11- Digestion and Absorption of Biomolecules
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Iron & Folate
Carbs, Proteins, & Fats
Lose absorption of THESE when the duodenum is removed.
Loss of Na+ Coupled transport of gluc/AA’s
Loss of pancreatic secretions allowing absorption of fats/lipids
NEC MOA
PAMPs/MAMPs bind TLR
Initiates transcription of pro-inflammatory/apoptotic genes
Note: there’s more bacterial infections with NEC
Transporters that increase in function post-SI resection:
SGLT1
PepT1
NHE3 7 DRA
SGLT1
Glucose and Na Symport
PepT1
Di/Tri peptides & H Symport
NHE3 & DRA
Na and Cl absorption
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
Lose absorption of THIS when Ileum is removed.
It’s only absorbed in the ileum!
2 methods for apoptosis:
Intrinsic
Mitochondria & Cytochrome C
Extrinsic
TLR mediated
Capase 8
Both affect Capase 3 → apoptosis
50
60
100
Chance of weaning parenteral nutrition:
30 cm of bowel remaining means _% chance
60 cm of bowel remaining means _% chance
100 cm of bowel remaining means _% chance
Length of SI left over
Determining factor for a pt having NEC and SI resection will be able to be taken off TPN is THIS.
Na
Water
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Ca
Mg
Phosphate
Iron
Lab values that need to be closely watched when losing a duodenum and proximal jejunum
SI Adaptations Post-Resection
Better absorption (adaptive mucosa)
Hypertrophy/Hyperplasia
Bowl lengthens/dilates
Functional changes (where transport happens, where enzymes are)
Duodenum & Jejunum
Where most hormones of the SI are secreted.
An issue when NEC causes resection of this region.
Bacterial Overgrowth Syndrome
Consequence of losing the ileocecal valve.
Causes lactic acidosis!
Ileum
Consequences of losing THIS:
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Steatorrhea (lose bile salts)
Diarrhea (bile salts/acids not absorbed anymore)
NF-Kappa B Pathway
The signaling pathway associated with NEC that leads to signaling of apoptosis and pro-inflammation.
Released from TLR, acts as transcription factor for pro-inflammatory and apoptotic genes.
Apoptosis
death of cell that doesn’t affect nearby tissues really
Necrosis
more inflammatory and damaging to nearby tissues
Water & SCFA (short chain fatty acids)
Lose absorption of THESE when you lose the colon.
Ileum (paracellular) or Distal Colon (active)
Loss of K absorption can happen when THIS or THIS are removed.
Sx of NEC (necrotizing enterocolitis)
bloody diarrhea
distended abdomen
penumatosis intestinalis
Mechanism of NEC
Bowel ischemia → damaged mitochondria → necrosis/apoptosis
No ATP production → loss of:
Na/K pump (ER swelling, loss of microvili)
Decreased pH (increased anaerobics)
Decreased protein synthesis
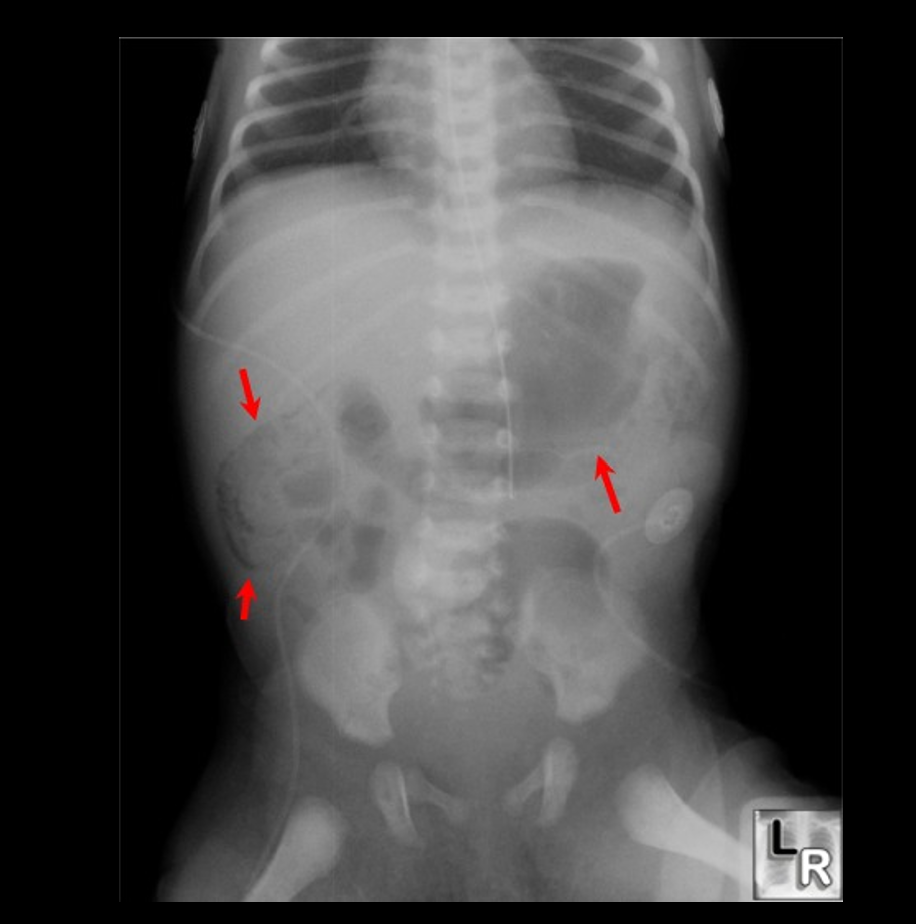
Pneumatosis Intestinalis
Gas bubbles/cysts in abdomen
Caused by bacterial colonization (fermentation byproducts)
Risk Factors of NEC
Prematurity
Intestinal Ischemia
Bacterial Colonization
Enteral feeding
Why premature babies are more at risk of NEC:
Immature intestinal barrier
Weak tight junctions
Bacterial colonization
Repeat infections, uncontrolled inflammation