GOTHIC ARCHITECTURE
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
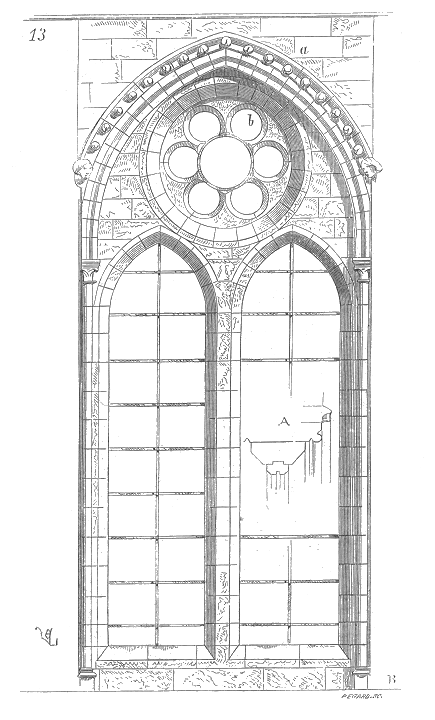
Tracery
–ornamental work of branchlike lines especially the lacy openwork in the upper part of the Gothic window

Plate tracery
early Gothic tracery formed by pierced slabs of stone set on edge. The design is based on the shape and disposition of the openings, called perforated tracery. This technique allows for intricate patterns and greater light transmission in Gothic architecture.

Curvilinear tracery
Gothic tracery characterized by pattern of irregular boldly curved forms. Also called flowing tracery

Reticulated tracery
gothic tracery consisting mainly of a netlike arrangement of
repeated geometric figures. Also called net tracery

Intersecting tracery
characterized by intersecting traceries

Geometric tracery
characterized by a pattern of geometric shapes such as circles and foils
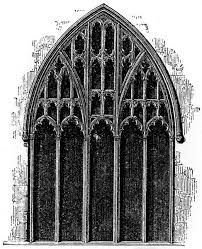
Perpendicular tracery
predominantly vertical gothic tracery having mullions rising to the curve of the arch, crossed the intervals by a horizontal transom. Also called rectilinear tracery

Triforium gallery
space above the nave

Pinnacle
architectural element originally forming the cap or crown of a buttress or small turret, but afterwards used on parapets at the corners of towers and in many other situations. The pinnacle looks like a small spire. It was mainly used in Gothic architecture
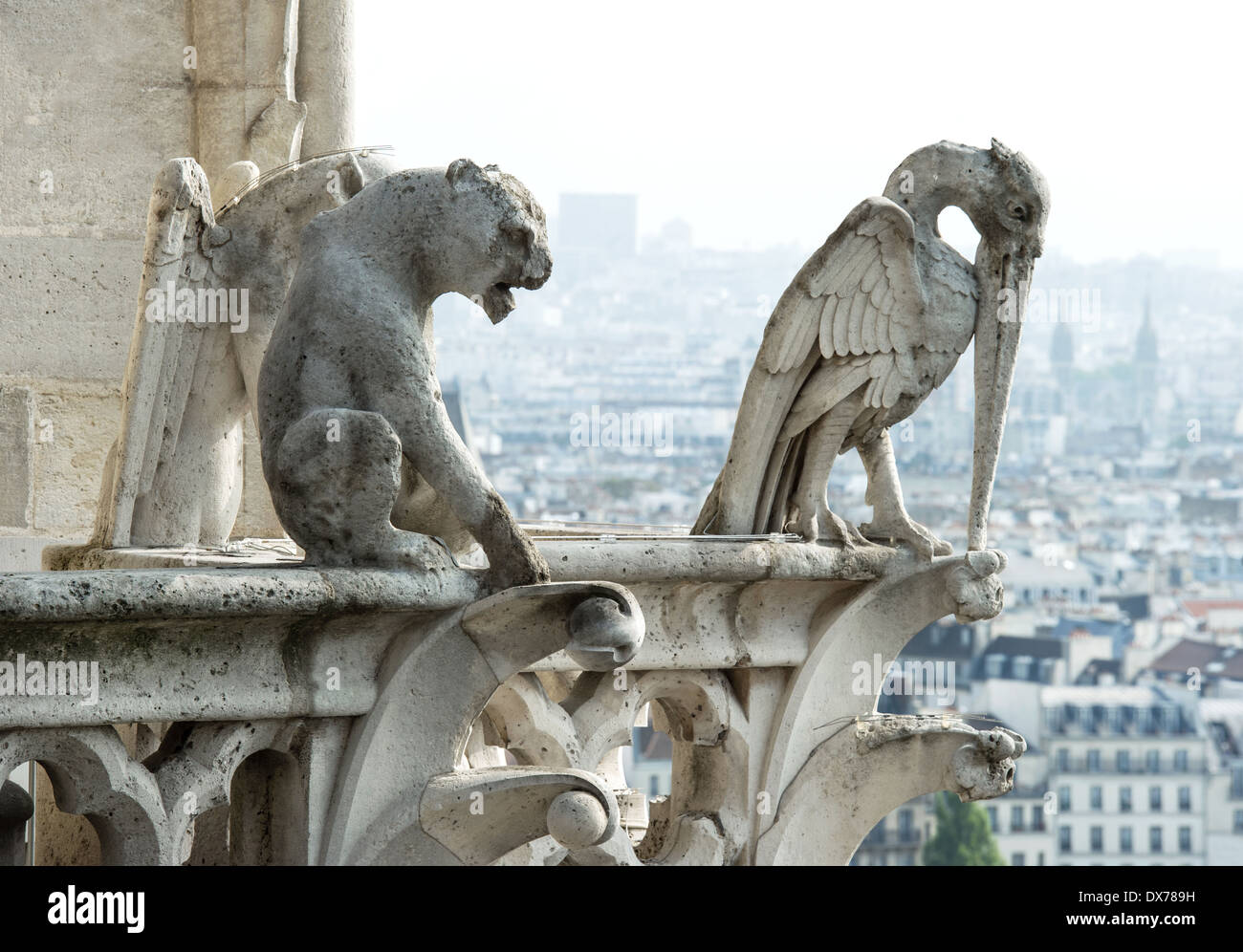

Chimera
a statue which is formed of various monstrous body parts but is there purely for decorative purposes.

