5. Viral skin diseases in respective pig categories – classifying
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Vesicular syndrome, Foot & mouth disease, Parvovirus dermatitis, Swine pox, Swine papillomatosis, Dermatitis-nephropathy syndrome).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are examples of viral skin diseases?
Vesicular syndrome
Foot & mouth disease
Parvovirus dermatitis
Swine pox
Swine papillomatosis
Dermatitis-nephropathy syndrome
Porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome (PRRS)
African swine fever
Classical swine fever
What is the vesicular stomatitis complex characterised by?
The formation of blisters-like sores inside the oral cavity
Which diseases are included in the vesicular stomatitis complex?
Foot and mouth
Swine vesicular disease
Vesicular stomatitis
Vesicular exanthema of swine
Which diseases of the vesicular stomatitis complex are zoonotic?
Swine vesicular disease
Vesicular stomatitis
(Humans can spread FMD but don’t get ill)
What family does Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD) belong to?
Picornaviridae
What family does Swine Vesicular Disease belong to?
Picornaviridae
What family does Vesicular Stomatitis belong to?
Rhabdoviridae
What family did Vesicular Exanthema of Swine belong to?
Caliciviridae (eradicated in swine in 1959)
What is the main characteristic of Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
Highly contagious viral disease of livestock with significant economic impact
What are the serotypes of FMD?
A, O, C, SAT1, SAT2, SAT3, Asia
What is the typical mortality rate of Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
1-5%, except piglets, which have high mortality (100% morbidity)
What regions are endemic to Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
Asia, Africa, South America
How can FMD be transmitted?
Direct contact → All body fluid, inhalation of infected aerosol (long distance spread - 60 km).
Indirect → Infected feed, water, bedding. Humans can spread it to animals through clothes, vehicles, & equipment.
What is the pathogenesis for Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
