PKG825 Exam 1 - Physical States and Transitions
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What are examples of amorphous polymers?
PMMA, PS, PVC, ABS
Are amorphous polymers transparent or opaque?
Transparent
What are examples of crystalline polymers?
PP, PE, PA
Are crystalline polymers opaque or transparent?
opaque
Polymers can be 100% crystalline (T/F)
False, polymers are never totally crystalline
How does size of polymer molecules affect crystallinity?
Large size of polymer molecules are difficult to be arranged in an orderly nature
What is a lamella?
A stack of polymer chains folded back on themselves
What is a spherulite?
Several lemellas
What is quenching and how does it affect transparency?
Fast cooling, makes polymer more transparent
What is annealing and how does it affect transparency?
Slow cooling, makes the polymer more opaque
Why does increased crystallinity lead to higher opacity?
The packed crystals scatter the light
How does crystallinity affect density?
Crystallinity inc, density inc
How does crystallinity affect permeability?
crystallinity inc, permeability dec
How does crystallinity affect tensile strength?
Crystallinity inc, tensile strength inc (higher rigidity provides higher resistance to deformation in the amorphous region)
How does crystallinity affect compression strength?
Crystallinity inc, compression strength inc (more resistant to deformation)
How does crystallinity affect clarity?
Crystallinity inc, clarity dec
How does crystallinity affect impact strength?
Crystallinity inc, impact strength dec (more brittle/prone to impact)
How does crystallinity affect ultimate elongation?
Crystallinity inc, ultimate elongation dec (crystallinity restricts movement of polymer chain)
How does crystallinity impact toughness?
Crystallinity inc, toughness dec (stiffer & more brittle)
What causes tight packing of molecules?
stereochemical regularity
What are differences in polymer appearance caused by?
bond rotation (NOT by chemical structure)
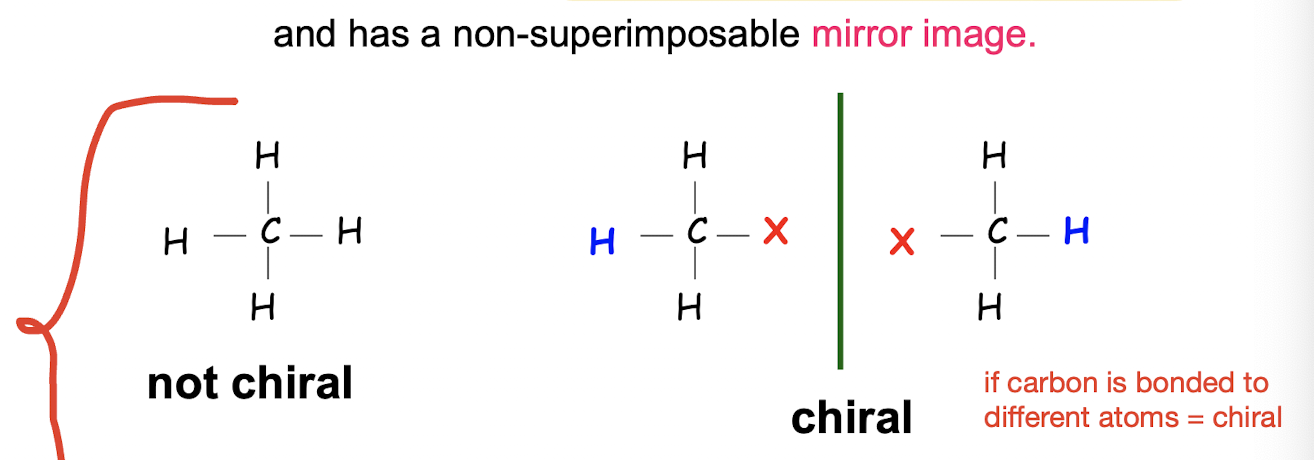
What is a chiral molecule?