Foil
–any of several arcs or rounded spaces divided by cusps and tangent to the interior of a larger arc as of an arch or a circle; trefoil- having 3 foils; quatrefoil-4 foils; cinquefoil-5 foils; multifoil- more than 5 foils
Foilation
ornamentation of an archway, window Or other openings with foils or representations Of foliage
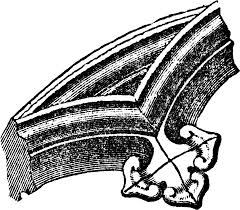
Cusp
a pointed projection formed by two Intersecting arcs used especially to vary the outlines of the intradoses or to form foils.
Cuspidation
decoration with cusp
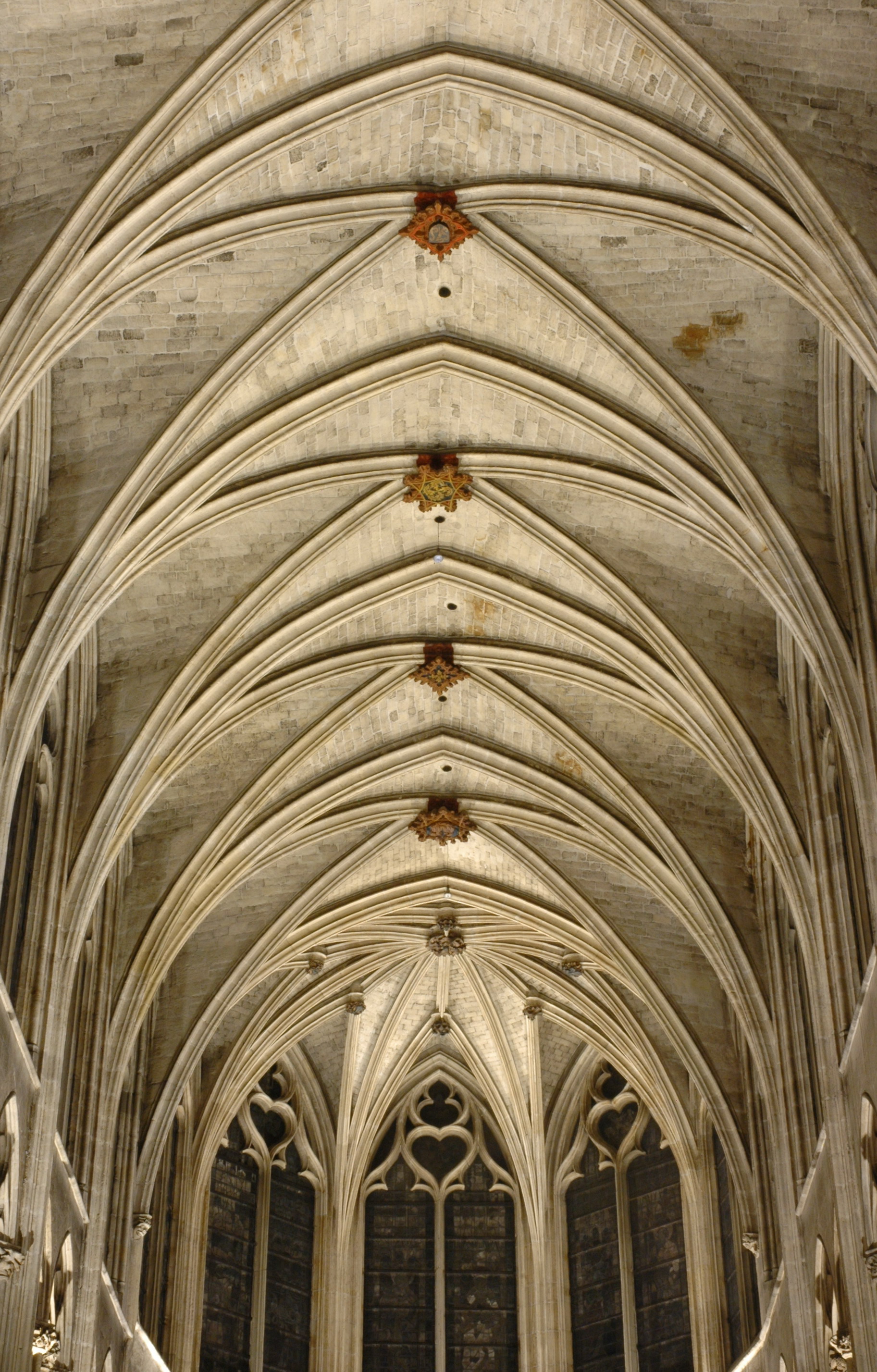

Vaults
an arched covering in stone or brick over any building.
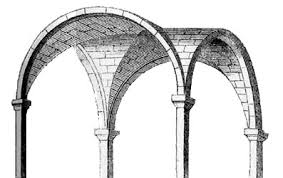
Groin
one of the curved lines of edges along which two intersecting vaults meet.
Web
a surface framed by the ribs of the ribbed vault.

