Test 3 BICH 410
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
222 Terms
What are the two requirements for life
Ability to self replicate
Ability to catalyze chemical reactions efficiently and selectively
What is a disadvantage of uncatalyzed reactions
Too slow to maintain life as we know it
What are the two types of biological catalyst
Enzymes
Ribozymes
What do most biological catalysts use
Enzymes
What are enzymes
Enormous catalytic power
High specificity for substrates
Accelerate chemical reactions
Where do enzymes function
Aqueous systems under very mild conditions of temperature and pH
Enzymes are the agents of
Metabolism
Every chem is, step of a metabolic pathway is catalyzed by
An enzyme
Free energy is
Large and exergonic
Enzymes bind at a specific molecule called _____ at a specific site on the enzyme surface called the ______
substrate
Active site
Catalytic power
Enzymes accelerate reactions by as much as 10^16 times greater than uncatalyzed
Enzymes accomplish there feats in aqueous solutions under mild temperatures and pH
Specificity
Extraordinary ability of an enzyme to catalyze one particular far action on a specific reactant called the substrate to produce a specific product
Enzymes can be very
Specific or broad
Active site
Specific site where an enzyme binds
Regulation of enzymes occurs
Control over amount of enzyme expressed
Reversible metabolic inhibitors and activators
How is specificity controlled
The structure of the enzyme
The unique fit of the substrate to the active site of the enzyme controls the selectivity for substrate and the product yield
Cofactors
May be one or more inorganic ions such as Fe2+, Mg2+, Zn2+
Can carry out their catalytic function relying solely on their structure
Many require no protein components
Coenzymes
Complex organic or organomteallic molecules
Actively involved in catalysis often serving as intermediate carriers of functional groups in converting substrate into product
How are coenzymes bound
Loosely bound by the enzyme and freely diffuse in and out of the active site
Bound tightly by the enzyme some are covalently attached
Protethic groups
Tightly bound or covalently bound coenzymes
Holoenzyme
Catalytic active enzyme with its coenzyme (or cofactor) bound
Apoenzyme
Protein with the Prost ethic group (or cofactor) removed
Cofactors are derived from
Vitamins
Vitamins
Organic nutrients required in small amounts from our diet
-ase
Traditional way to name an enzyme was to add the suffix
Oxidoreductases
Oxidation reduction reactions
Most abundant and common
E.C.1
Transferases
Transfer C,N, or P functional groups
Hexokinase
Transfer P groups to and from ATP
E.C.2.
Hydro leases
Cleavage of covalent bonds with water
Break down into two parts
H2O is a reactant
E.C.3
Urease
Lyases
Group additions to break double bonds or group eliminations that yield double bond
E.C.4
Aldolase
Fructosediphosphatealdioase
Isomerase
E.C.5
Rearrange molecules
Isomerazation reactoons
Ligases
Least common
E.C.6
Formation of bonds using the energy of AtP hydrolysis
Single bonds (endergonic)
the noncovalent interactions involved in substrate binding to the enzymes active site are the same interaction involved in
Tertiary and quartenary structure
What interactions are important in substrate specificity
Electrostatic
H bonding
Dipole dipole
Hydrophobic
Van der waal
Specificity of a substrate comes from
The complementary surfaces of the substrate molecule and the surface of the active site
Shape, polarity, charge
Substrates of different geometries or with different functional groups ____
Cannot productively bind to the enzymes active site
One of the first theories of specificity was the
Lock and key hypothesis
The enzyme is considered the
Lock
The substrate is considered the
Key
The lock and key model captures the
Nature of specificity
Enzymes in the lock and key hypothesis are
Not rigid like locks
Enzymes are
Flexible and dynamic molecules
Most enzymes undergo
Conformational changes upon substrate binding
The induced fit model of specificity
Hypothesizes that the shape of the enzymes active site changes upon substrate binding in a process of dynamic recognition between the substrate and the enzymes
What does the substrate alter
The confirmation of the enzyme so that the protein and the substrate will fit together precisely
Enzymes are ___ in both the both of chiral substrates and in chemistry of their reaction
Stereospecific
Enzymes are composed of _____ and or
L- amino acids
Asymmetric active sites
what do catalyst not affect
Reaction equilibrium
Corresponding free energy change
what are the two pathways we are looking for form a substrate to product
path for the uncatalyzed reaction
path for the catalyzed reaction
the change in free energy is
independent upon which of these paths the reaction takes
if the catalyst change the equilibria of a reaction then
would violate the laws of thermodynamics
ground state
is the starting point
