Chapter 12 Neurons & Nervous Tissue
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Sections of the Nervous System
Central
Peripheral
Central Nervous System comprises of
brain & spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System comprises of
nervous tissue outside CNS and ENS
Two Kinds of Cells in Nervous System
neurons
neuroglia (suppporting cells)
Special Sensory Receptors
monitor smell, taste, vision, balance, and hearing
Visceral Sensory Receptors
monitors internal organs
Somatic Sensory Receptors
monitor skeletal muscles, joints, and skin
movement, temp, pain, pressure, vibration
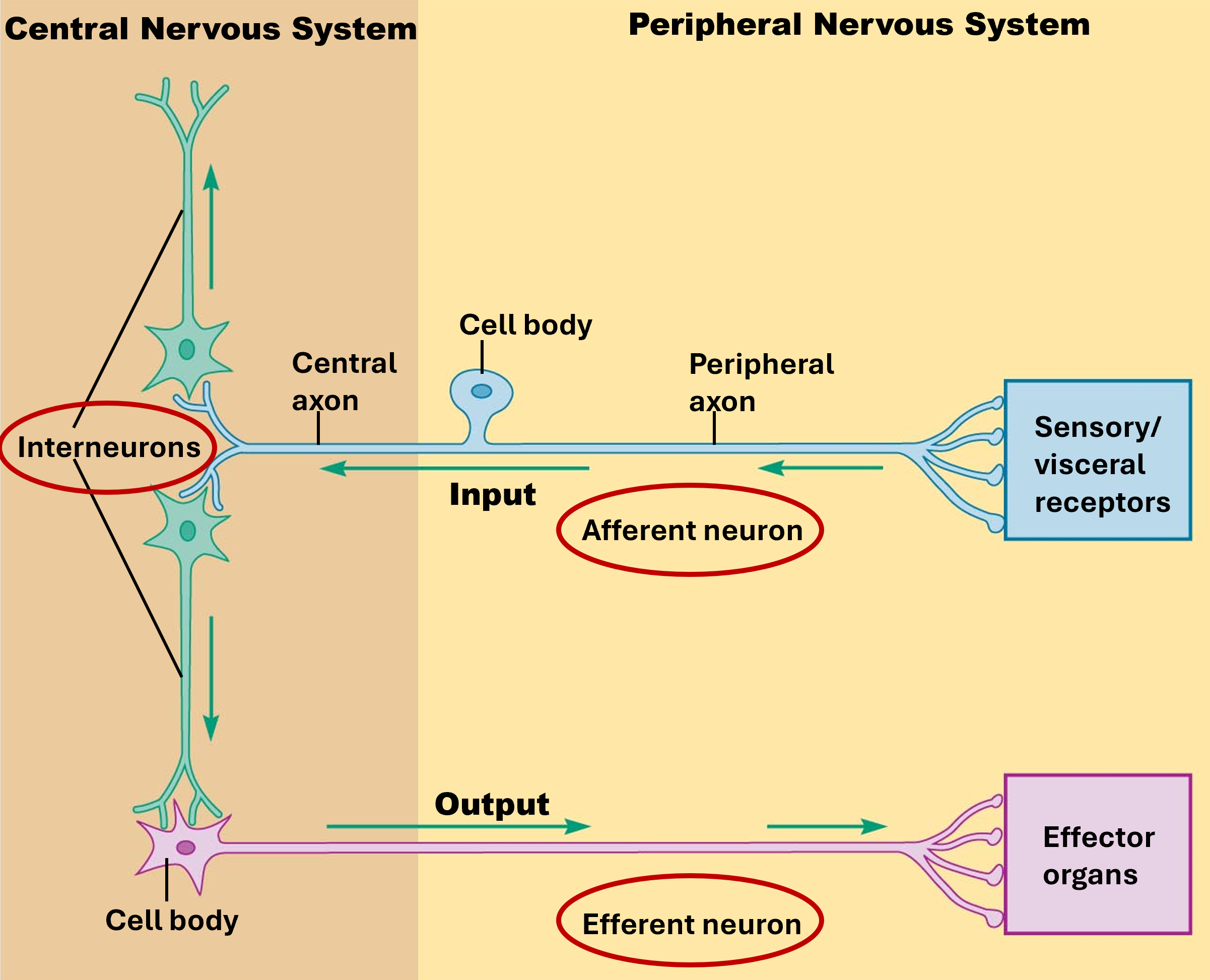
Afferent Division
part of PNS that is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the body's sensory receptors to the CNS
Effectors
structures that respond to incoming neural signals
Receptors
structures that detect changes
Information Processing in the CNS
integrates, processes, and coordinates sensory input and motor commands
Efferent Division
part of the PNS that is responsible for carrying signals from the CNS to the body
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
controls voluntary functions such as muscle movement
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
controls involuntary functions such as heart rate and digestion
automatically regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, gladular secretions, adipose tissue
Parasympathetic Division
controls the body during rest and digestion
Sympathetic Division
controls the body during times of stress
aka “fight or flight”
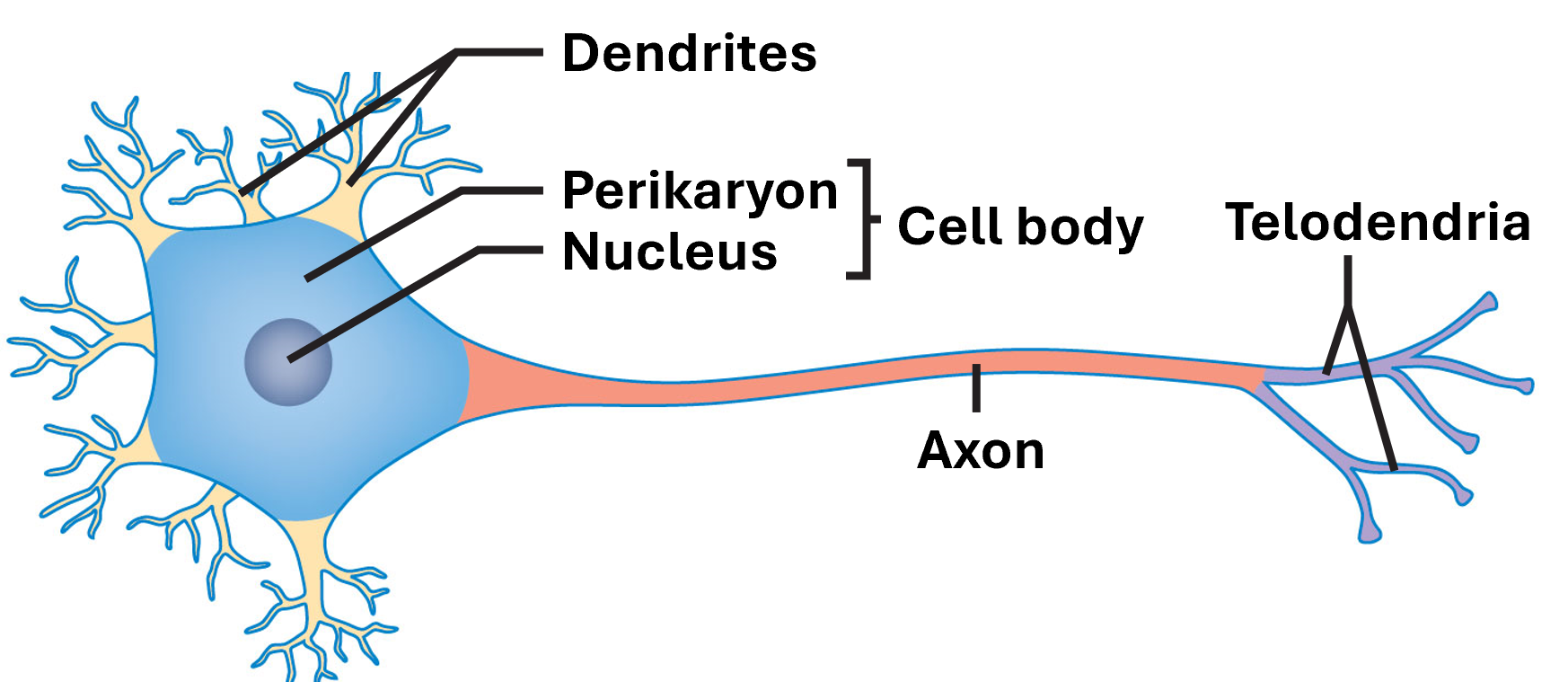
Regions of the Neuron
Axon
Cell Body
Perikaryon
Nucleus
Dendrites
Telodendria / Axon Terminal
Nissl Bodies
region of the cell body where RER and free ribosomes are located
only found in neurons
reason for gray matter
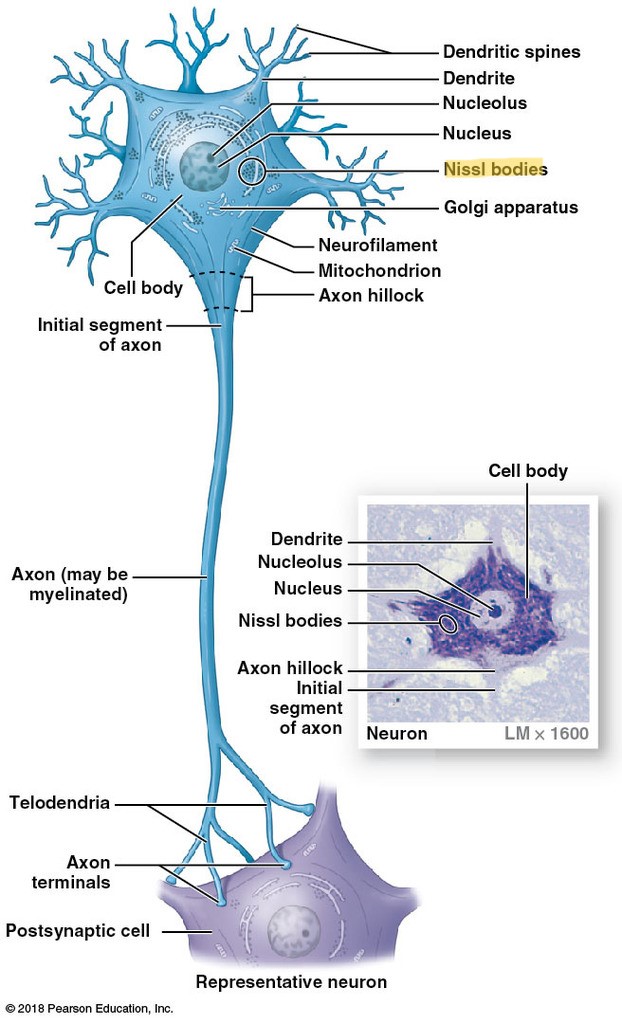
Gray Matter
regions containing cell bodies & unmyellinated axons
White Matter
regions dominated by myelinated cells
