Botany Exam 2
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane.
Osmotic pressure
Pressure required to prevent osmosis
Turgid cell
Firm cell due to water gained by osmosis
Out the stomata
Water travels through plant up the root hairs, through membrane of endodermis to the xylem, from xylem to leaves and they diffuse out where?
Plasmolysis
Loss of water through osmosis, accompanied by shrinkage of protoplasm from cell wall.
Imbibition
Large molecules (starch, cellulose) develop electrical charge when wet, attract H2O molecules resulting in swelling of tissue.
Active transport
Process used to absorb and retain solutes against a diffusion or electrical gradient by expenditure of energy.
Protein pump
Used to transfer things across membrane, usually energized by ATP.
transpiration
Water vapor loss from internal leaf atmosphere.
90%
What percent of the water entering a plant is transpired?
Cohesion-Tension theory
Transpiration generated tension to pull water columns through plants from roots to leaves.
Humidity, light, temp, and CO2 concentration
What affects transpiration rates?
Stomata close
When photosynthesis occurs, stomata open. When photosynthesis does not occur, what happens?
CAM Photosynthesis
CO2 converted to organic acids and stored in vacuoles at night. Organic acids converted to CO2 during day. (Desert plants)
Guttation
If cool night follows a warm, humid day, water droplets are produced through hydathodes at tips of veins.
Pressure-Flow Hypothesis
Organic solutes flow from source (leaves) where water enters by osmosis, to sinks (fruit/roots) where food is utilized and water exits.
Phloem loading
Sugar enters by active transport into sieve tubes.
Turgor pressure
What develops and dries fluid through sieve tubes towards sinks in Pressure-Flow theory?
Sink
Mass flow occurs from higher pressure at source to lower pressure where in the Pressure-Flow theory?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Non-mineral nutrients (3)
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur
Macronutrients- used by plants in greater amounts. (6)
Iron, chlorine, copper, boron, manganese, zinc, molybdenum, sodium, and cobalt
Micronutrients- needed by plant in very small amounts (9)
Photosynthesis
Process that converts light energy to stored energy
Respiration
Process that releases stored energy; facilitates growth, development, and reproduction
Metabolism
The sum of all interrelated biochemical processes in living organisms.
Anabolism
Forming chemical bonds to build molecules (Ex. Photosynthesis- energy storage)
Catabolism
Breaking chemical bonds (Cell. Respiration- release energy)
Photosynthesis-respiration cycle
This process involves transfer of energy via oxidation-reduction reactions.
Oxidation
Loss of electron(s)
Reduction
Gain of electron(s)
ATP
Energy for most cellular activity involves this molecule
Chloroplasts
Where does photosynthesis take place?
6 CO2 + 12 H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6H2O
Photosynthesis Equation
Carbon dioxide
What molecule reaches chloroplasts in mesophyll cells by diffusion though stomata into leaf interior?
0.04%
Carbon Dioxide makes up what percent of the atmosphere?
Water
What is the source of electrons in photosynthesis?
Visible light
About 40% of radiant energy from the sun is received on earth in what form?
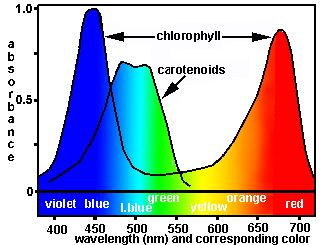
Absorption Spectrum
Each pigment has its own distinctive pattern of light absorption. What is this ‘spectrum’ called?
Energy levels are elevated
When pigments absorb light, what happens to the electrons in the pigment?
Light and Temperature
What two factors are primary effectors of photosynthetic rate?
Accelerates
When light and temperature become extreme it does what to photorespiration, which uses oxygen and releases CO2.
Photooxidation
If the light intensity is too high, chlorophyll is destroyed in a process called what?
A, b ,c, d, e
What are the five types of chlorophyll that capture energy named?
Chlorophyll a and b
Most plants contain these two chlorophyll types
Chlorophyll a
A chlorophyll that is blue-green in color and is the most common type
Chlorophyll b
A chlorophyll that is yellow-green in color.