a molecule that lacks an internal plane of symmetry
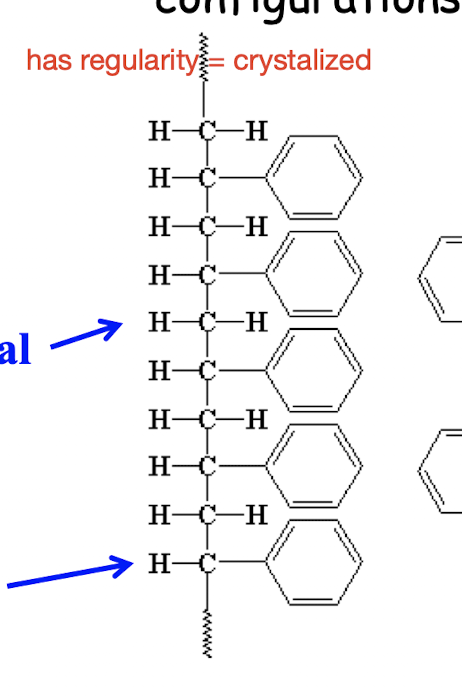
What is an isotactic molecule & is it crystallized?
same pattern, can be crystallized
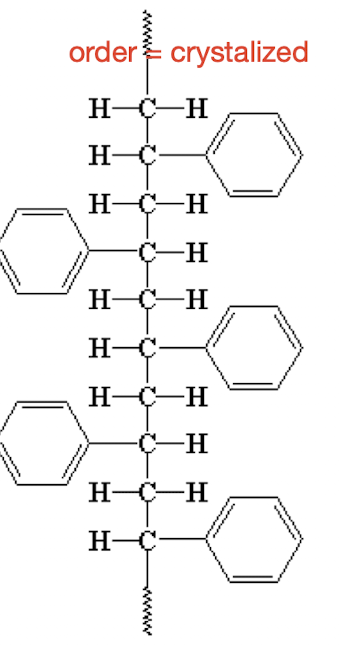
What is a syndiotactic molecule & can it be crystallized?
Alternating structure, crystallized
What is an atactic molecule?
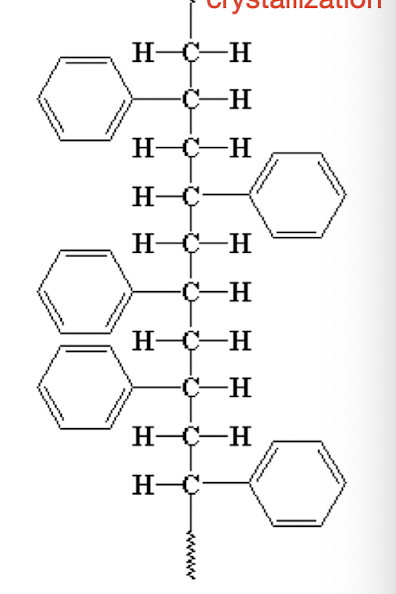
Random configuration, no crystallization
What is tactility?
The way pendant groups are arranged along the backbone chain of a polymer
Is HDPE branched or linear?
Linear (high crystallinity)
Is LDPE branched or linear?
Branched, low crystallinity
What are nucleating agents?
Enhance crystallization and reduce the size of the crystal to improve clarity (smaller crystals reflect less light)
Where does most permeation occur in polymers?
Through the amorphous regions
What is the tortuosity effect?
When crystals delay the time of diffusion by creating “crystal roadblocks” to permeants
How does the -OH functional group affect permeability?
Excellent O2 barrier, poor water barrier due to H-bonding. Strong polarity & promotes crystallinity
How does C6H5 (phenyl group) affect permeability?
Bulky side group & atactic structure cause there to be a noncrystalline structure, causing polymer to be a poor barrier
How does temperature affect permeability?
inc temp, inc permeability
How do strong intermolecular forces affect permeability?
