MICROBIO_LAB_MIDTERMS_MYCOLOGY
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
1
New cards
Nosocomial infections
What are hospital acquired infections called?
2
New cards
Cellulases
What are the extracellular enzymes that decompose hard part of plants?
3
New cards
Mycorrhizae
What symbiotic fungi do all plants depend on?
4
New cards
Helps roots absorb minerals & H2O from the soil
What is the use of Mycorrhizae?
5
New cards
Cellulose & Lignin
What do ants cultivate that breaks down to ______ & _____ from plants?
6
New cards
Glucose
What do ants get from Cellulose & Lignin?
7
New cards
Food = Mushroom, Bread & Citric Acid
Drugs = Penicillin & ROH
Drugs = Penicillin & ROH
What is the use of Fungi for Humans in terms of:
Food?
Drugs?
Food?
Drugs?
8
New cards
200
How many species of Fungi are pathogenic to Humans & Animals?
9
New cards
Mycology
What is the study of Fungi?
10
New cards
Require organic compounds for Energy & Carbon
What does it mean for Fungi to be chemoheterotrophs?
11
New cards
1. Aerobic
2. Facultative anaerobic = few only
2. Facultative anaerobic = few only
What are fungi in terms of oxygen?
12
New cards
1. Dark environment
2. Moist environment
3. Warm environment
2. Moist environment
3. Warm environment
What is conductive for the growth of Fungi?
13
New cards
1. Microscopic vs Macroscopic
2. Unicellular vs. Multicellular
2. Unicellular vs. Multicellular
What are the classification of Fungi?
14
New cards
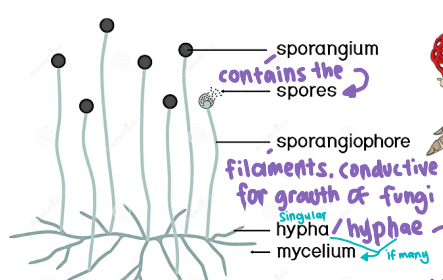
1. Sporangium = contains the Spore
2. Spore
3. Sporangiophore = filaments
4. Hypha / Hyphae
5. Mycelium = many hypha = like root
2. Spore
3. Sporangiophore = filaments
4. Hypha / Hyphae
5. Mycelium = many hypha = like root
What are the parts of Fungi?
15
New cards
1. Heterotrophic eukaryotes
2. Saprophytic
3. Reproduce sexually / asexually
4. Do not produce chlorophyll
5. Produce antibiotics
2. Saprophytic
3. Reproduce sexually / asexually
4. Do not produce chlorophyll
5. Produce antibiotics
What are the characteristics of Fungi?
16
New cards
Saprophytic
What does it mean when Fungi reproduce, live, recycle & consume dead matter?
17
New cards
Heterotrophic eukaryotes
What does it mean when Fungi are enclosed by nuclear membrane & contains membrane bound organelles?
18
New cards
Do not produce chlorophyll
What does it mean when Fungi cannot make their own food?
19
New cards
Penicillin
(Penicillin chrysogenum) (Penicillin notatum)
(Penicillin chrysogenum) (Penicillin notatum)
What is an example of Antibiotic from Fungi?
SN?
SN?
20
New cards
1. 40s = smaller
2. 60s = larger
2. 60s = larger
What are the Human Ribosomal subunits similar to Fungi subunits?
21
New cards
Chitin, Glucan, & Mannan
What is in the Cell Wall of Fungi?
22
New cards
Chitin
What is the hard & sturdy part of Fungi that is the cause why they are hard to kill?
23
New cards
Fungal infection (2wks)
What takes longer to cure, Fungal or Bacterial infection?
24
New cards
Peptidoglycan
What is in the cell wall of Bacteria?
25
New cards
No Cell Wall
What is in the call wall of Animal Cells?
26
New cards
1. NAG = N-acetylglucosamine
2. NAM = N-acetylmuramic acid
2. NAM = N-acetylmuramic acid
What is in the peptidoglycan of Bacteria?