Carotenoids
A photosynthetic pigment with the colors yellow and orange
Phycobilins
A photosynthetic pigment that is blue or red, in Cyanobacteria and red algae.
Photosynthetic unit
About 250-400 pigment molecules grouped in a light harvesting complex is called what?
Thylakoid membrane
Where do the light-dependent reactions take place?
Oxygen
What gaseous byproduct is released from the light dependent reactions?
O2, ATP, NADPH
What are the products of the light dependent reactions?
Photosystem I
P700; the second photosystem in the light dependent reaction process.
Photosystem II
P680; the first photosystem in the light dependent reaction process
Stroma of chloroplasts
Where do the light-independent reactions take place?
Calvin cycle
What is another name for the light independent reactions?
RuBP
What does CO2 combine with in the Calvin Cycle?
RuBisCo
What enzyme catalyses the reaction between CO2 and RuBP?
ATP and NADPH
What products from the light dependent reactions are used for energy in the Calvin Cycle?
Light
What excites electrons in the light dependent reactions?
3PGA
What is produced from the breakdown of the CO2 and RuBP combo molecule?
GA3P
What results from the reduction of 3PGA by NADPH and ATP?
Regenerated into 6 5-C RuBP
What happens to ten of the twelve GA3P molecules?
2 GA3P
What is the net gain from the Calvin cycle that can be used to make carbs, lipids, or amino acids?
Photorespiration
Competes with carbon-fixing role of photosynthesis by RuBisCo fixing oxygen instead of CO2.
Hot, dry conditions
Photorespiration allows C3 plants to survive under what conditions?
ATP and electrons
What does Photorespiration dissipate in order to prevent photooxidative damage?
4-Carbon pathway
Produces 4-carbon compound instead of the 3-carbon PGA during the initial steps of the light-independent reactions.
C4 plants
Tropical grasses and plants of arid regions are what kind of plants?
Kranz anatomy
C4 plants have Mesophyll cells with smaller chloroplasts and well developed grana. Bundle sheath cells with large chloroplasts and numerous starch grains. What is this called?
CO2 converted to organic acids in mesophyll cells
What happens to CO2 in the 4-carbon pathway?
O2
PEP carboxylase, which converts CO2 and PEP into 4-c oxaloacetic acid, is not selective for what molecule?
C3 plants
C4 plants photosynthesize at higher temperatures than what plants?
2 ATP
What is the cost for C4 photosynthesis?
4-carbon compounds
Like C4 photosynthesis, CAM photosynthesis also produces what?
Cellular Respiration
The release of energy from glucose molecules that are broken down to individual carbon dioxide molecules.
Aerobic respiration
Respiration that needs oxygen to continue
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP
Respiration Equation
Anaerobic respiration and fermentation
What two respiration processes happen in the absence of oxygen?
Glycolysis
Respiration step 1: In the cytoplasm, no O2 required, glucose converted to GA3P. For a net gain of 2 ATP.