Primary site of infection is mucosa of the pharynx → Enter the lymphatic system → replicates in epithelium of mouth, muzzle, teats, feet, + areas of damage skin → forms vesicles in the affected mucosa → infects the cell → multiplies → burst + release the virus in the blood.
What are the clinical signs (CS) of Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
Severe lameness, salivation, anorexia, fever, mastitis, sudden death, vesicles in mouth, nose, tongue, lips, between toes, coronary band, and teats
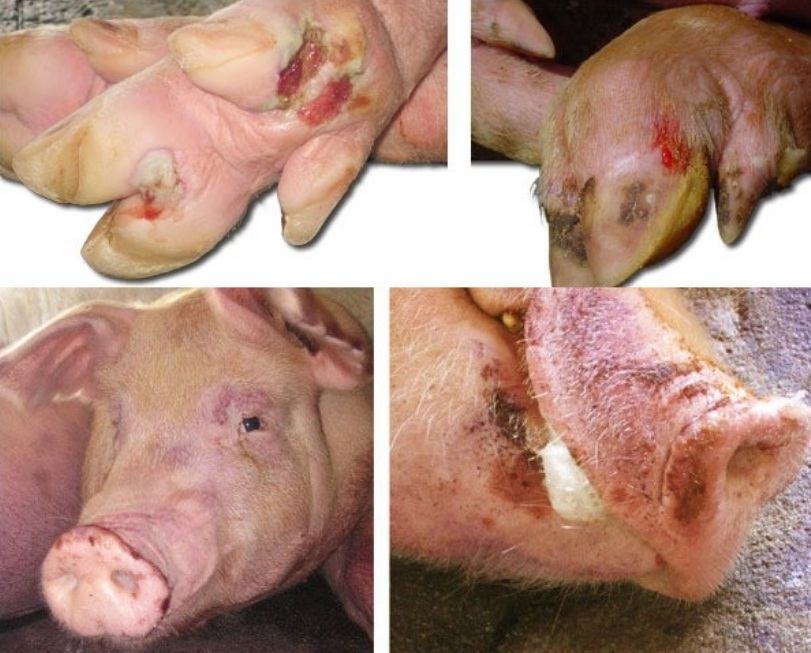
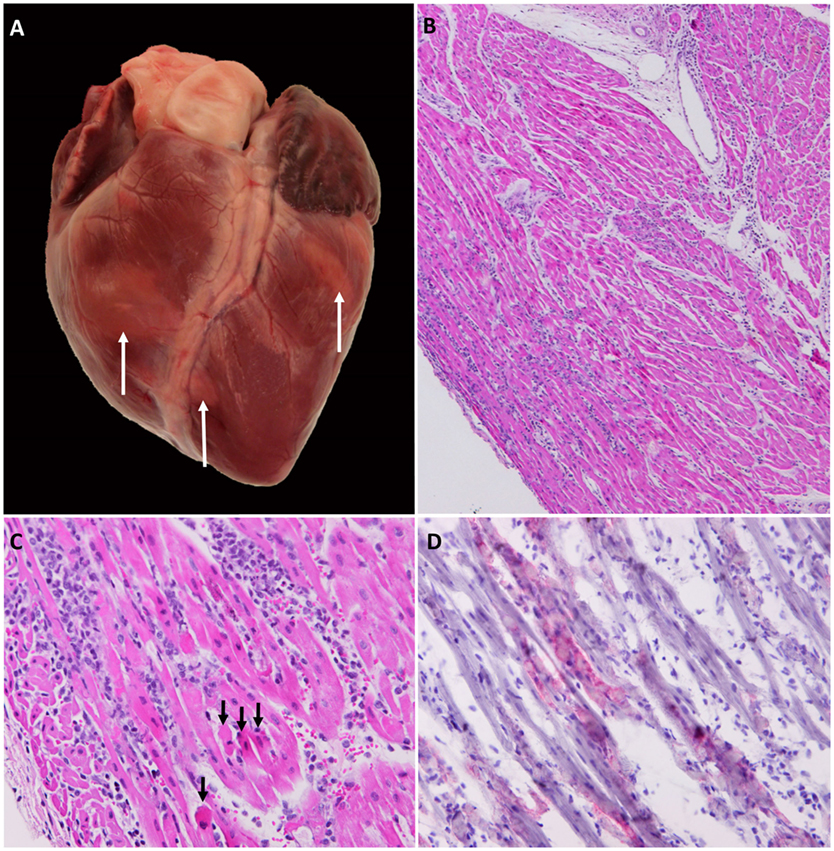
What are the post-mortem (PM) lesions seen in Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
Zenker's necrosis of the heart (Tiger Heart/myocarditis)
What diagnostic methods are used for Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
VNT. Clinical signs, post-mortem examination, swabs of ruptured vesicles, RT-PCR, and ELISA
What is the treatment for Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD)?
There is no treatment; emergency vaccination only and euthanasia of infected animals
What virus causes Swine Vesicular Disease?
Swine vesicular disease virus (Human Enterovirus B)
What is the main transmission route of Swine Vesicular Disease?
Direct or indirect contact or by ingestion of infected pork or pork products
What are the clinical signs of Swine Vesicular Disease?
Similar to FMD with jerking-type movements of legs (encephalitis)
What virus causes Vesicular Stomatitis?
Indiana vesiculovirus
What are the transmission routes of Vesicular Stomatitis?
Transcutaneous/transmucosal, saliva, exudate from open vesicles, arthropods (sand flies, mosquitoes, black flies)
What is the main clinical feature of Vesicular Stomatitis?
Very similar to FMD. Excessive salivation and vesicles
What is the main transmission route of Vesicular Exanthema of Swine?
Direct and indirect contact, with premises heavily contaminated serving as a source for months
What are the clinical signs of Vesicular Exanthema of Swine?
Similar to FMD. Abortion, pneumonia, myocarditis, encephalitis
What is the prevention against vesicular exanthema of swine?
Scraps and fish should be cooked before being fed to pigs. The virus still exists but circulates in marine mammals (seals)
What virus causes Parvovirus Dermatitis in pigs?
