SLP 456 quizzes (2,3,4,6,7,8)
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Quiz 2
Which pairs of words are minimal pairs? Choose all that apply.
Hear / beer
3 multiple choice options
The totality of motor processes involved in the planning and execution of sequences of overlapping gestures which result in speech refers to
articulation
3 multiple choice options
The clusters [sk] and [ks] cannot occur in the same word positions in General American English. This is an example of the ______ of a language.
phonotactics
3 multiple choice options
Articulation disorders mainly reflect difficulties with the ______ of speech.
motor production elements
3 multiple choice options
A(n) ___________________ disorder involves the impaired comprehension and/or use of the sound system of a language and the rules that govern the sound combinations. This type of disorder is focused on the linguistic function of speech and usually involves predictable, rule-based errors (e.g., fronting, gliding) that affect multiple speech sounds.
phonological
2 multiple choice options
A(n) _________________ disorder is an umbrella term that refers to disordered form and/or function of speech sounds with a specific language system.
speech sound
2 multiple choice options
A(n) ________________disorder is the difficulty with the motor production aspects of speech. This type of disorder is focused on the physical/acoustic form of speech and usually involves an inability to produce specific speech sounds (e.g., [s, z, ɹ]).
articulation
2 multiple choice options
_____________ are the smallest linguistic units that are able to distinguish meaning between words.
phonemes
speech sounds
are the end products of articulatory motor processes; they represent physical sound realities.