Intermolecular forces inc, permeability dec
What happens to a polymer’s barrier properties when they are above their Tg?
Barrier properties become poor
What are the barrier/transparency tradeoffs in (HDPE/LDPE/LLDPE)?
HDPE: high barrier but translucent
LDPE: transparent but low barrier
LLDPE: compromise between two
How do polar groups affect crystallinity?
CO groups in polymers may repel each other and prevent the formation of crystalline structures. Equally, some materials (like polyamides) form crystals very easily because of the attraction between sections of the main backbone chain (due to H2 bonding)
How does chain branching affect crystallinity?
highly branched polymers will generally be less crystalline
How are branches generated?
Reaction is promoted by high energy state of the free radical. The rate of propagation increases with increasing temperature
In what condition is LDPE produced?
High temperature and high pressure (shorter chain)
Under what conditions is HDPE produced?
milder conditions, so not as many frequent chain transfer reactions (catalyst is required)
What is conformational flexibility?
The ease of rotation of bonds in the polymer chain, which strongly affects its properties
What is segmental mobility?
rotation around a single bond
What Tg do frozen food packages want to have?
Low Tg so it stays flexible at low temperatures and does not get brittle
When do polymers have segmental mobility?
Above their Tg
Do amorphous polymers have a Tm?
No - Tm is what temperature is needed to melt crystals (only semi-crystalline polymers have a well defined Tm)
Is this graph for an amorphous or semi crystalline polymer?
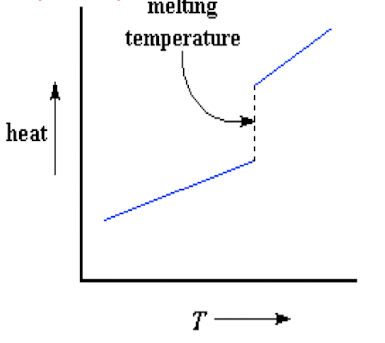
Crystalline
Is this graph for an amorphous or semi crystalline polymer?
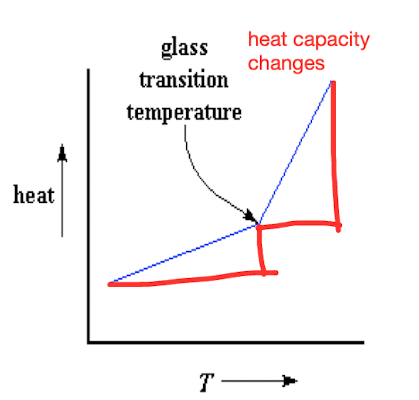
Amorphous
When a polymer is melted, does the temperature increase at a slower or faster rate?
slower - the molten polymer has a higher heat capacity
What is first order transition?
When a polymer is melted
What is a second order transition?
when the temp hits Tg and the polymer undergoes a change in heat capacity
What kind of polymers have a well defined Tg?
Semi crystalline and amorphous
What defines Tg?
How easily a chain moves
If a polymer chain can move around easily, will it have a high or low Tg?
Low Tg
What prohibits rotation?
Large side groups and high polarity
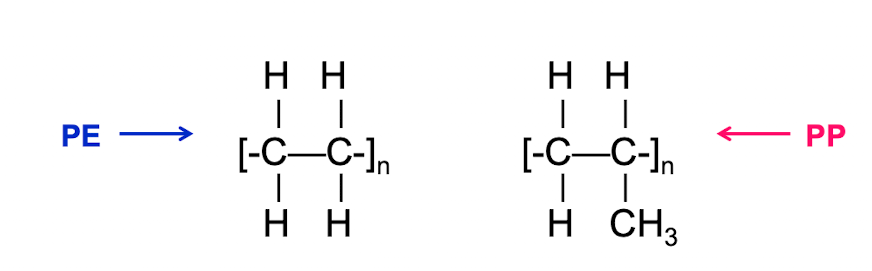
Which polymer will have a higher Tg?
