Chapter 6 Separation and identification of the components of mixtures | Chemistry for VCE Units 1 & 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
solubility
the ability of a substance to dissolve
solute
the substance being dissolved in the solvent

solvent
the substance that another is being dissolved in, e.g. water
dissolve
when solute–solute bonds break and the solute molecules mix evenly with the solvent molecules

chromatography
an analytical technique that separates the components of a sample mixture based on the properties of the molecules
phase
(in chromatography) a form of matter that has uniform chemical and physical properties; can be a pure substance or a mixture
mobile phase
the solvent phase that flows, moving the components of a sample over the stationary phase
stationary phase
the solid phase to which the components of a sample are adsorbed; can sometimes be a liquid coated onto a solid support
affinity
the strength of the interaction of a substance within a sample with the mobile or stationary phase
adsorption
the attraction of a substance within a sample to the stationary phase; how the substance 'sticks' to the stationary phase
desorption
the release of a substance within a sample from the stationary phase into the mobile phase; how the substance 'unsticks' from the stationary phase
paper chromatography
an analytical technique for separating and identifying mixtures; the stationary phase is a thin strip of absorbent paper
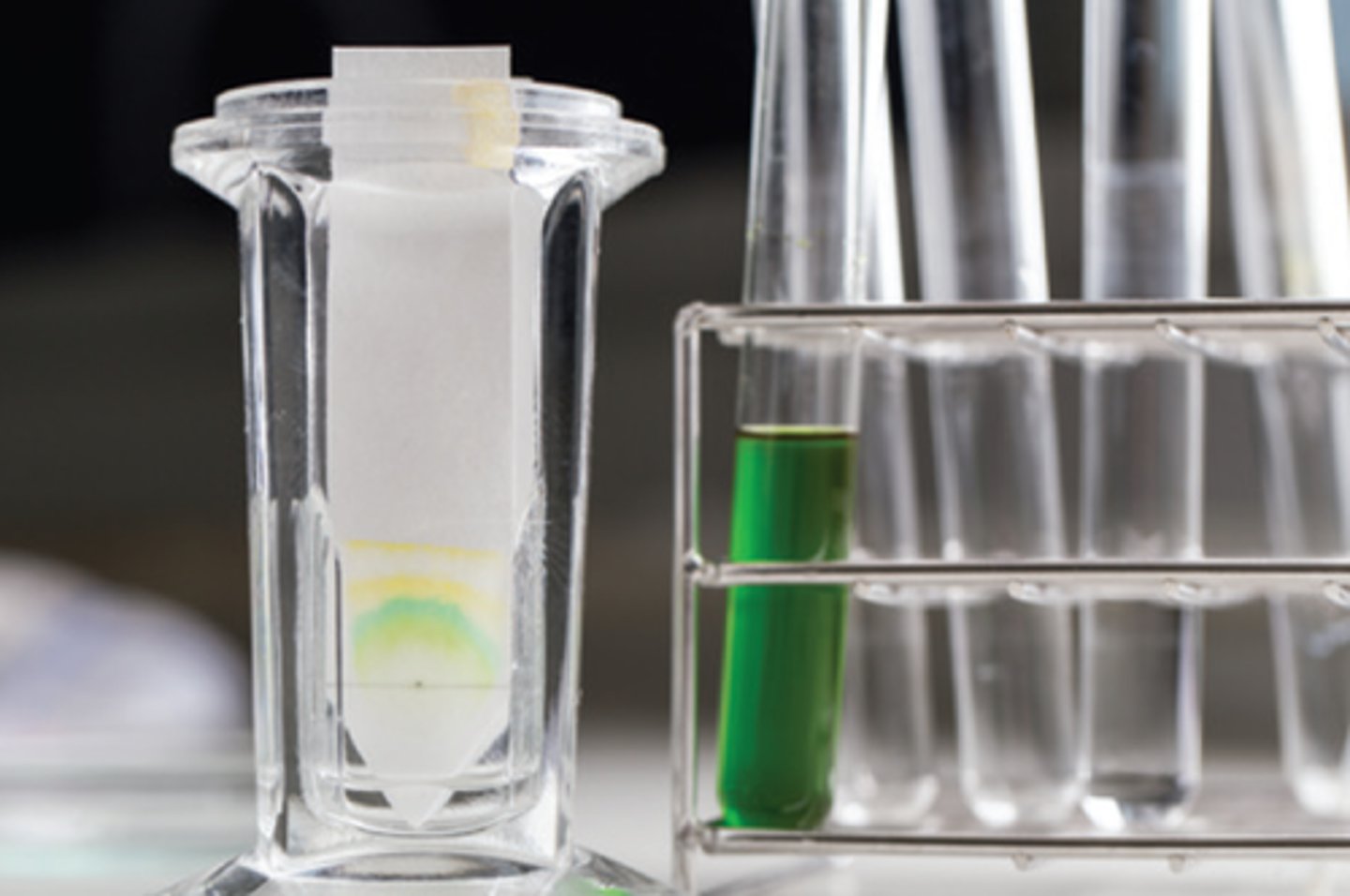

