ISAT 321 Exam 2
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
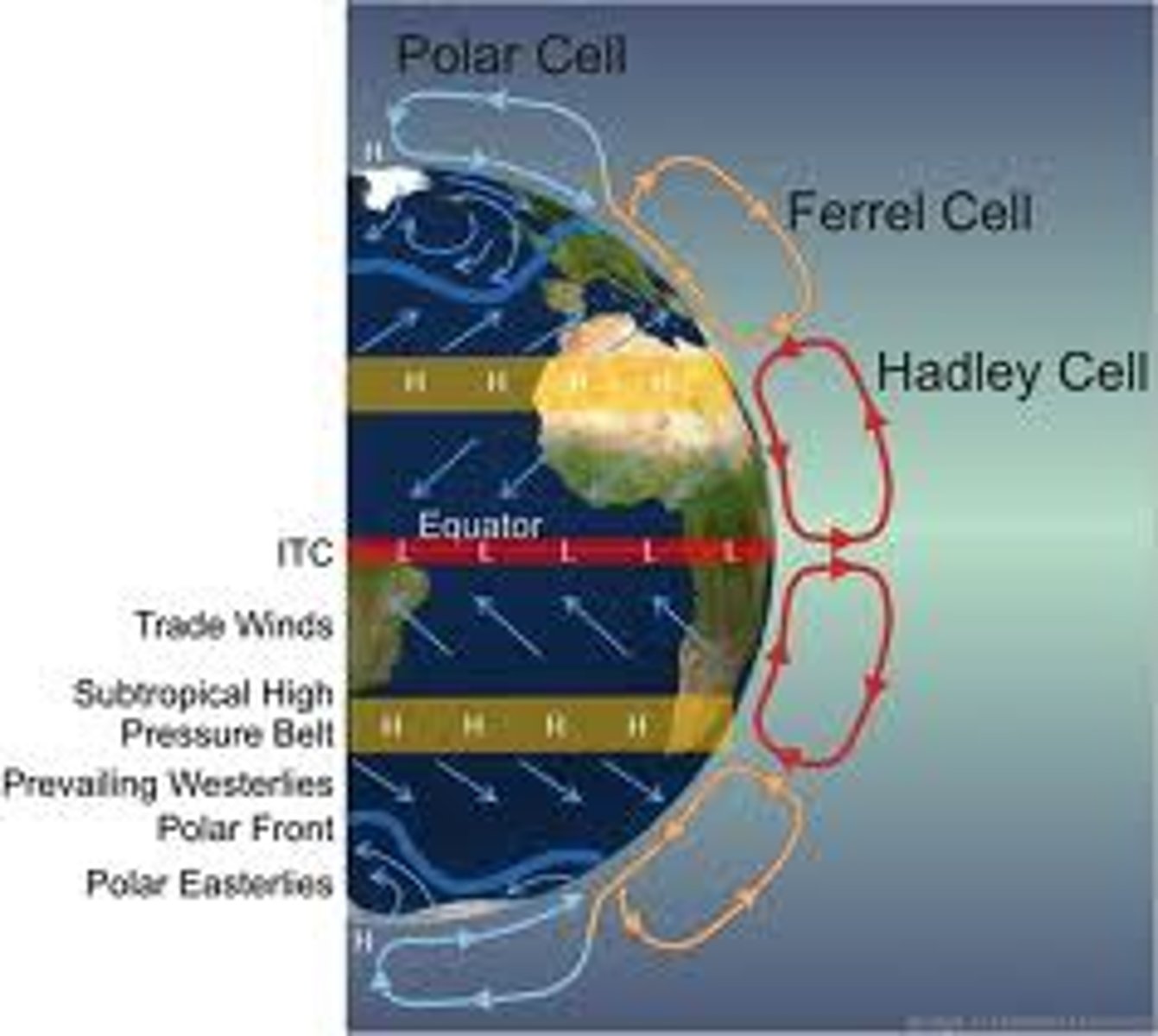
Where does weather come from?