Rib
any of the several arch-like members supporting a vault at groin, defining its distinct surfaces or dividing those surfaces into panels.
Key
the keystone at the crown of the arch or at the intersection of two or more vaulting rib.

Rose window
a circular window usually of stained
glass and decorated withtracery symmetrical about the centre.
Stained glass
–glass colored or stained having pigment baked onto its surface by having various metallic oxides fused while in molten state

wheel window
a circular window whose mullions converge like spokes of a wheel. Also called Catherine window or marigold window.
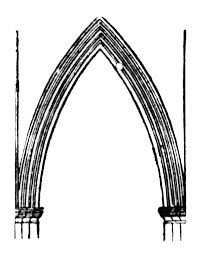
Lancet Arch
a pointed arch having two centers and radii greater than the span

Spire
a tall acutely tapering pyramidal structure surmounting a
steeple or a tower.
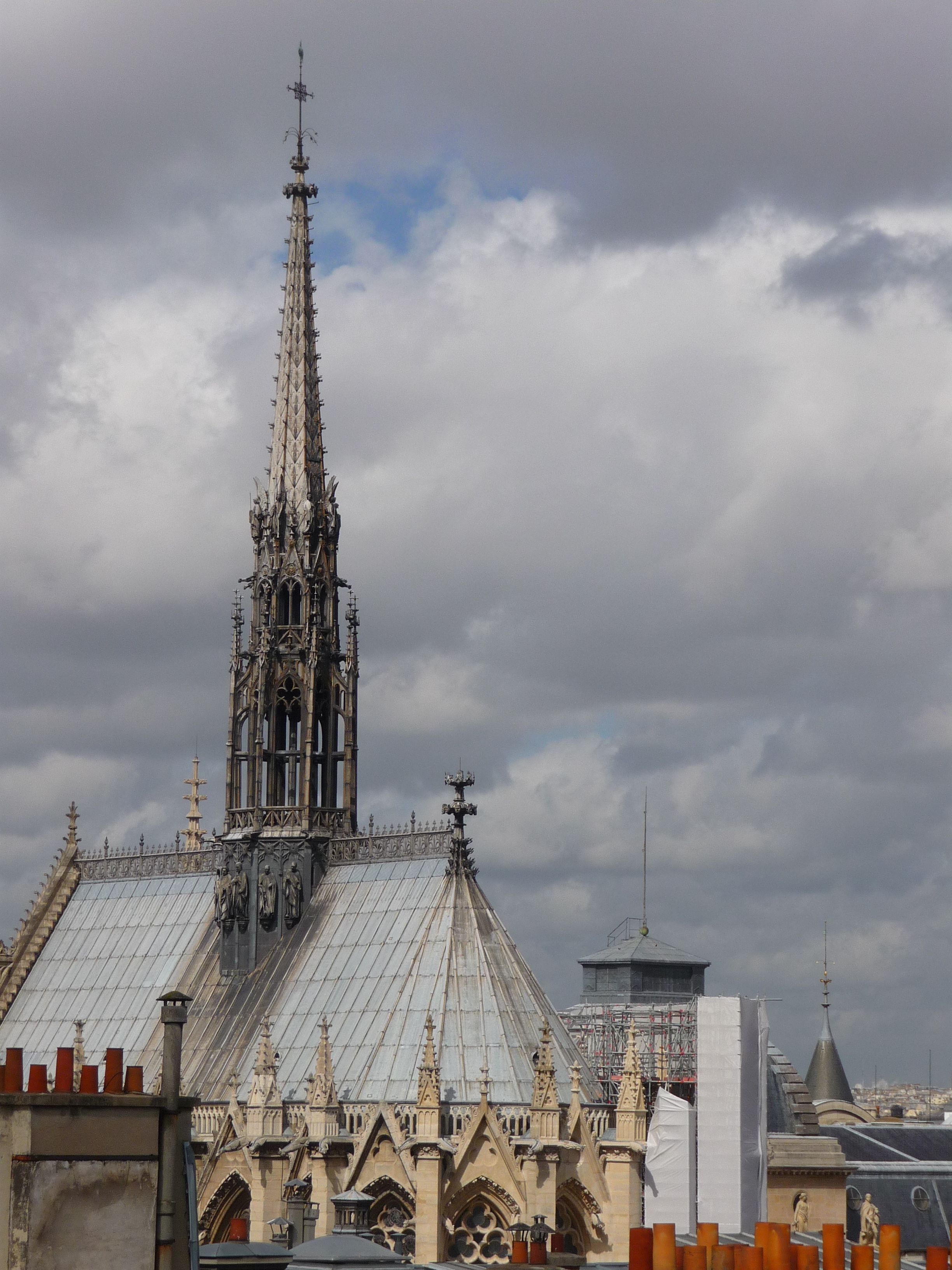

Fleche
a slender wooden spire on the roof especially at the crossing of a Gothic church.
Western towers
paired towers constructed on the western part of the Gothic Church.

