chem unit 4
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 4 chemistry honors vocabulary + key ideas
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
nuclear model
contains positively charged nucleus (no distinct protons) and electrons. most of the atom is empty space. RUTHERFORD
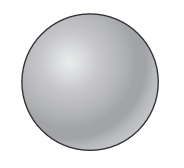
solid sphere model
cannot be divided up into smaller parts. DALTON
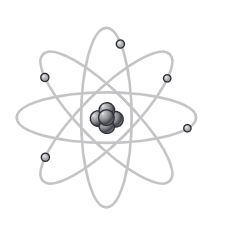
proton model
nucleus consists of protons and electrons, which circle the nucleus — similar to nuclear model. CHADWICK and RUTHERFORD
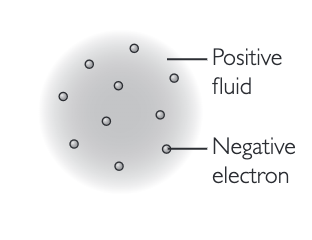
plum pudding model
positive fluid, no nucleus, electrons scattered throughout. THOMSON
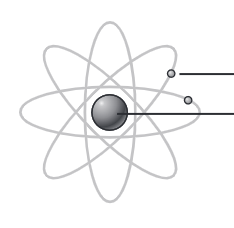
solar system model
nucleus at center (no distinct protons), electrons circle it at specified orbits. different distances from nucleus. BOHR
who discovered electrons?
thomson
who discovered protons?
rutherford
who discovered the nucleus?
rutherford, did NOT know about neutrons
who discovered neutrons?
rutherford / chadwick
how were electrons discovered?
cathode ray experiment (thomson)
how was the nucleus discovered?
gold foil experiment (rutherford)
how were neutrons discovered?
beryllium / boron / lithium sheet experiment (chadwick)
how were protons discovered?
scintillation detectors (in progress)
law of the conservation of mass
matter is neither created nor destroyed, just converted in some way
dalton’s atomic theory
- matter is made up of small particles called atoms
- atoms are indivisible and indestructible
- atoms of a particular element are identical in size, mass, and chemical properties
- atoms of other elements differ from each other
- different atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds
- chemical reaction: atoms are separated, combined, and rearranged
isotope
same element: same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus
mass number
total number of neutrons and protons
atomic number
number of protons
atomic mass
similar to mass number, but includes the electrons, so it is an approximation of an atom’s total mass
radioactive decay
emission of energy in the form of ionizing radiation
fusion
joining of 2 nuclei to form a larger nucleus. accompanied by a large amount of energy (e.g. hydrogen bombs)
fission
separation of a nucleus into 2 smaller nuclei. accompanied by a large amount of energy
electron, proton, neutron, gamma, beta, alpha symbols
e-, p+, no, γ, β, α (gamma and alpha are different)
beta decay (particles)
electron is emitted from a radioactive nucleus (neutron becomes proton, gives off electron; when writing an equation with β-, atomic # gains a proton. with β+, atomic # loses a proton.) negative charge, no mass
alpha decay (particles)
2 protons and 2 neutrons produced during alpha decay. 2 protons, 4 atomic mass
gamma radiation / particles
emitted from a radioactive nucleus. no charge, no mass
nuclear chain reaction
a series of reactions following fission, where the emitted neutrons can cause additional fission reactions.
average atomic mass of an isotope
1. change percent of abundance into decimal (divide by 100)
2. multiply by atomic mass
3. add together to get the average.
use % of abundance and mass number/actual mass