Cell Structures Bio 9H
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:05 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
What is a cell?
- Cells are the basic units that make up every living thing.
2
New cards
Scientist Robert Hooke
- first named “cells” because when he looked at a cork under one of
the first compound microscopes, the little boxes reminded him of
monastery cells/rooms.
- This discovery led to the development of the classical cell theory.
- Worked with Anton Van Leeuwenhoek, who first discovered
bacteria (he called them Animalcules)
the first compound microscopes, the little boxes reminded him of
monastery cells/rooms.
- This discovery led to the development of the classical cell theory.
- Worked with Anton Van Leeuwenhoek, who first discovered
bacteria (he called them Animalcules)
3
New cards
Cytology
The study of cells
4
New cards
What is the cell theory?
- The cell is the basic unit of all living things.
- Cells perform all the functions of living things.
- Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells.
- Cells perform all the functions of living things.
- Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells.
5
New cards
How are cells grouped together
- organized in multicellular (many-celled) organisms based on
function (so they all work together and efficiently)
function (so they all work together and efficiently)
6
New cards
How do cells build an organism?
1. Cells
2. Tissues
3. Organs
4. Organ Systems
5. Organism
2. Tissues
3. Organs
4. Organ Systems
5. Organism
7
New cards
2 major types of cells
- prokaryotic
- eukaryotic
- eukaryotic
8
New cards
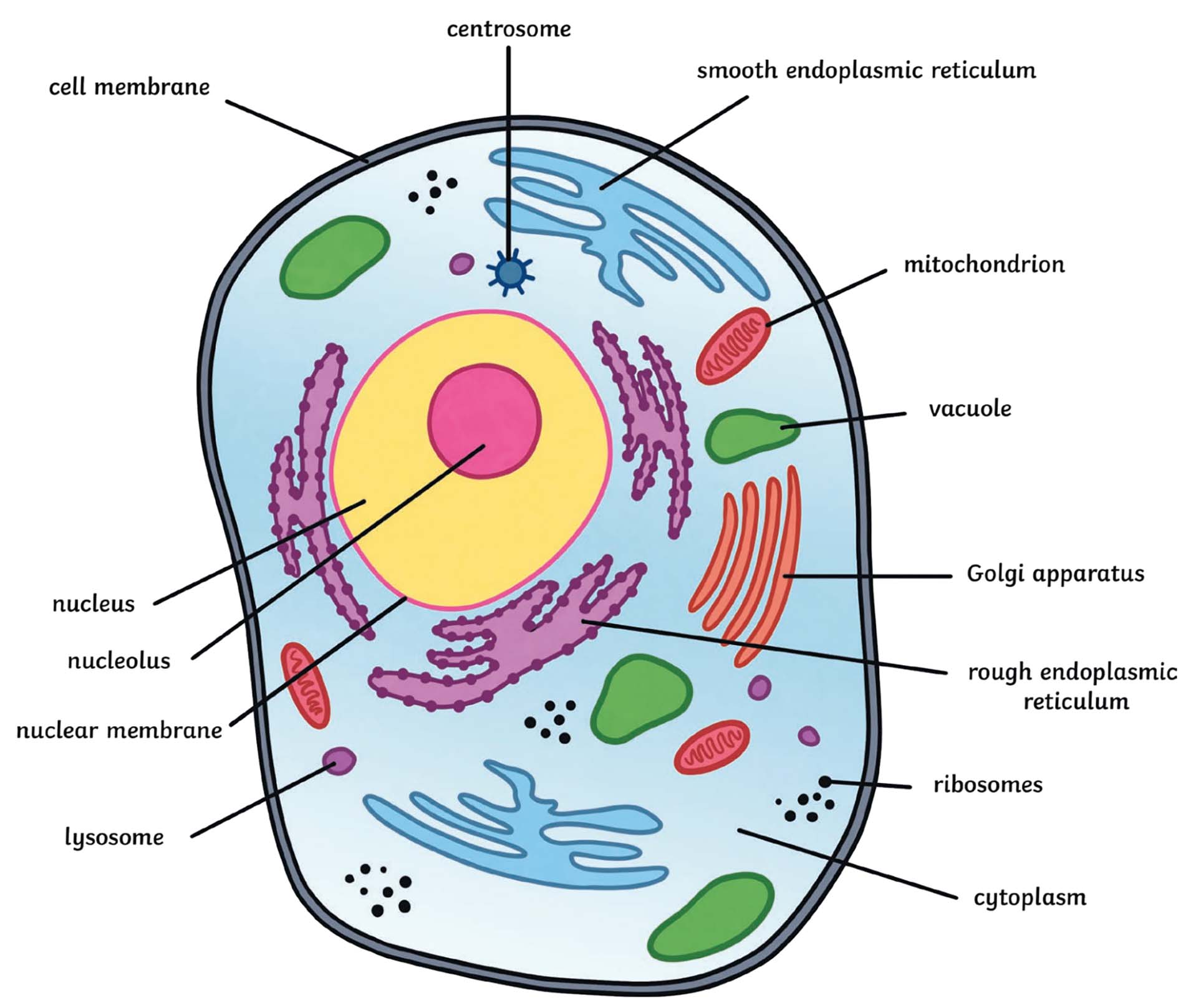
Eukaryotic cells
- Multi-celled organisms
- Plant and animal cells
- Eukaryotic cells have organelles bound by membranes.
- Each organelle performs a specific function in the cell.
- All eukaryotic cells consist of a nucleus, plasma membrane,
cytoplasm, peroxisomes, mitochondria, and ribosomes.
- Plant and animal cells
- Eukaryotic cells have organelles bound by membranes.
- Each organelle performs a specific function in the cell.
- All eukaryotic cells consist of a nucleus, plasma membrane,
cytoplasm, peroxisomes, mitochondria, and ribosomes.
9
New cards
Prokaryotic cells
- Single-celled organisms
- bacteria
- Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles
- bacteria
- Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles
10
New cards
Where is DNA stored in cells
- prokaryotic cells have circular, loosely packed DNA.
- Eukaryotic cells have DNA tightly packed into a nucleolus to
protect it
- Eukaryotic cells have DNA tightly packed into a nucleolus to
protect it
11
New cards
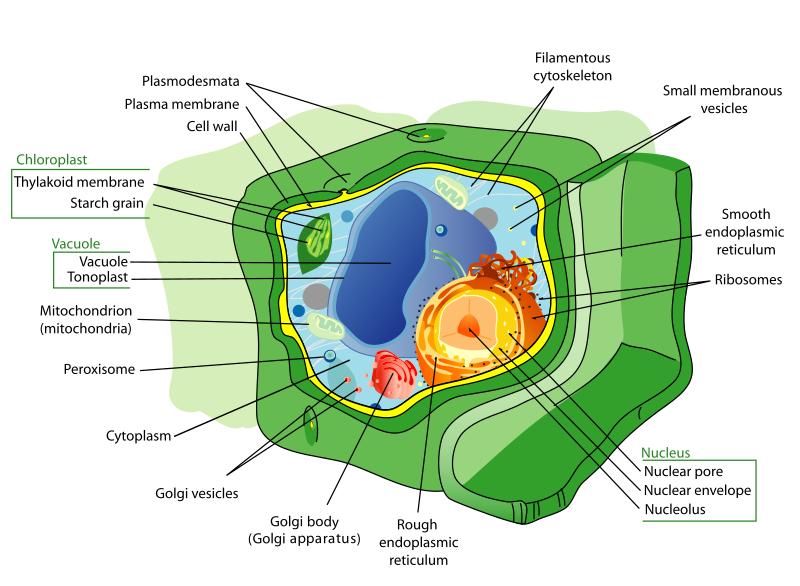
Animal cell vs Plant cells
- Animal cells each have a centrosome and lysosomes, whereas -
plant cells do not.