Niche
a recess on the wall, hollowed like a shell for statue or ornament
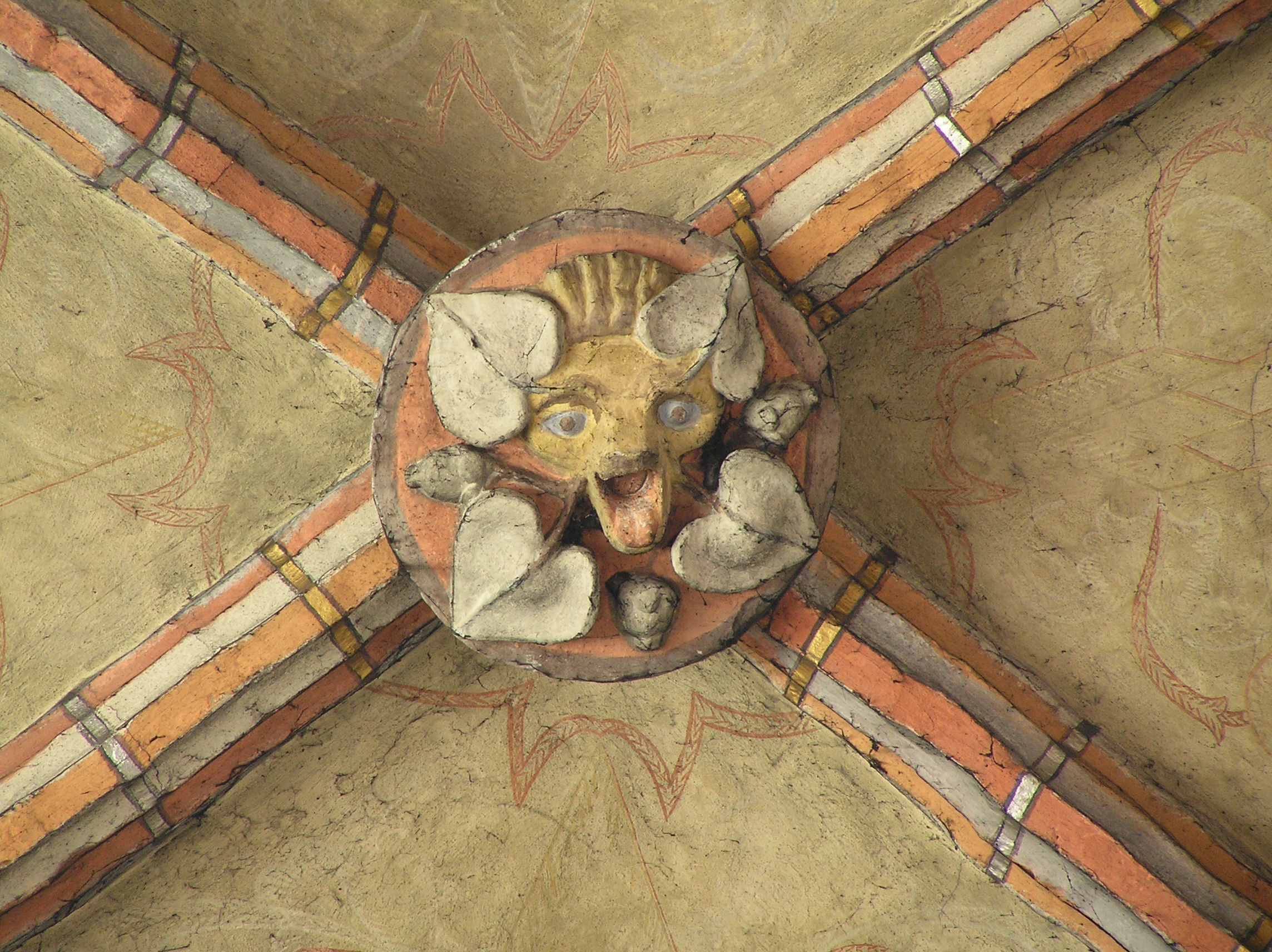