origin
the line applied to a chromatogram to mark the point where the sample or standard is placed
capillary action
the movement of a liquid through a narrow space (e.g. the cellulose network in absorbent paper) without any help; usually against gravity
solvent front
the point the mobile phase reached on a chromatogram before the analysis is terminated
chromatogram
the pattern of bands, spots or peaks formed on the chromatograph paper or TLC plate, demonstrating the separation of a mixture
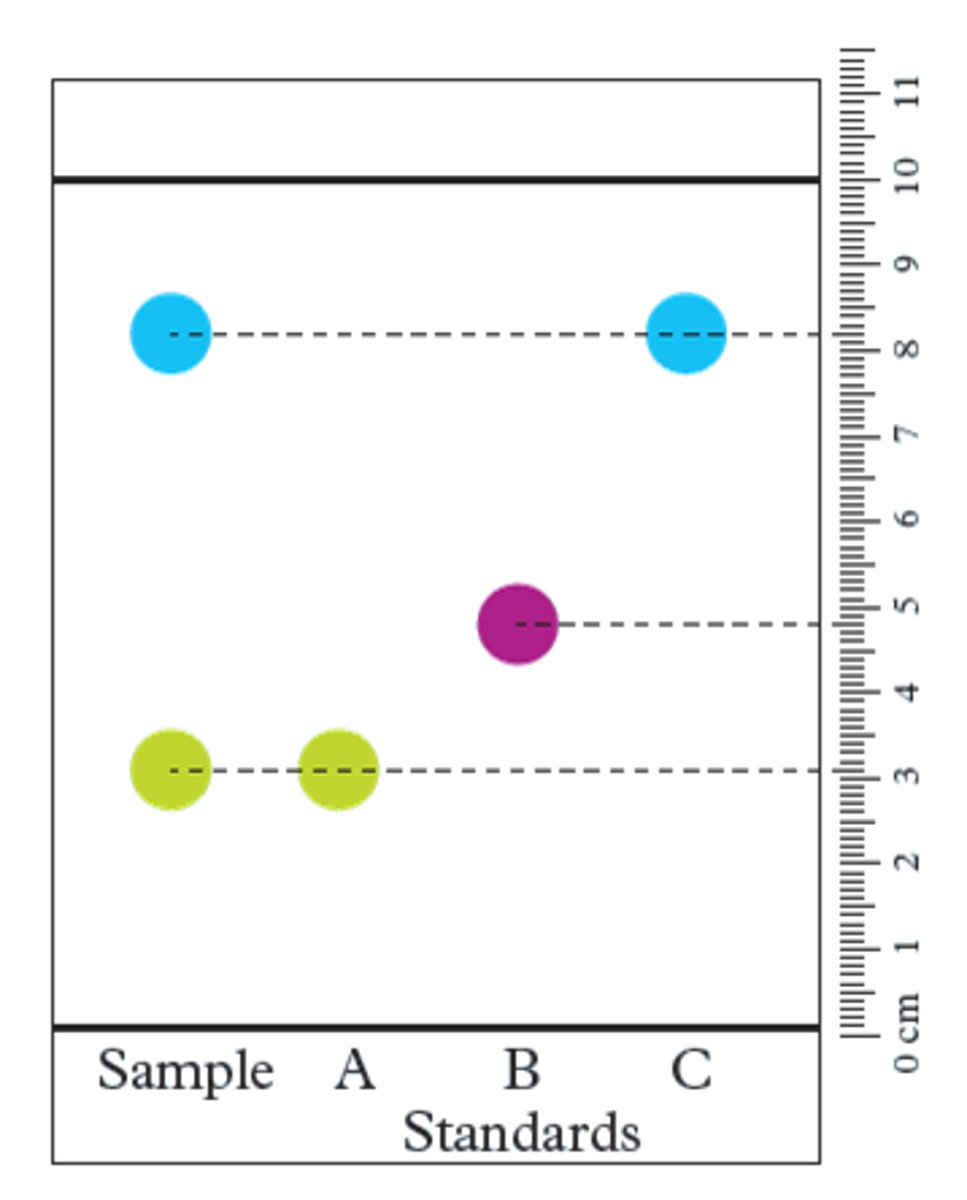
retardation factor (Rf)
the ratio of the distance travelled by a component of a sample, from the origin, in relation to the distance travelled by the mobile phase
thin-layer chromatography (TLC)
an analytical technique for separating and identifying mixtures; the stationary phase is typically a thin layer of silica gel, aluminium oxide or cellulose supported on a piece of glass or plastic
fluorescent
emitting visible light when exposed to radiation