Parvovirus (DNA virus, non-enveloped)
What age group of pigs is affected by Parvovirus Dermatitis?
Piglets aged 1-4 weeks
What are the clinical signs of Parvovirus Dermatitis?
Vesicles on the snout, coronary band, interdigital space, tongue, rupture forming erosions, diarrhoea, conjunctivitis, rhinitis
How is Parvovirus Dermatitis diagnosed?
Demonstrating parvovirus in the lesions using a fluorescent antibody microscope or virus isolation
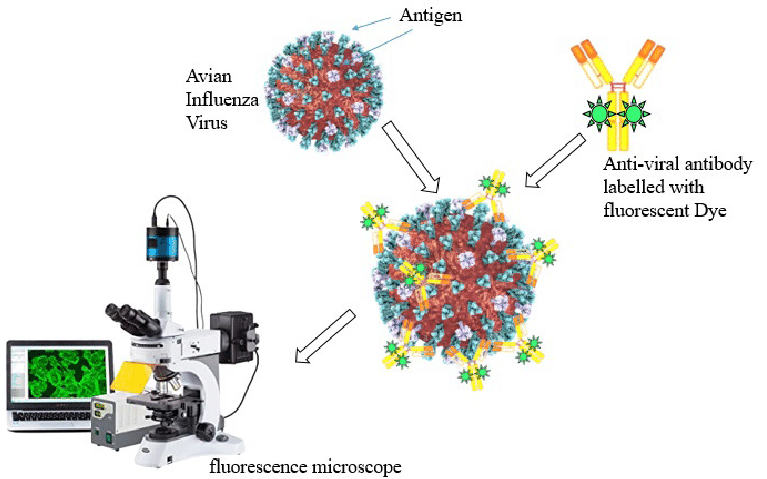
What treatment is available for Parvovirus Dermatitis?
No treatment; antibiotics for secondary infections and vaccination
What virus causes Suipox Virus (Pig Pox)?
Suipoxvirus (DNA virus, Poxviridae)
What is the primary transmission route of Suipox Virus?
Sucking lice/swine lice (Haematopinus suis)
What are the clinical signs of Suipox Virus in pigs?
Mostly affects piglets < 4 months. Macules, papules, vesicles, pustules, crusts on the ventral abdomen, inside legs, inguinal areas, non-pruritic lesions
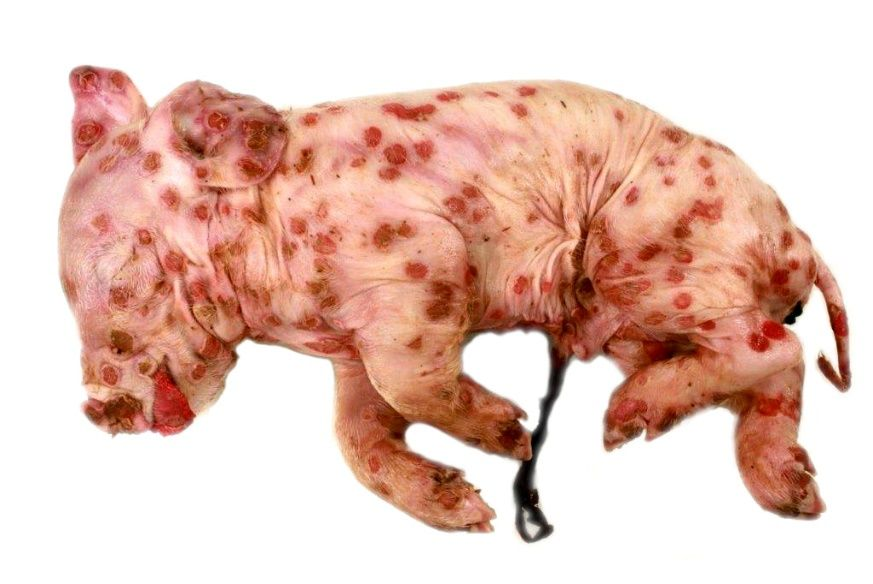
What is the treatment for Suipox Virus in pigs?