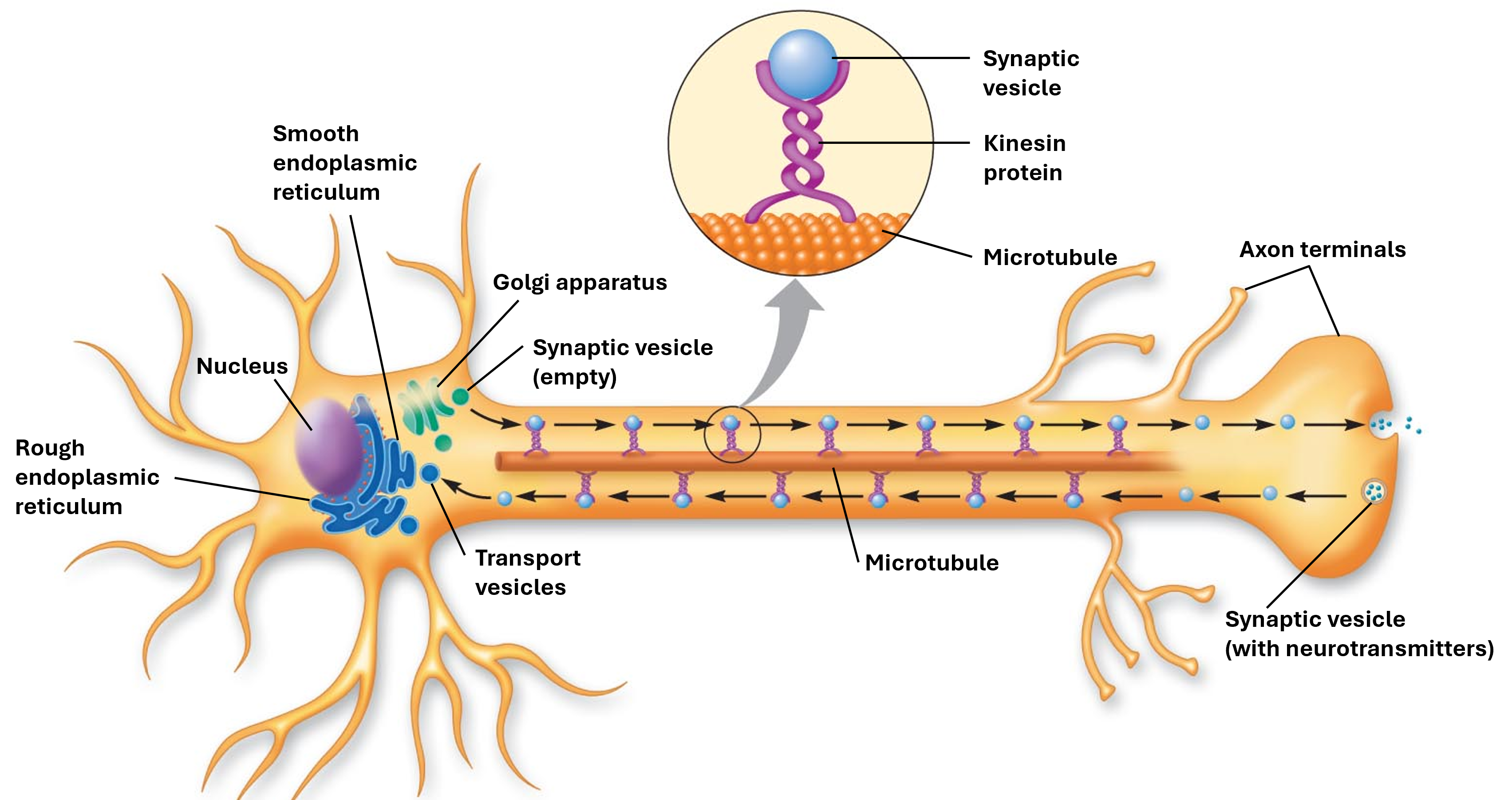
Anterograde Transports
from soma to terminals
Retrograde Transport
from terminals to soma
Synaptic Vesicle
store neurotransmitters that is moved via a kinesin protein in the axon
Structural Classes of Neurons
Anaxonic
Bipolar
Unipolar
Multipolar
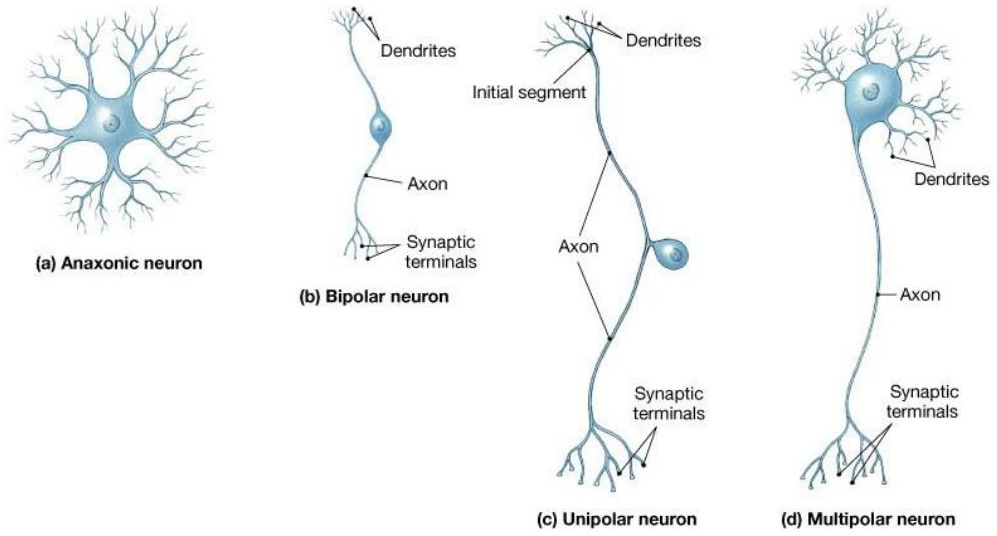
Anaxonic Neuron
have more than 2 processes and they may all be dendrites

Bipolar Neuron
have 2 processes separated by the cell body
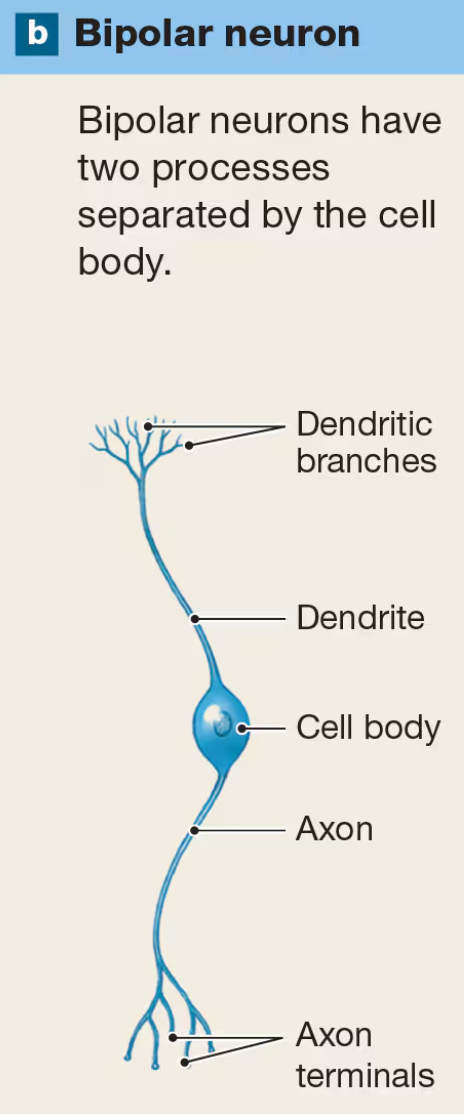
Unipolar Neurons
have single elongated process with cell body located off to the side of its axon
most common type of sensory neuron in PNS
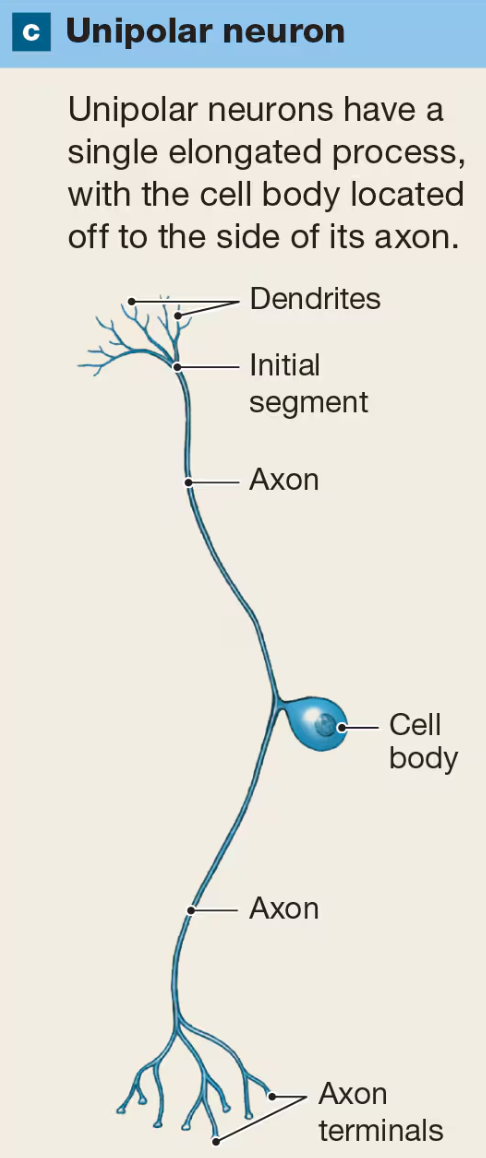
Multipolar Neuron
have more than 2 processes with a single axon and multiple dendrites
characteristic of all motor neurons
Functional Classes of Neurons
Sensory Neuron
Motor Neuron
Interneuron
Types of Sensory Neurons
Somatic Sensory Neurons
external environment
Visceral Sensory Neurons
internal environment
Sensory Receptors
Interal Systems (i.e. digestive, etc.)
Internal Senses (stretch, pain)
Somatic Senses (temp, pain, etc.)
Proprioceptors (position, movement of muscles & joints)
where do Motor (Efferent) Neurons send signals
Somatic MNs
skeletal muscle
Visceral MNs (ANS)
smooth, cardiac muscles, glands, adipose tissue
what chemical do MN Neurotransmitters sent to somatic MN
Achetylcholine
what chemical do MN Neurotransmitters sent to visceral MN
Acetylecholine (parasympathetic)
Norepinepherine (sympathetic)
MN Target Organ Receptors for Skeletal Muscles
nicotonic acetylcholine receptors
MN Target Organ Receptors for Smooth & Cardial Muscle, Glands, Adipose Tissue
Muscarinic AChRs
Adrenergic Receptors
Primary Location of Interneurons
brain & spinal cord
Purpose of Interneurons
distribute sensory info
cooridnate motor activity
involved in high functions (i.e., memory, planning)
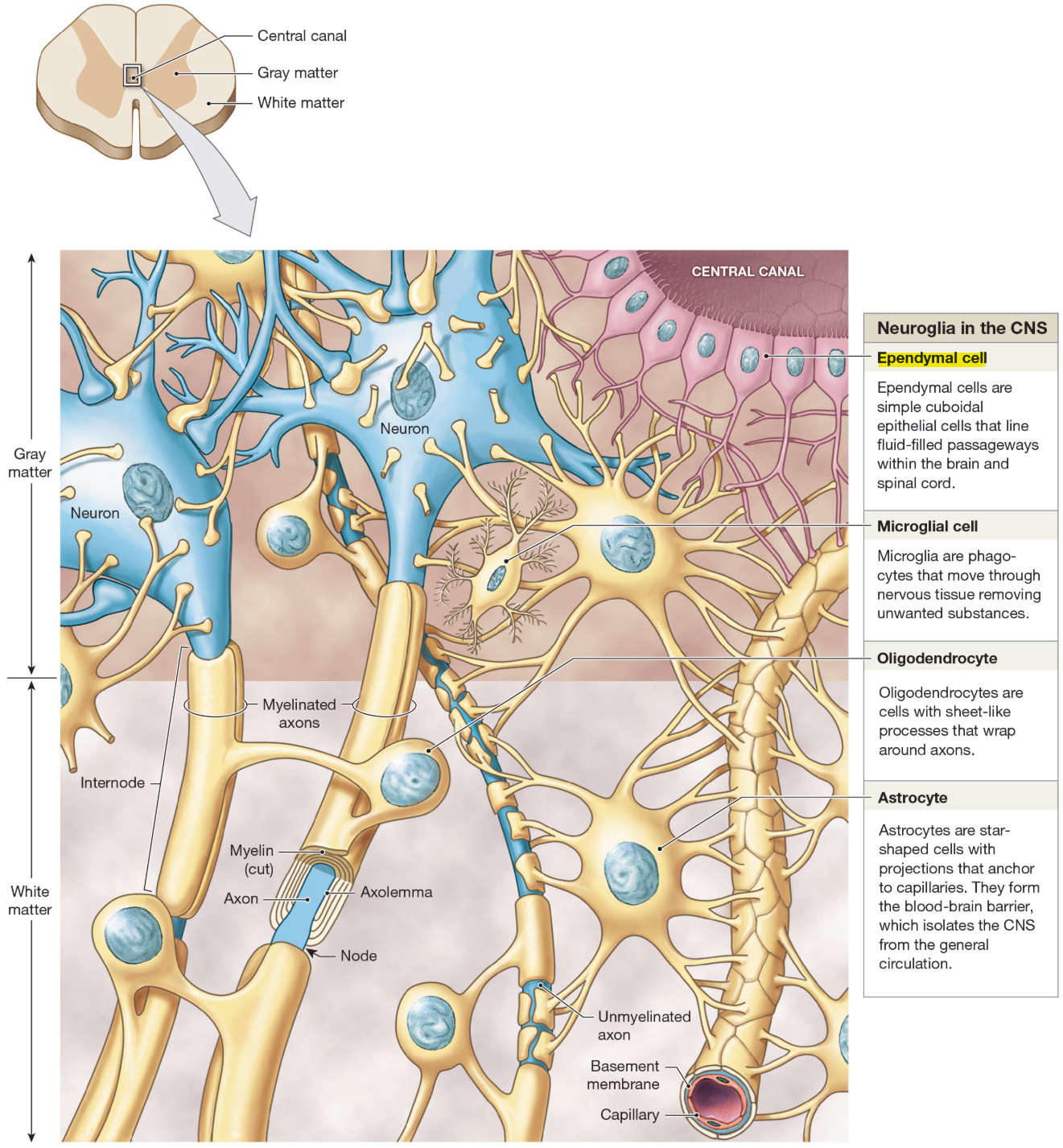
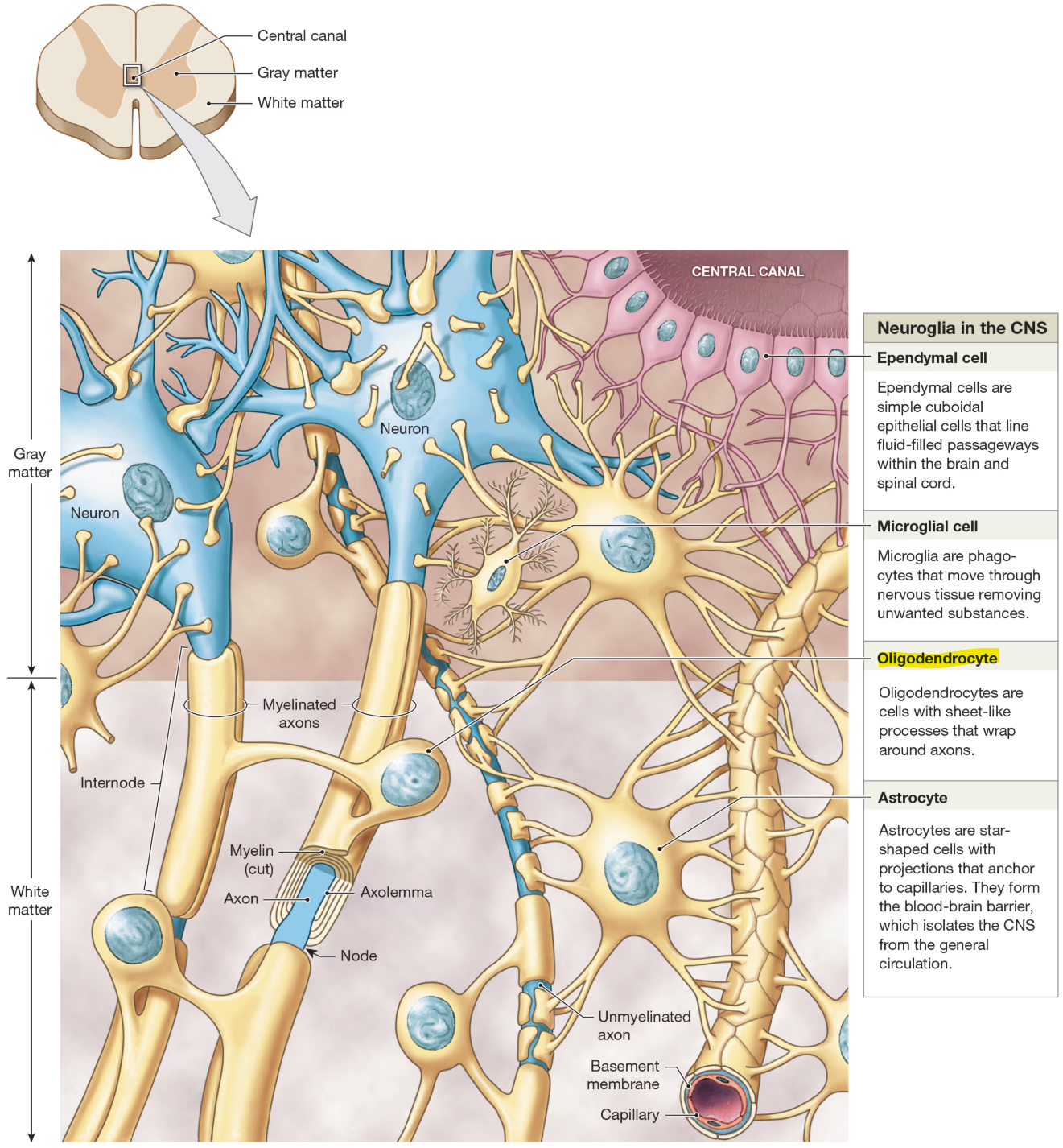