Krebs (Citric Acid) cycle
Respiration step 2: In matrix of cristae, high E electrons and hydrogen removed, NADH, FADH2 and a small amount of ATP made. CO2 byproduct
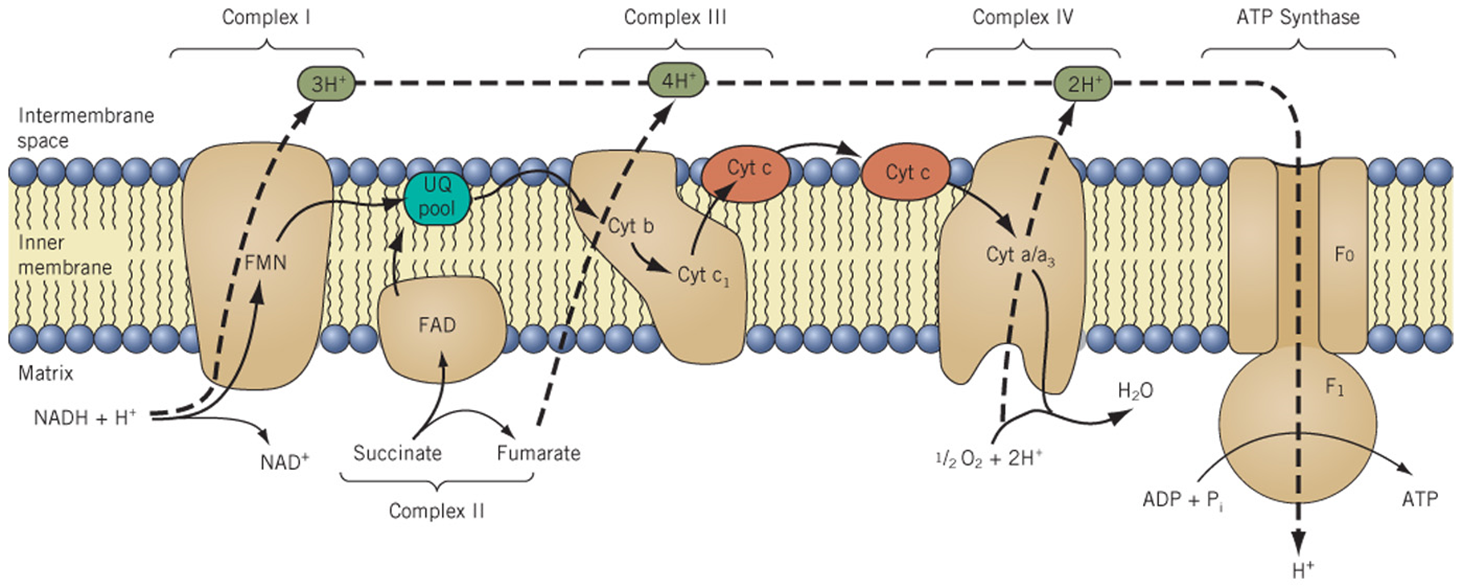
Electron Transport Chain
Respiration stage 3: Inner mitochondria membrane. NADH and FADH2 donate e- to the system, producing ATP, CO2, and H2O.
Glycolysis: Phosphorylation
Glucose becomes fructose carrying two phosphates: Requires 2 ATP.
Glycolysis: Sugar cleavage
Fructose split into two three carbon fragments: GA3P.
Glycolysis: Pyruvic acid formation
Hydrogen, energy and water removed, leaving pyruvic acid and 4 ATP.
Acetyl CoA
Before entering the Krebs cycle, pyruvic acid loses CO2 (by coenzyme A) and is converted to what?
Oxaloacetic acid (4C)
What does Acetyl CoA first combine with in the Krebs cycle?
Citric Acid (6C)
What does the combination of Acetyl CoA and oxaloacetic acid produce?
O.A. + Acetyl CoA + ADP+P +3 NAD + FAD → O.A. + CoA + ATP + 3 NADH + H+ + FADH2 + 2 CO2
Citric Acid Cycle Equation
Chemiosmosis
This couples transport of protons into matrix with oxidative phosphorylation: formation of ATP
Temperature, Water, Oxygen
What are factors that affect the rate of respiration?
Growth
Irreversible increase in mass due to division and enlargement of cells.
Determinate growth
Plant growth stops when fruit sets on the terminal bud, all fruit ripen at once, and then the plant dies.
Indeterminate growth
Plant continues to grow, flower, and ripen fruit simultaneously, and only stops when killed by frost.
Nutrients
Substances that furnish the elements needed for growth and development. (Obtained from air and soil)
Vitamins
Complex organic compounds used to facilitate enzyme reactions, commonly functioning as electron acceptors or donors. Synthesized in cell membrane and cytoplasm. Small amounts needed.
Hormones
These substances control growth and development. Produced in actively growing regions of an organism and transported to other regions. Produced and active in smaller amounts than vitamins and enzymes.
Auxins
Plant hormone with polar movement. Promotes cell enlargement and stem growth. Delays development: abscission, fruit ripening, etc. Inhibits lateral branching. (YOUNG)
Gibberellins (GA)
Plant hormone named from a fungus. Movement nonpolar. Increases stem growth and involved in same regulatory processes as auxins. Currently 110 known types. (YOUNG)