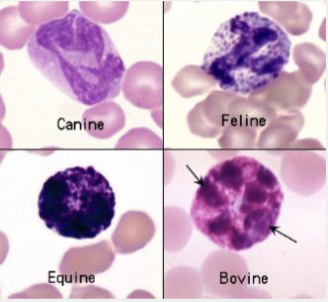
These are…
Basophils
Lobulated nucleus
Granulated
Purple granules
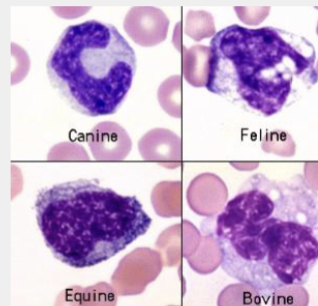
These are…
Monocytes
Horseshoe shape
No granules
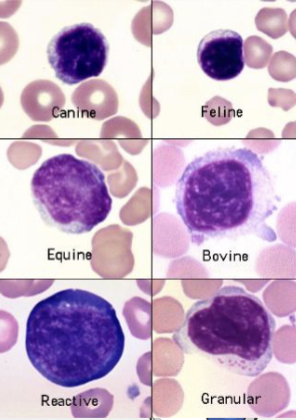
These are…
Lymphocytes
Round nucleus, little cytoplasm
No granules
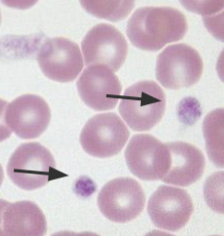
What are the arrows pointing to?
Platelets
Blood circulation
Transported through body in vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
Proper circulation provides oxygen and nutrients to different tissues and removes waste
Regulated by hormones and nervous system signals
Disruptions can lead to health problems
ex. stroke, heart disease, hypertension
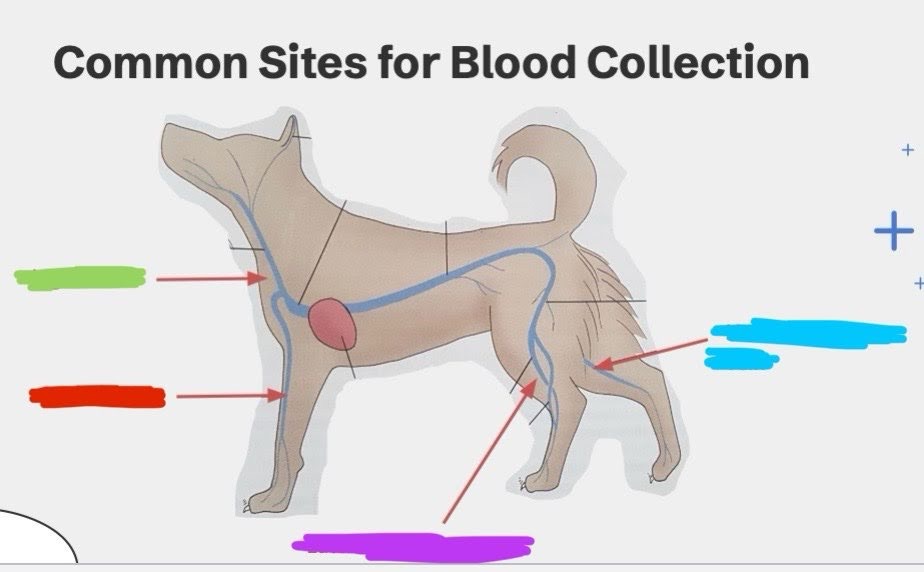
What is the green vein?
Jugular vein
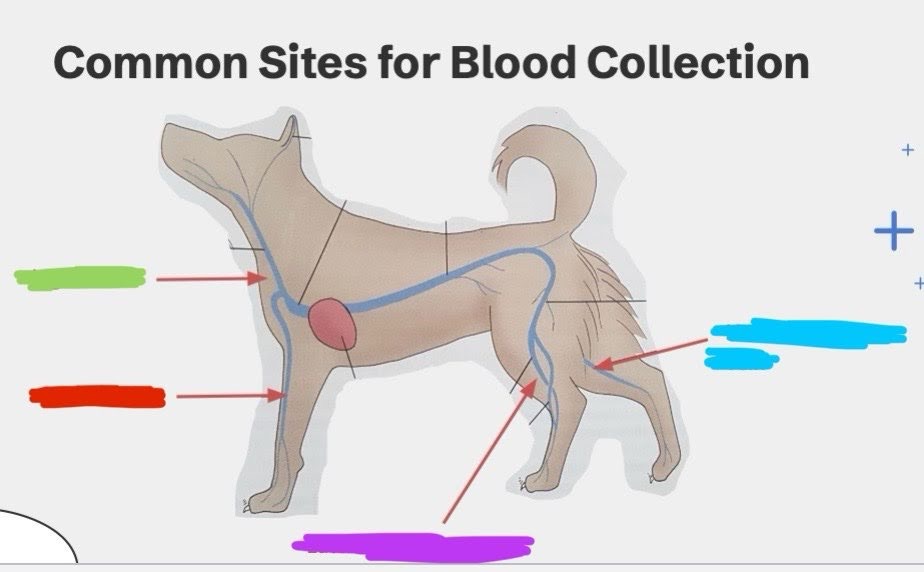
What is the red vein?