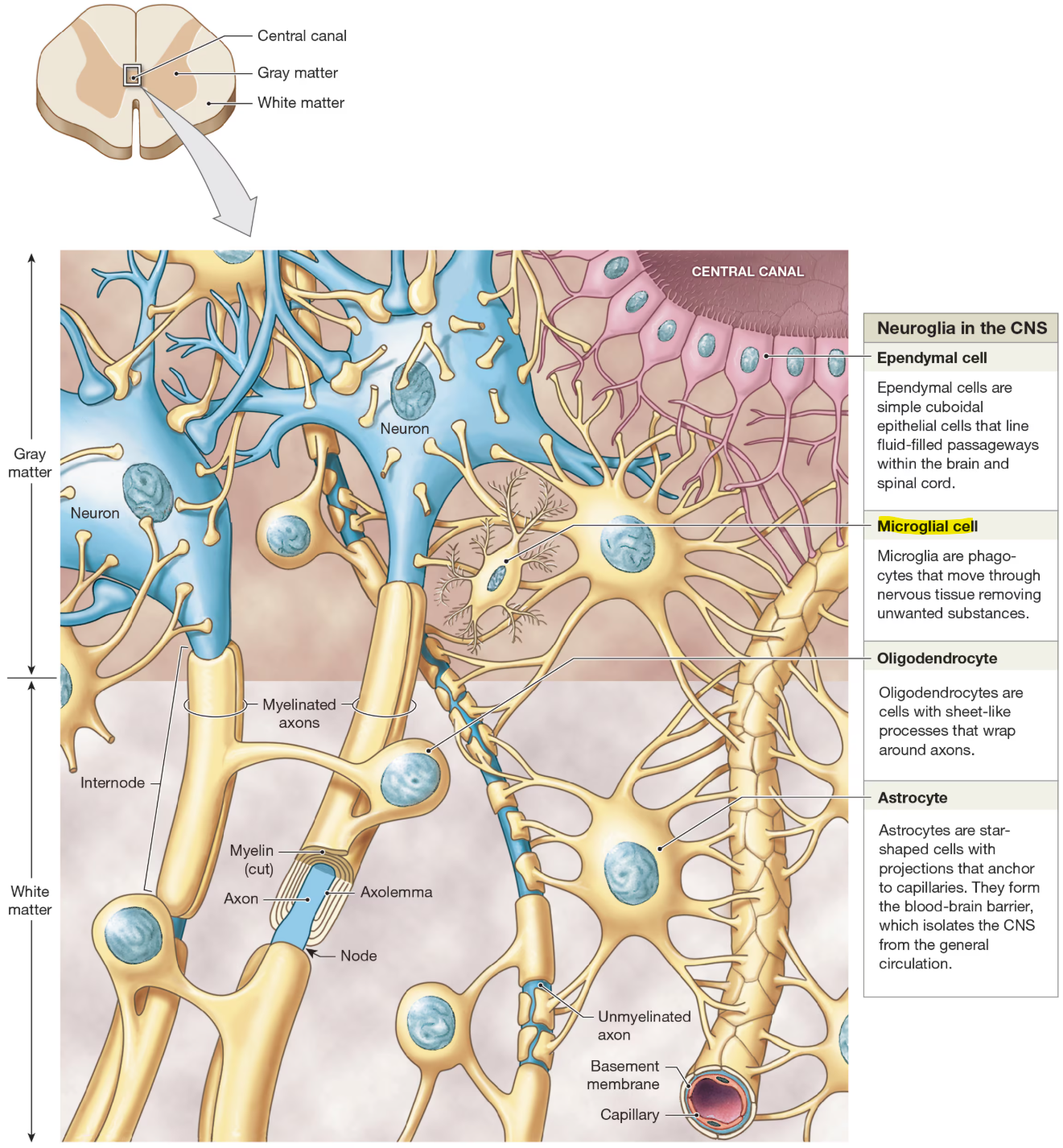
Types of Neuroglia of CNS
astrocytes
ependymal cells
oligodentries
microglia
Astrocytes
anchor nuerons to capillaries for material exchange
maintain BBB
provide strucutral support
regulate ion, nutrient, dissolved gas conc
absorb & recyle neutrotransmitters
form scar tissue after injury
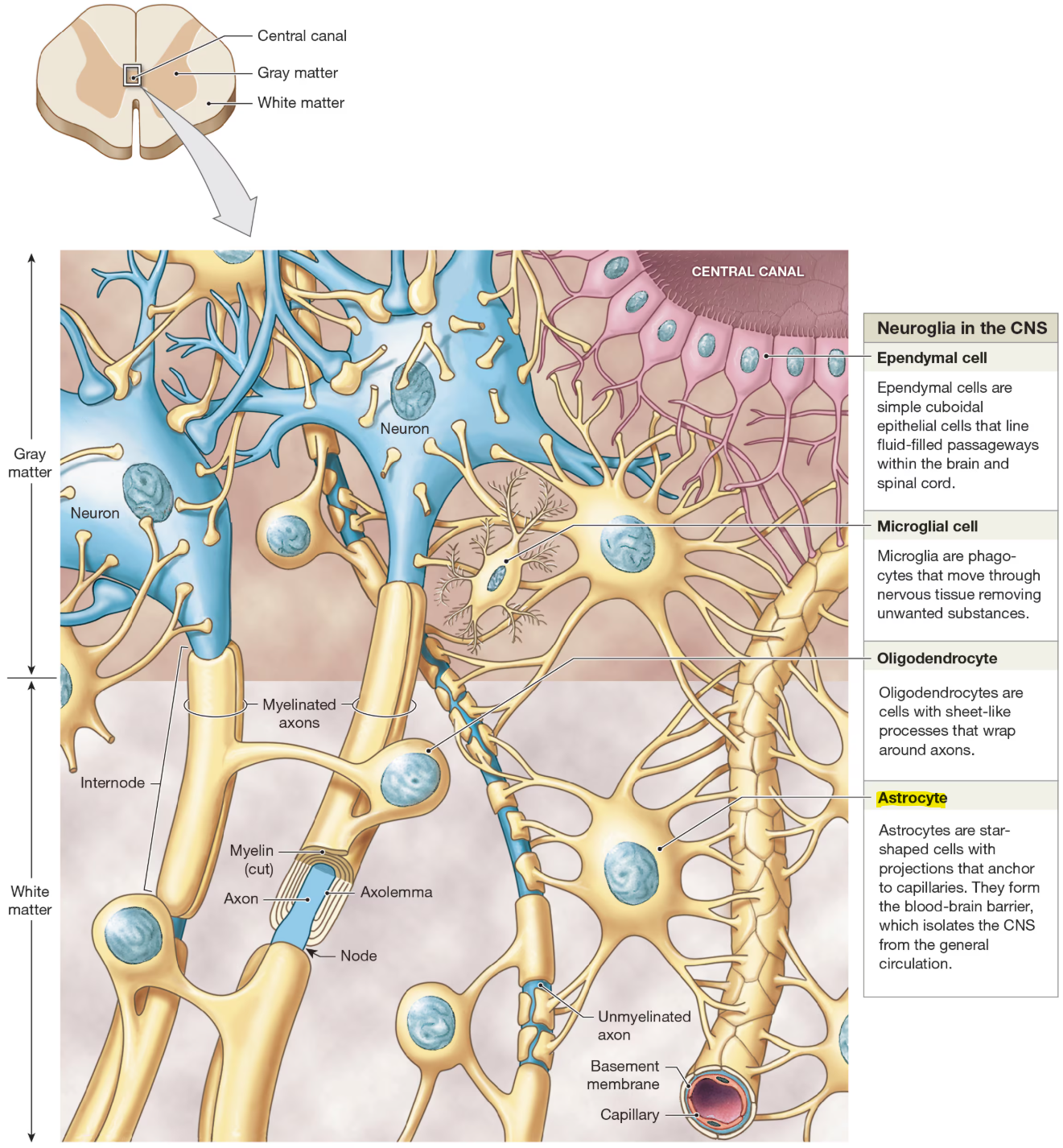
Ependymal Cells
simple cuboidal epithelial cells that line brain and spinal cord
produce, circulate, monitor cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Oligodendrocytes
cells with sheet-like processes that wrap around axons
help form myelin sheath
provide structural framework
Microglia
remove cell debris, waste, pathogens by phagocytosis
Purpose of Myelin Sheath
provides protective insulation
affects how fast signals travel through those nerve cells
maintains the strength of the impulse message as it travels down the axon
Types of Neurglia of PNS
Satellite Cells
Schwann Cells (Neurolemmocytes)
Satellite Cells
surround clusters of neuronal cell bodies or ganglia
regulates fluids around ganglionic neurons
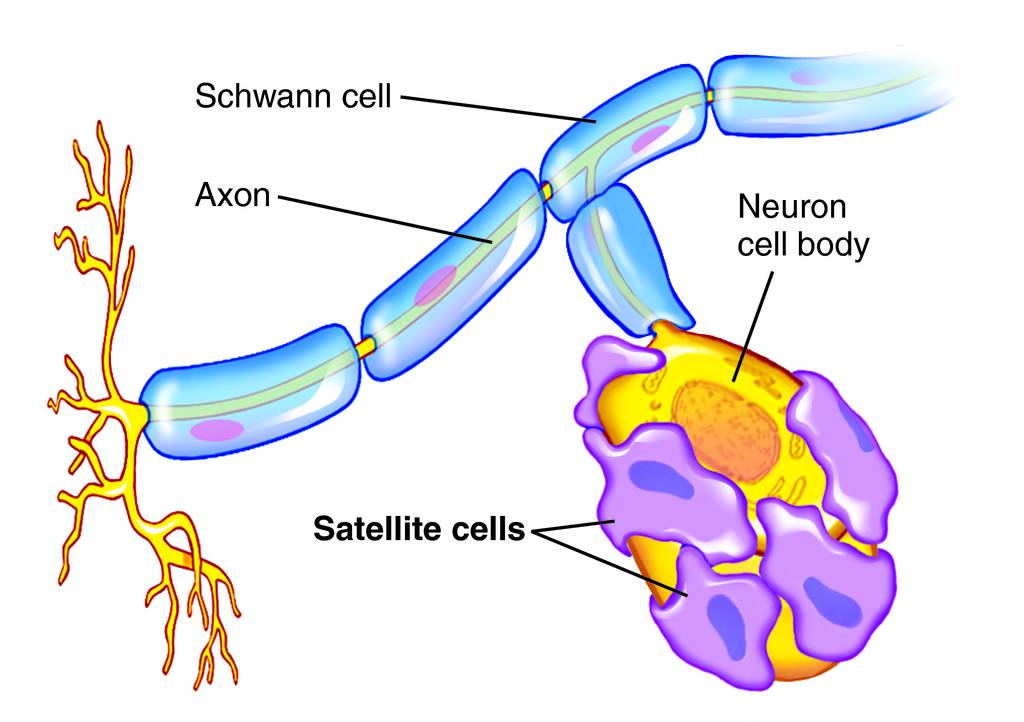
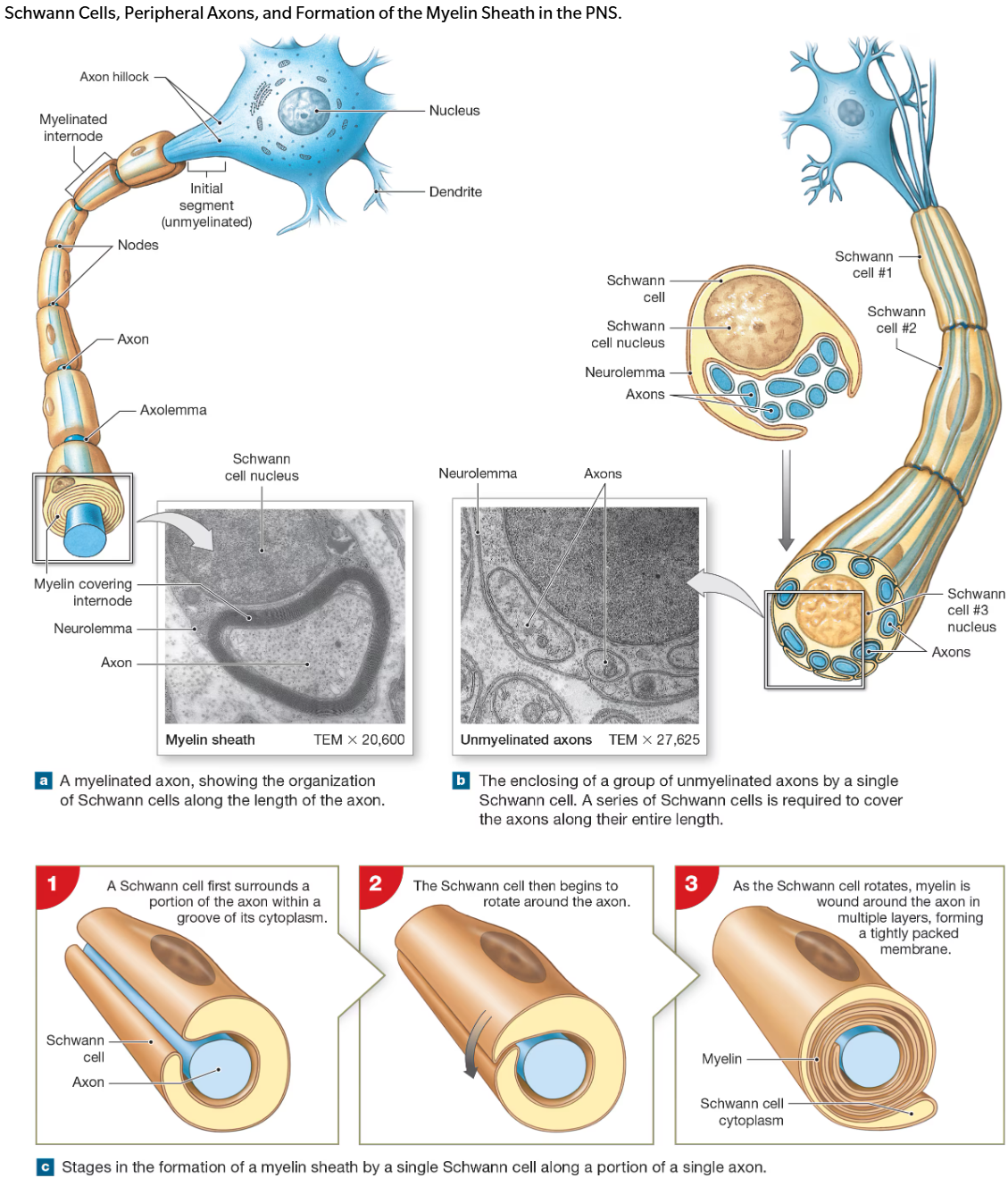
Schwaan Cells
wrap plasma membrane around axons
outer surface called neurolemma
each cell forms an individual myelinated internode
Rabies is a viral disease contracted from the bite of an infected animal. Rabies bypasses many immune system defenses by traveling in peripheral neurons to reach the CNS. Which methods of transport are used by the rabies virus to reach the CNS?
Axoplasmic Transport
virus particles can travel w other materials along molecular motors in cytoplasm
specifically Retrograde Flow (type of axoplamic)
substance flow from axon to cellbody and destroys neuron
Osmosis
viruses can dlow in & among cells by traveling along water routes
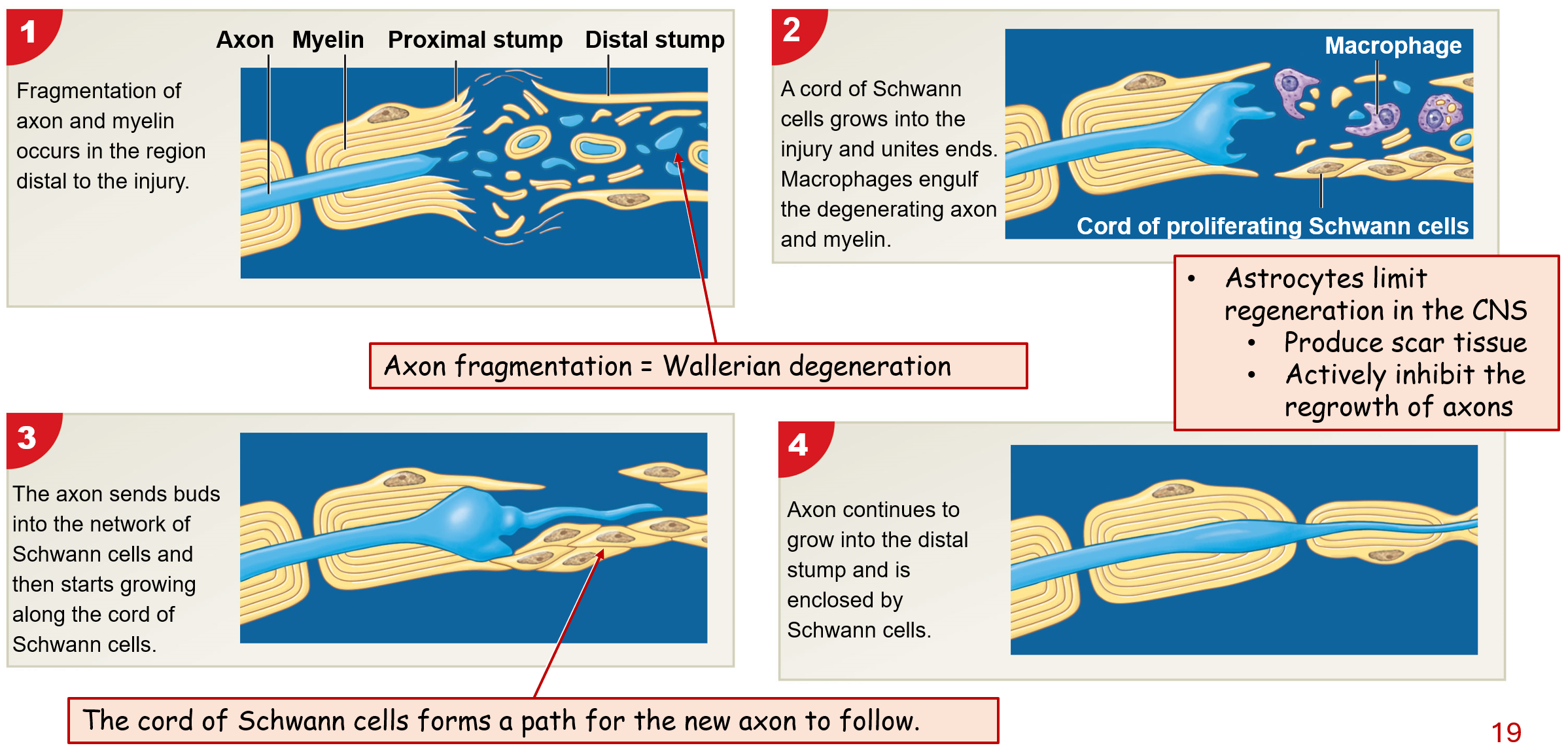
Response to Injury in PNS
1) Fragmentation of axon & myelin occurs in region distal to injury
2) Cord of Schwaan cell grows into injrt & unites ends