It is self-limiting; pigs become immune after infection. Ivermectin can be used against lice.
What virus causes Swine Papillomatosis?
Papilloma virus (DNA virus)
What are the clinical signs of Swine Papillomatosis?
Solitary or multiple nodules on the face and genitals
What is the causative agent of Porcine Dermatitis Nephropathy Syndrome?
Unknown, possibly immune-complex mediated. Some cases involve Porcine Circovirus 2 and Pasteurella multocida
What are the clinical signs of Porcine Dermatitis Nephropathy Syndrome?
Extensive dermatitis, purple-red bumps, glomerulonephritis, possible absence of skin lesions
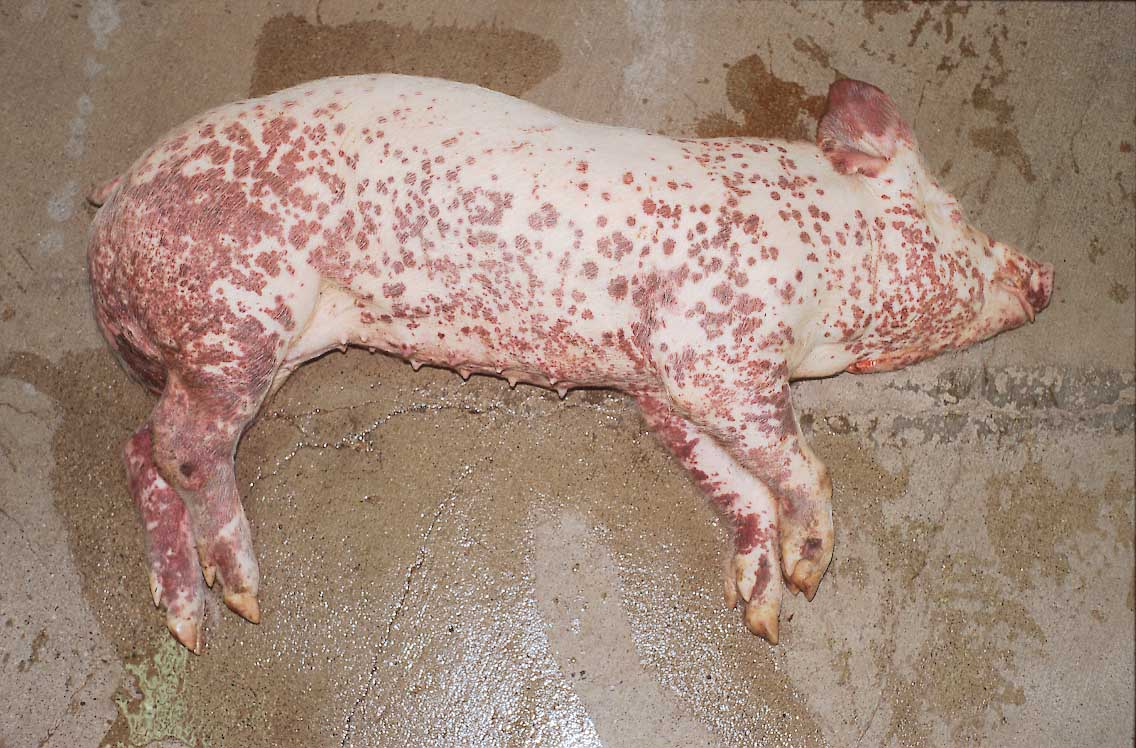
What is the treatment for Porcine Dermatitis Nephropathy Syndrome?
Not effective; euthanasia
What virus causes Porcine Respiratory & Reproductive Syndrome (PRRS)?
Arterivirus (RNA virus)
What is the main cutaneous clinical sign of Porcine Respiratory & Reproductive Syndrome (PRRS)?
