Unit 1 - Basics of Economics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
The basic economic problem
Finite resources and unlimited wants
factors of production
1. Land
2. Capital
3. Entreprise
4. Labour
Land
Natural resources

Capital
Man - made resources

Entreprise
having an idea to bring the other factors of production together to make a profit

Labour
Human skills and effort

Reward for land
Rent
Reward for capital
Interest
Reward for labour
Wages
Reward for enterprise
Profit
Production
Goods and services required to meet consumers needs
Organised by entrepreneurs in firms
Factor mobility
Occupational mobility → resource is able to change task (e.g. labourer goes from electrician to electrical engineer)
Geographic mobility → resource is able to move from 1 location to another (e.g. robot moved from India to China)
Economic goods
goods which are scarce in supply → only produced with an opportunity cost
Free goods
a good that is not scarce → available without limit
Firms
Includes all factors of production
Consumer goods
finished products that buyers buy for their use
Opportunity cost
The next best alternative sacrificed when an economic decisions is made → the choice that was given up
Free good
non - scarce → no opportunity cost
Economic good
scarce → have opportunity cost
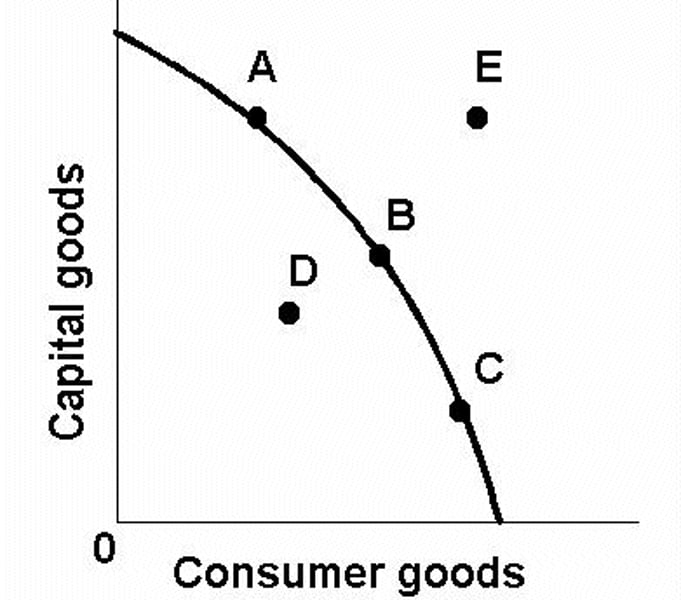
Why is a PPC useful?
Useful way of showing the opportunity cost of producing more of one product in terms of how much of another must be given up.
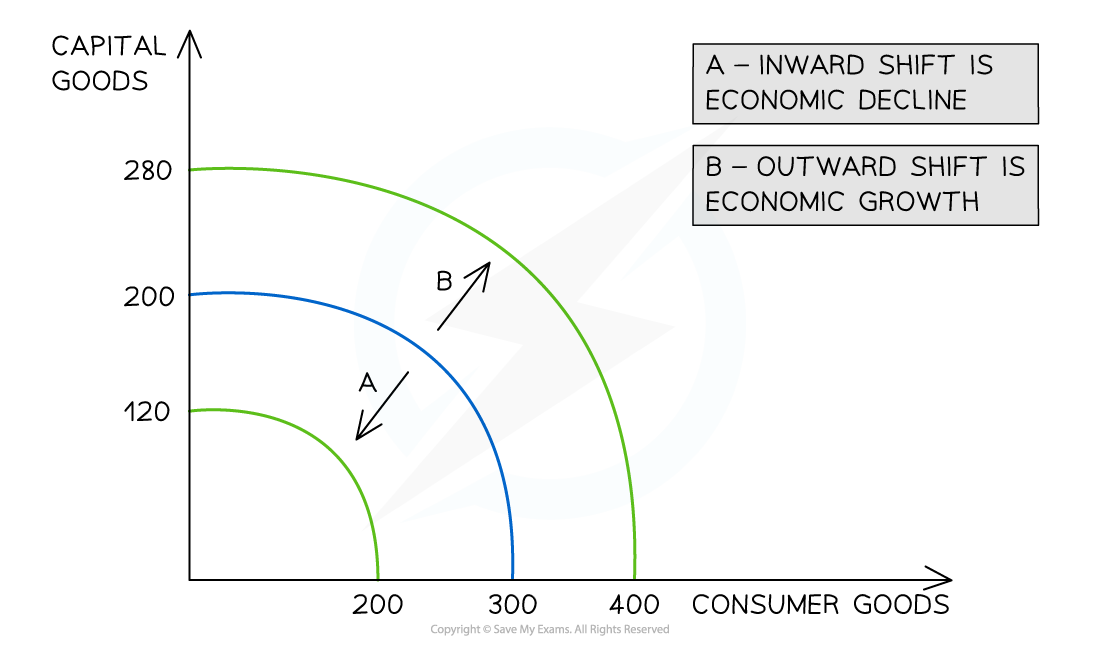
Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
show the maximum combined output of two or more products a firm (or an entire economy) can produce with available resources.
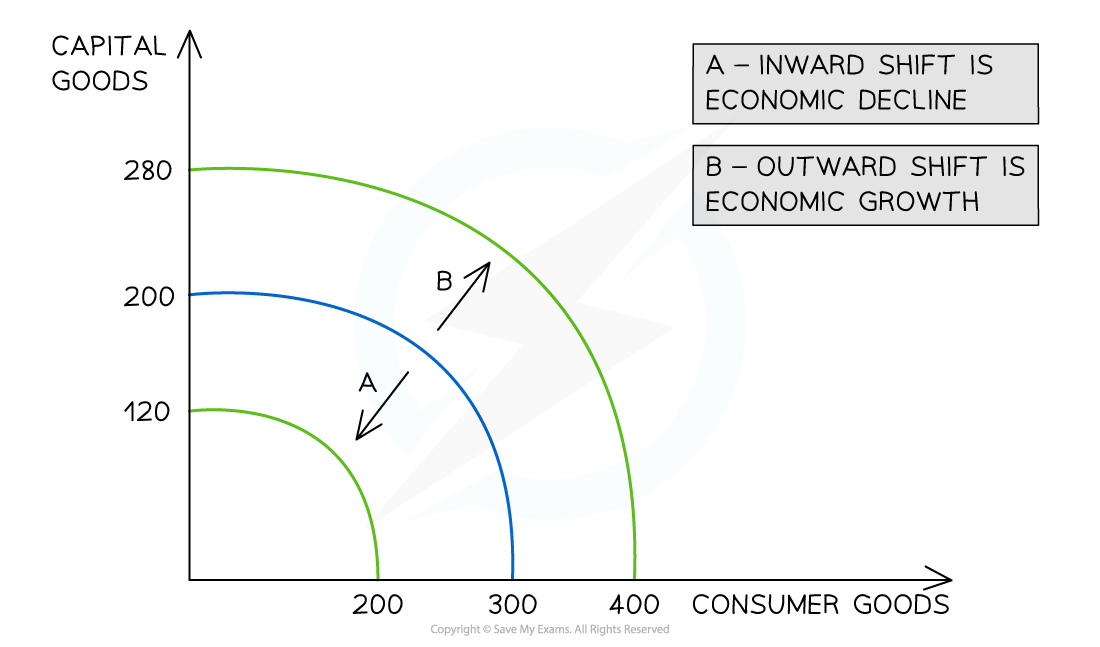
Why a PPC would move
shift to the right → increase resources
shift to the left → resources decreases