macrophages engulf degrading axon & myelin
3) Axon sends buds into network of Schwann cells & then starts growing along cord of Schwaan cells
4) Axon continues to grow into distal stump & is enclose by Schwann cells
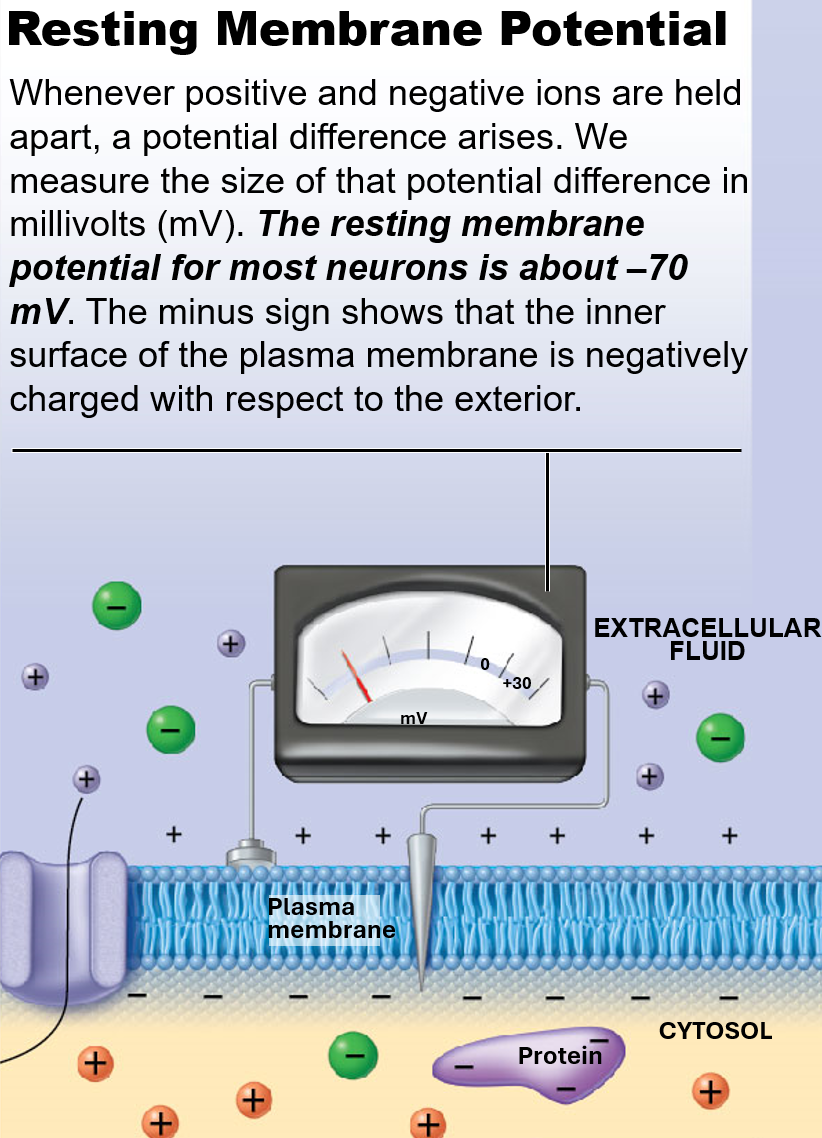
Neuronal Membrane Potential
movement of ions across plasma membrane of neurons
measured in voltage (mV)
Resting Membrane Potential
net positive charge outside neuron
net negative charge inside neuron
charges separated by plasma membrane
stabilized by action of Na+/K+ Exchange Pump
Features of Resting Membrane Potential
different ionic conc outside vs inside neuron
outside: high [Na+] & {Cl-]
inside: high [K+] & [negatively charged proteins]
neruonal membrane are high selective about what crosses in & out of neurons
@ rest, ions move through leak channels
neuronal membranes have different permeabilities for different ions
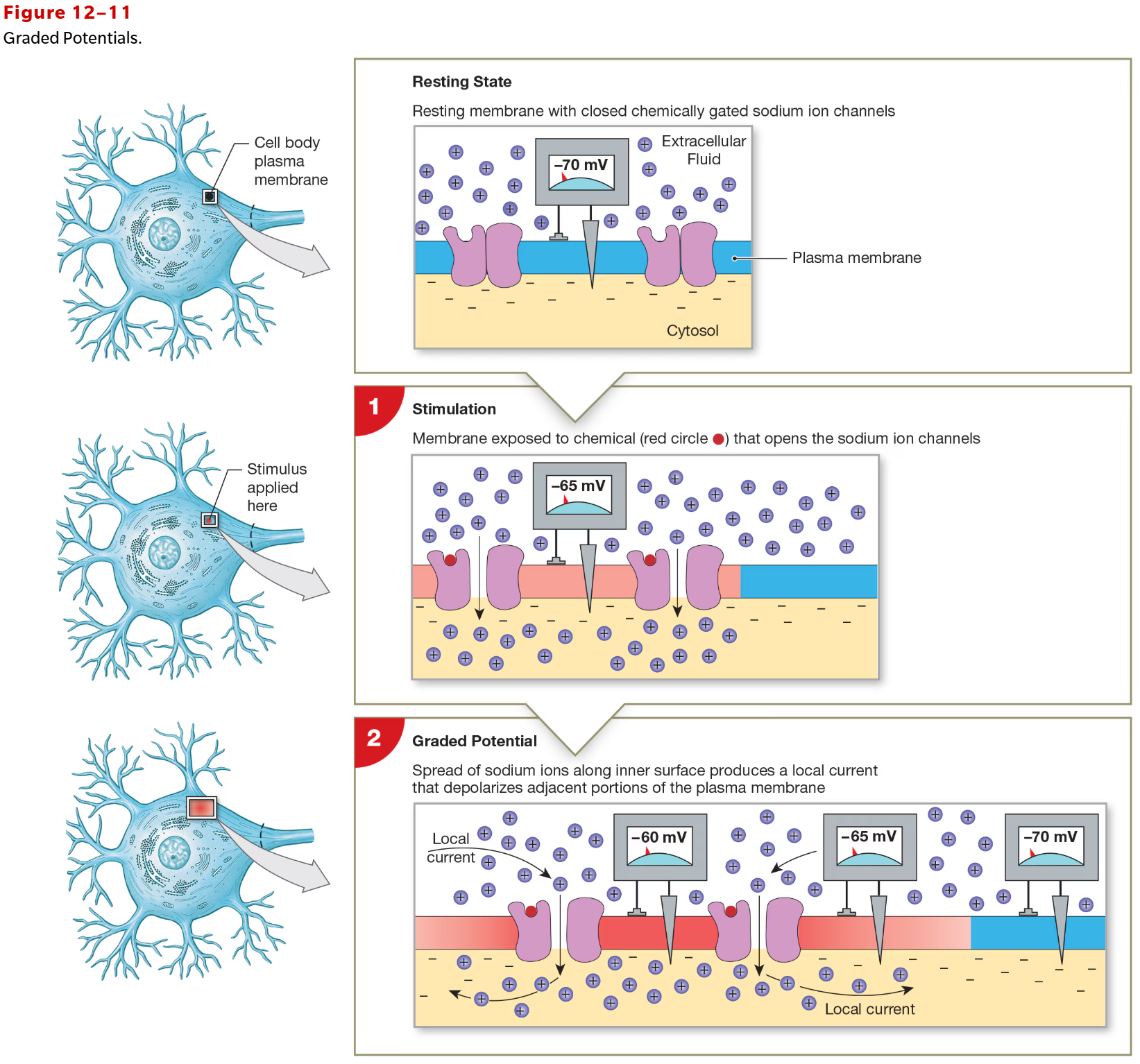
Graded Potential
transient (temporary), typically small, local change in membrane potential (mV)
caused by stimmulus intensity (i.e., neurotransmitter binding to receptor)
reversible
can be polarizing or depolarizing
Action Potential in Neurons
large change in membrane potential (+100mV) produced by summation of graded potentials at axon hillock
sends cascade of electrical changes that travels length of axon, ending at synaptic terminal
Current (I)
movement of ions
Resistance (R)
how much a barrier restricts ion movement
Voltage (V)
product of current & resistance is the membrane potential
V = IR
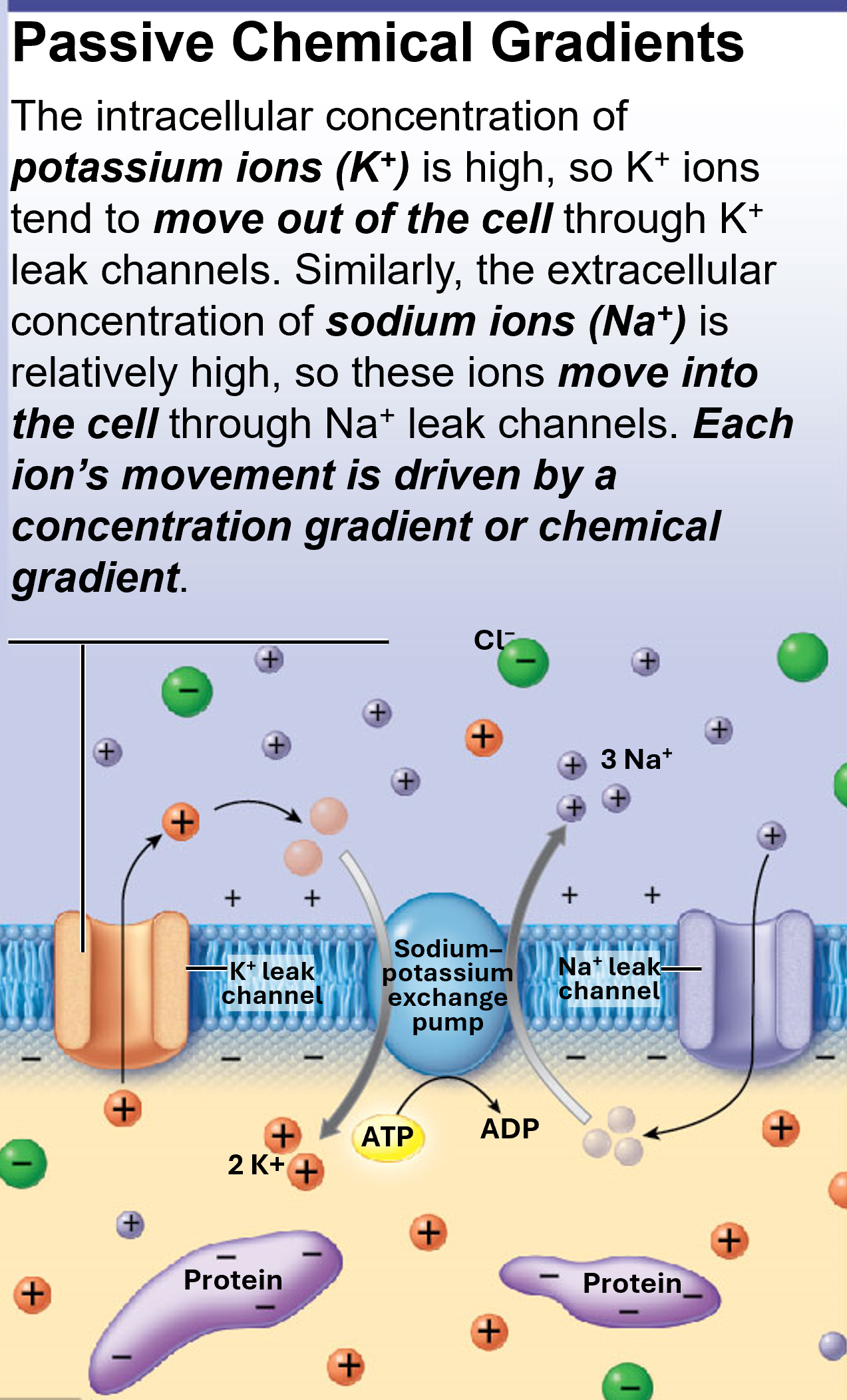
Passive Chemical Gradient
more K+ ions leak out of neuron than Na+ ions leak into neuron
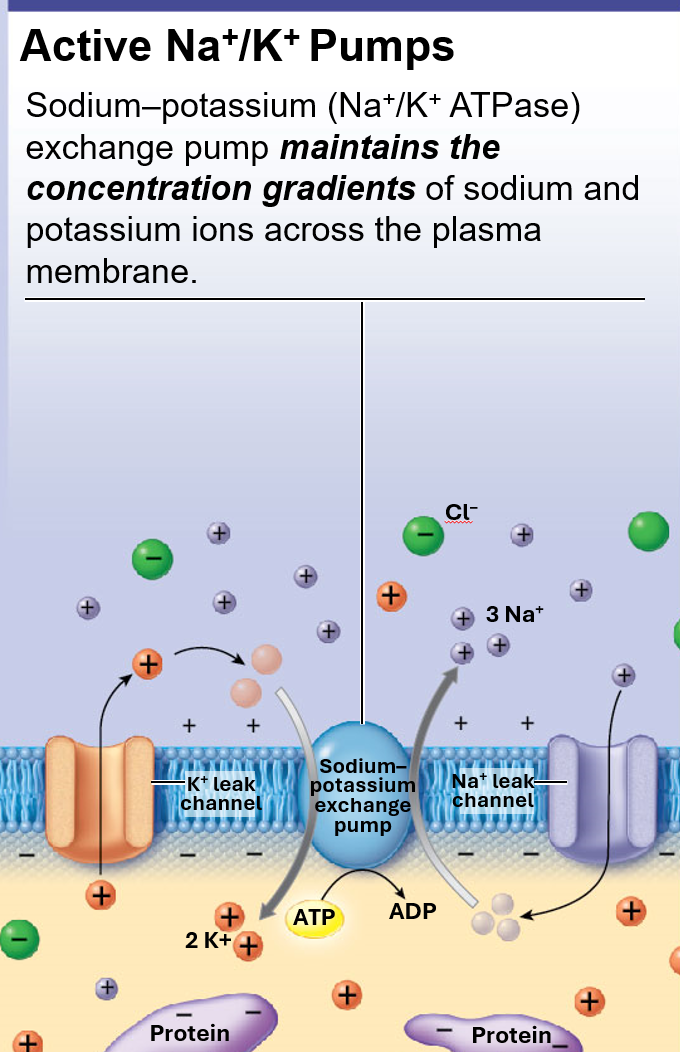
Active Na+/K+ Pump
aka Na+/K+ ATPase
pumps 3 Na+ out & 2 K+ in
results in net negative inside neuron (favoring Na+ to enter cell)
however, pu expels any Na ions entering cell
uses ATP to power pump
balances out passive forces (espcially after action potential)