Blue ear disease (blue discoloration of ears)
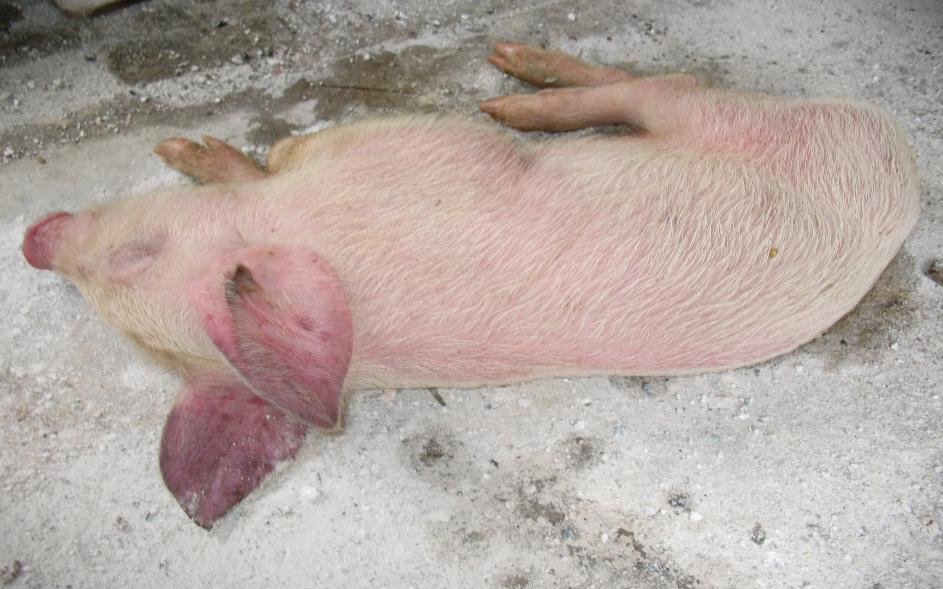

What family does the African Swine Fever virus belong to?
Asfarviridae, Asfivirus, ASFV (serotypes 1-8) (DNA virus, enveloped)
How is ASF transmitted?
Direct → Contact between sick/ healthy animals.
Indirect → All secretions + excretions. Fomites or vectors → Mosquitoes, Soft Ticks (Ornithodoros)
What is the primary pathogenesis of African Swine Fever?
Replicates in mononuclear phagocytic cells, causing splenomegaly and petechial haemorrhages on organs
What are the clinical signs of African Swine Fever?
Fever, necrotic skin changes, petechial haemorrhages, discharge from body openings, postural abnormalities, bloody diarrhoea, cyanotic mucous membranes
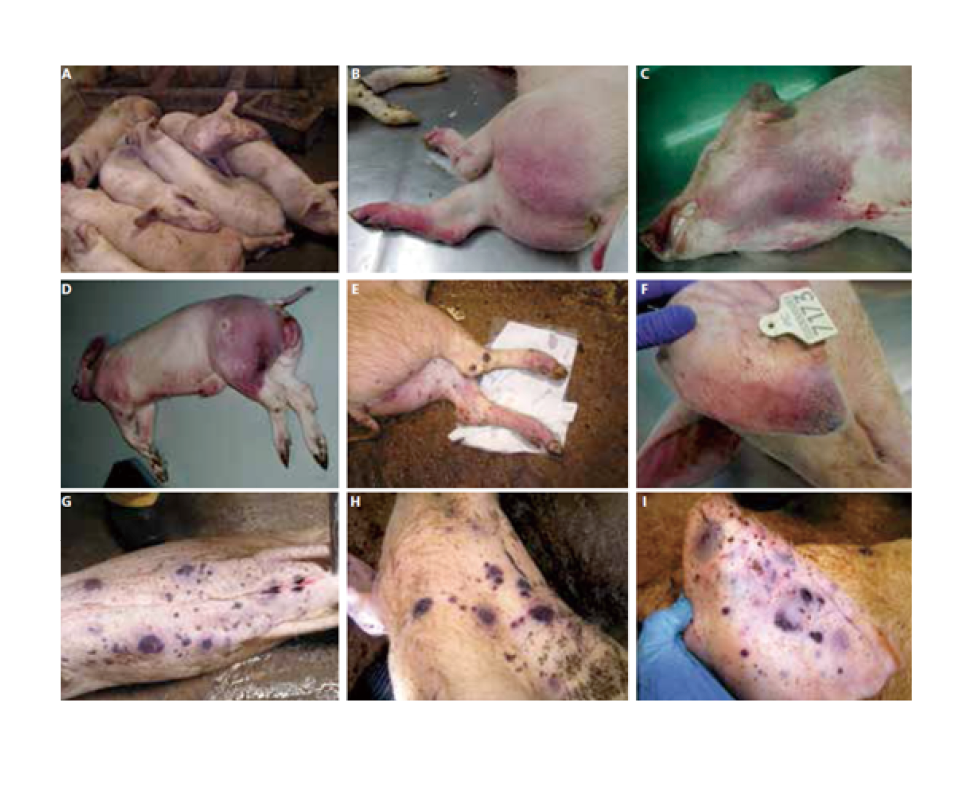
What skin changes can be seen in ASF?
Necrotic skin changes
Petechial haemorrhages on the ears
What family does Classical Swine Fever belong to?
Flaviviridae -pestivirus- CSFV (one serotype) (RNA virus, enveloped)
How is CSF transmitted?
Direct → Contact between sick/ healthy animals (secretions, excretions, blood, skin lesions), inhalation