PP (the methyl group on every other carbon brings more interference to rotation than the small hydrogen atoms of the PE)
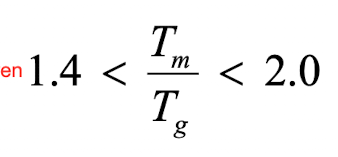
Tm (min) = 1.4 × 350K = 490K
Tm (max) - 2.0 × 350K = 700K
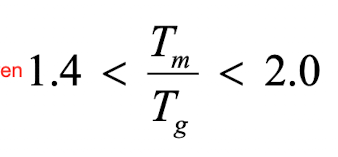
If the Tm is 600K, what is the Tg?
Tg (min) = (1/2.0) x 600K = 300K
Tg (max) = (1/1.4) x 600 = 428.6K
How does a double bond affect rotation?
It prohibits rotation, but since the double bond can only be bonded to one side group, there are fewer things to interfere with rotation about the single bond that is next to a double bond, making polymers with double bonds in the main chain have low Tgs and tend to be soft and flexible
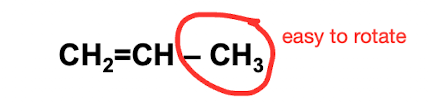
What are cis and trans isomers?
Cis-trans isomers are the substances which have same molecular formula with different arrangement of their atoms in space
What are the two main requirements for a molecule to show cis-trans isomerism?
Presence of a C=C bond or cyclic ring in the molecule
Different groups bonded on double bonded carbon atoms
Do cis or trans configurations pack tighter?
Trans molecules will pack tighter since the carbons are opposite, but both can pack easily since they are structured so they can both be crystallized. More linear trans chain pack can better reduce free volume and raise Tg
How do ring structures impact Tg and Tm?
Bulky ring structures prohibit rotation, causing it to be stiff with high Tg and Tm
How does the presence of oxygen in the main chain affect rotation?
It lowers the barrier to rotation, increasing flexibility
How do pendant groups affect rotation?
longer chains introduce more free volume, increasing rotational motion, and lowers Tg
How does cross linking affect Tg?
restricts movement, increases Tg
how do strong intermolecular forces affect Tg?
increased Tg- more thermal energy is needed to overcome the stronger attractive forces

Which has higher Tg?
PS (bulky group)
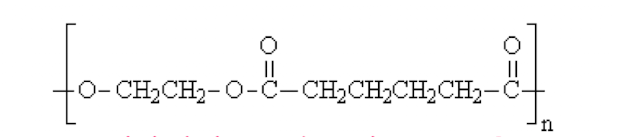
Which has higher Tg?
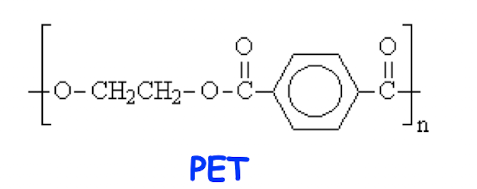
PET (rigid rigng group in backbone)
Which one has a higher Tg?

Which has higher Tg?
PVC (stronger intermolecular forces with Cl)

Which has a higher Tg?
PVOH (hydrogen bonding)
How does long chain length (high Mw) affect Tg?