maintains conc of Na & K ions across plasma membrane
Electrochemical Gradient
sum of chemical & electrical forces acting on an ion across the neural membrane
Equilibrium Potentials
membrane potential at which there is no net movement of a particular ion across cell membrane
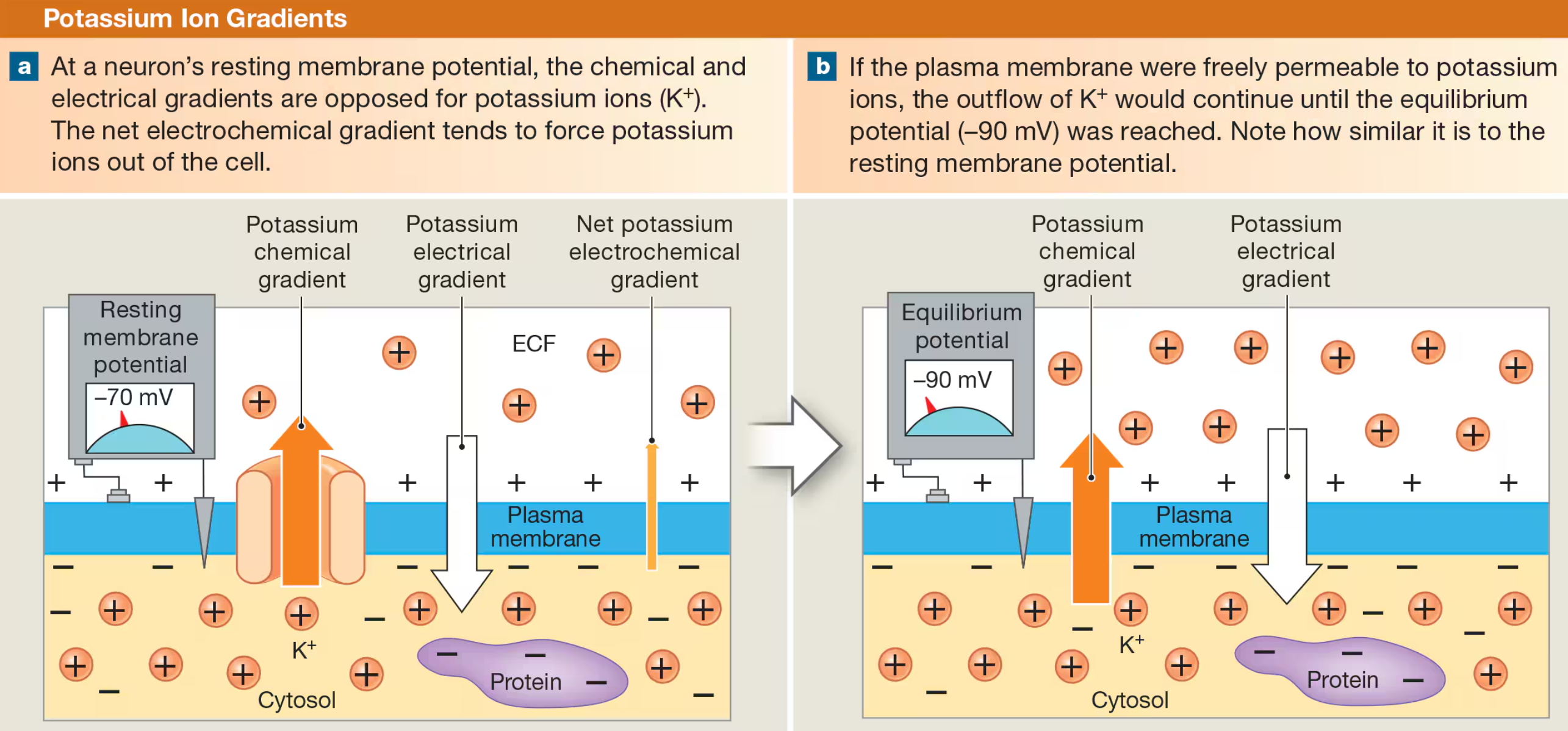
Potassium Ion Gradients
at neuron’s resting potential, the chemical & electrical gradients are opposites for K+ ions
net electrochemical gradient tends to force K+ out of cell
K+ Equilibrium Potential = -90 mV
only possible if there is no resistance to flow of K+ (free permeable membrane)
Sodium Ion Gradients
chemical & electrical gradients for Na+ are combined at resting membrane potential of neuron
net electrochemical gradient forces Na+ into cell
Na+ Equilibrium Potential = +66 mV
only possible if there is no ressitance to flow of Na+ ions (free permeable membrane)
Passive Channels
Na+ & K+ Leak Channels
always open
more K+ leak channels than Na+
Active Channels
gated ion channels
open & close by stimulus
most active channels are closed when neuron is at rest
Types of Active Channels
Chemically Gated
Voltage-gated
Mechanically gated
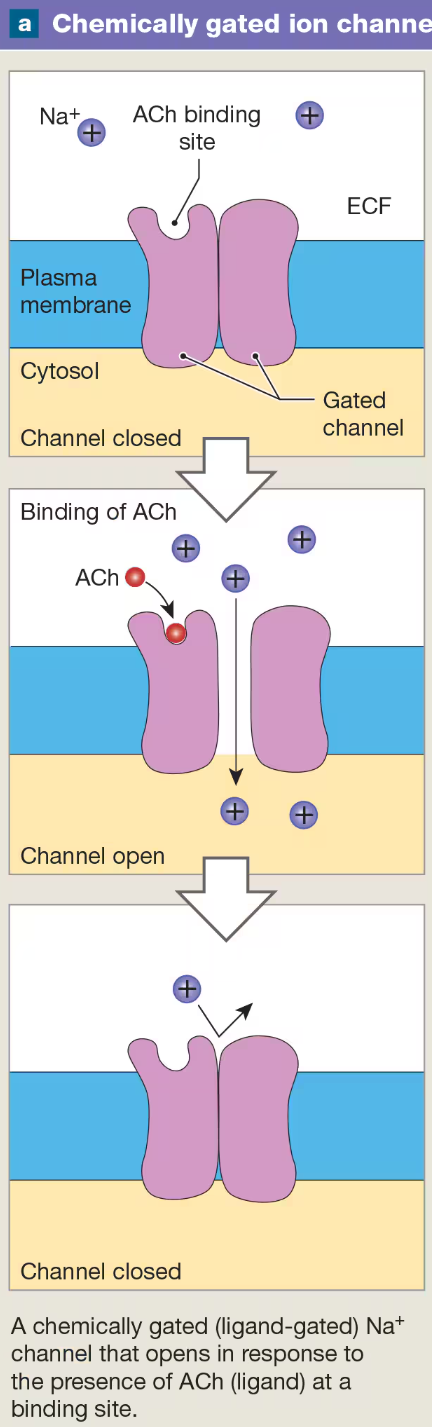
Chemically (Ligand-) Gated Ion Channels
open or close when they bind to specific chemicals or ligands (i.e., neurotransmitters)
found on soma (cell body) and dendrites of neurons
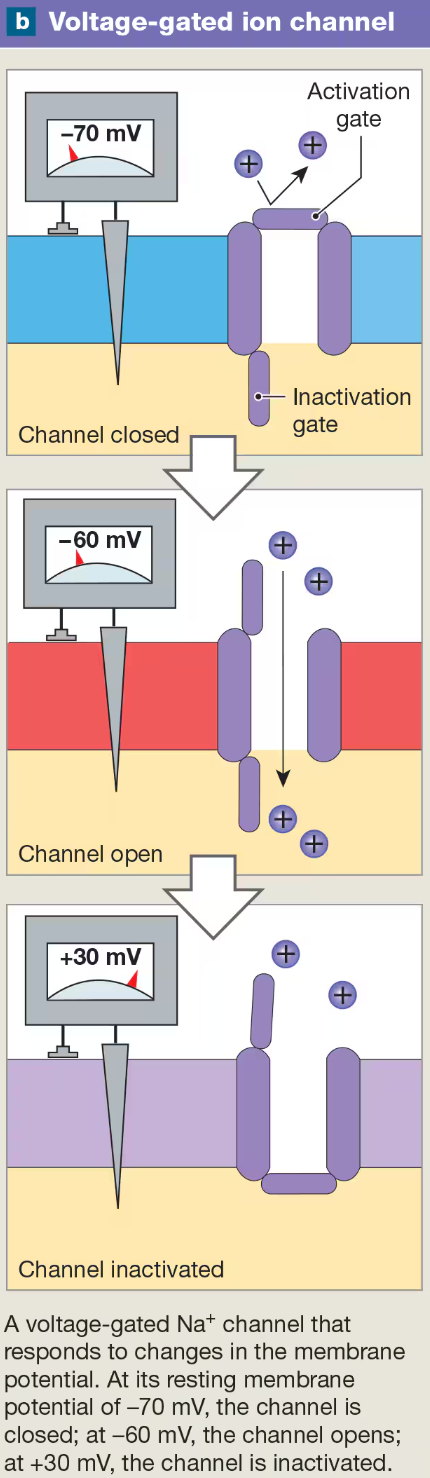
Voltage-gated Ion Channels
respond to changes in memebrane potential
found in axon, especially conc @ axon hillock, skeletal & cardial muscle cell membrane
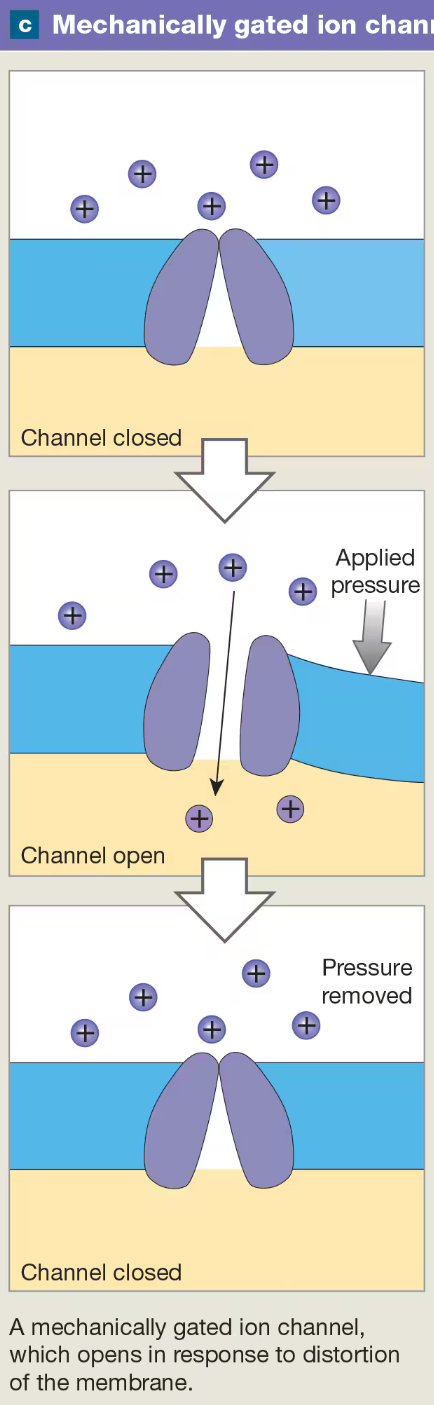
Mechanically Gate Ion Channels
respond to distortion of neural membrane
found in sensory neurons
skin
found in sensory cells
hair cells in ear canal & vestibular system
Graded Potential
transient, local change in membrane potential
change is stimulated by opening ion channel such as ligand or mechanically
change in voltage is proportional to stimulus
