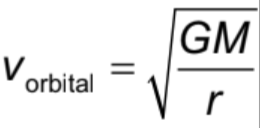D1: Gravitational fields
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics 11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Gravitational field strength
gravitational force exerted per unit test mass (g=F/m)
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of the masses causing it and the inverse square of their separation (F= GMm/r2)
Gravitational potential
the gravitational potential energy per unit mass The gravitational potential at a point: the work done in taking a unit mass from infinity to that point. (Potential at infinity taken as zero)
Gravitational Potential Energy
energy stored as a result of a body’s position in the field.
Field Strength =
- Potential gradient
Kepler’s First Law
Planetary orbits are elliptical with a star at a focus
Kepler’s Second Law
The radius vector of an orbiting body sweeps equal areas in equal times
Kepler’s Third Law
The square of the orbital period is proportional to the cube of the radius of the orbit (for circular orbits), T^2 ∝ r³
Gravitational force Formula
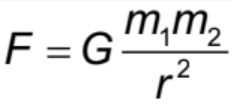
Gravitational field strength Formula
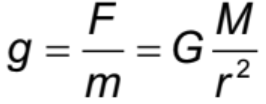
Gravitational potential Energy Formula
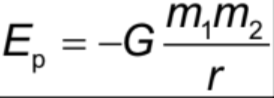
gravitational potential at a point in a gravitational field formula
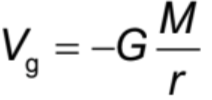
gravitational field strength formula
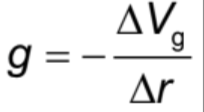
work done to move a mass in a gravitational field formula
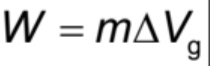
speed needed to escape a gravitational field Formula
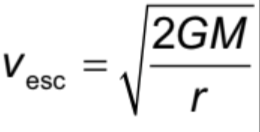
orbital speed formula