27
New cards
NAG = N-acetylglucosamine
What is in the Chitin of Fungi?
28
New cards
Proteins
What are the mannan in the Cell wall of Fungi?
29
New cards
Ergosterol
What is the cell membrane of Fungi?
30
New cards
Yes, they are heterotrophic eukaryotes
Do Fungi have cell-membrane organelles?
31
New cards
Septa / Septum
What is the part of Fungi that separates 2 fungal cells?
32
New cards
Many septum
Hoe many septum do a hypha have?
33
New cards
No, they are easer to kill
Is a fungi w/o septum not easier to kill?
34
New cards
Phytosterol
What is in the cell membrane of Plants?
35
New cards
Cholesterol
What is in the cell membrane of Humans & Animals?
36
New cards
Ergosterol
What is in the cell membrane of Fungi?
37
New cards
Eukaryote
What is the cell type of Fungi?
38
New cards
Sterols = Ergosterol
What is in the cell membrane of Fungi?
39
New cards
Chitin, mannans, & Glucan
What is the cell wall of Fungi?
40
New cards
Sexual & Asexually reproductive spores
How do Fungi spores reproduce?
41
New cards
Limited to heterotrophic; aerobic & facultative anaerobic
What is the metabolism of Fungi?
42
New cards
Prokaryote
What is the cell type of Bacteria?
43
New cards
No, sterols are absent except in Mycoplasma
Are sterols present in Bacteria?
44
New cards
Peptidoglycan
What is in the Cell Wall of Bacteria?
45
New cards
Endospores = not for reproduction ; some asexual reproductive spores
What are the spores in Bacteria?
46
New cards
Heterotrophic, autotrophic (make own food), aerobic, facultative anaerobic, anaerobic
What is the metabolism of Bacteria?
47
New cards
1. Ascomycota
2. Basidiomycota
3. Zygomycota
4. Deuteromycota
2. Basidiomycota
3. Zygomycota
4. Deuteromycota
What are the 4 medically important phylla of Fungi?
48
New cards
Sac fungi
What is the other name of Ascomycota?
49
New cards
Ascus: It contains specialized sac containing asexual spores
What makes ascomycata different?
50
New cards
Morels, Truffles, & Yeasts
What are examples of ascomycota?
51
New cards
Streptomyces = bacteria
What is the exception of Ascomycota?
52
New cards
Basidium: club-like structure containing asexual spores
What makes Basidiomycota different?
53
New cards
Toadstool & Puffballs
What are examples of Basiodiomycota?
54
New cards
1. Zygote Fungi
2. Zygomycetes
2. Zygomycetes
What are the other name of Zygomycota?
55
New cards
Zygospore
What is the thick walled spore in Zygomycota?
56
New cards
1. Meat
2. Cheese
3. Bread
2. Cheese
3. Bread
Where do Zygomycota grow?
57
New cards
(Rhizopus stolonifera)
Black Bread Mold
Black Bread Mold
What is the example of Zygomycota?
Common Name?
Common Name?
58
New cards
Mitosporic & Fungi Imperfecti (Imperfect Fungi)
What is the other name of Deuteromycota?
59
New cards
They reproduce through mitosis
Why are Deuteromycota called Mitosporic?
60
New cards
They have no asexual spores
Why are Deuteromycota called Imperfect Fungi?
61
New cards
(Penicillium notatum & Penicillium chrysogenum)
What are examples of Deuteromycota?
62
New cards
1. Mycoses
2. Hypersensitivity
3. Mycotoxins
4. Mycetismus
2. Hypersensitivity
3. Mycotoxins
4. Mycetismus
What are the 4 types of Fungal Condition?
63
New cards
Mycoses
What fungal condition is the general term for fungal infection?
64
New cards
Hypersensitivity
What is the fungal condition that is an allergic rxn?