Boss
a projecting ornament at the intersection of the ribs of the ceiling whether vaulted or flat .
CATHEDRAL
the principal church of a diocese containing the bishop’s throne called the cathedra
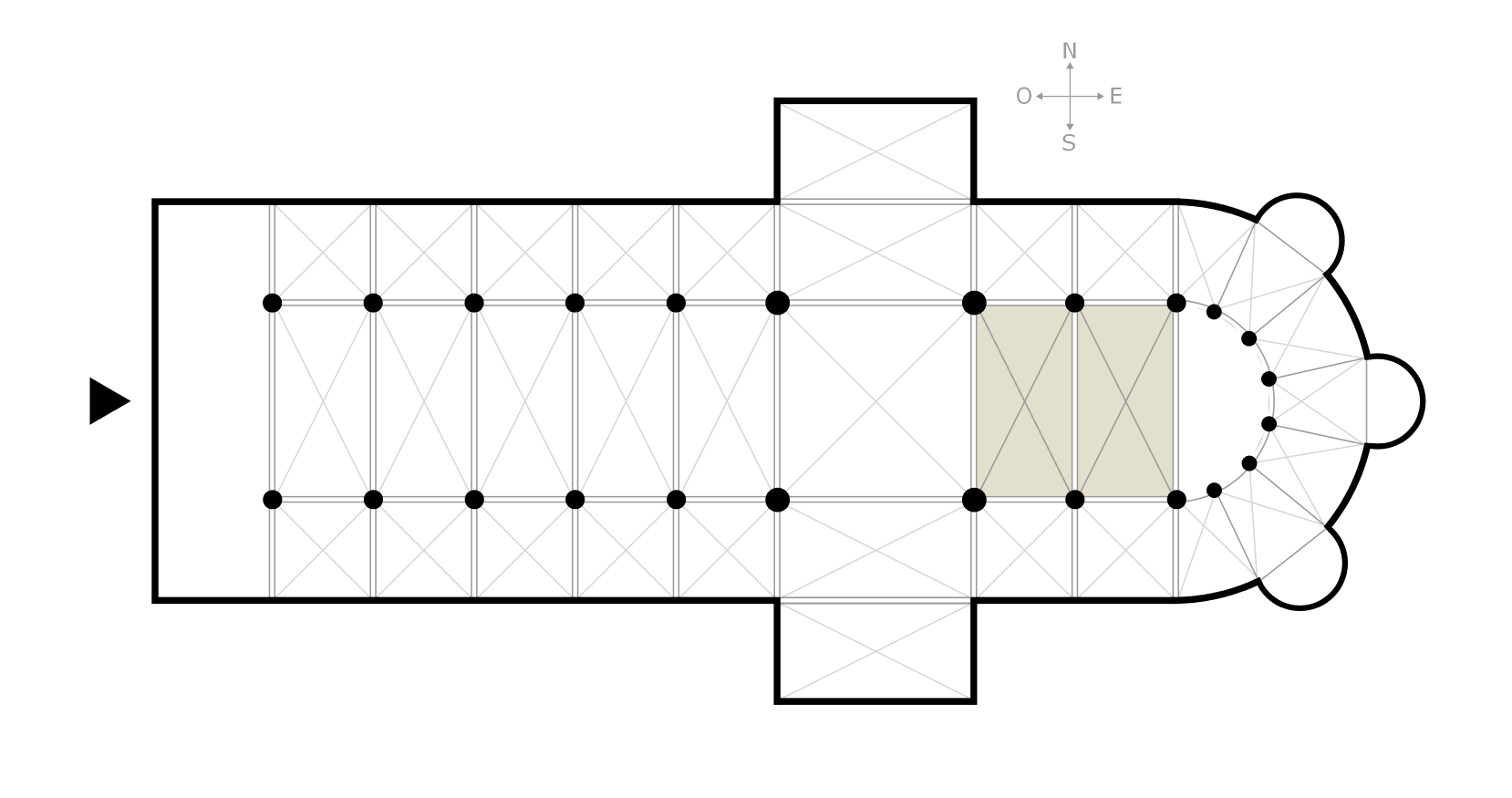
Choir
the part of the church occupied by the singers of a choir, usually part of the chancel
Retrochoir
a separate division behind the choir or high altar of a large church
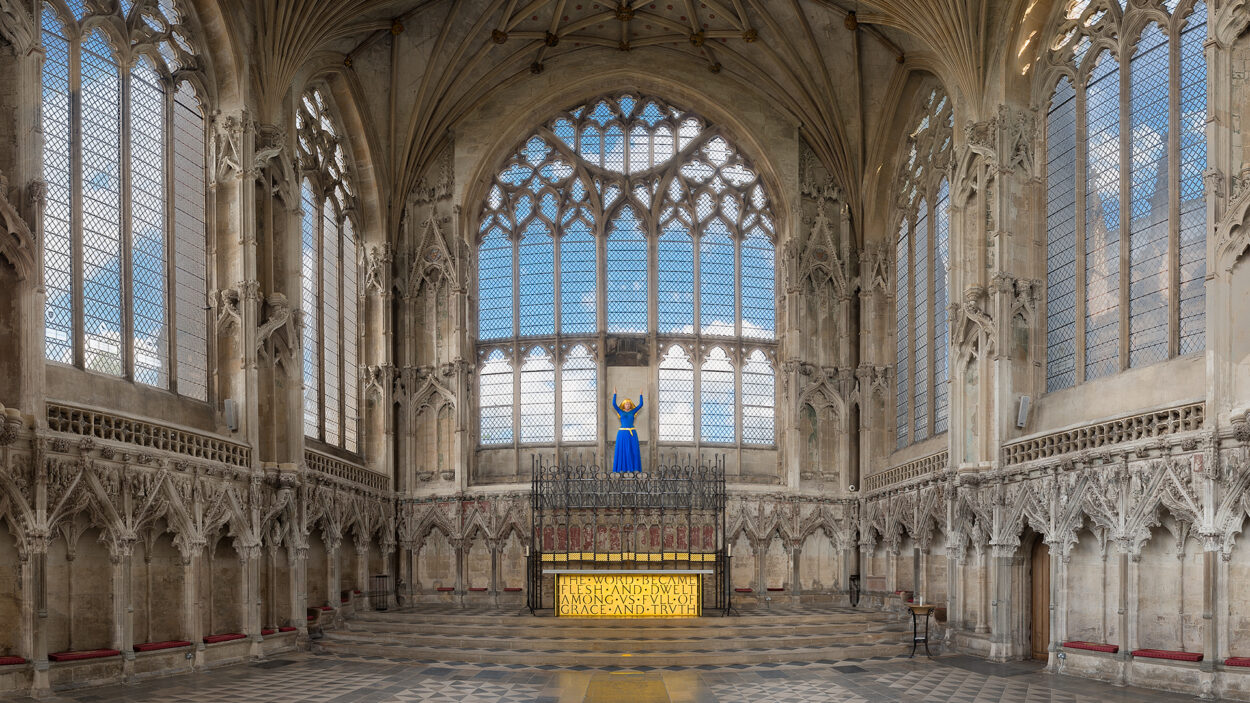