degree of depolarization decreases with increased distance from stimulation site
cyotosol offers resistance to ion movement
Example of Graded Poteintial Triggering Specific Cellular Function
exocytosis of glandular secretions are stimulated by graded potential
ACh stimulated nAChRs & cause graded potentials at neuromusclar junction (NMJ)
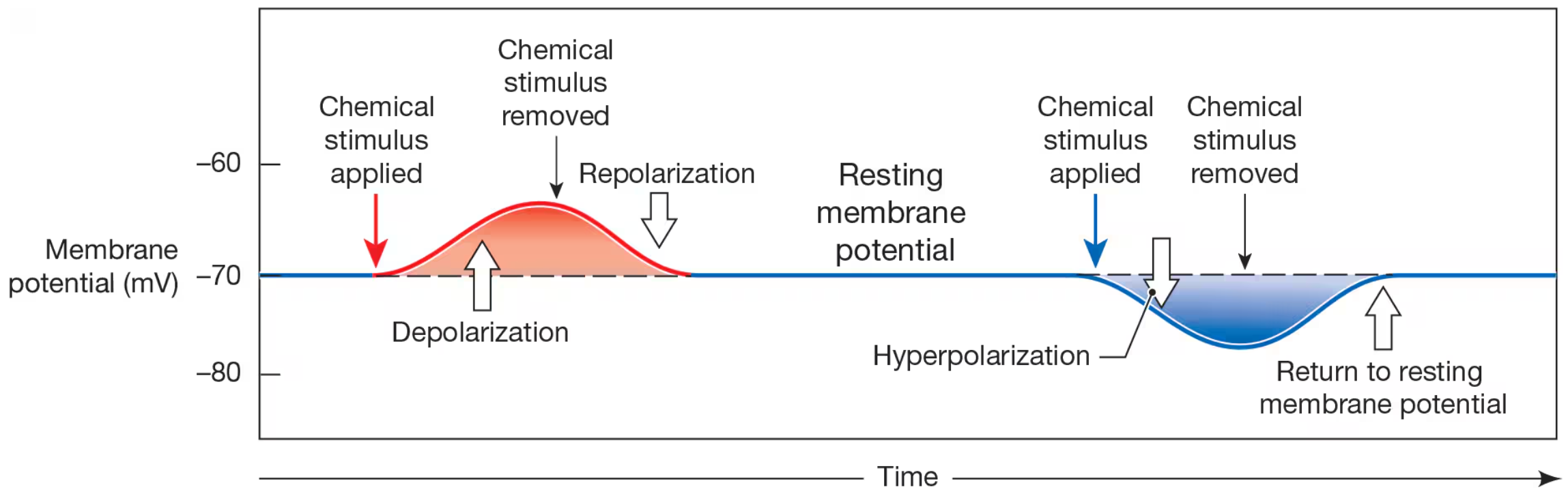
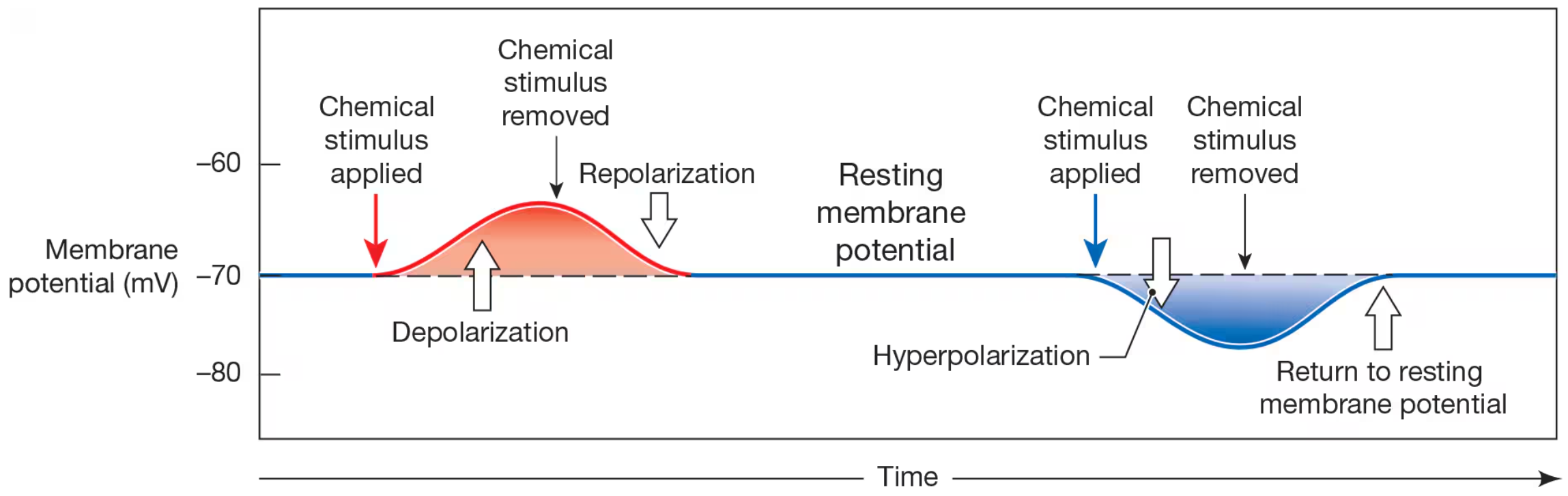
Depolarization
a change in membrane potential fron negative value toward 0 mV
Local Current
the movement of positive charges parallel to iner and outer surfaces of membrane to spread depolarization
Repolarization
return of membrane back to resting state
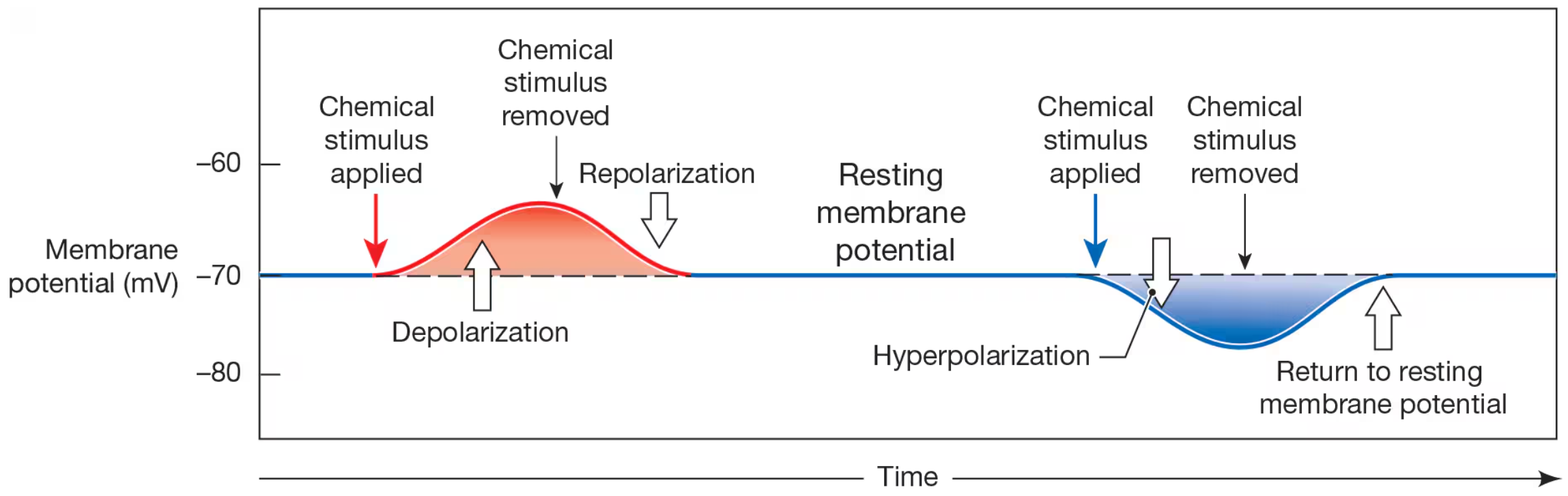
Hyperpolarization
movement of membrane potential away from normal resting potential and farther fron 0mV
Action Potential (Nerve Impluses)
wave of membrane depolarization that affects the entire neuronal membrane
begins at axon initial segment to axon terminals
propagated by opening voltage-gated ion channel
results in large depolarization that does not diminish as wave moves away from site of stimulus
occurs only if graded potentials change membrane potensial to threshold
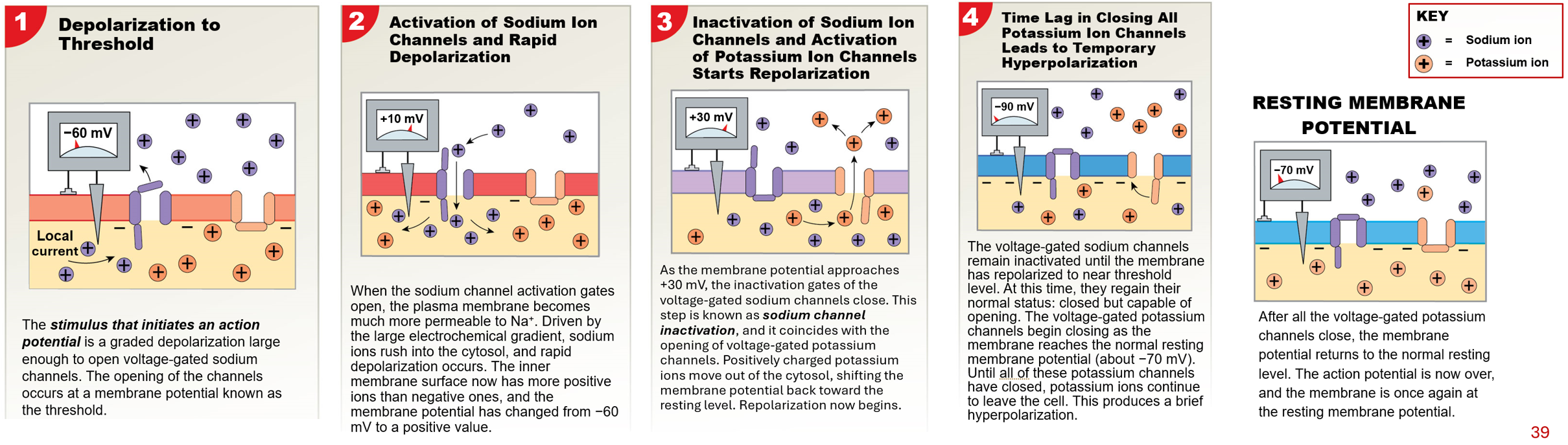
Threshold
membrane potential at which an action potential begins
for an axon, between -60 and -55 mV
All-or-None Principle
an action potential will always be propagated if stimulus reaches threshold
all action potnetials depolarize by the same amount
if theshold is not reached, action potential will not be triggered
Refractory Period
time between initiation of action potential and restoration of normal resting membrane potential
membrane will not respond normally to stimulation
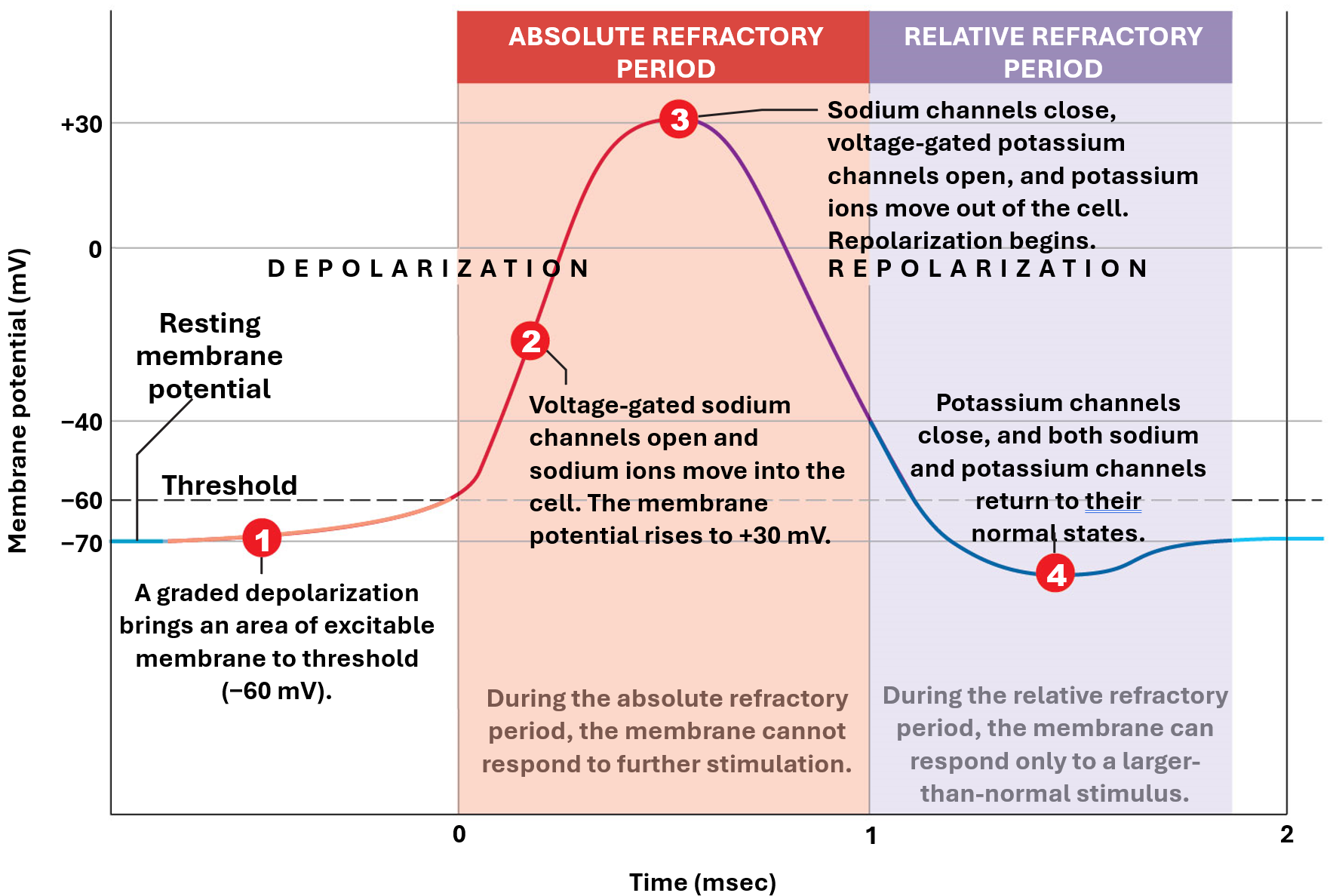
Absolute Refractory Period
first part of refractory period that lasts 0.4-1.0 msec
all voltage-gated Na+ channels are either open or inactive
mambrane cannot respond to any further stimullation
Relative Refractory Period