allophones
are phonetic variations in phoneme realizations; they do not change the meaning of a word when they are produced in differing contexts.
morphemes
are the smallest units of a language that can carry meaning
The _______________ inventory is the repertoire of phonemes used by a child to contrastively differentiate meaning.
phonemic
The _____________ inventory is the repertoire of all phones, including their variations.
phonetic
The majority of speech sound disorders in children have a(n) ______.
unknown cause
__________ is the study of the sound system of a language; including the arrangement, systematic organization, and rule system of vowels and consonants.
phonology
This is an inability to pronounce certain phones, typically s- and r-sounds. The child uses a consistent substitution or distortion for the target sound in both spontaneous and imitated productions.
articulation disorder
These children demonstrate phonological patterns that are evidenced in normal development but are typically noted at an earlier chronological age.
phonological delay
This involves regular use of some non-developmental error patterns. These children may demonstrate atypical and idiosyncratic error patterns.
consistent phonological disorder
The phonological systems of these children show at least 40% variability of production when asked to name 25 pictures on 3 separate trials within a single session. Thus, multiple errors are demonstrated for the same word.
inconsistent phonological disorder
This is seen as a multi-deficit motor-speech disorder involving phonological planning, phonetic, and motor programming difficulties.
childhood apraxia of speech
With the exception of the nasals, all phonemes of General American English direct airflow through, and ultimately exit the
oral cavity
Quiz 4
Two similar consonants that differ only in voicing are referred to as
cognates
Per Bauman-Waengler, select the three primary descriptive parameters of vowels.
tongue height, tongue advancement, roundedness
3 multiple choice options
_____________are the group of speech sounds produced with a relatively open vocal tract. No significant constriction of the oral and/or pharyngeal cavities is involved in the production of this group of sounds.
vowels
_________________ are the group of speech sounds that involve significant constriction of the oral and/or pharyngeal cavities during their production. During the production of this group of sounds, the airstream encounters some type of articulatory obstruction.
consonants
Which word contains a phonemic diphthong (as the words are typically pronounced in GAE)?
sky
3 multiple choice options
Sibilants are a subcategory of
fricatives
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following phonemes are NOT considered sonorants?
/ʒ/, /z/, /p/
2 multiple choice options
Which vowels typically display roundedness in GAE?
/u/
3 multiple choice options
/ŋ/
voicing:
voiced
place:
velar
manner:
nasal
/ɹ/
voicing:
voiced
place:
alveolar
manner:
approximant
/j/
voicing:
voiced
place:
palatal
manner:
approximant
/ʃ/
voicing:
voiceless
place:
postalveolar
manner:
fricative
/dʒ/
voicing:
voiced
place:
postalveolar
manner:
affricate
/v/
voicing:
voiced
place:
labiodental
manner:
fricative
/p/
voicing:
voiceless
place:
bilabial
manner:
plosive
/k/
voicing:
voiceless
place:
velar
manner:
plosive
/s/
voicing:
voiceless
place:
alveolar
manner:
fricative
/w/
voicing:
voiced
place:
labio-velar
manner:
glide
/θ/
voicing:
voiceless
place:
dental
manner:
fricative
Quiz 3
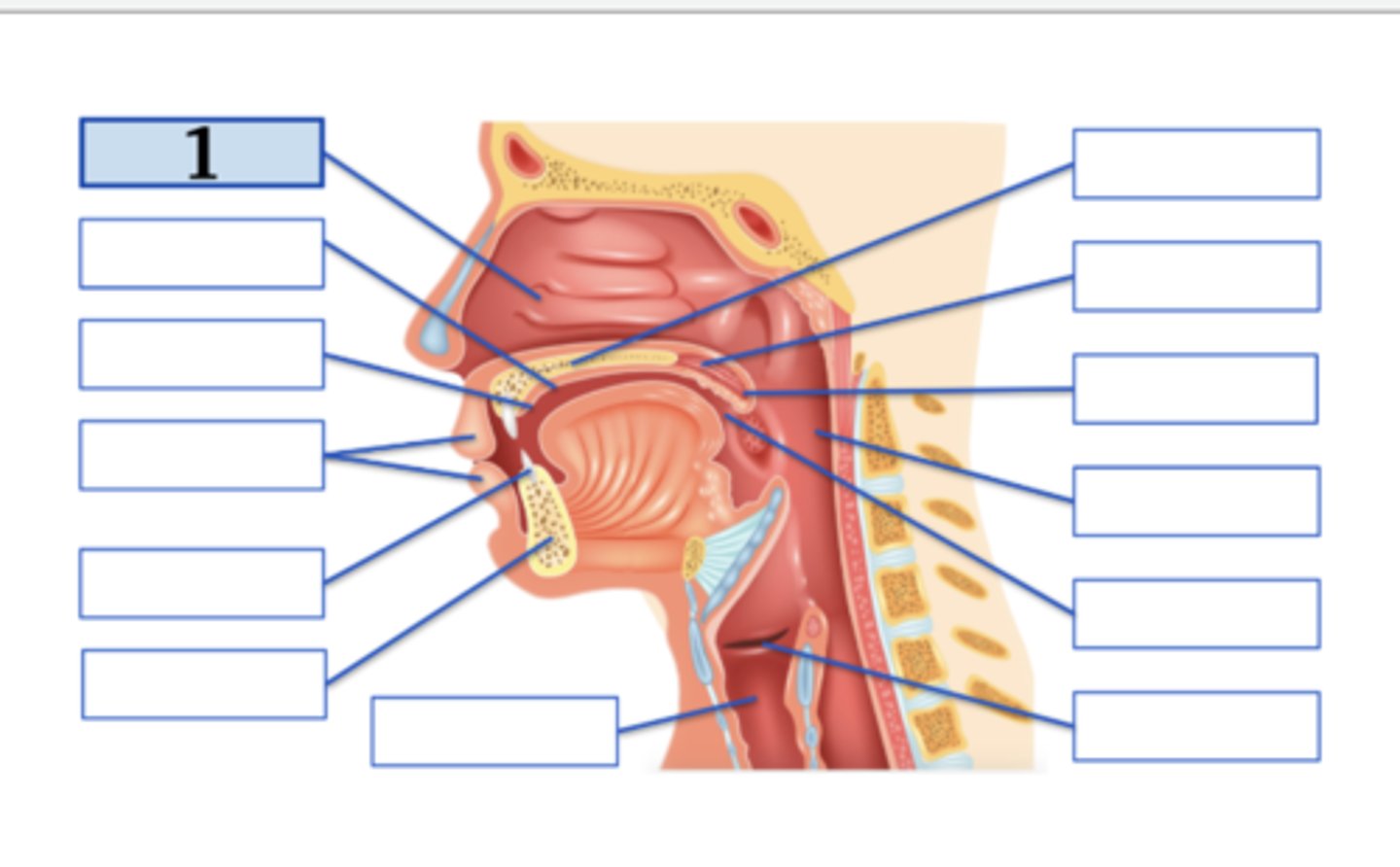
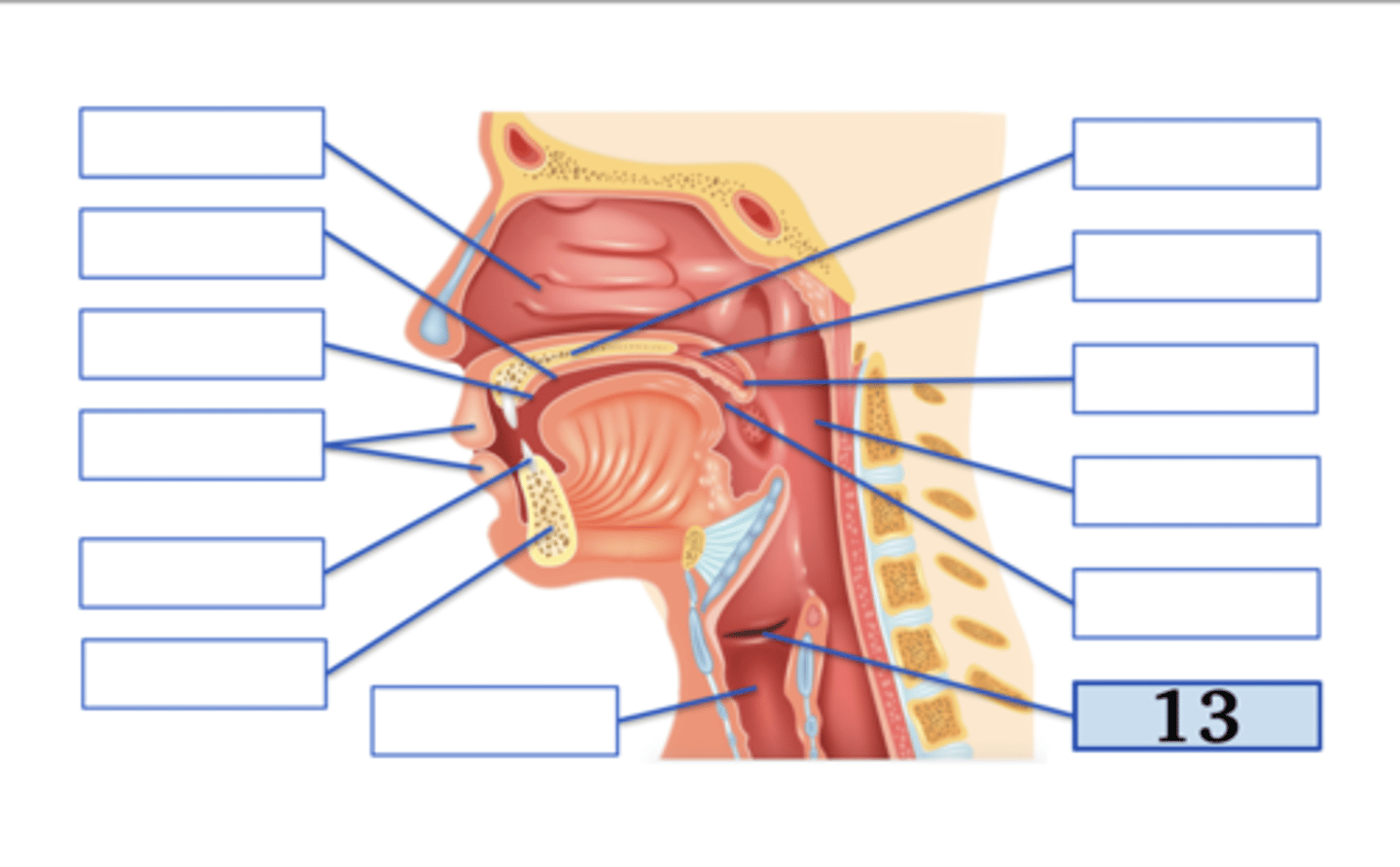
Name the anatomical structure:
nasal cavity
Type the voicing, place, and manner for ONE English phoneme with this place of articulation (e.g., voiced uvular trill)
voiced postalveolar fricative
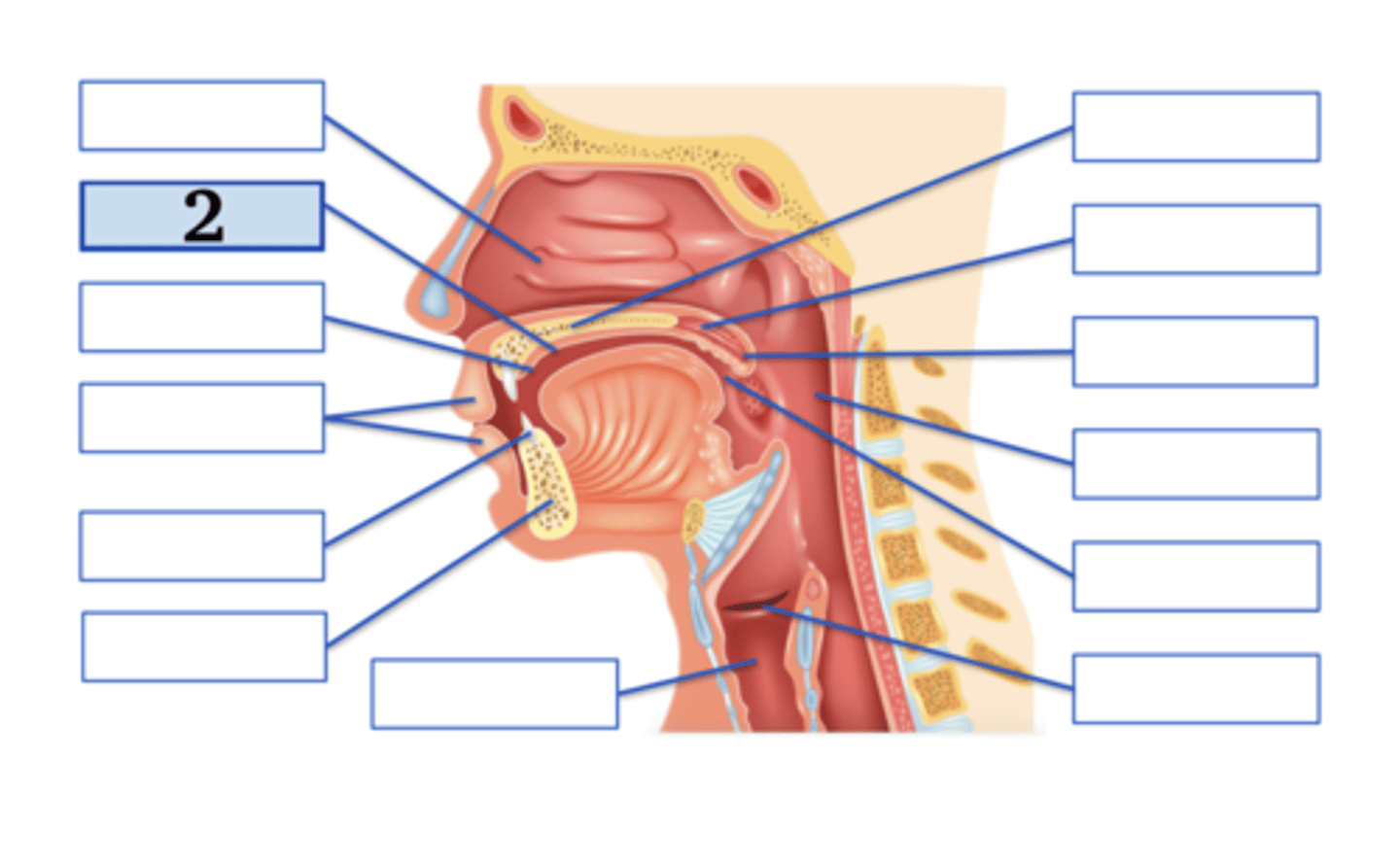
Name the anatomical structure:
Type the voicing, place, and manner for ONE English phoneme with this place of articulation (e.g., voiced uvular trill):
alveolar ridge;
voiced alveolar plosive
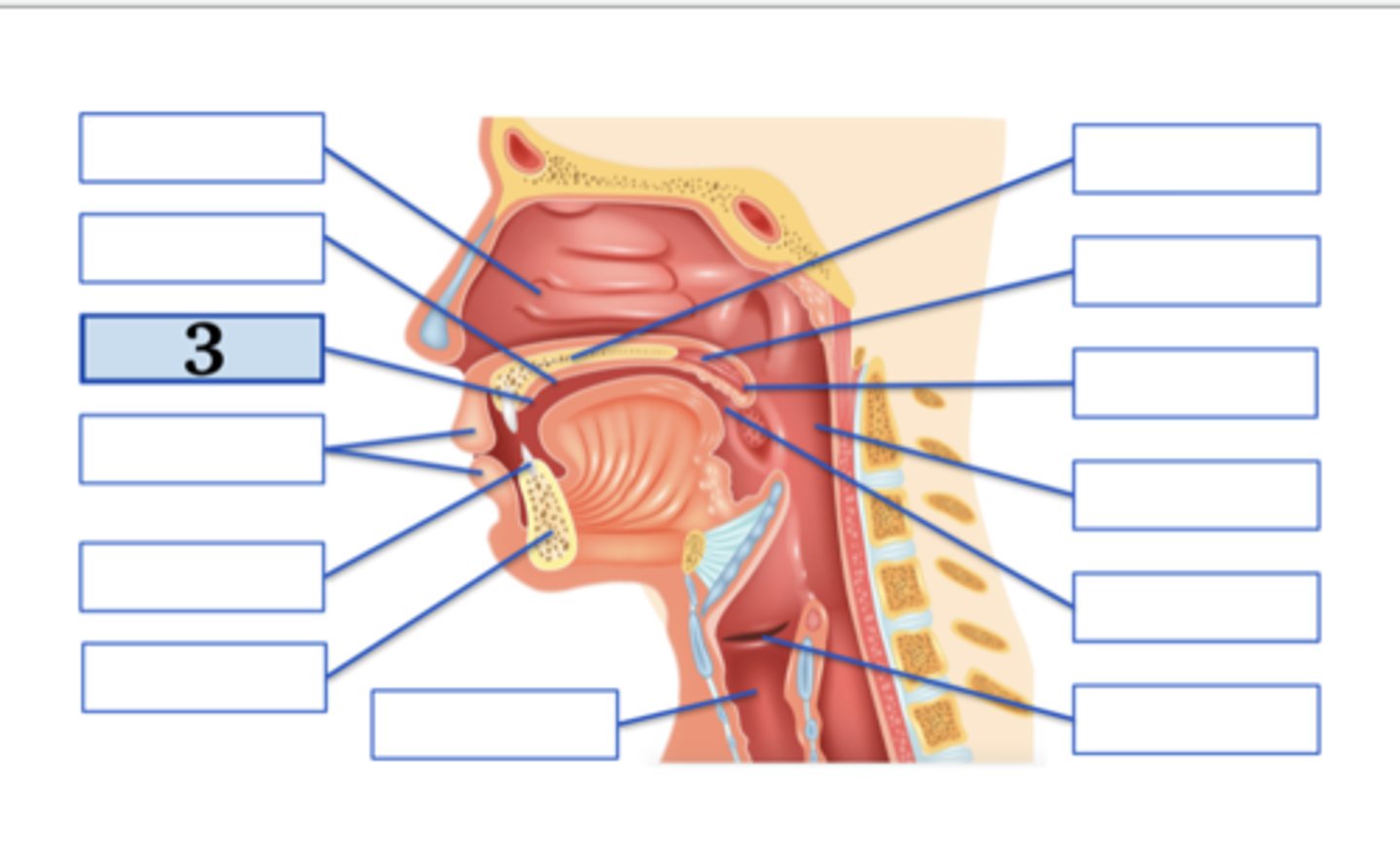
Name the anatomical structure:
Type the voicing, place, and manner for ONE English phoneme with this place of articulation (e.g., voiced uvular trill):
lips;
voiced bilabial plosive
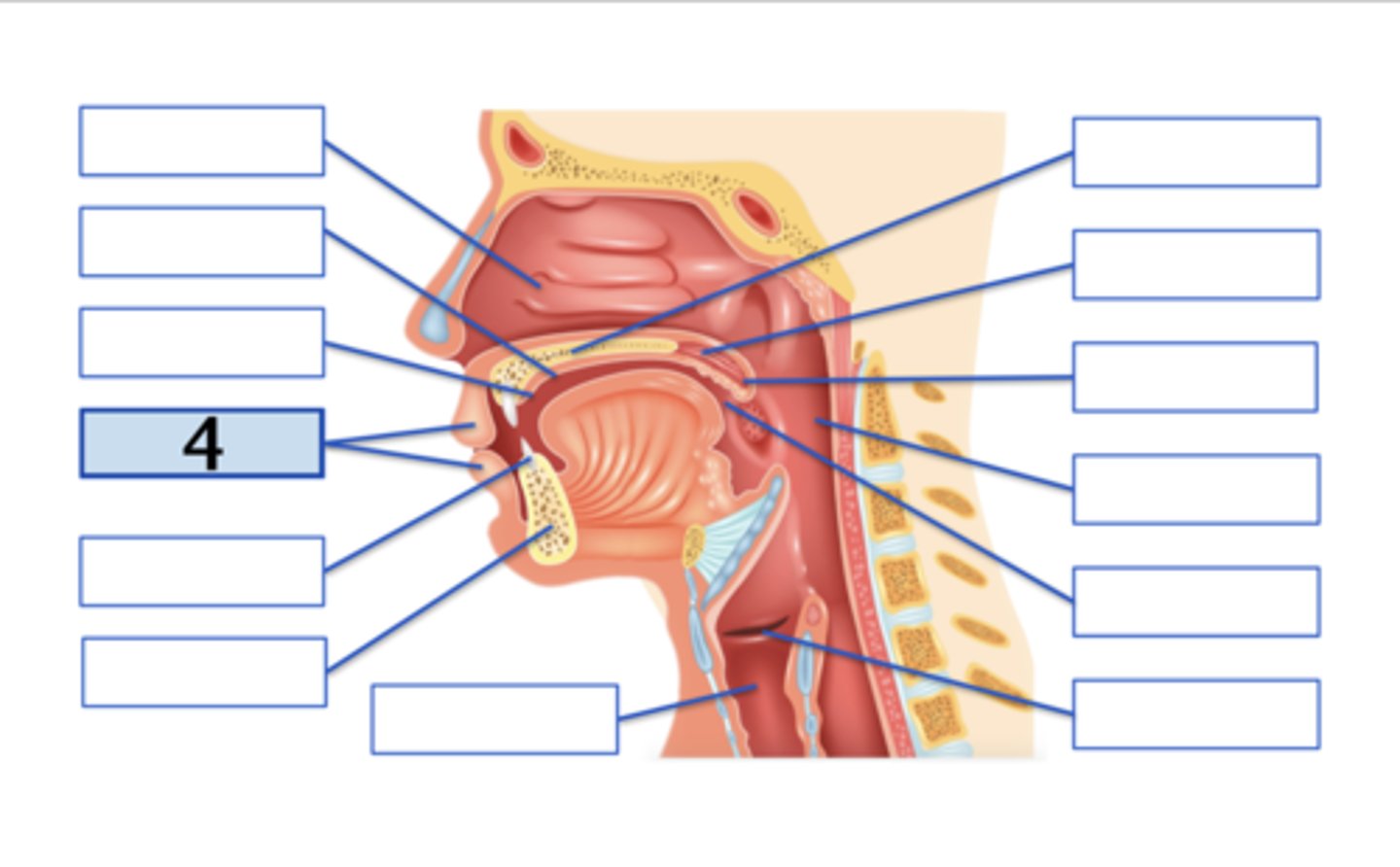
Name the anatomical structure:
Type the voicing, place, and manner for ONE English phoneme with this place of articulation (e.g., voiced uvular trill):
teeth;
voiced dental fricative
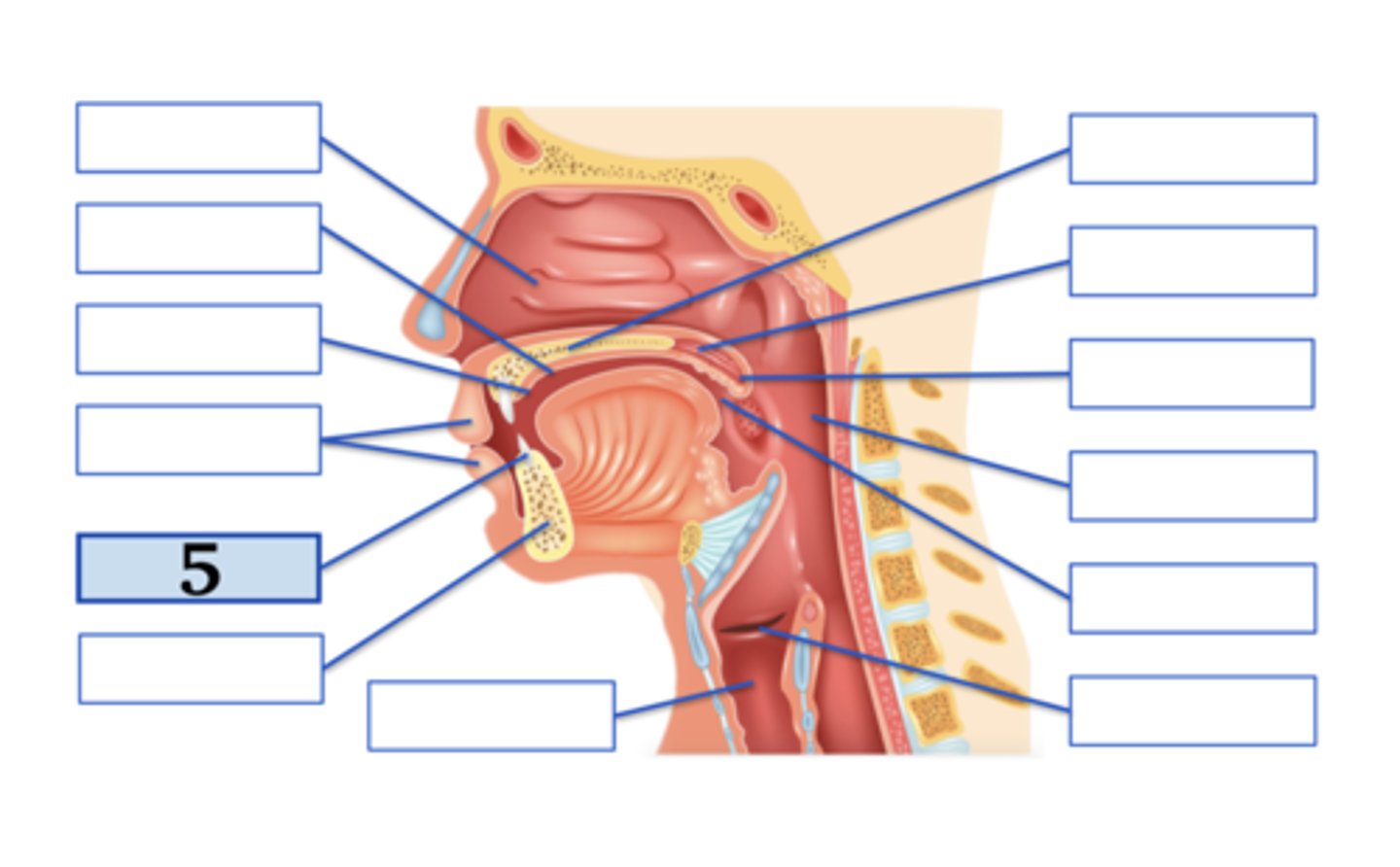
Name the anatomical structure:
mandible
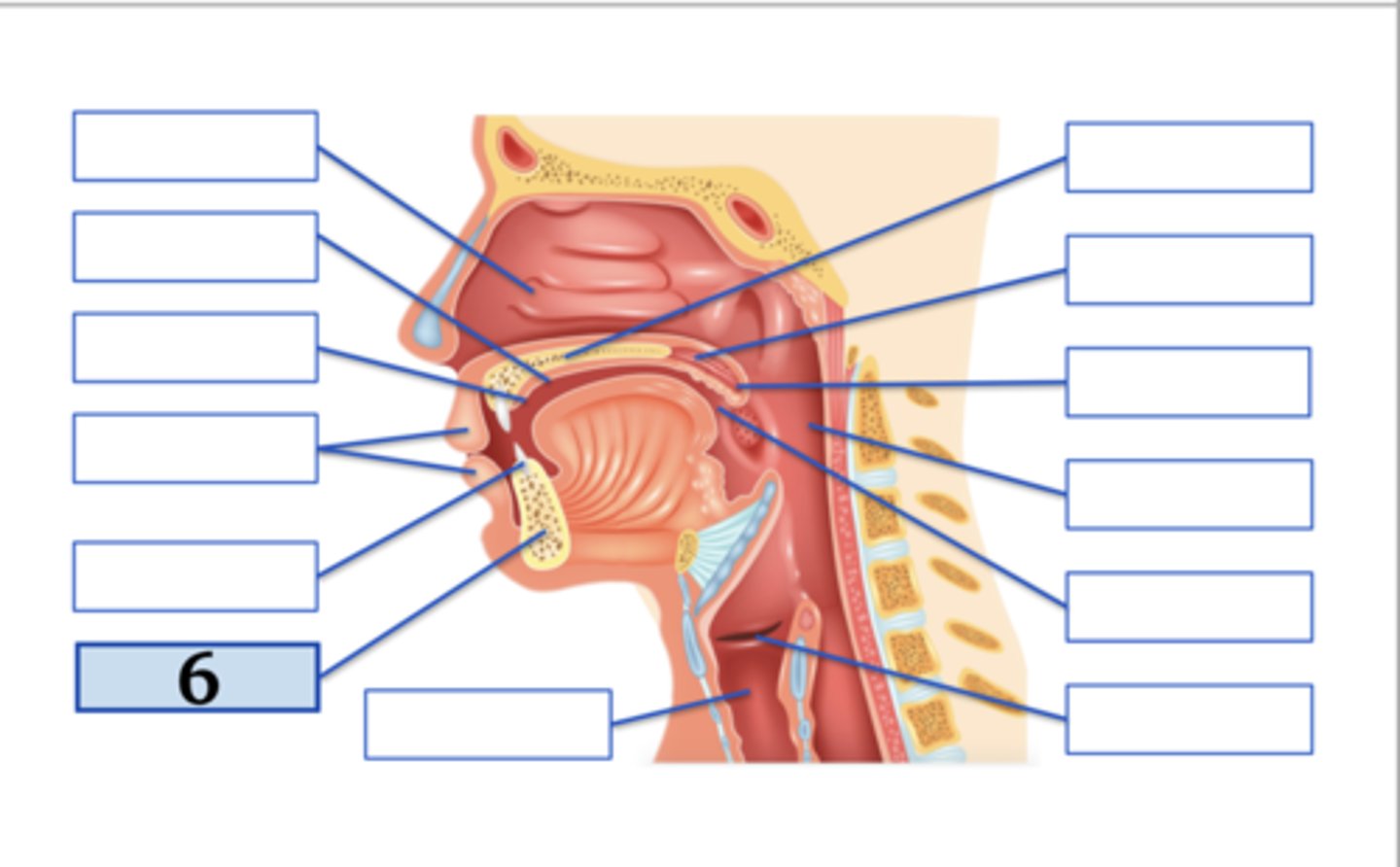
Name the anatomical structure:
larynx
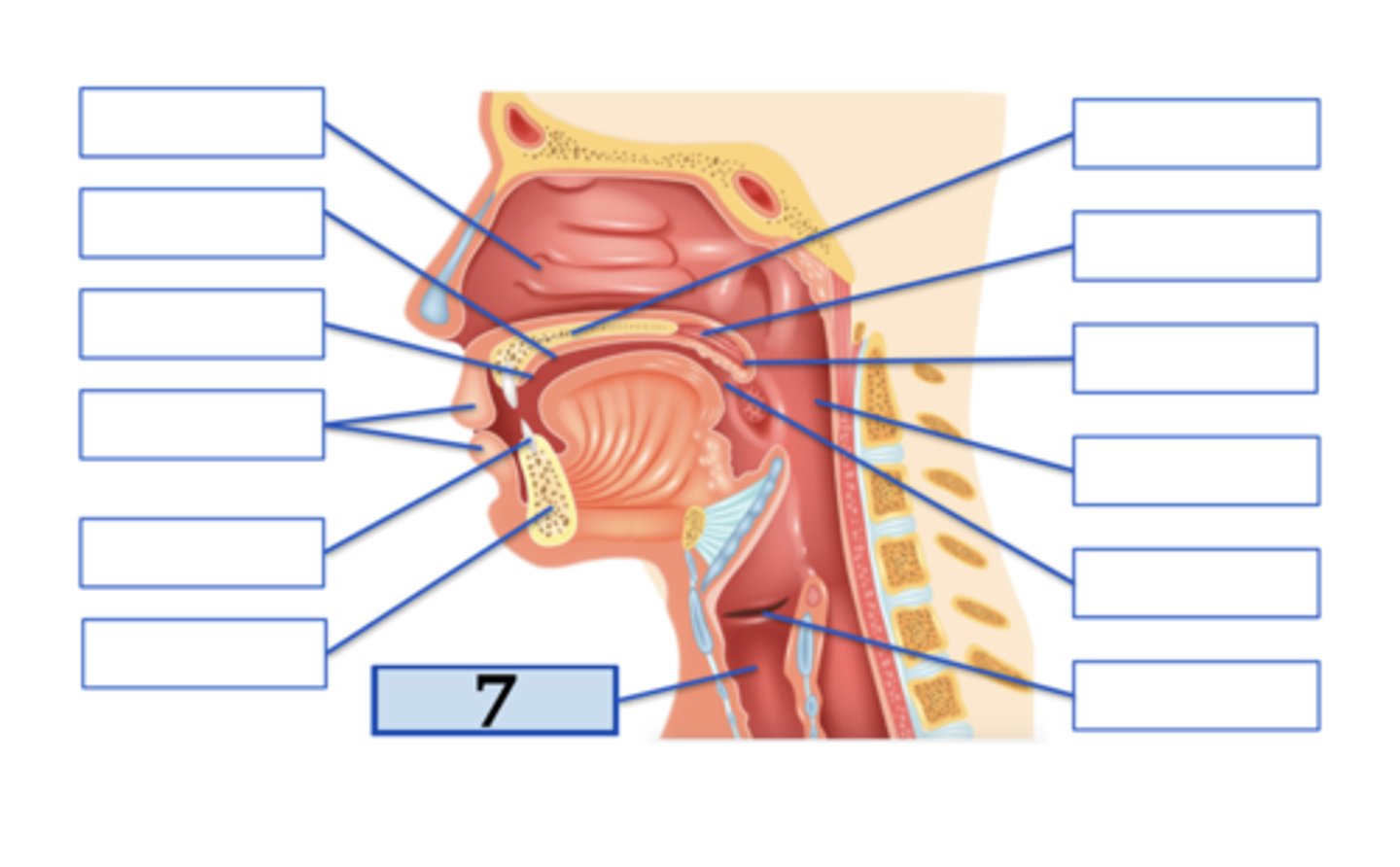
Name the anatomical structure:
Type the voicing, place, and manner for ONE English phoneme with this place of articulation (e.g., voiced uvular trill):
hard palate;
voiced palatal approximant
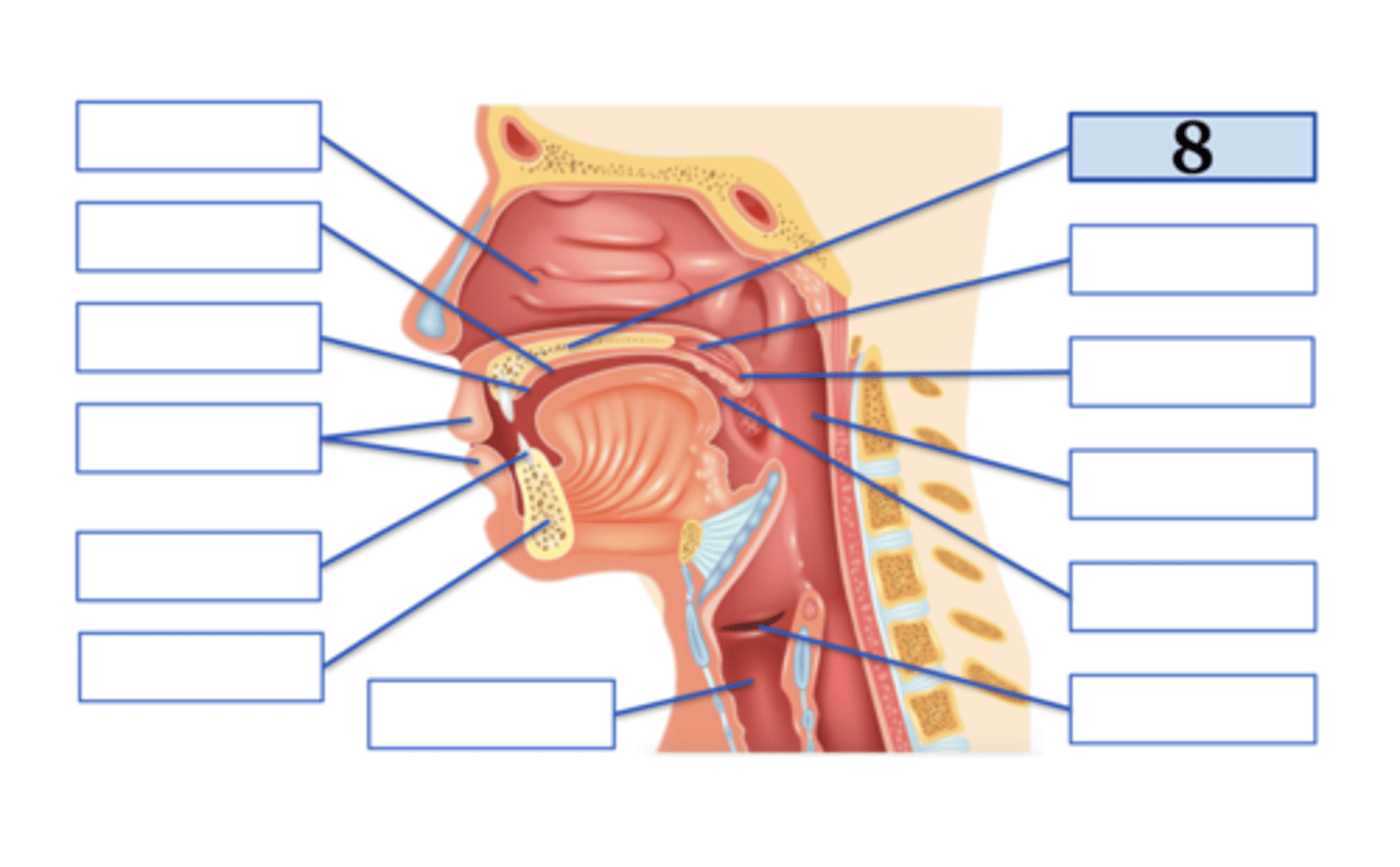
Name the anatomical structure:
Type the voicing, place, and manner for ONE English phoneme with this place of articulation (e.g., voiced uvular trill):
velum;
voiced velar plosive
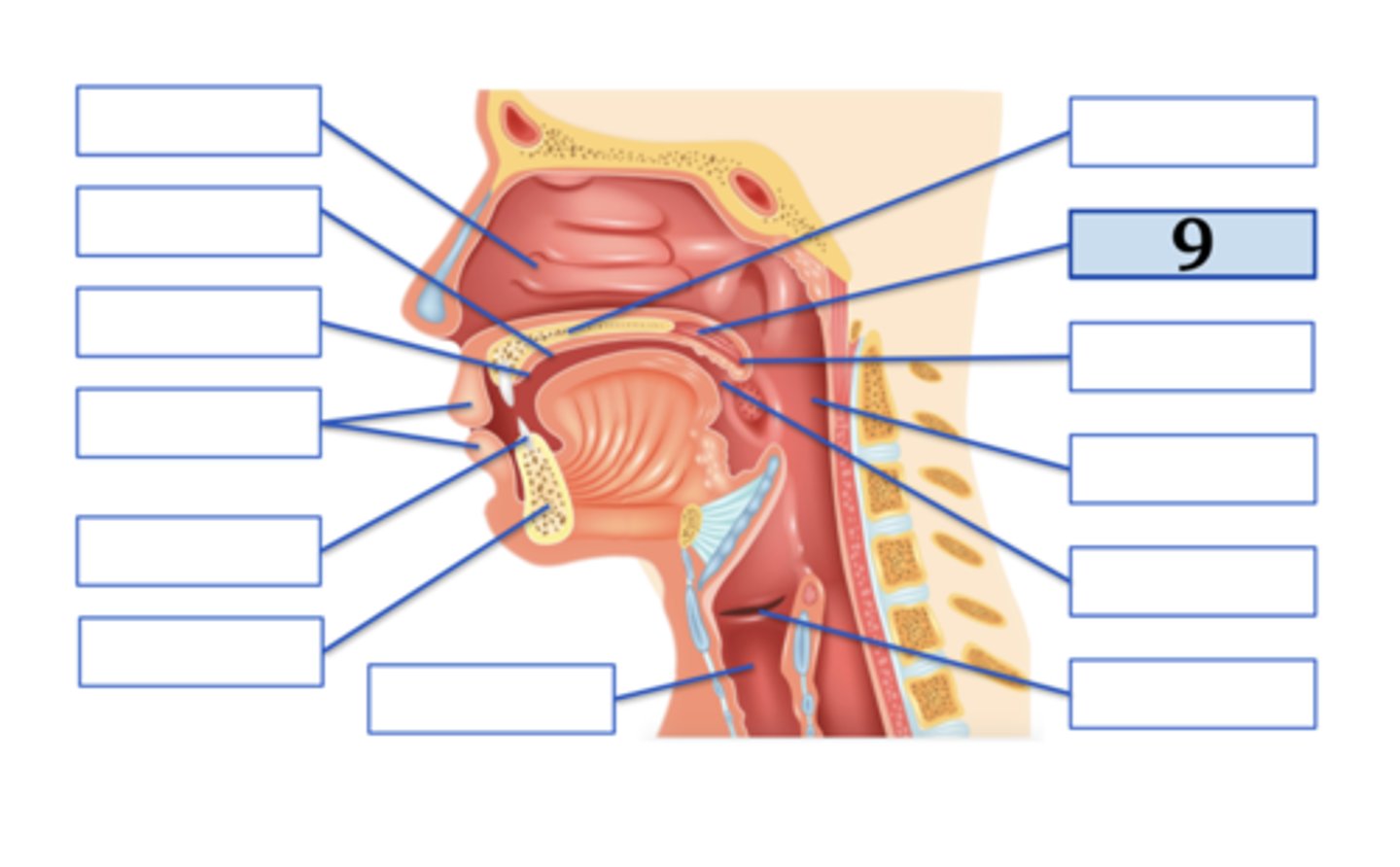
Name the anatomical structure:
uvula
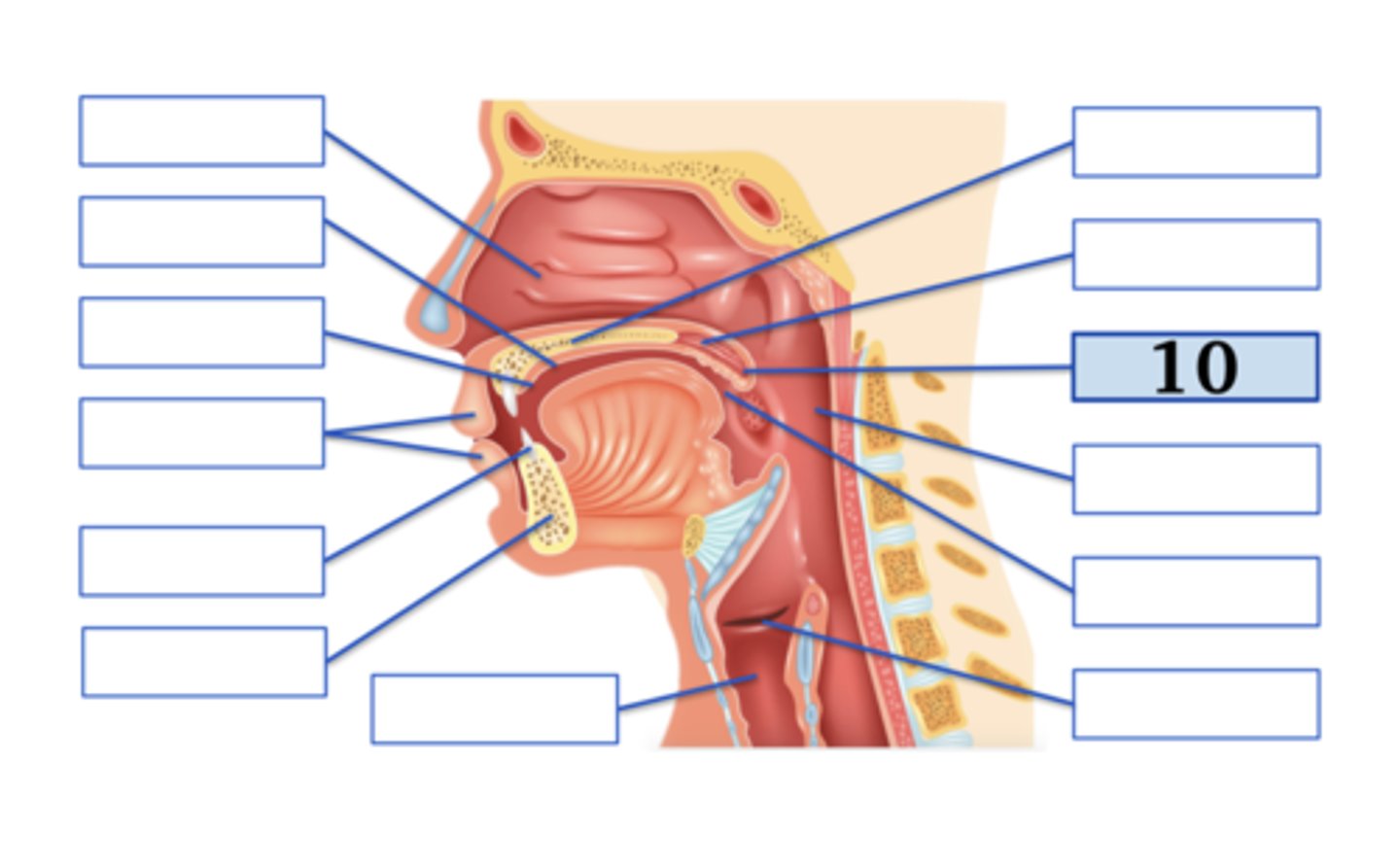
Name the anatomical structure:
pharynx
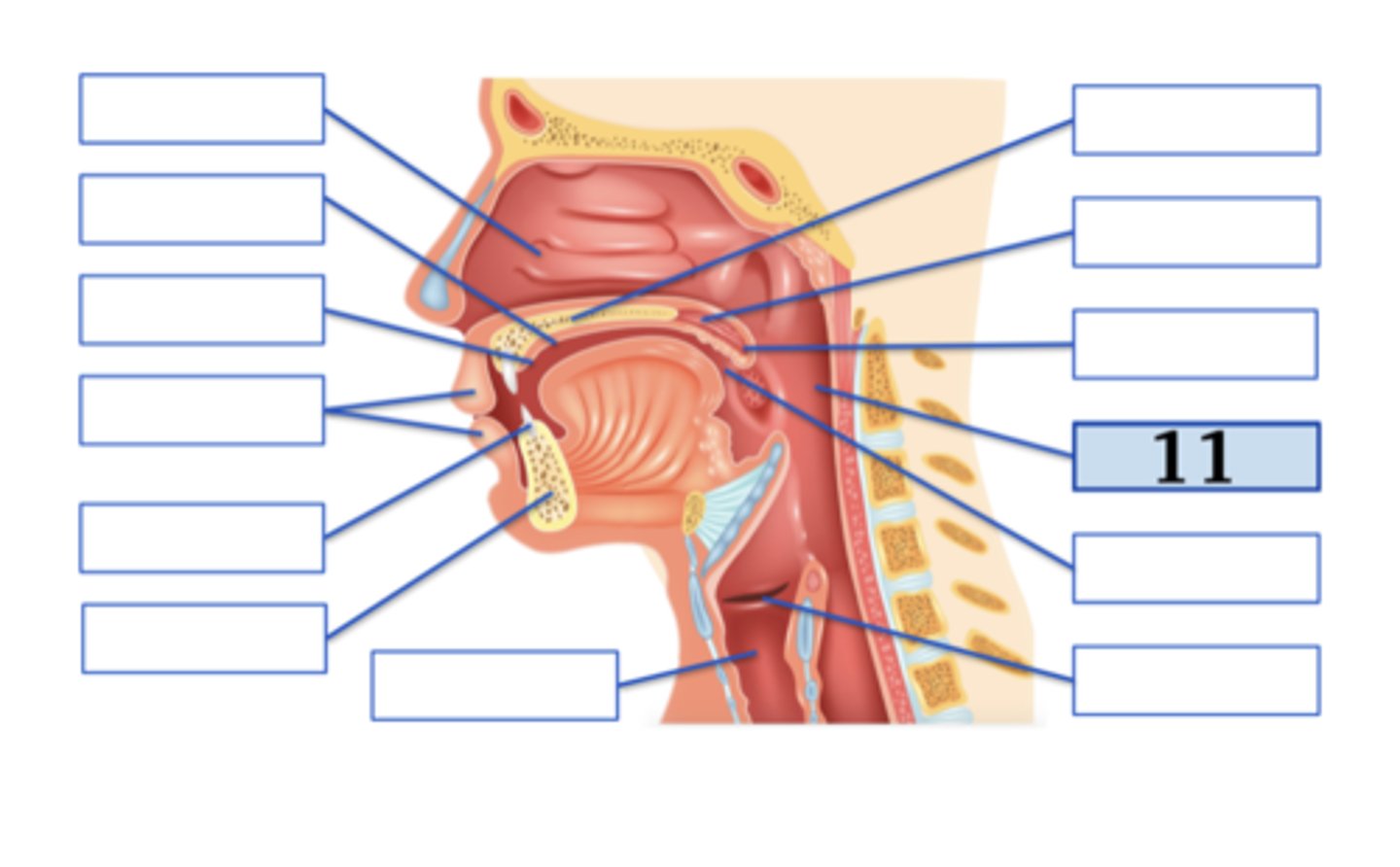
Name the anatomical structure:
oral cavity
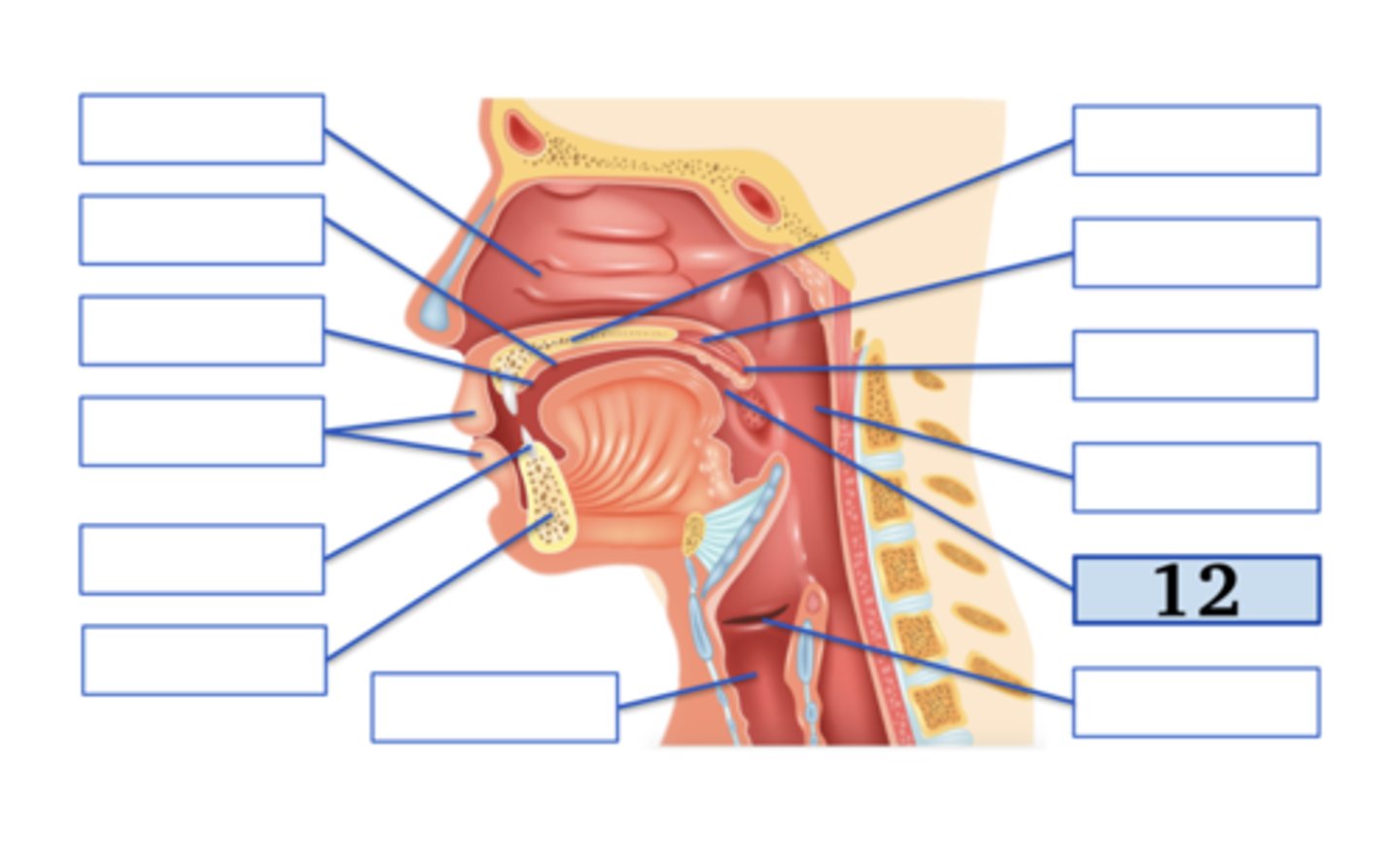
Name the anatomical structure:
Type the voicing, place, and manner for ONE English phoneme with this place of articulation (e.g., voiced uvular trill):
glottis;
voiceless glottal fricative
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: known
cvc
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: typed
cvcc
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: fuel
ccvc
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: breathe
ccvc
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: ox
vcc
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: through
ccv
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: show
cv
Type in the syllable (CV) shape for the following word: itch
vc
Which one of the following words has twoopen (a.k.a. unchecked) syllables?
away
3 multiple choice options
Select the type and degree of assimilation demonstrated in the following examples:
1. "dog" → [gɑg]
Type: remote assimilation and regressive/anticipatoryassimilation
Degree: total assimilation
Select the type and degree of assimilation demonstrated in the following examples:
2. "frogs" → [frɑgz]
Type: contact assimilation andprogressive/perseverative assimilation
Degree: partial assimilation
quiz 6
Earlier developing (typically acquired before 36 months of age)
CVCV
[h]
[w]
[k]
CVC
CV
[p]
[n]
Later developing (typically acquired after 24 months)
[z]
VCC
CCVC
[ɹ]
[tʃ]
[ð]
[ʒ]
CCV
Which of the following are characteristics of the First-50-Word stage?
- frequent use of approximants, plosives, and nasals