65
New cards
Mycotoxicosis
What is the type of fungal condition that is the ingestion of food contaminated w/ fungal toxin?
66
New cards
Alfatoxin
What is an example of Mycotoxicosis?
67
New cards
Improperly dried peanuts
What do alfatoxin contaminates?
68
New cards
1. Carcinogenic
2. Teratogenic
2. Teratogenic
What are the effects of Alfatoxin?
69
New cards
Cause abnormalities in new borns
What is the effect of Teratogenic?
70
New cards
Mycetismus
What fungal condition is the ingestion of poisonous fungi?
71
New cards
Poisonous mushroom
What is an example of poisonous fungi?
72
New cards
1. Superficial
2. Cutaneous
3. Subcutaneous
4. Systemic / Deep
2. Cutaneous
3. Subcutaneous
4. Systemic / Deep
What are types of Mycoses?
73
New cards
Epidermis
What is the site of infection of Superficial?
74
New cards
Dermis
What is the site of infection of Cutaneous?
75
New cards
Fatty layer of skin
What is the site of infection of Suncutaneous?
76
New cards
Blood
What is the site of infection if Systemic / Deep?
77
New cards
1. Black Piedra
2. White Piedra
3. Tinea Versicolor / Ptyriasis Versicolor
4. Tinea Nigra
2. White Piedra
3. Tinea Versicolor / Ptyriasis Versicolor
4. Tinea Nigra
What are examples Superficial Mycoses?
78
New cards
(Piedra hortae)
h = hair shaft
h = hair shaft
What is the CA of Black Piedra?
79
New cards
Firm & Hard nodules in the hair shaft
What is the symptoms of Black Piedra?
80
New cards
Trichosporon beigelii
beige = white color
beige = white color
What is the CA of White Piedra?
81
New cards
Soft friable, beige, white nodule
What is the symptoms of White Piedra?
82
New cards
Malassezia furfur
What is the CA of Tinea Versicolor / Ptyriases versicolor?
83
New cards
Multi coloration of skin
What is the symptoms of Tinea versicolor?
84
New cards
Spaghetti & Meatballs
What is the appearance of Malassezia furfur under the microscope?
85
New cards
Yes,
Warm = Yeast
Cold = Mold
Warm = Yeast
Cold = Mold
Is Malasezzia furfur a dimorphic fungi?
86
New cards
Phaeoannellomyces werneckii
What is the CA of Tinea Nigra?
87
New cards
Silver nitrate like stains on the palms & soles
What is the symptoms of Tinea Nigra?
88
New cards
Dermatophytes / Ringworm
What are the other names for Cutaneous Mycoses?
89
New cards
Ring = w/ ring like appearance
Worm = looks like worm under the microscope
Worm = looks like worm under the microscope
Why are Cutaneous Mycoses also called Ringworm?
90
New cards
METh
1. Microsporum
2. Epidermophyton
3. Trichophyton
1. Microsporum
2. Epidermophyton
3. Trichophyton
What are the causes of Cutaneous Mycoses?
91
New cards
1. KOH Mount
2. Wood's Lamp
2. Wood's Lamp
What are the ways of Identification of Cutaneous Mycoses?
92
New cards
Wood's Lamp
What is the means of Cutaneous identification that uses UV light?
93
New cards
Tinea capitis
Cap = placed in the head
Cap = placed in the head
What is the ringworm of the Head?
94
New cards
Tinea corporis
What is the ringworm of the Body?
95
New cards
Tinea facie
Fac= Face
Fac= Face
What is the ringworm of the Face?
96
New cards
Tinea barbae
B = Beard
B = Beard
What is the ringworm of the Beard?
97
New cards
Tinea manuum
man = manicure
man = manicure
What is the ringworm of the Hand?
98
New cards
Tinea unguium
What is the ringworm of the Nails?
99
New cards
Tinea axillaris
What is the ringworm of the Underarm?
100
New cards
Tinea cruris
What is the ringworm of the Groin?