begins when Na+ channels regain resting condition
continues until resting memebrane potential stabilizes
only strong stimulus can initate another action potential
Flushing a Toilet Analogy
Nothing happens while pressing handle, until water stars flowing (threshold is reached)
after, the amount of water released is independent of how hard or quickly the handle is pressed (all-or-nothing principle)
finally, toilet cannot be flushed again until tank refills (refractory period)
Propagation
steps for moving an action potential along an axon
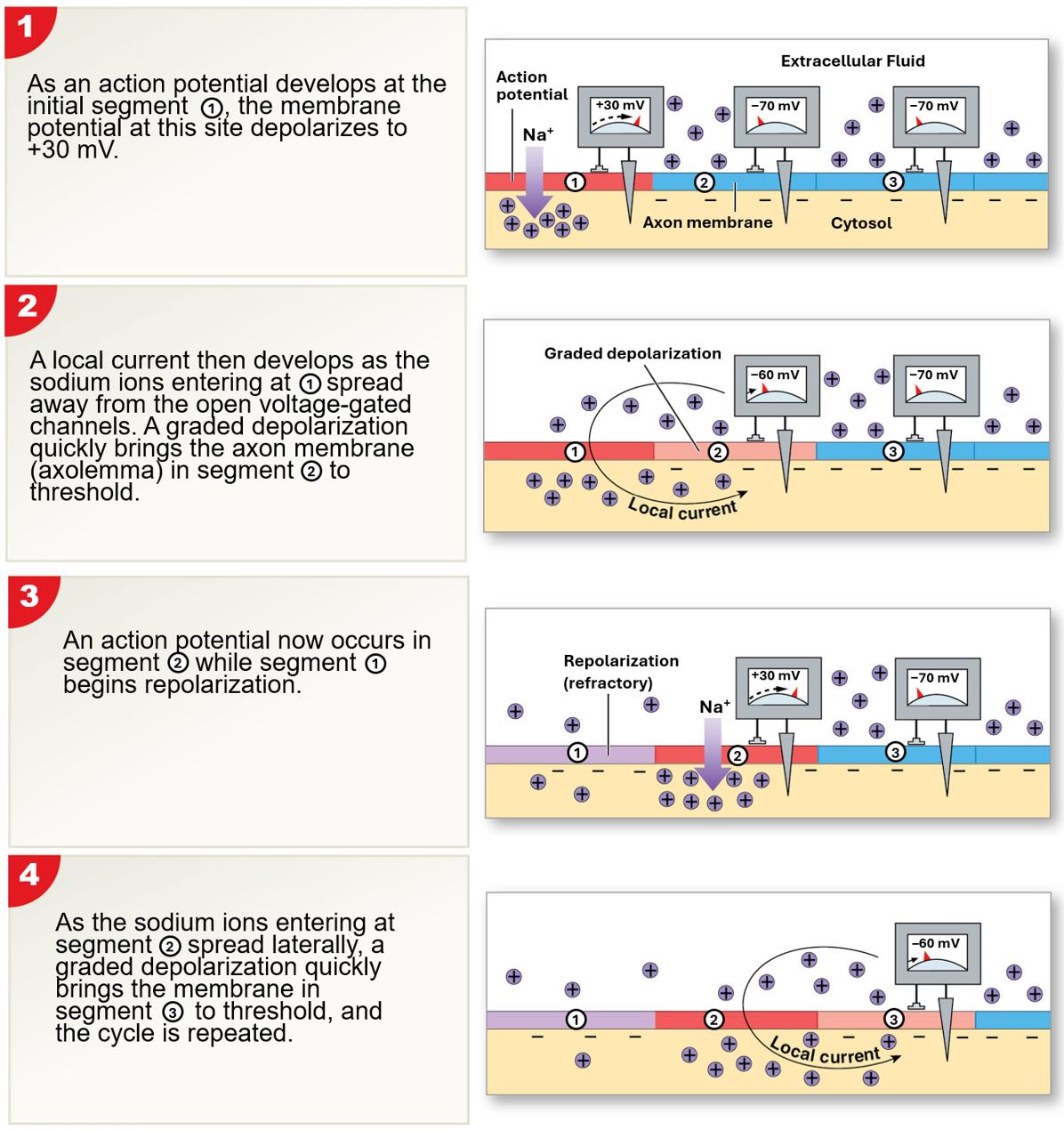
Continuous Propagation
occurs in unmyelanated axons
affects one segment of an axon at a time
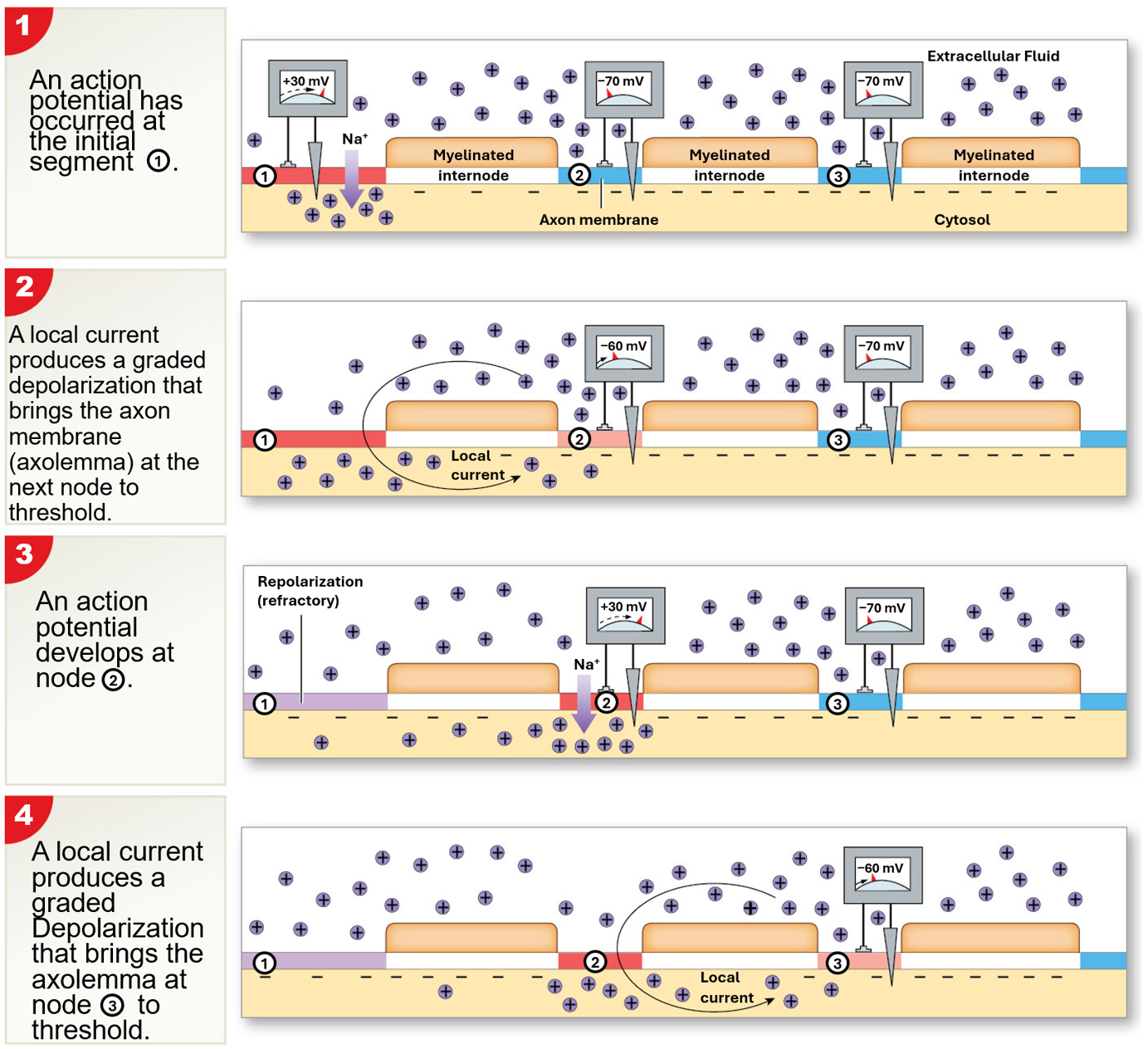
Saltatory Progagation
occurs in myelinated axons
faster than continous propagation & requires less energy
myelin sheath prevents continous propagation
local current “jump” from node to node
depolarization occurs only at nodes
how does refractory period affect propagation of action potentials
neuronal membrane upstream of depolarizing signal is either difficult or impossible to fire action potential
keeps propagation of action potential toward acon terminals
how does axon diameter affect propagation of action potentials
large diameter is faster, has less resistance
small diameter is slower, has more resistance
how does myelination affect propagation of action potentials
saltatory propagation or cunduction is faster
continuous conduction is slower
Type A Nerve Fibers
myelinated, large diameter neurons
fast transmission
sensory fibers transmitting info about body position & balance
motor fibers send signals to skeletal muscles
Type B Nerve Fibers
myelinated, large diameter neurons
intermediation transmission speeds
sensory & motor fibers from internal organs transmit signals via ANS
Type C Nerve Fibers
unmyelinated, small diameter neurons
slow neurotransmission
most sensory info is transmitted to brain via C fibers, including temp & pain
Which neuron fiber types takes priority