- phonetic variability
- limited variety of syllable structures
Given what we've learned about phonological development and phonetic complexity (esp. regarding syllable structure), newly acquired consonants are most likely to appear in which position in a child's speech?
word-initial position
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following syllable structure phonological processes is most likely to be suppressed at a relatively later age?
consonant cluster reduction
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following substitution phonological processes is most likely to be suppressed at a relatively later age?
gliding of liquids
3 multiple choice options
Select the term below that refers to: the ability to perceive speech sounds (varied along an acoustic continuum) according to the phonemic categories of one's native language
categorical perception
3 multiple choice options
During which prelinguistic stage does the child begin to communicate to adults through imitation games with vocal productions?
Stage 4: Canonical babbling
3 multiple choice options
During which prelinguistic stage does the child begin to produce strings of utterances which are modulated primarily by intonation, rhythm, and pausing?
Stage 5: Advanced forms (Jargon stage)
3 multiple choice options
The largest growth within a child's phonological system typically occurs during which period of development?
Preschool (approximately age 2 to 6)
3 multiple choice options
The respiratory, phonatory, resonatory, and articulatory speech systems of the newborn
reflect exclusively primary functions
3 multiple choice options
proto-words
Consistently used vocalizations with meaning for the child but no recognizable adult model
jargon
Strings of babbled utterances that are modulated primarily by intonation, rhythm, and pausing
Strings of similar consonant-vowel productions
reduplicated babbling
All vocalizations before first meaningful words
prelinguistic behavior
Nonphonemic consonant-like productions
contoids
Protophones made by the infant during comfortable states with the uncoordinated tongue body contacting the back of oral cavity or pharynx.
Correct match:
coos/goos
variegated babbling
Strings of varied consonant-vowel productions
vegetative sounds
Non-speech sounds with no communicative function that accompany feeding and other activities
vocoids
Nonphonemic vowel-like productions
reflexive vocalizations
Non-speech sounds that indicate an infant's physical or internal states
quiz 7
_________________ is the ability to recognize and manipulate sound segments in a language, and it plays an essential role in the developing _____________ skills of young children
phonological awareness; reading
Which activities below would be considered metaphonological tasks (i.e., tasks that demonstrate phonological awareness)?
- A child points to pictures of animals that start with the "s" sound.
- A child matches pairs of animal picture cards that have rhyming names.
- A child counts the number of syllables in the names of various animals.
1 multiple choice option
Based on the phonological awareness continuum, which task is the least difficult
A child claps along with her classmates to the rhythm of the syllables in a nursery rhyme.
3 multiple choice options
Based on the phonological awareness continuum, which task is the second least difficult
A child points to pictures of words that rhyme with with the word "ball."