- Animal cells have multiple large central vacuoles, and plants have only one large central vacuole,
- Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and other specialized
plastids, whereas animal cells do not.
plant cells do not.
- Animal cells have multiple large central vacuoles, and plants have only one large central vacuole,
- Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and other specialized
plastids, whereas animal cells do not.
12
New cards
Plasma Membrane
- Both prokaryotes & eukaryotes have plasma membranes.
- The cell membrane is a semipermeable layer surrounding the cell.
- It helps to give the cell shape and move materials in and out.
- The cell membrane is a semipermeable layer surrounding the cell.
- It helps to give the cell shape and move materials in and out.
13
New cards
Semipermeable
- allows some things through but not others
14
New cards
Cell Wall
- Plant cells also have cell walls surrounding the plasma membrane
- The cell wall is rigid and comprised of cellulose and water.
- It provides protection and shape for the cell but contains pores to
allow materials to pass through.
- The cell wall is rigid and comprised of cellulose and water.
- It provides protection and shape for the cell but contains pores to
allow materials to pass through.
15
New cards
Mitochondria
- “Powerhouse” of the cell
- Responsible for metabolic reactions that turn sugar into energy for
the cell
- Comprised of 2 layers:
- Outer membrane
- Folded inner cristae to increase surface area for chemical
reactions
- Responsible for metabolic reactions that turn sugar into energy for
the cell
- Comprised of 2 layers:
- Outer membrane
- Folded inner cristae to increase surface area for chemical
reactions
16
New cards
Ribosomes & Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Ribosomes- small organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
Can be free-floating or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- ER is made of folded membranes that transport materials around
the cell
- Can be smooth (no ribosomes on the surface) or rough (has
ribosomes attached to the surface)
Can be free-floating or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- ER is made of folded membranes that transport materials around
the cell
- Can be smooth (no ribosomes on the surface) or rough (has
ribosomes attached to the surface)
17
New cards
Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Bodies)
- Curved, flattened stack of sacs that sorts proteins & lipids
- Small sacs called vesicles can break off and carry materials to
other parts of the cell.
- Small sacs called vesicles can break off and carry materials to
other parts of the cell.
18
New cards
Lysosomes
- Small, round organelles filled with digestive enzymes
- Responsible for breaking down waste, invading bacteria or viruses
- Responsible for breaking down waste, invading bacteria or viruses
19
New cards
Plastids
- Surrounded by 2 membranes, like mitochondria
- Not found in humans or animals
- Contain either starches or pigments
- Chloroplasts are the most common type- responsible for
photosynthesis and contain the pigment chlorophyll
- Not found in humans or animals
- Contain either starches or pigments
- Chloroplasts are the most common type- responsible for
photosynthesis and contain the pigment chlorophyll
20
New cards
Vacuoles
- Can be various sizes
- Used for storage or water or wastes
- Plant cells usually have one large vacuole for water storage
- Animal cells often have many smaller vacuoles
- They can also secrete substances and/or water
- Used for storage or water or wastes
- Plant cells usually have one large vacuole for water storage
- Animal cells often have many smaller vacuoles
- They can also secrete substances and/or water
21
New cards
Nucleus
- Control center of the cell
- Easiest structure to see through a microscope
- Contains the genetic material (DNA) for the cell, which provide all
of the instructions for cellular processes
- Surrounded by a nuclear envelope to protect the DNA
- Materials can pass in and out through nuclear pores
- Easiest structure to see through a microscope
- Contains the genetic material (DNA) for the cell, which provide all
of the instructions for cellular processes
- Surrounded by a nuclear envelope to protect the DNA
- Materials can pass in and out through nuclear pores
22
New cards
Nucleolus
- Within the nucleus is the nucleolus, which creates ribosomes.
- Ribosomes are the protein-making factories within the cell.
- Ribosomes are the protein-making factories within the cell.
23
New cards
Centrioles
- Centrioles are cylinder-shaped organelles that aid in the process of
cell division (mitosis).
cell division (mitosis).
24
New cards
Label the plant cell
25
New cards
Label the animal cell