Type A because sensory & motor messages are transmitted according to priority
i.e., life-threatening sensory info or motor commands that prevent injury
Synapses
specialized sites where neurons communicate w another cell
Presynaptic Neuron
sends message
Postsynaptic Neuron
receives message
Electrical Synapses
direct physical contact between cells
i.e., gap junctions
pre- & postsynaptic membranes work together to allow ions to pass through pores
fast propagation of action potentials
found in some areas of brain & cardiac smooth muscle
Chemical Synapses
NTs cross gap (synaptic cleft) to target cell
most common synaptic connection between neurons
only way for neurons to communication w non-neural cells
Function of Chemical Synapses
NTs from presynaptic cell are released into synaptic cleft
NTs bind to receptors in postsynaptic cell
binding events may trigger opening of ion channel, leading to graded potentials
if change in potential is large enough to reach threshold, action potential will be generated
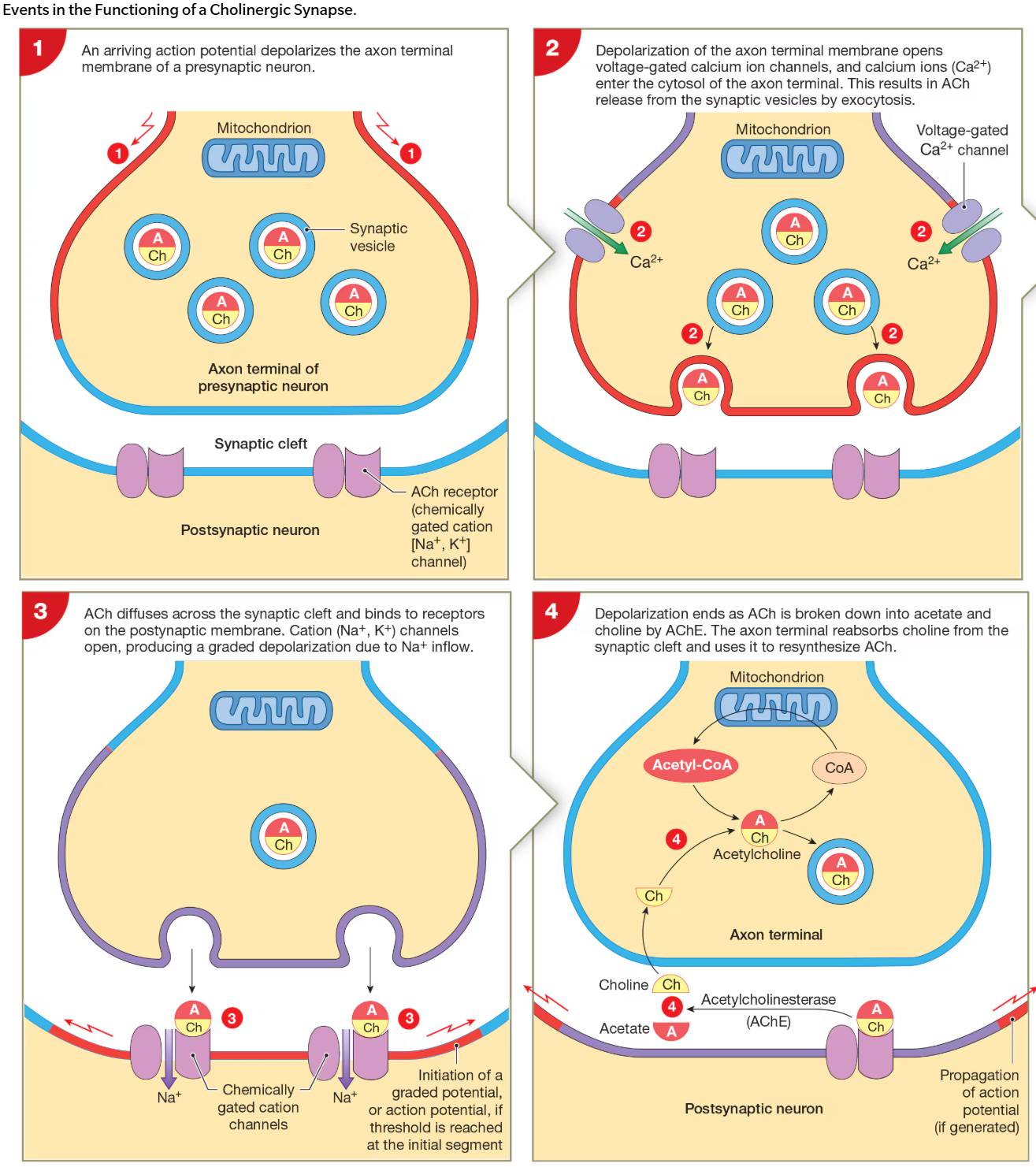
What happens during cholinergic synapse
1) action potential arrives at axon terminal & depolarizes membrane
2) voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open in terminal & Ca2+ flow into terminal
3) increase in extracellular Ca2+ trigger fusion of synaptic vesicles w presynaptic membrane
4) synapse releases NT, ACh
e.g., all synpases involving skeletal muscles & may CNS synapses
5) ACh binds to AChRs on postsynaptic membrane & depolarizes membrane
6) ACh is metabolized by acetylecholiinesterase (AChE), which is found in high conc in synaptic cleft
7) AChE metabolizes ACh into acetate & choline
8) transporter proteins bring choline back into terminal to allow for synthesis of ACh
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers
packaged into synaptic vesicles
released into synaptic cleft response to action potential
often transported back into nerve terminal unchanged (or as metabolite)