Cephalic vein
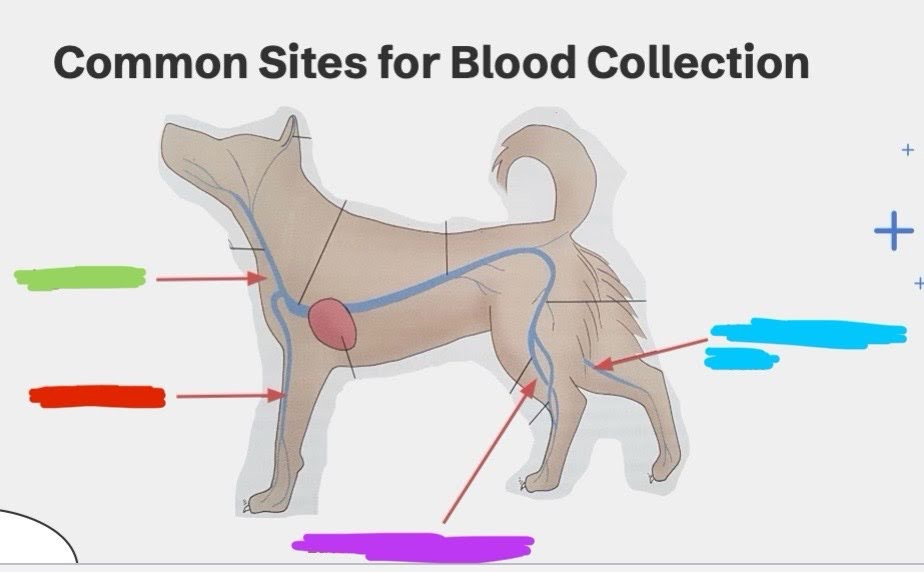
What is the purple vein?
Lateral saphenous vein
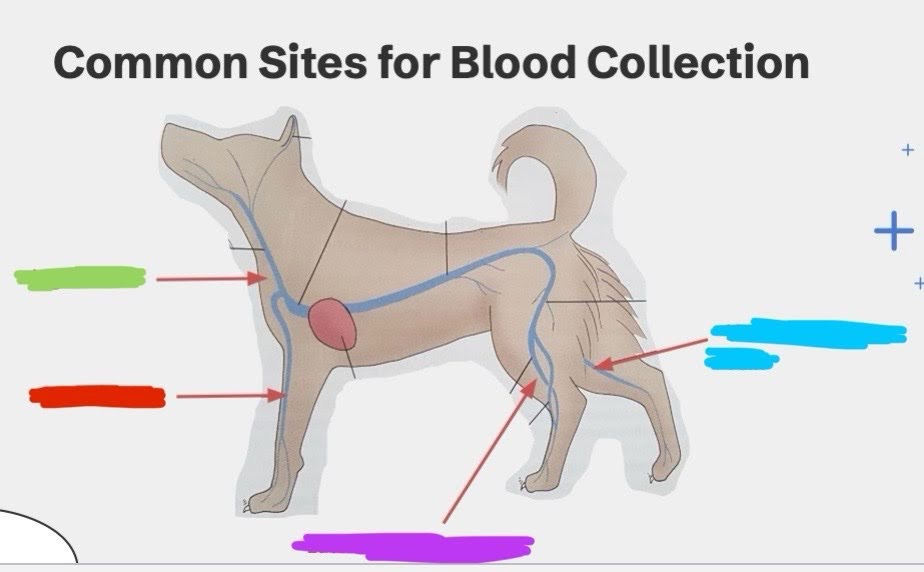
What is the blue vein?
Medial saphenous vein
What blood collection site is typically used for dogs / larger animals?
Cephalic vein
What blood collection site is typically used for cats / smaller animals?
The saphenous veins
Blood tubes with purple tops
Contain EDTA as an anticoagulant
Used for complete blood count
Blood tubes with green tops
Contains heparin as an anticoagulant
Used for chem panels
Blood tubes with blue tops
Contains citrate as an anticoagulant
Used for coagulation panels
Blood tubes with red tops
No additives
Used for chem panels
What does a complete blood count test?
What does a chem panel test?
Analyzes non-cellular components of blood (proteins, electrolytes, minerals)
What does a blood smear test?
The morphology of blood cells
Organ system hierarchy
Subcellular structures → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems
Epithelial tissues shape
Continuous sheets that cover body surfaces (interior and exterior) and secretary portions of glands
Main roles of epithelial tissues
protection, absorption, and secretion
How are epithelium described?
shapes
squamous if flat
cuboidal if cube-shaped
columnar if they look like columns
layers
simple if there is one cell layer
stratified if there is more than one cell layer
pseudostratified if it initially appears stratified but isn’t
What are the specialized modifications on the surface of epithelial tissues
microvilli or cilia that I can allow for more surface area for absorption (places like the gut) or allow them to move fluid or particles along the surface(respiratory tract)
What is contained in an extracellular matrix?
water gel, rich in negatively charged molecules (to attract water)
fibrous compounds, like collagen and elastic fibers, for flexibility and tensile strength to create a supportive framework