-the rotation of the earth creates large-scale prevailing winds
-tilt provides seasons
Coriolis effect
-prevailing winds
-curves to the right in northern hemisphere
-curves to the left in southern hemisphere
Hadley Cells
Dry adiabatic lapse rate
-how long it takes a dry parcel of air to rise (-10 degrees Celsius per km)
-used as a standard for measuring atmospheric conditions
Stable conditions
-air unable to mix
-line to the right of the dry adiabatic lapse rate
unstable conditions
-air is able to mix
-line to the left of the dry adiabatic lapse rate
lofting plume
stack is above inversion layer
coning plume
-neutral atmosphere
-line is on the dry adiabatic lapse rate
looping plume
-unstable conditions
-air moving up and down
fanning plume
-stable conditions
-vertical movement is limited, so plume goes horizontal
fumigation plume
-stack is below inversion layer
-most dangerous
inversion
ambient temperature increases with elevation
radiation inversion
nocturnal cooling of earth's surface of clear winter nights; ground cools more quickly than air
subsidence inversion
-sustained high pressure systems
-descending air warms more than air below it
Gaussian Dispersion Model: C
ground level concentration at some point
Gaussian Dispersion Model: Q
source strength
Gaussian Dispersion Model: sigma y and sigma z
standard deviation of the dispersion
Gaussian Dispersion Model: u
wind speed at the elevation of the centerline of the plume
Gaussian Dispersion Model: y
distance horizontally
Gaussian Dispersion Model: H
effective stack height
Why is indoor air quality important?
we spend a lot of our time inside, so we are exposed much more to indoor air pollutants
emissions
where the pollutants come from
exposures
how we are exposed to these pollutants
pollutants that are less concern indoors
-SOx
-NOx
-O3
pollutants that are equal concern indoor and outdoor
-CO
-PM
pollutants that are greater concern indoors
-Radon
-asbestos
-hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) and VOCs
-biogenic contaminants
Radon entry
Enters homes through foundation cracks and groundwater.
radon
naturally occurring radioactive noble gas
why is radon a concern?
It breaks down into lead over time and can cause lung cancer
how to mitigate radon?
add tubes and fans to your house to blow the basement air/radon directly outdoors
Asbestos Health Effects
-inhalation can cause: mesothelioma and asbestosis
Asbestos Abatement
-ban and phase-out (now overturned)
-leave in place and encase to prevent it from becoming airborne
-removal if airborne
Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPS)
-known to cause cancer or other serious health impacts
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
-common air contaminants, and many synthetic materials inside buildings emit them
HAP and VOC sources
-paints, carpets, electronics, fabrics, composite wood
-cleaners, air fresheners, cosmetics
-smoking, cooking, wood stoves, dry cleaning
Managing Indoor VOCs
-source control: product selection, product testing and labeling, allow for degassing, eliminate source activities
-ventilation: natural ventilation, mechanical HVAC, exhaust venting
Ozone air purifiers: "junk science"
-generates ozone to "purify air"
-oxidize and reduce many odor causing organics, but pushes ozone into your space
why are freshwater resources scarce?
not a lot of usable water on earth, despite the fact that there is so much (only about 2.5%)
domestic water usage
-partially consumptive
-public supply
-private wells
agricultural water usage
-consumptive
-irrigation
-livestock
industrial water usage
-mostly non-consumptive
-mostly for cooling
in-stream water usage
-non-consumptive
-hydroelectric power
-recreation
-navigation
which usage is dominant?
agricultural, then industrial
What is the first step in drinking water treatment?
Preliminary treatment: screens, primary settling
What is the purpose of coagulation in drinking water treatment?
Neutralizing particle charges: alum
What is flocculation in the context of drinking water treatment?
Sticking particles together so they can settle
What does softening refer to in drinking water treatment?
Removing hardness to reduce scale formation
What is the process of sedimentation in drinking water treatment?
Removing flocculated particles
What is the purpose of filtration in drinking water treatment?
Removing smaller particles
What is disinfection in drinking water treatment?
Killing harmful microbes
What is fluoridation in drinking water treatment?
Adding beneficial chemicals
chlorination byproducts
-trihalomethanes
-toxic
-reduced by reducing the chlorination levels
what effects water runoff?
-rainfall and intensity
-drainage area
-soils
-land use
-topography
-antecedent soil moisture
what is the impact of land use on runoff?
effects how much water can infiltrate. for example, in cities there is a lot of runoff due to impervious surfaces
estimating pollutant loads
-L = A + C
-L: load in mass of pollutant
-A: area for a given land use
-C: export coefficient for each land use type
JMU BMPs
-detention and retention ponds
-underground detention
-bioretention filter (rain gardens)
-sand filter
-green roof
-tree in a box
-oil/water separator
-storm filter treatment system
-hydrodynamic separator
stormwater regulation and control
-not really regulated unless you are an industry
-use BMPs for control
Why do we need wastewater treatment?