longer chains have less end of chain units (more end of chain units = more free volume), raising Tg
What is the relationship between average molecular weight (Mn) and Tg
As molecular weight increases, Tg increases and then levels off
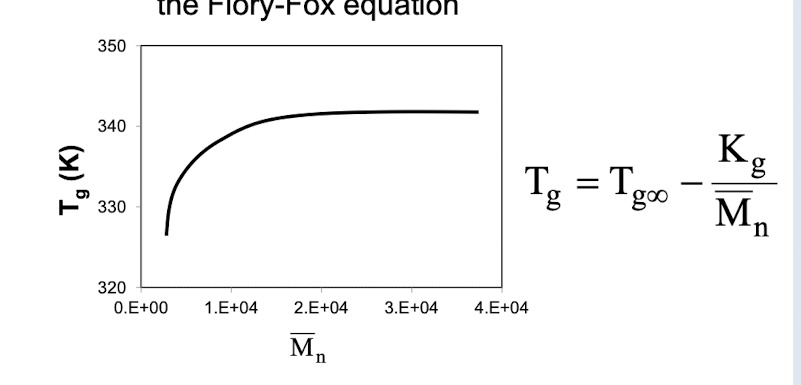
What does plotting Tg vs 1/
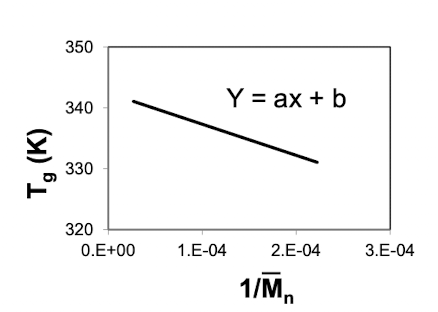
Kg is the slope
Tg inf is the intercept
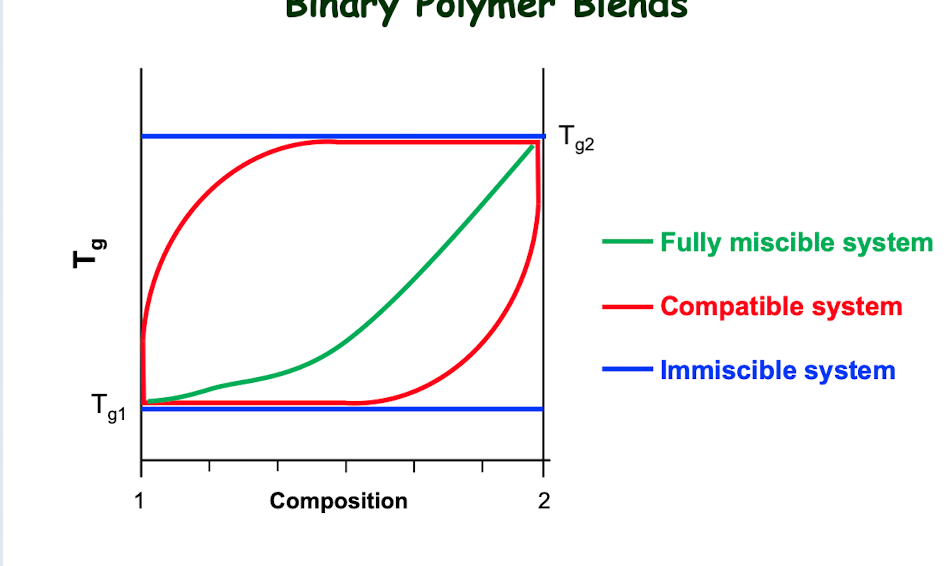
How do you know if a composition is fully miscible, compatible, or immiscible?
Fully miscible: a single Tg value is observed for the system
Compatible: multiple Tg values are observed depending on the number of components and their fractions
immiscible: Tg values of pure components do not change with composition
What is the effect of molecular weight on Tm
Inc molecular weight inc Tm initially, but long polymer chains make it more difficult to pack polymer molecules
what does increasing molecular weight do to impact resistance, toughness, and tensile strength?
increases
Do crystalline polymers typically give off or take energy (exo or endo)
Give off energy (exo)
What is Tc?
Crystallization temperature (indicates that polymer can crystallize, atactic materials would not have a Tc peak)
What is the benefit of interpreting heat-cool-heat results?
If the materials are different then there will be differences in the cool and second heat results
if the materials are the same and they have had the same thermal history then all three segments will be similar
if the materials are the same but they have different thermal histories, then the cool and second heat segments are similar but the first heats are different