two-dimensional paper or thin-layer chromatography
an analytical technique used to separate components; a first paper or thin-layer chromatography analysis is completed, and the sheet is rotated 90° and a second analysis is run using a different mobile phase
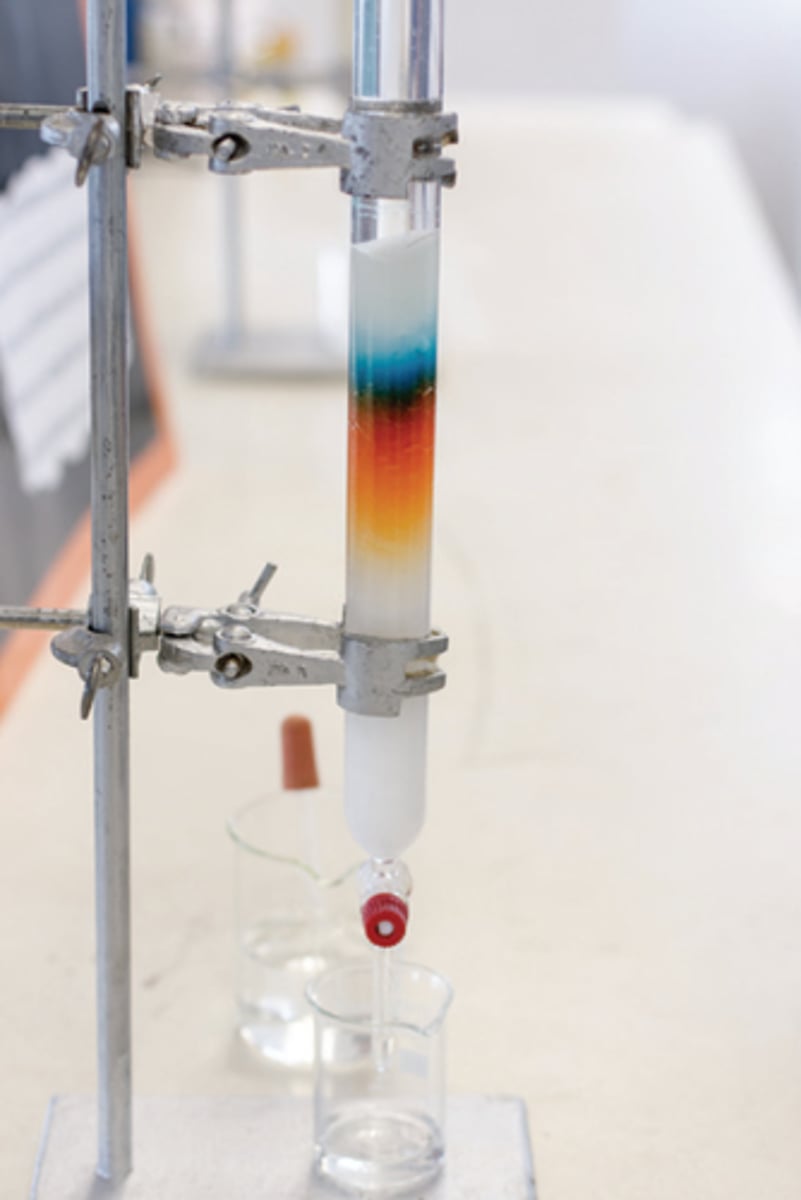
column chromatography
a technique used to separate and purify individual components from mixtures of compounds

separation science
the science of separating a mixture on the basis of the different properties of its components
column
the tube-like structure that contains the stationary phase in column chromatography, through which the mobile phase and sample flow
elute
come out of the bottom of a chromatography column
retention time (Rt)
the time that a component is retained by a chromatography column
high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
a form of column chromatography in which the mobile phase is pumped through a column at a controlled flow rate; the particles of the stationary phase are much smaller than in column chromatography and are densely packed to make separation more sensitive and efficient
mass spectrometry
an analytical technique in which a sample is bombarded with electrons to form charged fragments; the fragments are analysed and put together like a puzzle to identify the substances present