-to protect human health from pathogens in the waste
-to protect the environment from ecological effects of various pollutants like pathogens, solids, nutrients, and more
Septic system
A relatively small and simple sewage treatment system, made up of a septic tank and a leach field, often used for homes in rural areas
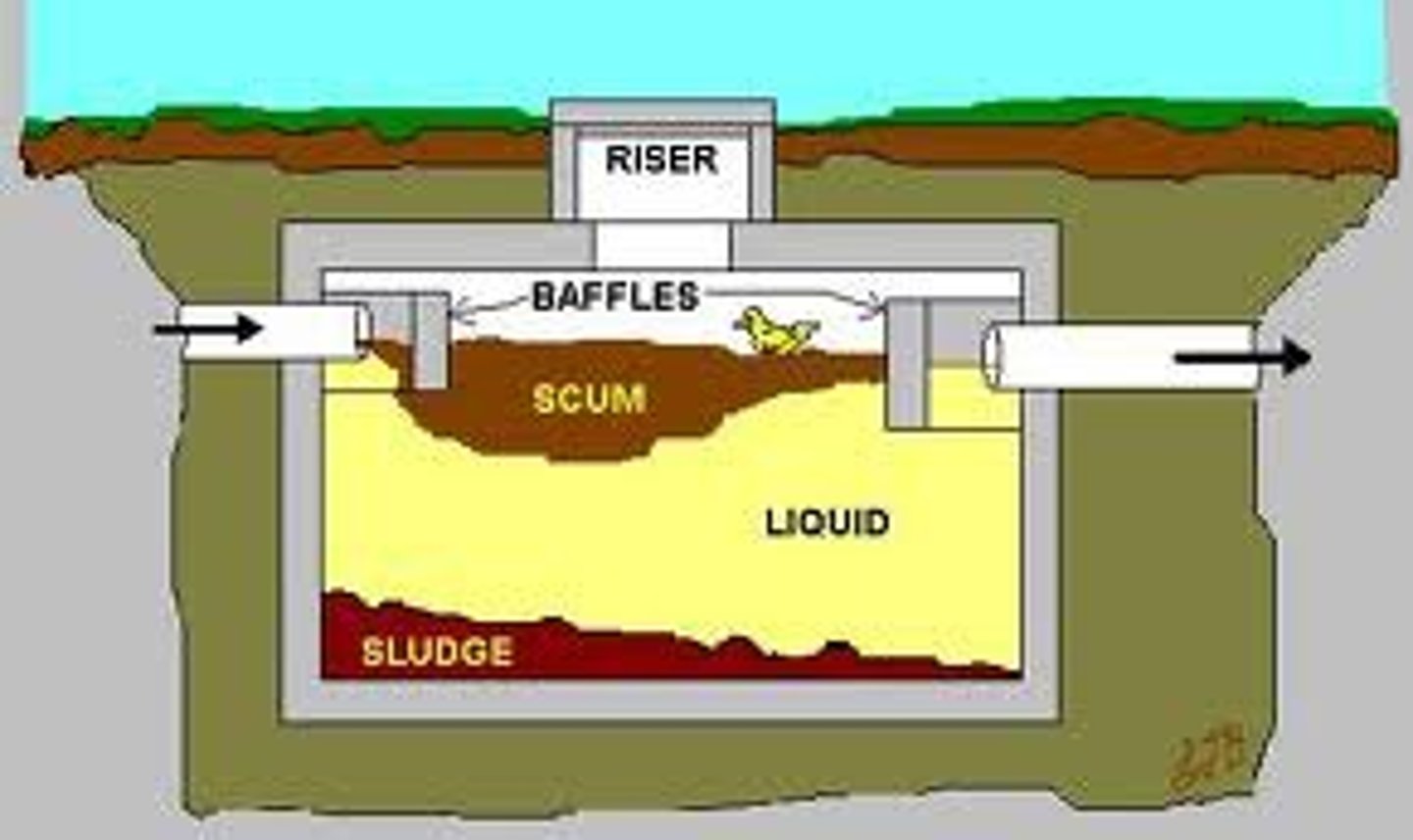
primary wastewater treatment
-screens and grit chambers: remove debris and very large particles
-primary clarifier: remove suspended particles
bioreactor (wastewater)
biologically degrade waste using microbes
return activated sludge
recycling a portion of sludge keeps beneficial microbes in the bioreactor
trickling filter (wastewater)
-microbes grown on fixed media
-waste is allowed to trickle through media
rotating biological contactor
microbes grown on media that is rotated in and out of the water
final clarifier (wastewater)
settle microbes produced in biological reactor
disinfection (chlorine) (wastewater)
-kill remaining microbes
-contact time and residual chlorine concentration are critical
-dichlorination required
nitrogen cycle
-Ammonification: organic N -> ammonia
-Nitrification (aerobic): ammonia -> nitrite -> nitrate
-denitrification (anaerobic): nitrate -> gaseous nitrogen
phosphorous removal (wastewater)
incorporation into sludge