3 multiple choice options
Based on the phonological awareness continuum, which task is the most difficult
A child replaces the final sound in "cap" with [t] and says the new word "cat."
3 multiple choice options
Based on the phonological awareness continuum, which task is the second most difficult
A child identifies and says the individual sounds of a CVC word (e.g., "dog" = [d] + [ɑ] + [g]).
3 multiple choice options
Per ASHA and the Bauman-Waengler text, a comprehensive evaluation for a suspected SSD requires at least which five components?
- screenings in additional areas as needed (e.g., language, phonological awareness, prosody)
- spontaneous speech sample
- speech mechanism examination
- hearing screening
- standardized speech assessment
1 multiple choice option
Which evaluation task best represents stimulability testing during an assessment for a suspected speech sound disorder?
Provide a model of correct speech sound production and observe the client's ability to imitate it
3 multiple choice options
When evaluating the speech mechanism of a young child with an emerging phonological system, which of the following tasks would be most appropriate and effective for an SLP to perform?
- Ask caregivers to keep a log of the child's utterances and language usage
- Employ a play-based approach with engaging activities like flashlight games
- Analyze the child's babbling, focusing on consonant use and syllable shapes
1 multiple choice option
Why can scripted and routine events be helpful when collecting a spontaneous speech sample from an unintelligible child?
Because the predictability of these events provide more context to infer the intended meanings of word approximations
3 multiple choice options