Lady chapel-
a chapel dedicated to the Virgin Mary usually located behind the high altar of a cathedral at the extremity of the apse
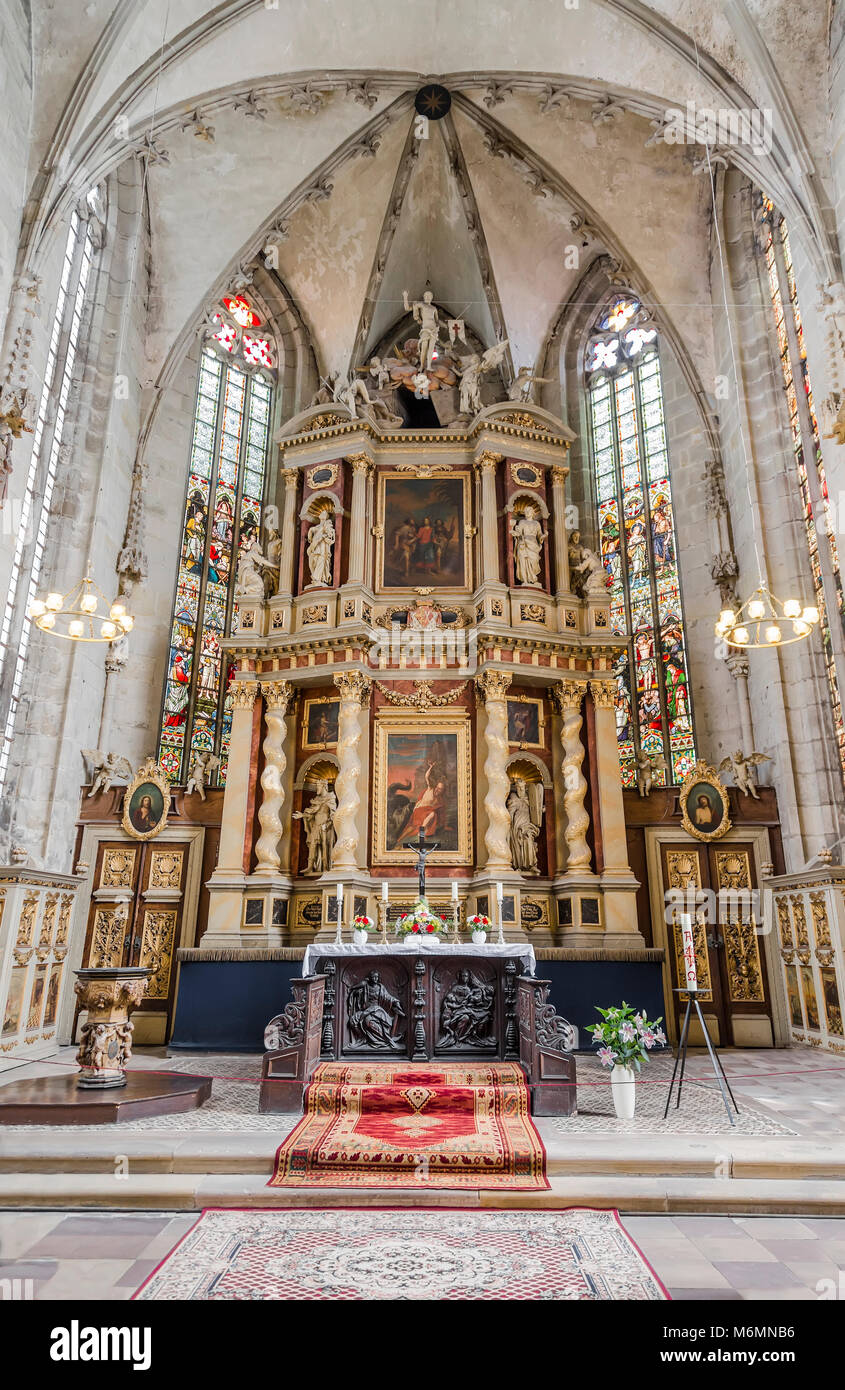