Indirect → Ingestion of contaminated feed/ garbage. Open wounds, fomites, insects.
Transplacental
What is the pathogenesis of CSF?
Virus primarily targets the lymphoreticular tissue → tonsils & bone marrow → replicated in + destroy lymphoid tissue → spread through body → viremia + destruction of endothelium = haemorrhages, we find lower numbers of B- lymphocytes the circulatory system + destruction of lymphoid tissues
What are the clinical signs of Classical Swine Fever in young pigs (acute)?
Fever, diarrhoea, lethargy, skin discoloration, hyperaemia, haemorrhages, dyspnoea, coughing, swollen lymph nodes, ataxia, and death within 5-25 days
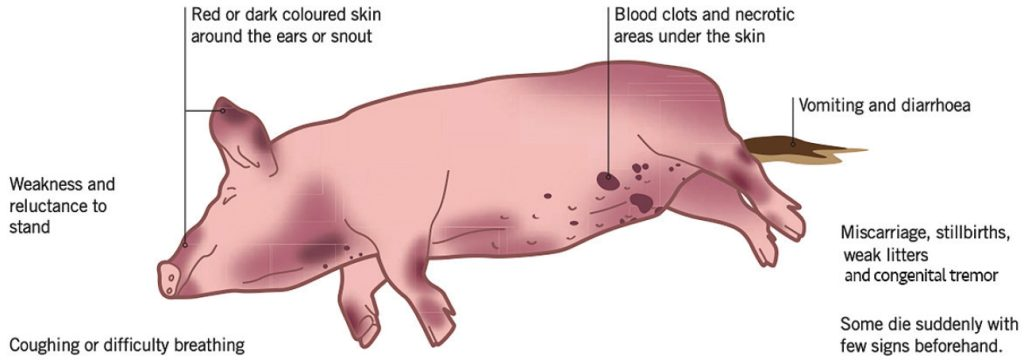
What are the clinical signs of Classical Swine Fever in older pigs (chronic)?
Depressed pigs, growth retardation, GIT-ulcers, death
What are the clinical signs of the congenital form of Classical Swine Fever?
Foetal death, resorption, mummification, stillbirth, abortion
What are examples of parasitic skin diseases?
Sarcoptes
Demodex
Lice
Myiasis