contribution to the free energy of the system by the average substrate or product our biochemical standard condition
reaction coordinate
the free energy of a system is often plotted against the progress of the reaction
the equilibria between S and P reflect
the difference in the free energies of their ground states
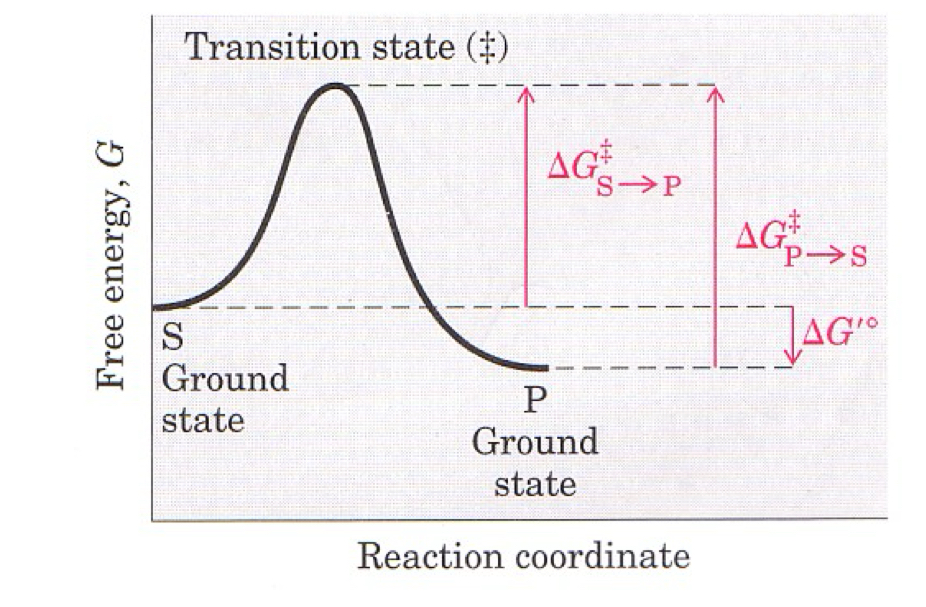
What characteristics does this graph show
P has lower ground state than S
ΔG’ is negative, and spontaneous
position of equilibria not affected by catalysis
what will thermodynamic parameters tell us
is a reaction is exergonic or not
thermodynamic potential of a factor
what does a favorable oror equivalently a large negative ΔG’
does NOT tell us anything about the rate of the reaction
the rate of reaction is
dependent on the pathway going form reactants to products
what opposes the conversion of S→P (an d vice versa)
energy barrier
the energy barrier consists of
energy required to bring reactants together
the energy required for the alignment of reacting groups
the energy required for the transient formation of unstable charges
the energy for bond rearrangements
other transformations required for the reaction to proceed in either direction
transition state
the top of the hill
what happens at the transition state
either direction on the reaction coordinate is down hill
the probability of reverting back to the substrate is equal to the probability of going on to product formation
activation energy
the difference in the energy levels between the ground state and the transition state
the activation energy is designated
ΔG++
the greater the activation energy
the slower the reaction
where does the intermediate occur
between the two activation energies
occupy the valleys between transition states
rate determining step
the overall rate of the conversion of reactants to products is determined by the slowest step (highest activation energy)
reaction rates can be increased by
raising temperatures which increases the population of molecules with sufficient energy to overcome the energy barrier
the activation energy can be elowered by
adding catalyst
catalysts enhance reaction rates by
lowering activation energy
binding energy
the energy derived from enzyme-substarte interactions
binding energy is a major source of
energy used to lower the activation energy
binding energy contributes to
specificity
binding energy is optimized in
the reaction transition state
enzyme active sites are NOt complementary to
the substrate but to the transition state
what would happen if an enzyme were completely complementary to the substrate
the substrate fit the enzyme as a key fits a lock then the ES would be incredibly stable and low in energy and have less free energy than the free substrate
weak non-covalent interactions are formed in
ES complex
if an enzyme were completely complementary to the substrate such that the substrate fit the enzyme as a key fits a lock then
the ES would be incredibly stable and low in energy and have less free energy than the free substrate
a perfect complementary ES results in
an increase in the activation energy since any changes in ES complex towards the transition state would interrupt optimized binding interaction
the binding energy is maximized when
the substrate reaches the transition state
free energy of a substrate binding lowers the
lowers the activation energy by binding the substrate tightest at the transition state
weak noncovalent forces between enzymes and substrate are a
major driving force in enzymatic catalysis
_____ of enzymes require cofactors
1/3
prosthetic group
covalently attached to active site of enzyme (require biotin coenzyme)
biotin
needed from diet can synthesize vitamin from body
coenzyme A
fatty acid metabolism
co-substrate
holoenzyme
enzyme w cofactor bound
100% enzymatic activity
apoenzyme
0% enzymatic activity
just enzyme w/o cofactor inactive form
how is an enzyme potrayed
as rigid but it is actually NOT rigid
why don’t we want the surface of a substrate to be perfect
it will then become an inhibitor
transition state analogs
very tight binding to the enzyme active site
affinity of the enzyme for the transition state may be as high as
10-15 M
stable molecules that mimic the transition state are called
transition state analogs
transition state analogs bind much tighter than the
substrates or products
catalytic antibodies dont have
catalytic power of enzymes
abzymes
generated to accelerate reactions
antibody that binds to a substrate and catalyzes a specific chemical reaction, just like an enzyme.
what is another name for catalytic antibodies
abzymes
kinetics is a took used to
evaluate reaction mechanisms that provide descriptions of the individual steps that occur along a reaction pathway
kinetics is a study of
a chemical system whose composition changes with time
how can the changes in kinetics be described
by stoichiometric rate equations
a chemical reactions stoichiometry does NOT refflect
the sequence of molecular events that are involved