High altar
the main altar of the church
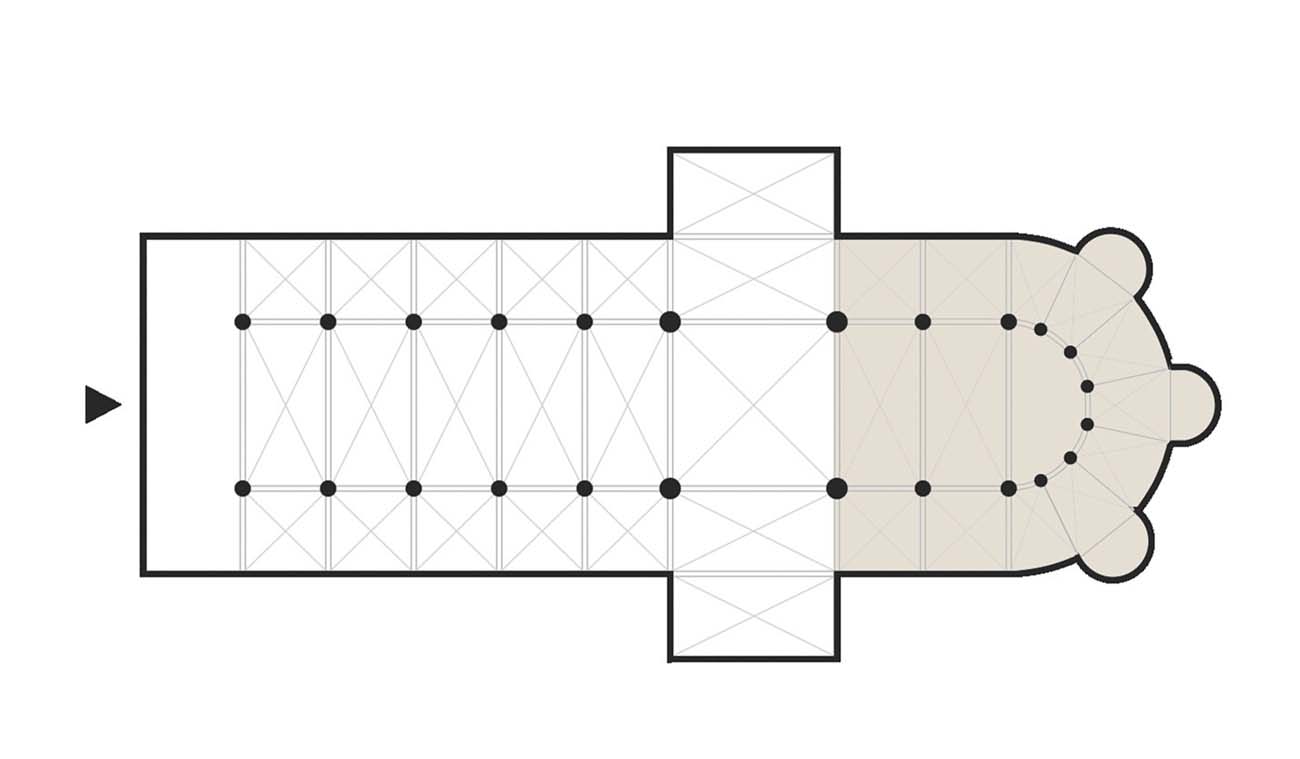
Presbytery
the part of the church reserved for the officiating clergy
Close
an enclosed space especially the land surrounding or beside the cathedral
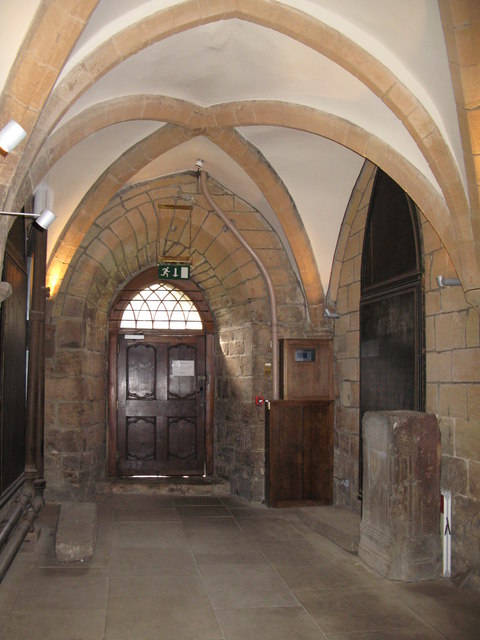

Slype
covered passage especially one between the transept and chapter house of a cathedral. Also alip
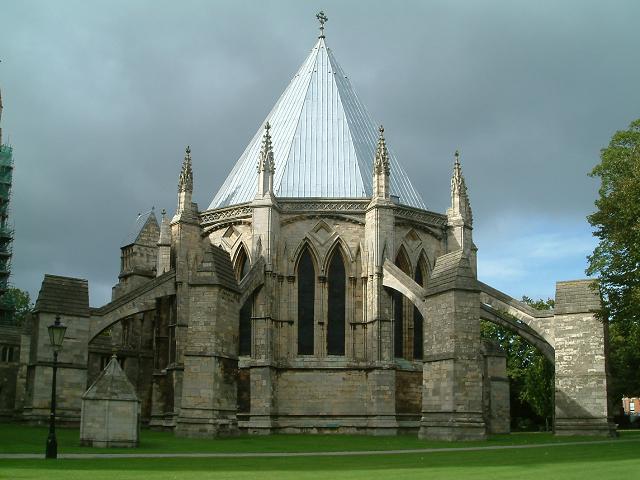

Chapter house
the place where the chapter of the cathedral or monastery meets, usually a building attached to or a hall forming part of the cathedral or monastery
Chapter
an assembly of the monks in a monastery, or the members of a religious orders
Paradise
an atrium or cloister beside the church

Cloister
covered walk having an arcade or colonnade on one side opening onto a courtyard
Garth-
a courtyard or a quadrangle enclosed by a cloister.
Allure
a walk or a passage along a cloister or behind the parapets of a castle
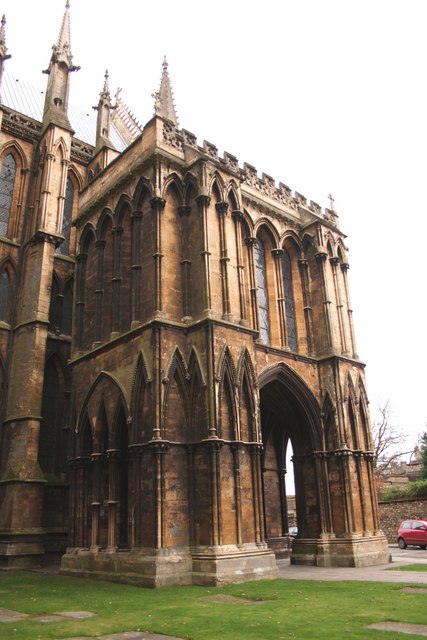

Galillee
small porch used as a chapel for penitents at the west end of some medieval and English churches
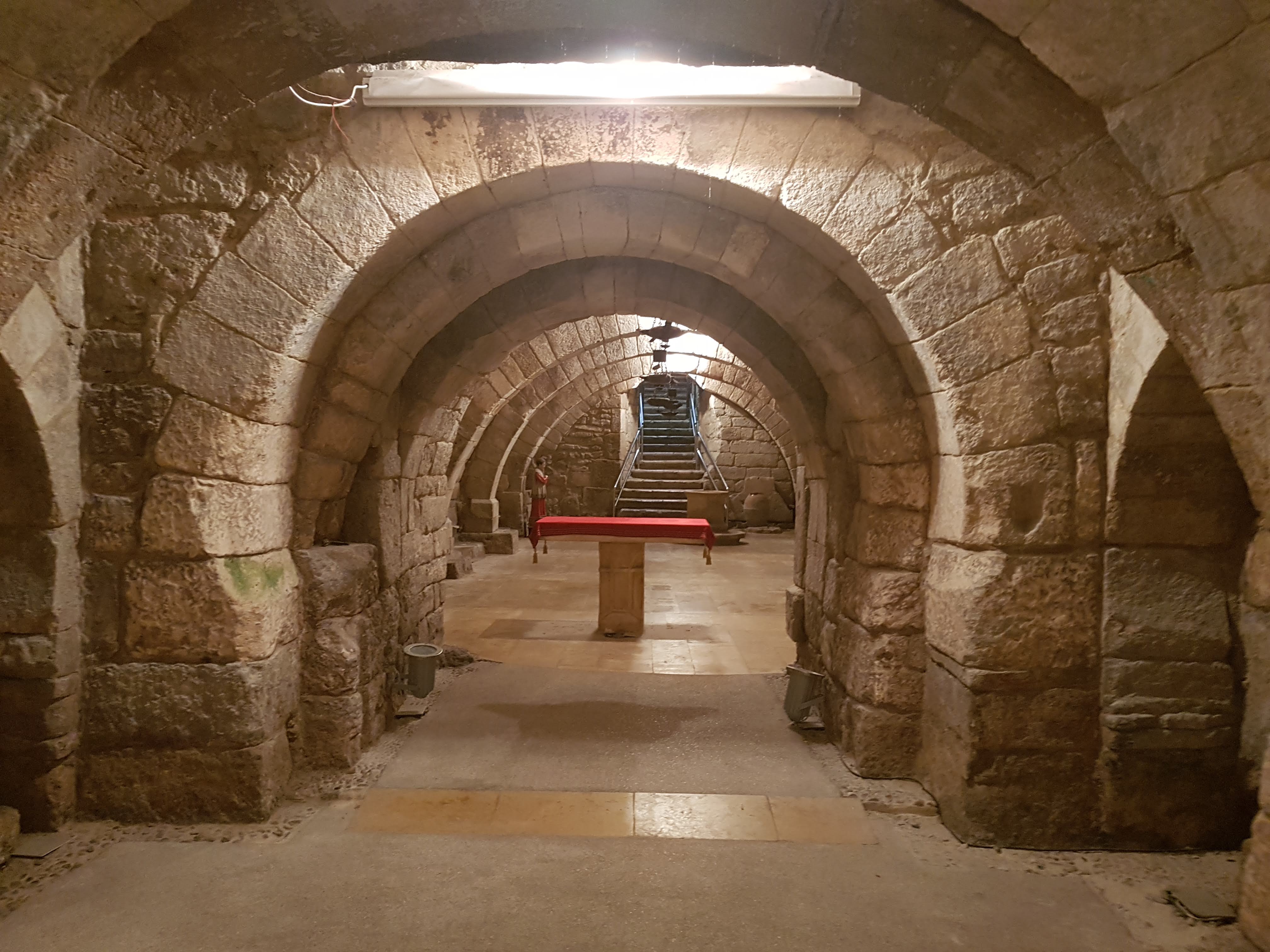

Crypt
an underground chamber or vault used as a burial place, especially one beneath the main floor of the church.
Chantry
a chapel endowed for saying of masses and prayers for the souls of the founders or of persons named by them.
Labyrinth
a mazelike pattern inlaid in the pavement of a medieval church.
Chapel
a separately dedicated part of the church for private prayer, meditation, or small religious services.
Chevet
the rounded east end of a Gothic Cathedral including the apse of the ambulatory
Ambulatory
an aisle encircling the end of the choir or chancel of the church. Also called deambulatory.
Rood
a crucifix symbolizing the cross on which Christ was crucifix, especially a large one set above the entrance to the choir or chancel of a medieval church.
Rood screen
a screen often elaborately adorned and properly surmounted by rood, separating the chancm the nave of a medieval church.
Key Features:
Pointed arches and ribbed vaults
Flying buttresses for structural support
Large stained glass windows
Emphasis on verticality and divine light

.
Basilica of Saint-Denis, France

.
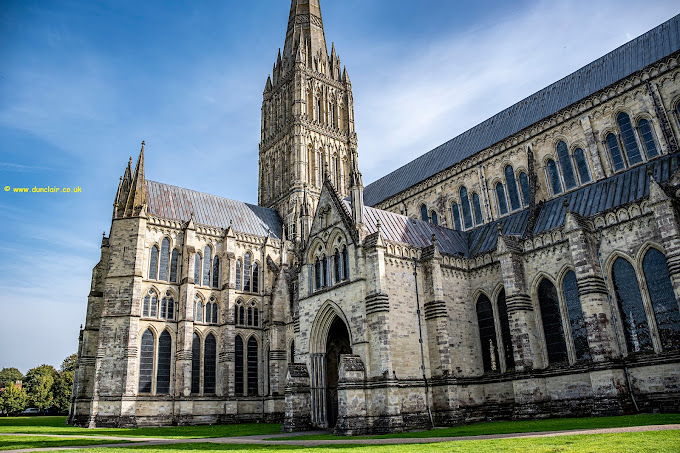
Salisbury Cathedral, England

.
Barcelona Cathedral, Spain

.
Cologne Cathedral, Germany

.
Westminster Abbey, 1269

.
Laon Cathedral, 1235

.
Guildhall, 1411

.
Notre Dame, 1345
Paris, France

.
Reims Cathedral